

英创信息技术标准socket编程应用于英创主板的蓝牙接口
描述
蓝牙(bluetooth)技术是一种低功耗短距离的无线通信技术,被广泛应用于10米以内的嵌入式设备通信当中。其最高传输速度根据蓝牙协议的版本不同,有1Mbps(BR、LE)、2-3Mbps(EDR)、24Mbps(HS)之分。在工业现场,蓝牙技术可以代替串行线缆,实现无线通信。在智能手机普及的今天,通过蓝牙与手机建立连接,手机作为上位机发送指令给下位机,可以实现低成本的UI控制方案。
BlueZ是当前比较成熟的蓝牙协议栈,作为Linux系统的官方协议栈,集成在Linux内核之中。英创公司在ESM928x的Linux系统中,又移植了BlueZ用户空间协议栈和相关工具,使得ESM928x Linux平台能够支持蓝牙技术,通过socket编程实现蓝牙无线连接,代替串行线缆进行通信。

图1 ESM928xW系列主板+底板
用户使用蓝牙串口功能主要分为两个步骤:蓝牙功能配置和socket应用程序编写。
1、蓝牙功能配置
1、加载ap2610蓝牙模块上电驱动
insmod /lib/modules/4.1.14/ap6210_bt_bcm20710.ko
2、加载蓝牙固件,设定波特率、蓝牙地址、使能hci等
brcm_patchram_plus --patchram /lib/firmware/ap6210/bcm20702a.hcd --baudrate 3000000 --enable_hci --bd_addr aa:00:55:44:33:22 --no2bytes --tosleep 5000 /dev/ttyS5 1> /dev/null&
3、启动dbus后台服务
dbus-daemon --system --nofork --nopidfile &
4、以兼容模式启动bluetooth后台服务
/libexec/bluetooth/bluetoothd -C &
5、启动hci0,并设置name和可见属性
hciconfig hci0 up
hciconfig hci0 name esm9287
hciconfig hci0 piscan
hciconfig hci0 reset
以上5个步骤已经写成一个shell脚本set_bluetooth.sh,用户也可以直接运行该脚本完成以上设置。至此,完成了对蓝牙的设置,可以通过hciconfig hci0 -a来查看蓝牙信息,如图2。这时,其他蓝牙设备就可以搜索到esm9287,图3所示是android手机搜索到esm9287蓝牙设备,点击即可完成配对。

图2 使用hciconfig查看蓝牙信息
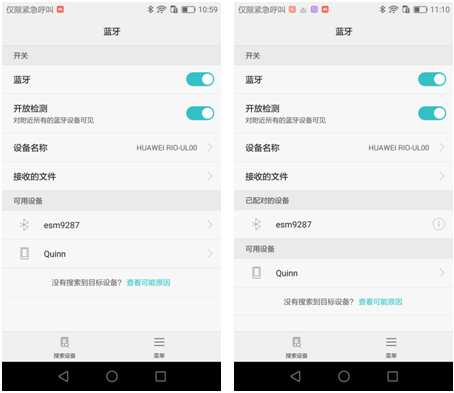
图3 搜索esm9287并配对
2、Socket应用编程
蓝牙协议栈中的RFCOMM协议实现了对串口RS232的仿真,最多能提供两个蓝牙设备之间60路的连接。应用程序中,可以使用socket进行服务端和客户端的编程,其过程与TCP/IP的socket通信没有太大区别。
a)环境配置
开发bluez协议栈的蓝牙应用需要用到libbluetooth.so和相关头文件,需要添加到eclipse对应的蓝牙项目中。libbluetooth.so是编译bluez协议栈生产的动态链接库,提供了头文件bluetooth.h、hci_lib.h、sdp_lib.h中的函数实体,实现蓝牙地址与常用数据类型的转换、hci设备和sdp服务的一系列操作函数。
1、在项目中新建文件夹include/bluetooth,其中放入蓝牙协议相关头文件;新建文件夹lib,其中放动态链接库libbluetooth.so。

图4 新建include和lib文件夹
2、进入项目Properties设置,添加项目下的include文件夹为GCC C++ Compiler和GCC C Complier编译器的头文件路径(下图是GCC C++ Compiler的设置,GCC C Compiler设置步骤相同)。

图5 添加头文件搜索路径
3、为Sourcery G++ Lite C++ Linker链接器添加libbluetooth.so库文件及搜索路径,如下图。
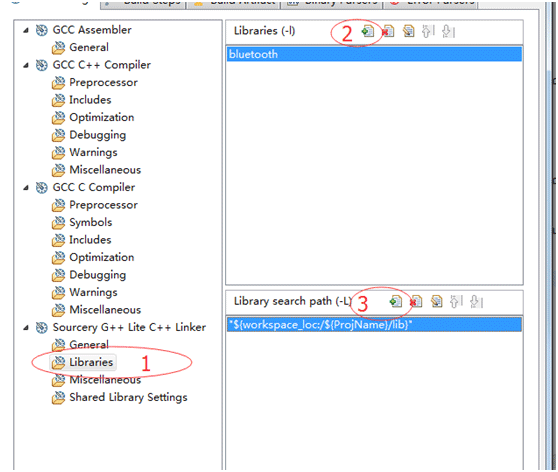
图6 添加编译库及搜索路径
b)服务端程序
1、申请蓝牙RFCOMM socket
s = socket(AF_BLUETOOTH, SOCK_STREAM, BTPROTO_RFCOMM);
2、绑定本地适配器,BDADDR_ANY默认为第一个可用蓝牙适配器
loc_addr.rc_family = AF_BLUETOOTH;
loc_addr.rc_bdaddr = *BDADDR_ANY;
loc_addr.rc_channel = (uint8_t) 1;
bind(s, (structsockaddr *)&loc_addr,sizeof(loc_addr));
3、设置socket监听模式,这里只允许建立一个连接
listen(s, 1);
4、等待连接
client = accept(s, (structsockaddr *)&rem_addr, &opt);
5、select模式读取socket数据流
while(1)
{
FD_ZERO(&working_set);
max_sd = client;
FD_SET(client, &working_set);
timeout.tv_sec = 3 * 60;
timeout.tv_usec = 0;
// Call select() and wait 5 minutes for it to complete.
printf("Waiting on select() %ld sec...\n", timeout.tv_sec);
intrc_select = select(max_sd + 1, &working_set, NULL, NULL, &timeout);
// Check to see if the select call failed.
if(rc_select < 0)
{
perror(" select() failed");
break;
}
elseif(rc_select > 0)
{
if(FD_ISSET(max_sd,&working_set))
{
// read data from the client
bytes_read = read(client, buf,sizeof(buf));
if( bytes_read > 0 ) {
printf("received: [%s]\n", buf);
}
else
{
break;
}
write(client,ack,sizeof(ack));
}
}
// Else if rc_select == 0 then the 5 minute time out expired.
else
{
printf(" select() timed out.\n");
break;
}
}
6、关闭套接字
close(client);
close(s);
c)客户端
1、申请蓝牙RFCOMM socket
s = socket(AF_BLUETOOTH, SOCK_STREAM, BTPROTO_RFCOMM);
2、设置蓝牙连接服务器的地址
structsockaddr_rc addr = { 0 };
// set the connection parameters (who to connect to)
addr.rc_family = AF_BLUETOOTH;
addr.rc_channel = (uint8_t) 1;
str2ba( dest, &addr.rc_bdaddr );
3、连接蓝牙服务器
// connect to server
status = connect(s, (structsockaddr *)&addr,sizeof(addr));
4、读写socket数据流
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
// send a message
write(s, message[i], strlen(message[i])+1);
printf("write \"%s\" to %s\n", message[i],dest);
bytes_read = read(s, buf,sizeof(buf));
if( bytes_read > 0 ) {
printf("received: [%s]\n", buf);
}
}
其中,message[i]为发送内容的地址。
5、关闭socket
close(s);
在一张板子上运行蓝牙rfcomm服务程序,在另一张板子上运行蓝牙rfcomm客户端程序,如图6、图7所示:
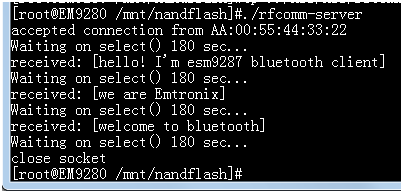
图7 服务端程序
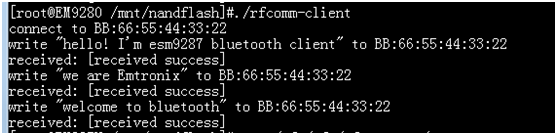
图8 客户端程序
通过socket编程,蓝牙应用程序可以像tcp/ip的网络编程一样,建立连接,实现无线通信。如果有用户对蓝牙的串口socket编程感兴趣,可以联系我们。我们将提供驱动文件、蓝牙库文件及相应的示例程序。
-
英创信息技术基于英创主板快速构建整机应用方案简介2020-02-12 1859
-
英创信息技术ESMARC工控主板升级简介2020-02-07 2259
-
英创信息技术获取英创Linux主板型号的方法简介2020-02-06 1768
-
英创信息技术Linux主板Qt网络应用程序简介2020-01-17 1537
-
英创信息技术英创工控主板支持电力终端标准显示介绍2019-11-15 2231
-
英创主板JAVA应用开发简介2017-10-20 2425
-
英创嵌入式主板的无线通讯解决方案2017-03-24 3183
-
英创工控主板产品选型指南2017-02-28 3573
-
标准socket编程应用于英创主板的蓝牙接口2017-01-18 3437
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

