

HDI的IPC模式具体实现方法和驱动框架能力
描述
转自:OpenAtom OpenHarmony
HDI接口概述
HDF 驱动框架的一个重要功能是为系统提供稳定的统一的硬件接口,这样才能保证系统服务可以运行在不同硬件上而不需要额外的适配工作,而HDI(Hardware Device Interfaces)正是为了实现该目的而设计。
HDI 是对硬件功能的较高层次抽象接口,各类外设完成 HDI 接口定义后便只会在 HDI 的兼容性规则下进行变更,从而保证接口的稳定性。具体的驱动实现不需要再重复定义 HDI 接口,只需要按需实现即可接入系统功能。
在不同量级的 OpenHarmony 系统上,HDI 存在两种部署形态,IPC 模式和直通模式。
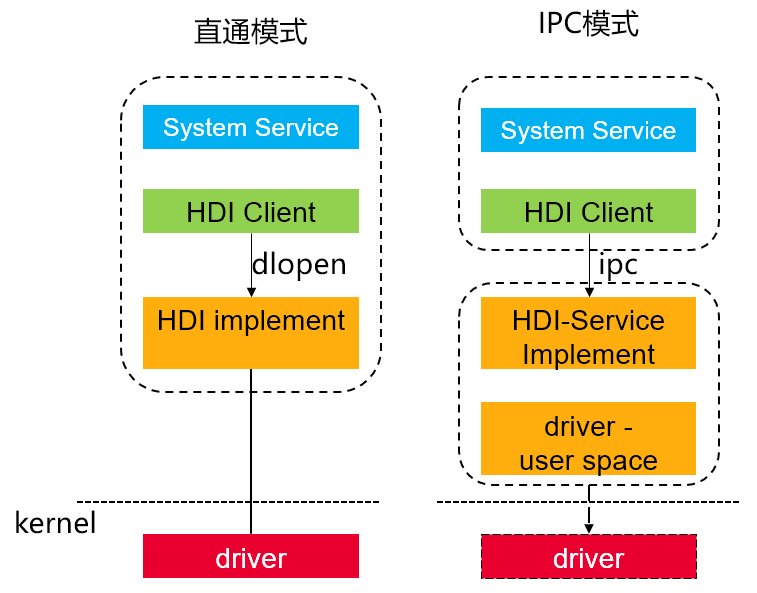
在轻量级 OpenHarmony 系统上,出于减小系统性能负载考虑,HDI 实现为用户态共享库,由系统服务直接加载 HDI 实现到自己进程中函数调用使用。HDI 实现封装具体的用户态-内核态交互过程,当需要访问驱动程序时使用 IO Service 请求将消息通过 system call 方式调用到内核驱动实现。
在 OpenHarmony 系统上,HDI 以独立服务进程方式部署,系统服务只加载 HDI 客户端实现到自己进程中,实际业务运行在独立进程中,客户端通过 IPC 与服务端交互,便于架构解耦、权限管理。
HDI接口实现
直通模式为函数实现方式,无论调用还是实现都不需要其他组件支持即可实现,这里将重点分析 IPC 模式的实现。
HDI发布
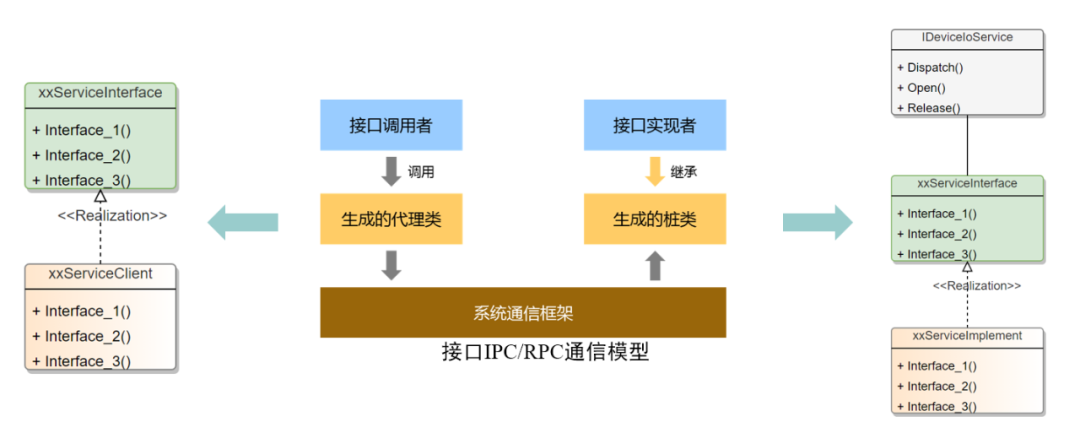
HDI IPC 模式基于 OpenHarmony 系统通信框架的通用模型,但是因为驱动很多时候涉及到底层操作和多系统迁移的场景而使用C语言编写,所以驱动框架还提供了 HDI 服务的 C 语言实现的基础组件,C++实现则主要使用系统通信框架组件。
HDI 服务发布基于 UHDF(用户态 HDF 驱动框架)实现,通用的服务发布实现如下。
1.实现驱动入口
int SampleDriverBind(struct HdfDeviceObject *deviceObject){ HDF_LOGE(“SampleDriverBind enter!”); static struct IDeviceIoService testService = { .Dispatch = SampleServiceDispatch, // 服务回调接口 }; deviceObject-》service = &testService; return HDF_SUCCESS;} int SampleDriverInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *deviceObject){ HDF_LOGE(“SampleDriverInit enter”); return HDF_SUCCESS;} void SampleDriverRelease(struct HdfDeviceObject *deviceObject){ HDF_LOGE(“SampleDriverRelease enter”); return;} struct HdfDriverEntry g_sampleDriverEntry = { .moduleVersion = 1, .moduleName = “sample_driver”, .Bind = SampleDriverBind, .Init = SampleDriverInit, .Release = SampleDriverRelease,};
HDF_INIT(g_sampleDriverEntry);
首先要添加一个 UHDF 驱动用于发布 IoService 服务,IoService 设备服务即为 HDI 服务实体。实现方式与 KHDF 驱动一致。
2.实现服务响应接口
int32_t SampleServiceOnRemoteRequest(struct HdfDeviceIoClient *client, int cmdId, struct HdfSBuf *data, struct HdfSBuf *reply){ switch (cmdId) { case SAMPLE_SERVICE_PING: return SampleServiceStubPing(client, data, reply); … … default: HDF_LOGE(“SampleServiceDispatch: not support cmd %d”, cmdId); return HDF_ERR_INVALID_PARAM; }}static int32_t SampleServiceDispatch(struct HdfDeviceIoClient *client, int cmdId, struct HdfSBuf *data, struct HdfSBuf *reply){ return SampleServiceOnRemoteRequest(client, cmdId, data, reply);}
当收到 HDI 调用时,服务响应接口“SampleServiceDispatch”将会被调用。
client 调用者对象,在用户态驱动中暂时未支持
cmdId 调用命令字,用于区分调用的 API
data 调用入参序列化对象,在 IPC 调用场景为 parcel 对象的 C 语言封装,入参需要使用序列化接口从 data 对象中获取后再使用
reply 调用出参对象,需要返回给调用的信息写入该序列化对象
如果 C++实现客户端可以使用下面接口将 sbuf 对象转换为 parcel 对象后操作:
int32_t SbufToParcel(struct HdfSBuf *sbuf, OHOS::MessageParcel **parcel);
3.UHDF 驱动配置
platform :: host { hostName = “sample_host”; priority = 50; sample_device :: device { device0 :: deviceNode { policy = 2; priority = 100; moduleName = “libsample_driver.z.so”; serviceName = “sample_driver_service”; } }}
参数说明:
host 一个 host 节点即为一个独立进程,如果需要独立进程,新增属于自己的 host 节点
policy 服务发布策略,HDI 服务设置为 2
moduleName 驱动实现库名
serviceName 服务名称,请保持全局唯一性
因为 HDI 服务 C 和 C++实现使用的 IPC 组件不一样,面向对象实现也不一致,所以在具体实现上存在一些差异。
HDI基础组件UHDF 框架为了支持 HDI 实现,提供了以下基础组件(仅用于 C 语言 HDI 实现):
SBuf
SBuf 是同时支持 KHDF 和 UHDF 驱动 IoService 消息序列化的工具对象。在 UHDF IPC 通信场景中,SBuf 可以与系统 IPC 框架序列化对象 MessageParcel 对象(仅支持 C++)相互转换,从而实现 C 和 C++实现的 IPC 互通。
常用 API 如下:
struct HdfSBuf;struct HdfSbufImpl;struct HdfRemoteService;
/** * @brief HdfSBuf类型定义。 * * @since 1.0 */enum HdfSbufType { SBUF_RAW = 0, /* 用于用户态内核态通信的sbuf类型 */ SBUF_IPC, /* 用于跨进程通信的sbuf类型 */ SBUF_IPC_HW, /* 用于扩展的预留类型 */ SBUF_TYPE_MAX, /* sbuf类型最大值 */};
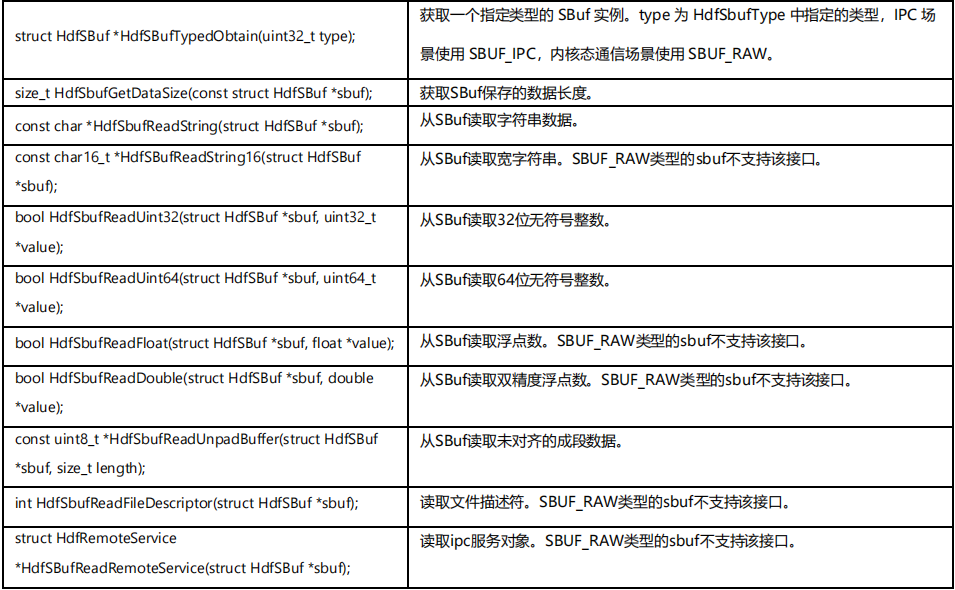
上述接口均有对应的写入接口,不再一一列举,可查阅官网API参考文档。
RemoteService
RemoteService 对象和系统 IPC 框架中的 IRemoteObject 对象(仅支持 C++)对应并可以相互转换,表示一个 IPC 对象。相关 API 说明:
// 消息分发器,用于服务端响应调用或者在客户端发起调用struct HdfRemoteDispatcher { int (*Dispatch)(struct HdfRemoteService *, int, struct HdfSBuf *, struct HdfSBuf *);};
// RemoteService 死亡回调对象struct HdfDeathRecipient { void (*OnRemoteDied)(struct HdfDeathRecipient *, struct HdfRemoteService *);};
struct HdfRemoteService { struct HdfObject object_; struct HdfObject *target; struct HdfRemoteDispatcher *dispatcher; bool isHw;};// 以自定义的消息分发器实例化一个RemoteServicestruct HdfRemoteService *HdfRemoteServiceObtain( struct HdfObject *object, struct HdfRemoteDispatcher *dispatcher);
// 回收RemoteService对象void HdfRemoteServiceRecycle(struct HdfRemoteService *service);
// 添加RemoteService的死亡通知,如果对应RemoteService的进程异常退出,HdfDeathRecipient的回调接口将被调用void HdfRemoteServiceAddDeathRecipient(struct HdfRemoteService *service, struct HdfDeathRecipient *recipient);
基于 RemoteService 实现一个服务端的示例:
int SampleServiceStubDispatch( struct HdfRemoteService* service, int code, struct HdfSBuf *data, struct HdfSBuf *reply){ // IPC 调用响应接口 int ret = HDF_FAILURE; switch (code) { case SAMPLE_IF_0: { // do something break; } default: { ret = HDF_ERR_INVALID_PARAM; } } return ret;}bool SampleStubConstruct(){ // 构造消息分发器,实现消息处理回调 static struct HdfRemoteDispatcher dispatcher = { .Dispatch = SampleServiceStubDispatch};// 实例化RemoteService inst-》remote = HdfRemoteServiceObtain((struct HdfObject *)inst, &dispatcher); if (inst-》remote == NULL) { HDF_LOGE(“Device service manager failed to obtain remote service”); return false;}… …
直接基于 RemoteService 实现服务端只适用于需要实现匿名 IPC 服务的情况,基于 UHDF 发布 HDI 服务只需要实现 Driver 绑定的 IoService 即可。
RemoteService 客户端对象只能从 SBuf HdfSBufReadRemoteService 接口获取。
HDI实现
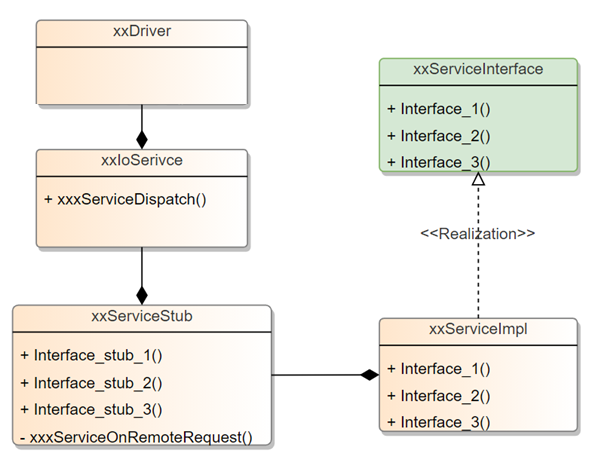
Driver 为 HDI 服务的驱动入口实现
IoService 为 HDI 服务的服务入口实现,IoService 的 Dispatch 方法中调用 ServiceStub 中的真正服务响应接口(OnRemoteRequest)
ServiceStub 为服务端实现对象,主要处理与 IPC 相关的业务逻辑,在这里完成参数反序列化后调用真正的 Service 实现接口,即 ServiceImpl 接口
ServiceImpl 为 HDI 接口的真正实现,这里不关注 IPC 过程,只实现函数接口。
驱动框架提供了实现的样例代码,可参考 gitee driver 代码仓。
HDI接口调用
HDI驱动框架HDI接口
HDI 服务管理功能由驱动框架 DeviceManager 实现,所以驱动框架提供了 HDI 服务管理相关 HDI 接口。
C++实现:
namespace OHOS {namespace HDI {namespace ServiceManager {namespace V1_0 {
struct IServiceManager : public IRemoteBroker {public: DECLARE_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR(u“HDI.IServiceManager.V1_0”); // get()静态方法用于获取IServiceManager对象实例 static ::sptr《IServiceManager》 Get(); // GetService()接口是真正提供的HDI接口,用于查询并获取其他HDI服务的客户端对象 virtual ::sptr《IRemoteObject》 GetService(const char* serviceName) = 0;};} // namespace V1_0} // namespace ServiceManager} // namespace HDI} // namespace OHOS
C 实现:
#ifdef __cplusplusextern “C” {#endif /* __cplusplus */
struct HDIServiceManager { struct HdfRemoteService *remote;
struct HdfRemoteService *(*GetService)(struct HDIServiceManager *self, const char* serviceName);};
struct HDIServiceManager *HDIServiceManagerGet(void);void HDIServiceManagerRelease(struct HDIServiceManager *servmgr);
#ifdef __cplusplus}#endif /* __cplusplus */
C 语言因为缺少原生的面向对象支持,这里我们采用 OOC 的实现,函数方法 HDIServiceManagerGet/Release 用于 HDIServiceManager 对象的实例化和释放,HDI 接口关联在接口对象内部成员中,与 C++实现类似。
HDI客户端实现
HDI 客户端同时支持 C 和 C++实现,实现方法较为简单,只需 realize HDI 接口类即可。提供 C++实现基于系统 IPC 子系统的统一模型,C 语言基于 RemoteService 和 SBuf 组件实现,但是有一些公共的约定:
1.客户端提供接口对象,接口与对象绑定且必须与 HDI 一致
2.提供服务接口对象的实例化和释放接口。
3.客户端实现 IPC 过程,只为调用者暴露函数化接口。
HDI接口调用
HDI 客户端接口已经提供了服务获取接口,调用者调用服务获取接口后再调用服务对象方法即可完成 HDI 调用。
这里以服务管理 HDI 接口为例:
C++接口调用:
#include 《iservmgr_hdi.h》
void GetTestService(){ auto servmgr = IServiceManager::Get(); if (servmgr == nullptr) { HDF_LOGE(“failed to get IServiceManager”); return; }
auto sampleService = servmgr-》GetService(TEST_SERVICE_NAME); if (sampleService == nullptr) { HDF_LOGE(“failed to get TEST_SERVICE”); return; } // do something}
C 接口调用:
#include 《servmgr_hdi.h》
void GetTestService(){ struct HDIServiceManager *servmgr = HDIServiceManagerGet(); if (servmgr == nullptr) { HDF_LOGE(“failed to get IServiceManager”); return; }
struct HdfRemoteService *sampleService = servmgr-》GetService(servmgr, TEST_SERVICE_NAME); if (sampleService == nullptr) { HDF_LOGE(“failed to get TEST_SERVICE”); return; } // do something}
总结
本文介绍了 HDI 的总体方案,重点介绍了 HDI 的 IPC 模式具体实现方法和驱动框架能力,相信对读者理解和使用 HDI 有所帮助。
编辑:jq
- 相关推荐
- API
- HDI
- IPC
- OpenHarmony
-
DM8168 DVR_RDK_GUI框架的具体实现框架是什么?2020-04-16 0
-
什么是HDI PCB2020-06-19 0
-
HarmonyOS HDF驱动框架---驱动开发2020-09-16 0
-
框架设计中的常用模式有哪些2020-12-17 0
-
OpenHarmony HDF 驱动框架介绍和驱动加载过程分析2021-08-31 0
-
OpenHarmony HDF HDI基础能力分析与使用2021-09-02 0
-
OpenHarmony系统平台驱动与驱动框架概述2022-03-28 0
-
OpenHarmony 3.1 Release版本关键特性解析——HDI硬件设备接口介绍2022-06-07 0
-
HDI的CAM制作方法大全2010-03-15 1189
-
HDI的IPC模式具体实现方法和驱动框架能力2021-09-02 3951
-
HDI接口中如何实现驱动入口2021-09-08 2149
-
OpenHarmony HDF HDI的IPC模式具体实现方法和驱动框架能力2021-09-22 2811
-
HDI硬件设备接口介绍2022-06-02 1593
-
Linux的PWM驱动框架及实现方法2023-05-14 1008
-
Linux Regmap 驱动框架2023-07-06 728
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

