

怎样通过蓝牙仅使用Android手机为树莓派配置Wi-Fi网络
电子说
描述
如果你已经使用Raspberry Pi一段时间了,你可能会遇到几个您需要连接并重新连接Pi的Wi-Fi网络的情况。这样做可能需要您将Pi连接到显示器,键盘和整个设备,或者使用其他设备直接在存储卡上进行配置。
在本教程中,我想向您展示一种通过蓝牙仅使用Android手机为Raspberry Pi配置Wi-Fi网络的简便方法。
使用此技术,您不再需要担心在无头Raspberry Pi上切换Wi-Fi网络。
必备材料
首先,您需要:
Raspberry Pi 3
Raspbian加载到microSD
Android手机
APK文件和Python运行脚本
在Raspbian上安装Bluez
在Raspbian终端中逐步输入以下命令,从安装Bluez(Python蓝牙库)开始:
$ sudo apt-get install python-bluez
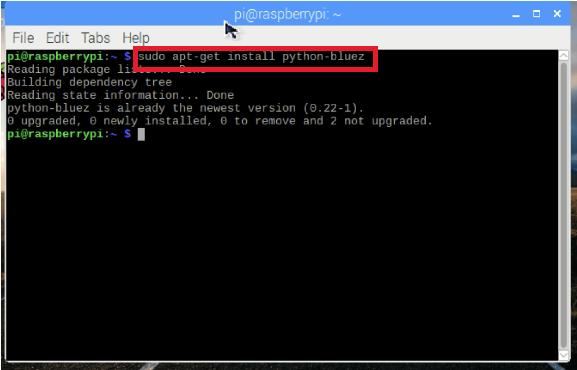
启动蓝牙守护程序兼容模式,编辑/etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.bluez.service ,输入以下命令:
$ sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.bluez.service
并修改ExecStart参数
ExecStart =/usr/lib/bluetooth/bluetoothd -C
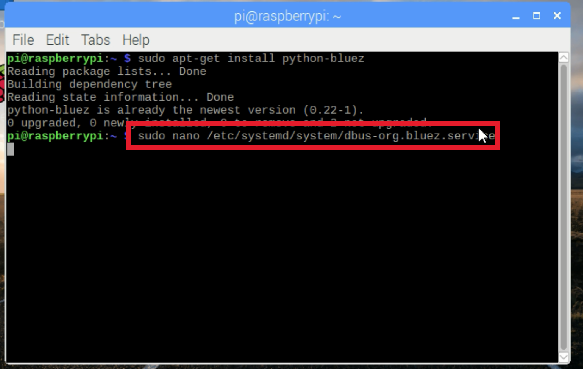

加载串口配置文件:
$ sudo sdptool add SP
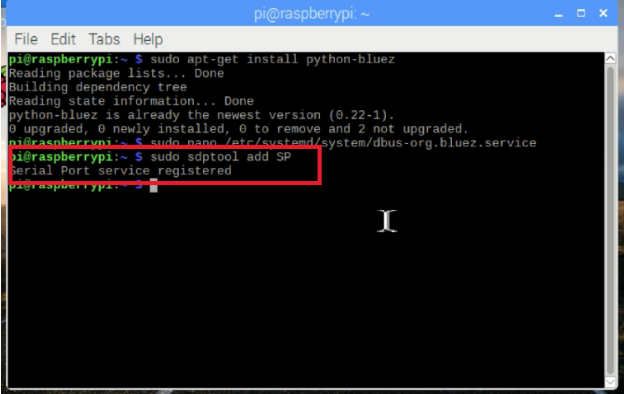
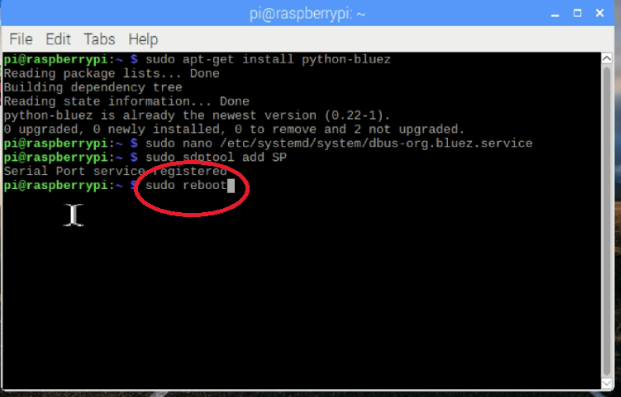
重新启动你的Pi:
$ sudo reboot
将Pi的蓝牙与Android配对
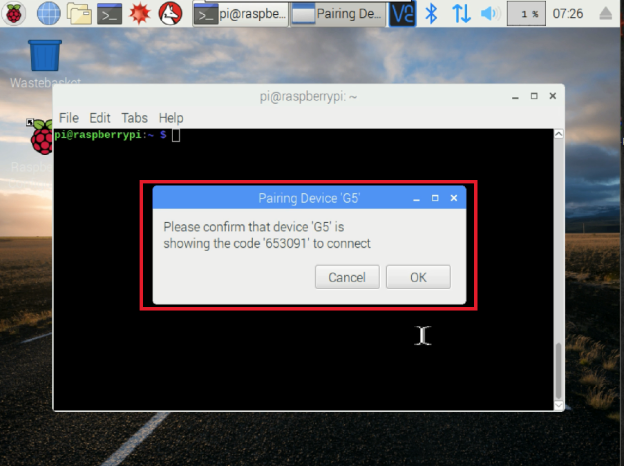
重启后,将Pi的蓝牙与Android手机配对。
配对蓝牙:
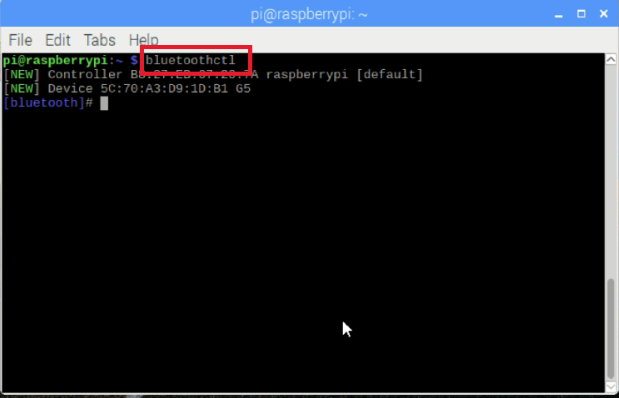
打开手机的蓝牙,将手机与Raspberry Pi配对。接下来,在您的Pi上输入:
$ bluetoothctl
power on
discoverable on
scan on
您的手机将显示在可用设备列表中。记下您手机的地址。
信任
对
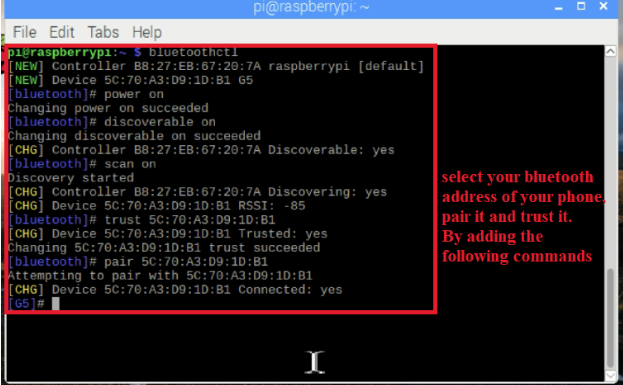
要退出蓝牙ctl,请输入退出命令:
退出
您也可以跳过以上设置如果您发现可以使用Raspbian的UI轻松设置蓝牙。
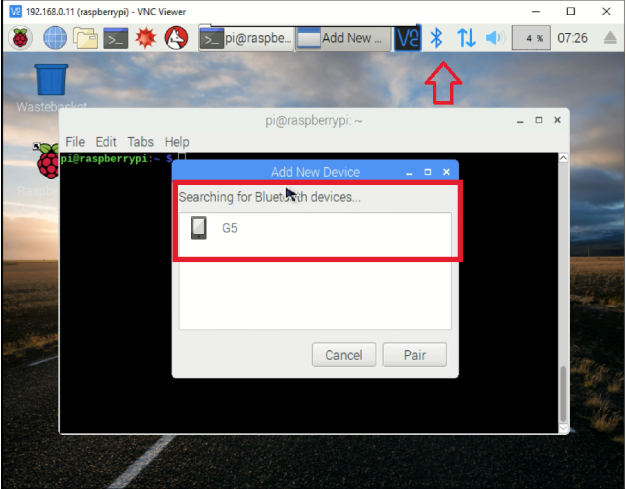
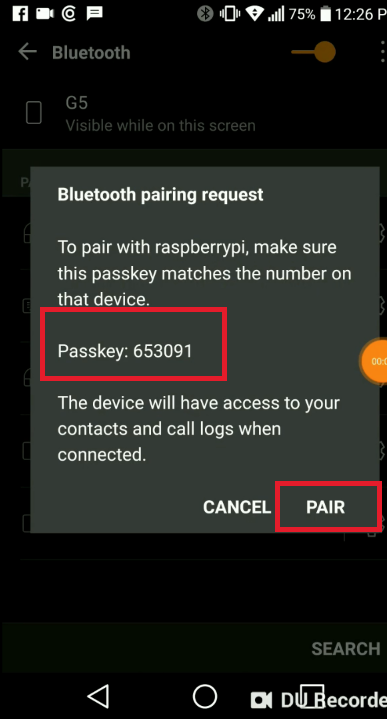
在配对蓝牙后,通过输入nano命令并复制/粘贴源代码,将Python脚本直接添加到Raspbian中:
$ sudo python run.py
你也可以在这里直接复制run.py文件。
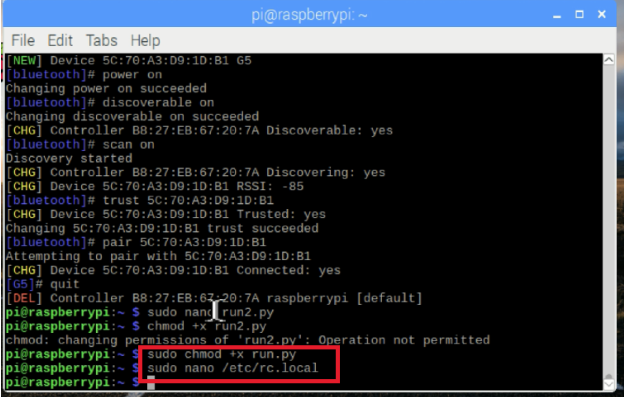
接下来,您可以运行该脚本。但首先使脚本可执行:
$ chmod +x run.py
运行:
$ sudo 。/run.py
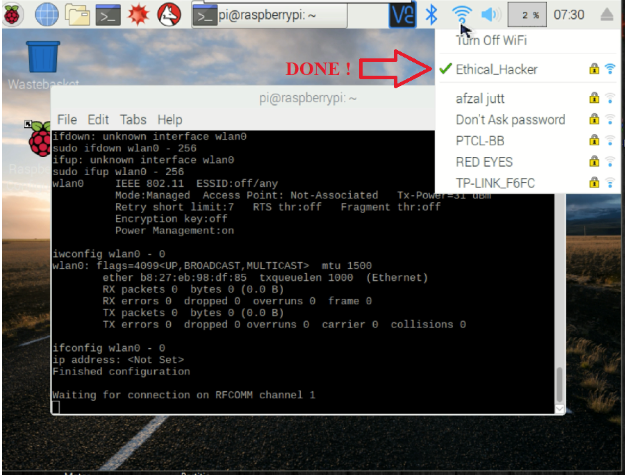
执行此操作后,现在需要打开Android应用程序。为此,请使用此处的.apk文件下载并安装应用程序。
在蓝牙配对设备中选择Raspberry Pi。输入SSID,PSK并点击开始配置按钮。在几秒钟内,您的Raspberry Pi的Wi-Fi应该连接,如下图所示。


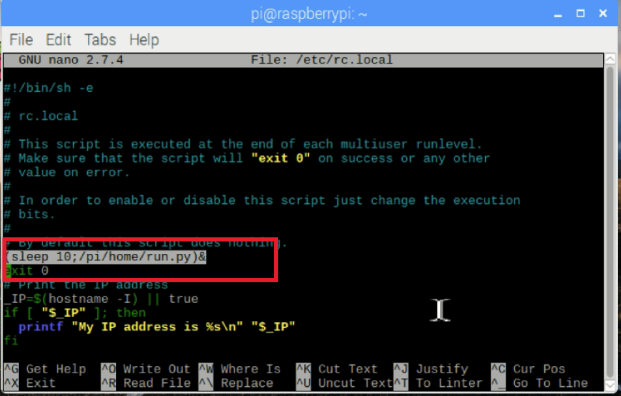
要在启动时运行此脚本,请编辑/etc/rc.local 并添加:
(睡10;/path/to/script/。/run.py)&
源代码(run.py)
#!/usr/bin/env python
import os
from bluetooth import *
from wifi import Cell, Scheme
import subprocess
import time
wpa_supplicant_conf = “/etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf”
sudo_mode = “sudo ”
def wifi_connect(ssid, psk):
# write wifi config to file
cmd = ‘wpa_passphrase {ssid} {psk} | sudo tee -a {conf} 》 /dev/null’.format(
ssid=str(ssid).replace(‘!’, ‘\!’),
psk=str(psk).replace(‘!’, ‘\!’),
conf=wpa_supplicant_conf
)
cmd_result = “”
cmd_result = os.system(cmd)
print cmd + “ - ” + str(cmd_result)
# reconfigure wifi
cmd = sudo_mode + ‘wpa_cli -i wlan0 reconfigure’
cmd_result = os.system(cmd)
print cmd + “ - ” + str(cmd_result)
time.sleep(10)
cmd = ‘iwconfig wlan0’
cmd_result = os.system(cmd)
print cmd + “ - ” + str(cmd_result)
cmd = ‘ifconfig wlan0’
cmd_result = os.system(cmd)
print cmd + “ - ” + str(cmd_result)
p = subprocess.Popen([‘hostname’, ‘-I’], stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
out, err = p.communicate()
if out:
ip_address = out
else:
ip_address = “”
return ip_address
def ssid_discovered():
Cells = Cell.all(‘wlan0’)
wifi_info = ‘Found ssid : ’
for current in range(len(Cells)):
wifi_info += Cells[current].ssid + “ ”
wifi_info+=“!”
print wifi_info
return wifi_info
def handle_client(client_sock) :
# get ssid
client_sock.send(ssid_discovered())
print “Waiting for SSID.。.”
ssid = client_sock.recv(1024)
if ssid == ‘’ :
return
print “ssid received”
print ssid
# get psk
client_sock.send(“waiting-psk!”)
print “Waiting for PSK.。.”
psk = client_sock.recv(1024)
if psk == ‘’ :
return
print “psk received”
print psk
ip_address = wifi_connect(ssid, psk)
print “ip address: ” + ip_address
client_sock.send(“ip-address:” + ip_address + “!”)
return
try:
while True:
server_sock=BluetoothSocket( RFCOMM )
server_sock.bind((“”,PORT_ANY))
server_sock.listen(1)
port = server_sock.getsockname()[1]
uuid = “815425a5-bfac-47bf-9321-c5ff980b5e11”
advertise_service( server_sock, “RPi Wifi config”,
service_id = uuid,
service_classes = [ uuid, SERIAL_PORT_CLASS ],
profiles = [ SERIAL_PORT_PROFILE ])
print “Waiting for connection on RFCOMM channel %d” % port
client_sock, client_info = server_sock.accept()
print “Accepted connection from ”, client_info
handle_client(client_sock)
client_sock.close()
server_sock.close()
# finished config
print ‘Finished configuration ’
except (KeyboardInterrupt, SystemExit):
print ‘ Exiting ’
-
Wi-Fi 定位服务2025-04-17 520
-
#硬声创作季 树莓派教程:Wi-fi Hacking with Raspberry Pi 3 - WPA_WMr_haohao 2022-10-02
-
搞定华为手机Wi-Fi时好时坏或者Wi-Fi,就用这个两招搞定即可#手机评测#手机维修 #硬声创作季深海狂鲨 2022-10-08
-
仅售229软妹币的树莓派三代,你心动了么?2016-03-01 3380
-
树莓派三代:搭载Wi-Fi 和蓝牙,更好更强大2016-03-09 8287
-
Wi-Fi网状网络解决方案扩展连接边界2018-08-30 3311
-
Wi-Fi入门Android?2018-10-10 1472
-
请问如何解决手机中WiMax、蓝牙和Wi-Fi共存问题?2021-06-02 1715
-
适用于iOS和Android系统,支持Wi-Fi配置与亚马逊账号登陆功能的开源手机APP有吗?2023-02-17 622
-
手机内置Wi-Fi是什么2010-01-28 5084
-
全球Wi-Fi联盟:对中国取消Wi-Fi手机禁令表示欢迎2010-04-07 889
-
Ubuntu 16.04 MATE树莓派3版本开始支持板载Wi-Fi和蓝牙2019-04-02 560
-
如何在树莓派3上设置Wi-Fi和蓝牙2019-12-05 5858
-
快速提升Wi-Fi网络体验的小技巧2021-07-22 2866
-
通过BLE实现Wi-Fi配置2022-05-17 1072
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

