

SSH命令详解
电子说
描述
SSH命令详解
ssh是一种安全的远程登录及传输协议。ssh可用于远程登录、远程文件传输等。ssh是安全的shell。
使用ssh协议可以安全地将客户端与服务端通过网络连接起来,这为远程调试设备提供了可能性。ssh远程登录后的操作完全同本地shell的操作一致。
ssh安全登录的方式有2种,密码口令验证和密钥验证。
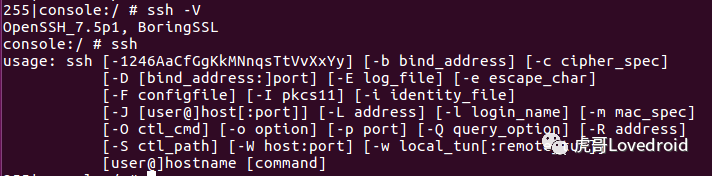
ssh命令选项
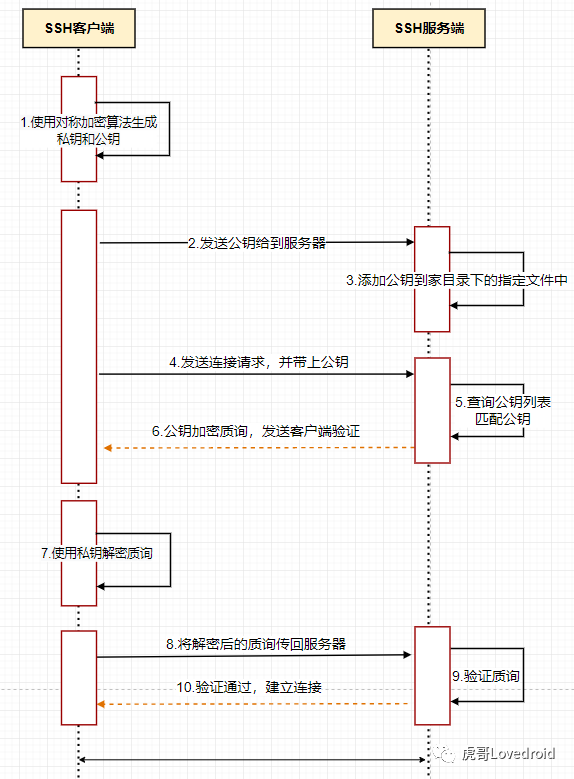
密钥验证流程
ssh命令选项
要查看ssh详细的命令选项,请在Linux系统终端键入
$man ssh
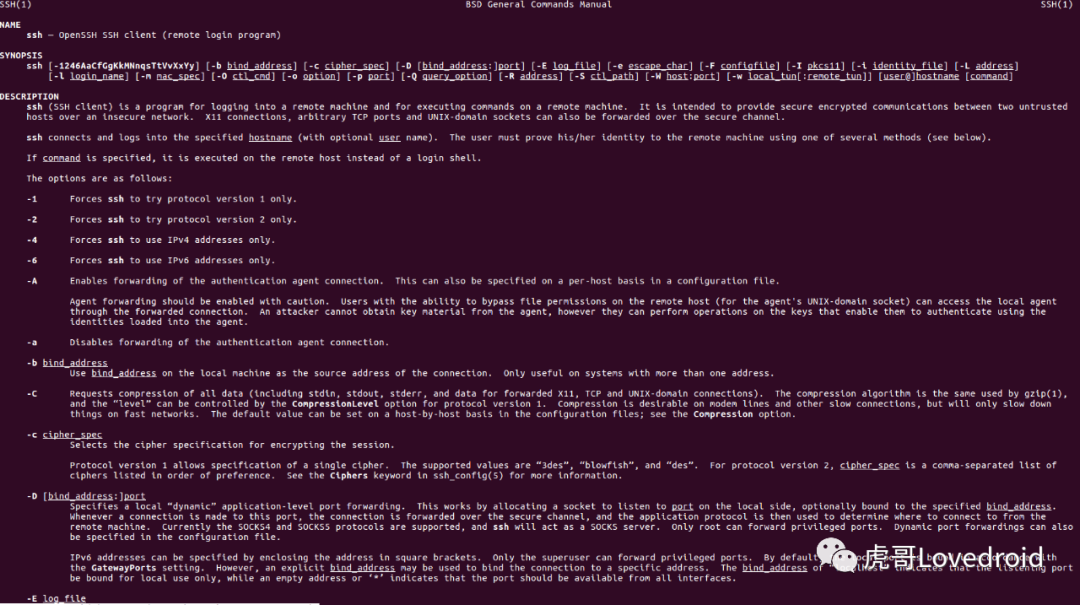
man ssh
man ssh翻译内容参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/f-ck-need-u/p/7120669.html
ssh命令详解及使用
1.ssh连接远程主机
$ ssh user@hostname
最简单的用法只需要指定用户名和主机名参数即可,主机名可以是 IP 地址或者域名。例如:
# ssh cl@192.168.125.103
2.ssh连接指定端口的ssh服务
$ ssh -p 10022 user@hostname
SSH 默认连接到目标主机的 22 端口上,可以使用-p选项指定端口号 例如:
ssh cl@192.168.125.103 -p 5030
3.连接到ssh服务并执行一条命令,打印结果到本地
$ ssh pi@10.42.0.47 ls -l
直接连接并在后面加上要执行的命令就可以了 4.ssh及sshd配置
ssh配置在/etc/ssh目录下
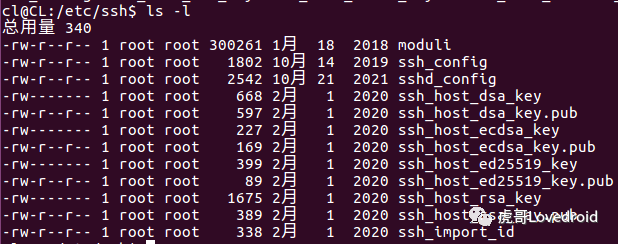
ssh配置目录
SSH 的配置文件在 /etc/ssh/ssh_config 中,你可以看到端口号, 空闲超时时间等配置项,可以看到ssh非对称密钥有dsa、ecdsa、rsa等几种,sshd的配置文件在/etc/ssh/sshd_config目录下。
5.构建ssh密钥对
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
使用 ssh-keygen -t +算法 ,现在大多数都使用rsa或者dsa算法
6.查看是否已经添加了对应主机的密钥
$ ssh-keygen -F 222.24.51.147
7.删除主机密钥
$ ssh-keygen -R 222.24.51.147
使用-R选项,也可以在~/.ssh/known_hosts文件中手动删除
8.绑定源地址
$ ssh -b 192.168.0.200 root@192.168.0.103
如果客户端有多于两个以上的 IP 地址,你不确定使用哪个IP来连接ssh服务器。我们可以使用 -b 选项来指定一个IP 地址。这个 IP 将会被用作建立连接的源地址。
9.对数据请求压缩
$ ssh -C root@192.168.0.103
使用 -C 选项,所有通过 SSH 发送或接收的数据将会被压缩,并且仍然是加密的
10.打开调试模式
$ ssh -v root@192.168.0.103
-v参数可以打印出调试信息,如下图所示:
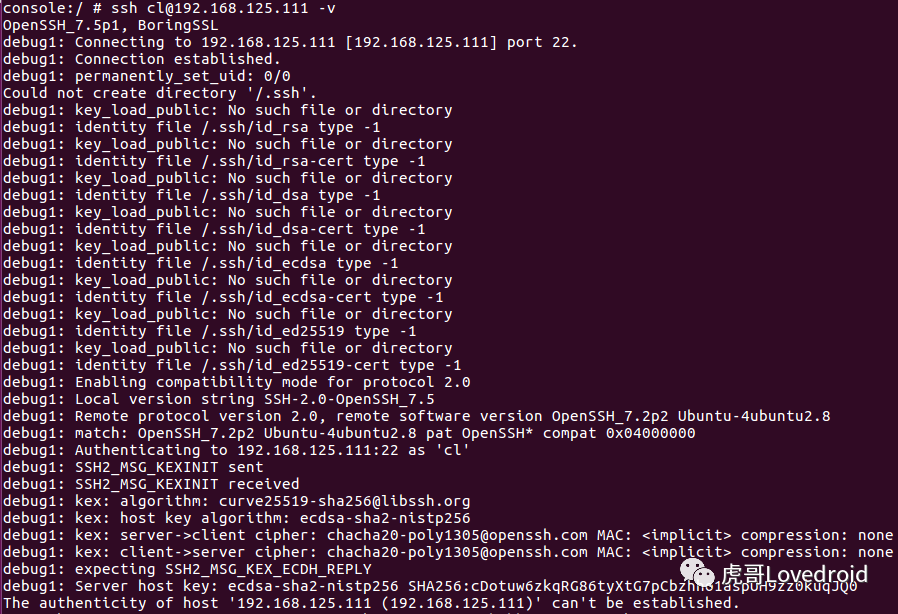
ssh调试信息
11.当前用户的ssh密钥
cl@CL:~/.ssh$ ls
id_rsa id_rsa.pub known_hosts
12.known_hosts文件
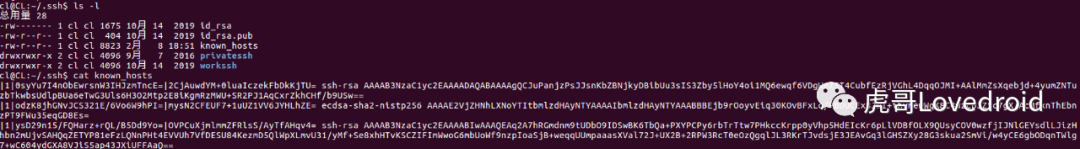
known_hosts内容
当服务端被连接会在该路径下known_hosts生成key验证信息,用来验证客户端的IP地址与公钥。
首次ssh连接服务端,服务端就会记录连接的IP地址以及公钥信息,存放在known_hosts文件里面,后续再次连接就不需要检查指纹信息了。
13.查看服务端指纹信息
cl@CL:/etc/ssh$ sudo ssh-keygen -lf ssh_host_rsa_key -E sha256
2048 SHA256:Nr865fluVGxdxHnWCts9+ye/enB3pokV64w+qvRElTs root@CL (RSA)
cl@CL:/etc/ssh$ sudo ssh-keygen -lf ssh_host_rsa_key -E sha1
2048 SHA1:EVIobIZxbqHJs3RA/eefuog13EI root@CL (RSA)
cl@CL:/etc/ssh$ sudo ssh-keygen -lf ssh_host_rsa_key -E md5
2048 MD5:41:63:ed:9f:d6:ad:46:27:a1:cc:d5:36:1b:0e:cc:5a root@CL (RSA)
附ssh配置文件信息/etc/ssh/ssh_config
cl@CL:/etc/ssh$ cat ssh_config
# This is the ssh client system-wide configuration file. See
# ssh_config(5) for more information. This file provides defaults for
# users, and the values can be changed in per-user configuration files
# or on the command line.
# Configuration data is parsed as follows:
# 1. command line options
# 2. user-specific file
# 3. system-wide file
# Any configuration value is only changed the first time it is set.
# Thus, host-specific definitions should be at the beginning of the
# configuration file, and defaults at the end.
# Site-wide defaults for some commonly used options. For a comprehensive
# list of available options, their meanings and defaults, please see the
# ssh_config(5) man page.
Host *
# ForwardAgent no
# ForwardX11 no
# ForwardX11Trusted yes
# RhostsRSAAuthentication no
# RSAAuthentication yes
# PasswordAuthentication yes
# HostbasedAuthentication no
# GSSAPIAuthentication no
# GSSAPIDelegateCredentials no
# GSSAPIKeyExchange no
# GSSAPITrustDNS no
# BatchMode no
# CheckHostIP yes
# AddressFamily any
# ConnectTimeout 0
# StrictHostKeyChecking ask
# IdentityFile ~/.ssh/identity
# IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa
# IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_dsa
# IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_ecdsa
# IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_ed25519
# Port 22
# Protocol 2
# Cipher 3des
# Ciphers aes128-ctr,aes192-ctr,aes256-ctr,arcfour256,arcfour128,aes128-cbc,3des-cbc
# MACs hmac-md5,hmac-sha1,umac-64@openssh.com,hmac-ripemd160
# EscapeChar ~
# Tunnel no
# TunnelDevice any:any
# PermitLocalCommand no
# VisualHostKey no
# ProxyCommand ssh -q -W %h:%p gateway.example.com
# RekeyLimit 1G 1h
SendEnv LANG LC_*
HashKnownHosts yes
GSSAPIAuthentication yes
GSSAPIDelegateCredentials no
KexAlgorithms +diffie-hellman-group1-sha1
附sshd配置文件信息/etc/ssh/sshd_config
cl@CL:/etc/ssh$ cat sshd_config
# Package generated configuration file
# See the sshd_config(5) manpage for details
# What ports, IPs and protocols we listen for
Port 22
# Use these options to restrict which interfaces/protocols sshd will bind to
#ListenAddress ::
#ListenAddress 0.0.0.0
Protocol 2
# HostKeys for protocol version 2
HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key
HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_dsa_key
HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key
HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key
#Privilege Separation is turned on for security
UsePrivilegeSeparation yes
# Lifetime and size of ephemeral version 1 server key
KeyRegenerationInterval 3600
ServerKeyBits 1024
# Logging
SyslogFacility AUTH
LogLevel INFO
# Authentication:
LoginGraceTime 120
PermitRootLogin prohibit-password
StrictModes yes
RSAAuthentication yes
PubkeyAuthentication yes
#AuthorizedKeysFile %h/.ssh/authorized_keys
# Don't read the user's ~/.rhosts and ~/.shosts files
IgnoreRhosts yes
# For this to work you will also need host keys in /etc/ssh_known_hosts
RhostsRSAAuthentication no
# similar for protocol version 2
HostbasedAuthentication no
# Uncomment if you don't trust ~/.ssh/known_hosts for RhostsRSAAuthentication
#IgnoreUserKnownHosts yes
# To enable empty passwords, change to yes (NOT RECOMMENDED)
PermitEmptyPasswords no
# Change to yes to enable challenge-response passwords (beware issues with
# some PAM modules and threads)
ChallengeResponseAuthentication no
# Change to no to disable tunnelled clear text passwords
#PasswordAuthentication yes
# Kerberos options
#KerberosAuthentication no
#KerberosGetAFSToken no
#KerberosOrLocalPasswd yes
#KerberosTicketCleanup yes
# GSSAPI options
#GSSAPIAuthentication no
#GSSAPICleanupCredentials yes
X11Forwarding yes
X11DisplayOffset 10
PrintMotd no
PrintLastLog yes
TCPKeepAlive yes
#UseLogin no
#MaxStartups 10:30:60
#Banner /etc/issue.net
# Allow client to pass locale environment variables
AcceptEnv LANG LC_*
Subsystem sftp /usr/lib/openssh/sftp-server
# Set this to 'yes' to enable PAM authentication, account processing,
# and session processing. If this is enabled, PAM authentication will
# be allowed through the ChallengeResponseAuthentication and
# PasswordAuthentication. Depending on your PAM configuration,
# PAM authentication via ChallengeResponseAuthentication may bypass
# the setting of "PermitRootLogin without-password".
# If you just want the PAM account and session checks to run without
# PAM authentication, then enable this but set PasswordAuthentication
# and ChallengeResponseAuthentication to 'no'.
UsePAM yes
