

N-MOS工艺芯片与P-MOS工艺芯片对比
描述
一、How does Over Current Protection (OCP) work?
When over-current protection (OCP) is enabled, the power system turns off the output if the output current reaches the current limit setting and transitions from constant voltage (CV) operation to constant current (CC) operation.
With OCP turned on, the OCP takes over after a specified time delay and shuts down the output of the power supply. The delay time is programmable. This prevents OCP from shutting down the DC power supply from short current spikes and other acceptably short overloads that are not considered harmful. In comparison, with Over Voltage Protection (OVP), the output is disabled immediately. OVP is usually always enabled and cannot be turned off. However, unlike OVP, OCP can be turned on and off and its default is usually off. A typical OCP event is illustrated here:
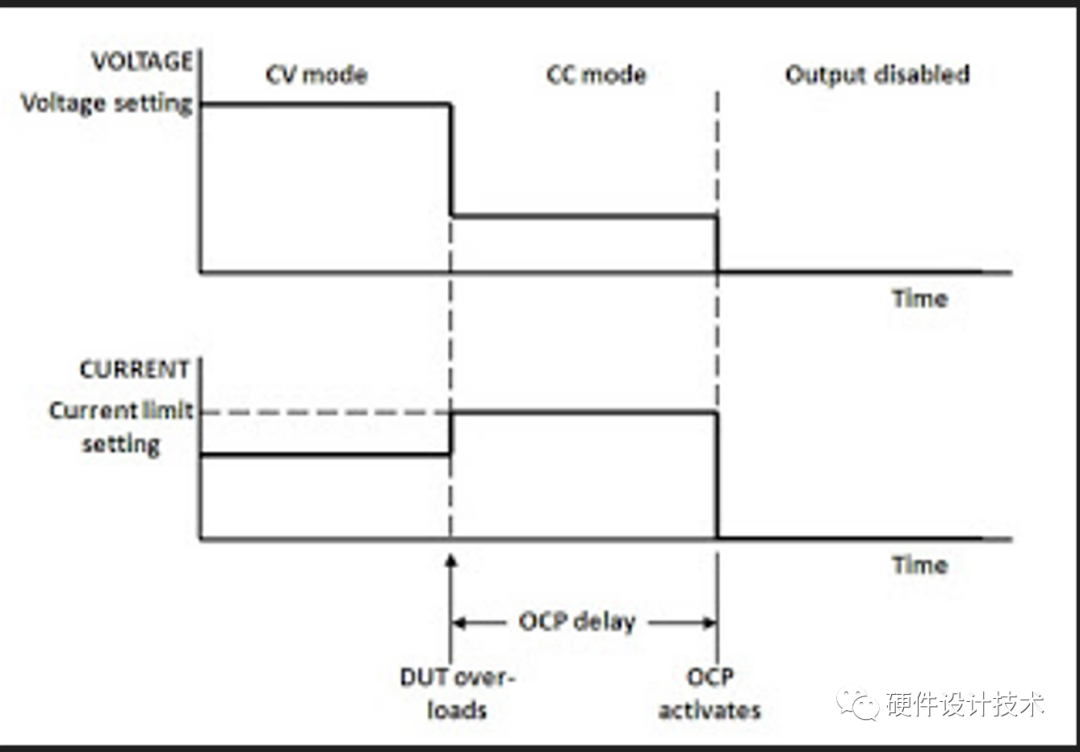
We can specify an OCP delay to prevent momentary output settings, load, and status changes from tripping the over-current protection. In most cases these momentary conditions would not be considered an over-current protection fault, and having an OCP condition disable the output when they occur would be a nuisance. Specifying an OCP delay lets the OCP circuit ignore these momentary changes during the specified delay period. Once the OCP delay time has expired and the over-current condition persists, the output will shut down. Other factors include the difference between old output value and new output value, the current limit setting, and the load capacitance in CV operation or load inductance in CC operation. The delay required must be determined experimentally on a case-by-case basis.
二、N-MOS & P-MOS 工艺芯片对比:
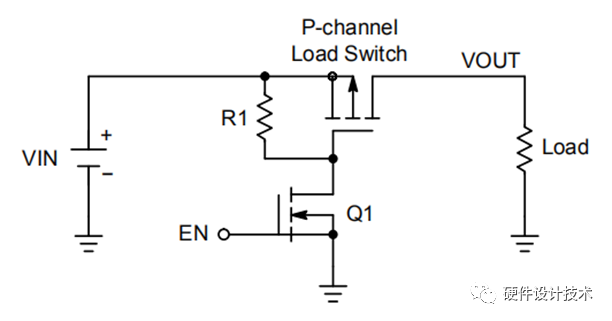
P-MOS OCP原理简介
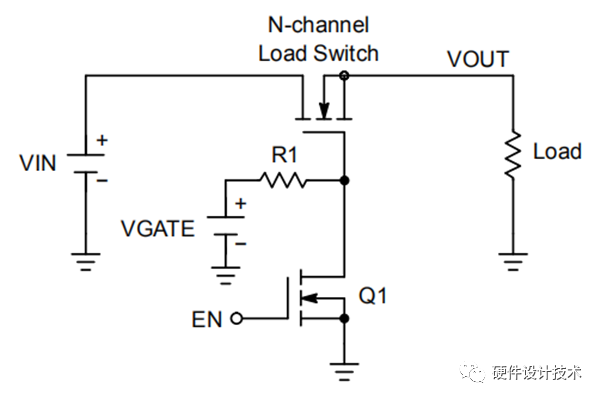
N-MOS OCP原理简介
| NMOS | PMOS | |
| Ron | 较小 | 较大 |
| Io | 较大 | 较小 |
| Charge pump | 需要 | 不需要 |
| Parasitic capacitance | 较小 | 较大 |
| Cost | 较高 | 较低 |
性能指标对比
三、镜像电流采样技术:
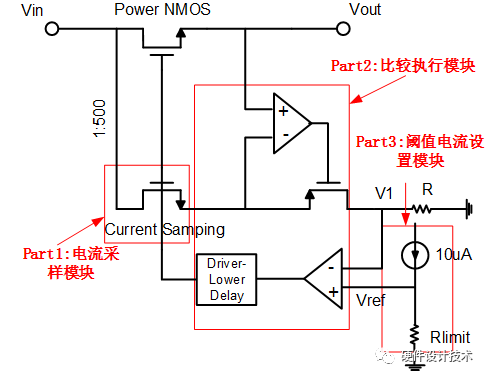
1、外部设置Rlimit,确定触发Rlimit时的电流为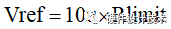
2、随着负载电流的增加,成比例的镜像电流也逐渐增加
3、当镜像电流达到满足, 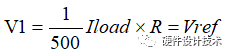 此时,触发限流机制
此时,触发限流机制
4、低延时的驱动单元将功率管的栅极电压拉低,达到限制PowerNMOS电流的大小的目的
四、PCB Layout注意事项
1、输入输出电容靠近芯片PIN脚摆放
2、输入输出电容两端端就近打足够的GND-VIA
3、芯片及周边元件尽量靠近负载端摆放,减小路径上的寄生参数
4、TVS靠近芯片PIN脚摆放,电流流过顺序为先TVS,再过电容,最后到芯片PIN脚
5、Rlimit电阻选用的精度至少±1%
五、OVP 与 OCP 对比:
This is quite different than the almost immediate response time of an OVP system. Even if the OCP delay time was set to zero, the response is still on the order of milliseconds instead of microseconds compared to an OVP event. And when the amount of overdrive is small, as is the case for the 6 A loading, providing just 1 A of overdrive, the total response time is much greater.
Unlike the OVP system, which operates totally independent of the voltage limit control system, the OCP system is triggered off the current limit control system. Thus the total response time includes the response time of the current limit as well. The behavior of a current limit is quite different than a simple “go/no go” threshold detector like OVP. A limit system, or circuit, needs to regulate the power supply’s output at a certain level, making it a feedback control system. The stability of this system is important, both with crossing over from constant voltage operation as well as maintaining a stable output current after crossing over. This leads to the slower and overdrive dependent response characteristics that are typical of current limit systems.
审核编辑:刘清
-
如何通过一个微分电路和一个P-MOS做到如下要求2017-02-09 0
-
P-MOS输出控制请教2017-12-24 0
-
请MOS管大神指点:MOS管H 半桥电磁阀驱动电路2018-04-06 0
-
优奈斯代理(恒泰柯HUNTECK)全系列MOS:低压低内阻MOS2018-08-07 0
-
关于P-MOS开关电路中MOS管烧坏的求助2018-12-03 0
-
给大家分享一个N-MOS和P-MOS驱动的应用实例2019-08-29 0
-
mos管发热原因2020-10-10 0
-
N-MOS管的原理是什么?N-MOS管为什么会出问题?2021-07-05 0
-
N-MOS管是如何接线的2021-10-11 0
-
N-MOS H桥有哪几种结构模式?分别有何优缺点2022-02-11 0
-
SW2N6 N-MOS2017-10-18 758
-
如何区分P-MOS和N-MOS?如何区分MOS的G、D、S管脚?MOS管如何导通?2018-07-17 101570
-
模块工艺——双阱工艺(Twin-well or Dual-Well)2022-11-14 7276
-
CMOS集成电路的双阱工艺简析2022-11-14 7076
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

