

炫彩LED灯带的制作
电子说
描述
概述
永恒的时尚标准,带有声音感应,全彩LED动画,并可以通过手机无线控制。
受约翰G启发,此经典Ampli-Tie的更新使用了 Circuit Playground Bluefruit 和 Neopixel LED ,可将领带变成便携式的,可自定义的灯光秀-无需焊接。这肯定会在舞池和绝大多数正式活动中引起您的注意。
您需要什么
电路场Bluefruit-低功耗蓝牙
产品ID:4333
电路游乐场Bluefruit是电路游乐场系列中的第三块板,朝着完美介绍电子学和编程迈出了一步。我们已经。..
$ 24.95
进货
添加到购物车
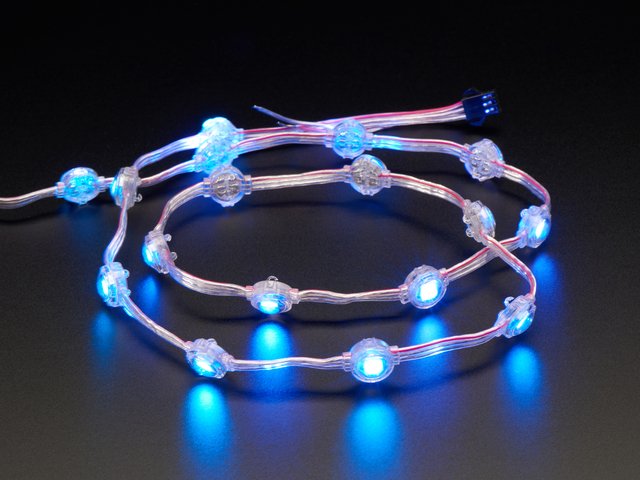

Adafruit NeoPixel LED点链-20“,间距2”
产品ID:3630
将NeoPixel条形连接到服装上可能会很费力,因为柔性PCB弯曲得过多时会破裂,因此如何添加少量的颜色点呢?搁浅的NeoPixel点!。..
$ 27.50
入库存
添加到购物车

USB电缆-USB A到Micro-B
产品ID:592
这是您的标准A到Micro-B USB电缆,用于USB 1.1或2.0,非常适合将PC连接到Metro,Feather,Raspberry Pi或其他dev-board或。..
$ 2.95
进货
添加到购物车

电路场的螺栓固定套件, micro:bit,Flora或Gemma
产品ID:4103
您有一个Circuit Playground Express,想连接一些电线以添加LED或传感器或扬声器吗?您可以使用我们的。..
$ 1.50
入库存
添加到购物车
1 x 锂离子聚合物电池-3.7v 1200mAh
力量
添加到购物车
1 x 剥线钳
用于暴露引线
添加到购物车
1 x 剪刀
用于修剪电线,螺纹等
添加到购物车
1 x 口袋螺丝刀
用于固定电线
添加到购物车
1 x 缝制针
缝制这些像素
添加到购物车
Plus…
分离式或夹式领带-如果您想要一个不错的领带,请参见
织物(用于电池袋)
螺纹
10毫米下摆带
铁和熨衣板
iPhone/iPad(iOS 11.3或更高版本)或带有BLE的Android设备(Android 4.4或更高版本)
Circuit Playground Bluefruit上的CircuitPython
安装或更新CircuitPython
按照以下快速分步操作,在Circuit Playground Bluefruit上安装或更新CircuitPython。
Circuit Playground Bluefruit需要CircuitPython 5.0+。 CircuitPython 5.0当前处于Alpha状态。这意味着我们仍在努力添加功能并解决问题。如果遇到任何问题,请通过#help-with-circuitpython频道的Discord(https://adafru.it/discord)与我们联系,或者在GitHub上通过https://github.com/adafruit/提交问题。
此外,如果要使用要使用此开发板的蓝牙(BLE)功能,您需要adafruit_ble库的预发行版本。从https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit_CircuitPython_BLE/releases
中选择最新的预发布版本,可通过circuitpython.org 《

点击链接上方并下载最新的UF2文件
下载并将其保存到桌面(或任何方便的地方)
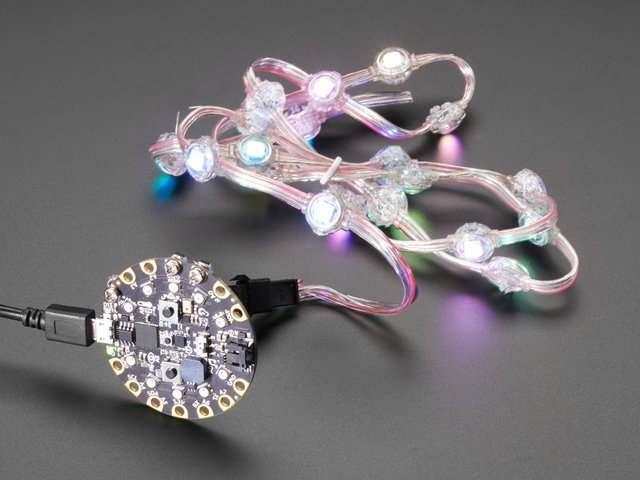
使用已知的具有良好数据功能的USB电缆将Circuit Playground Bluefruit插入计算机。
许多人最终使用仅可充电的USB电缆,这非常令人沮丧!因此,请确保您拥有知道对数据同步有用的USB电缆。
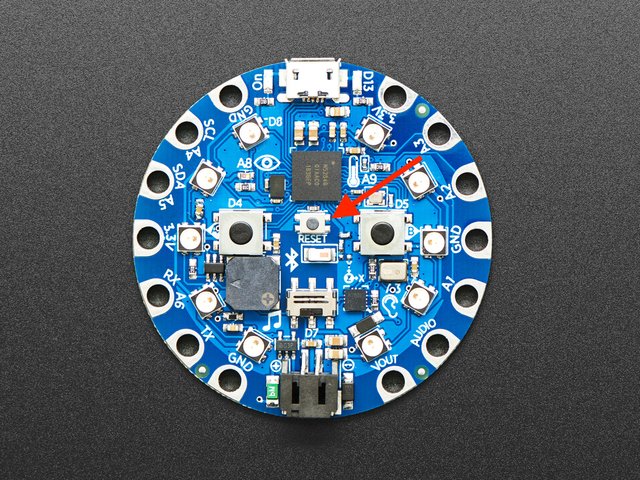
双击CPB中间的小 Reset 小按钮(由表示图片中的红色箭头)。十个NeoPixel LED将全部变为红色,然后全部变为绿色。如果它们全部变为红色并保持红色,请检查USB电缆,尝试使用另一个USB端口,等等。USB连接器旁边的红色LED指示灯将呈红色闪烁-可以!
如果双击鼠标不第一次没有工作,请再试一次。有时可能需要一些尝试才能使节奏正确!
(如果双击不起作用,请单击一下!)
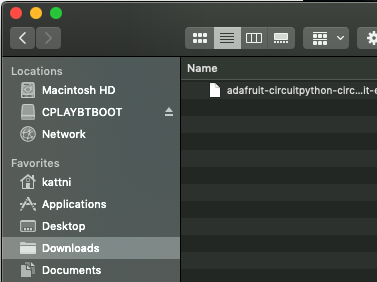
您将看到一个名为 CPLAYBTBOOT 的新磁盘驱动器。
将 adafruit_circuitpython_etc.uf2 文件拖到 CPLAYBTBOOT。
LED将变为红色。然后, CPLAYBTBOOT 驱动器将消失,并出现一个名为 CIRCUITPY 的新磁盘驱动器。
就这样,您就完成了! :)
软件
现在在CPB上安装了 CircuitPython ,我们可以继续安装项目软件。
安装Bluefruit Connect和Neopixel库
项目代码需要两个代码库才能协助蓝牙通讯。 点击下面的链接以下载CircuitPython库捆绑包:
库捆绑包
解压缩库捆绑包,然后打开其中的 lib 文件夹。
找到名为 adafruit_bluefruit_connect 的文件夹和名为的文件neopixel.mpy – 两者复制并将它们粘贴到 CIRCUITPY 驱动器的 lib 文件夹。
安装BLE库
要下载我们需要的最后一个库,请单击下面的按钮:
BLE库
解压缩,已下载的zip文件,并打开其中的 lib 文件夹。复制名为 adafruit_ble 的文件夹,并将其粘贴到 CIRCUITPY 驱动器的 lib 文件夹中。
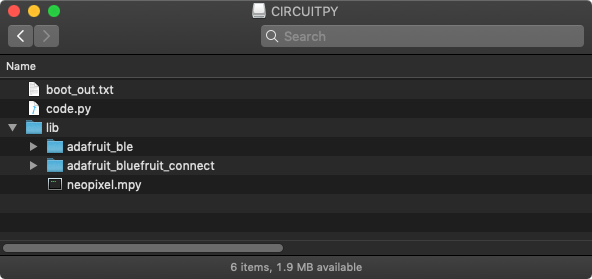
您的CIRCUITPY驱动器的文件结构现在应该看起来像这样:
上传代码
复制下面的代码并将其粘贴到新文本文件中。
将文本文件另存为 code.py 到 CIRCUITPY的根目录中驱动器。
下载:Project Zip 或代码.py | 在Github上查看
复制代码
“”“
LED Disco Tie with Bluetooth
=========================================================
Give your suit an sound-reactive upgrade with Circuit
Playground Bluefruit & Neopixels. Set color and animation
mode using the Bluefruit LE Connect app.
Author: Collin Cunningham for Adafruit Industries, 2019
”“”
# pylint: disable=global-statement
import time
import array
import math
import audiobusio
import board
import neopixel
from adafruit_ble.uart_server import UARTServer
from adafruit_bluefruit_connect.packet import Packet
from adafruit_bluefruit_connect.color_packet import ColorPacket
from adafruit_bluefruit_connect.button_packet import ButtonPacket
uart_server = UARTServer()
# User input vars
mode = 0 # 0=audio, 1=rainbow, 2=larsen_scanner, 3=solid
user_color= (127,0,0)
# Audio meter vars
PEAK_COLOR = (100, 0, 255)
NUM_PIXELS = 10
CURVE = 2
SCALE_EXPONENT = math.pow(10, CURVE * -0.1)
NUM_SAMPLES = 160
# Restrict value to be between floor and ceiling.
def constrain(value, floor, ceiling):
return max(floor, min(value, ceiling))
# Scale input_value between output_min and output_max, exponentially.
def log_scale(input_value, input_min, input_max, output_min, output_max):
normalized_input_value = (input_value - input_min) / \
(input_max - input_min)
return output_min + \
math.pow(normalized_input_value, SCALE_EXPONENT) \
* (output_max - output_min)
# Remove DC bias before computing RMS.
def normalized_rms(values):
minbuf = int(mean(values))
samples_sum = sum(
float(sample - minbuf) * (sample - minbuf)
for sample in values
)
return math.sqrt(samples_sum / len(values))
def mean(values):
return sum(values) / len(values)
def volume_color(volume):
return 200, volume * (255 // NUM_PIXELS), 0
# Set up NeoPixels and turn them all off.
pixels = neopixel.NeoPixel(board.A1, NUM_PIXELS, brightness=0.1, auto_write=False)
pixels.fill(0)
pixels.show()
mic = audiobusio.PDMIn(board.MICROPHONE_CLOCK, board.MICROPHONE_DATA,
sample_rate=16000, bit_depth=16)
# Record an initial sample to calibrate. Assume it‘s quiet when we start.
samples = array.array(’H‘, [0] * NUM_SAMPLES)
mic.record(samples, len(samples))
# Set lowest level to expect, plus a little.
input_floor = normalized_rms(samples) + 10
# Corresponds to sensitivity: lower means more pixels light up with lower sound
input_ceiling = input_floor + 500
peak = 0
def wheel(wheel_pos):
# Input a value 0 to 255 to get a color value.
# The colours are a transition r - g - b - back to r.
if wheel_pos 《 0 or wheel_pos 》 255:
r = g = b = 0
elif wheel_pos 《 85:
r = int(wheel_pos * 3)
g = int(255 - wheel_pos*3)
b = 0
elif wheel_pos 《 170:
wheel_pos -= 85
r = int(255 - wheel_pos*3)
g = 0
b = int(wheel_pos*3)
else:
wheel_pos -= 170
r = 0
g = int(wheel_pos*3)
b = int(255 - wheel_pos*3)
return (r, g, b)
def rainbow_cycle(delay):
for j in range(255):
for i in range(NUM_PIXELS):
pixel_index = (i * 256 // NUM_PIXELS) + j
pixels[i] = wheel(pixel_index & 255)
pixels.show()
time.sleep(delay)
def audio_meter(new_peak):
mic.record(samples, len(samples))
magnitude = normalized_rms(samples)
# Compute scaled logarithmic reading in the range 0 to NUM_PIXELS
c = log_scale(constrain(magnitude, input_floor, input_ceiling),
input_floor, input_ceiling, 0, NUM_PIXELS)
# Light up pixels that are below the scaled and interpolated magnitude.
pixels.fill(0)
for i in range(NUM_PIXELS):
if i 《 c:
pixels[i] = volume_color(i)
# Light up the peak pixel and animate it slowly dropping.
if c 》= new_peak:
new_peak = min(c, NUM_PIXELS - 1)
elif new_peak 》 0:
new_peak = new_peak - 1
if new_peak 》 0:
pixels[int(new_peak)] = PEAK_COLOR
pixels.show()
return new_peak
pos = 0 # position
direction = 1 # direction of “eye”
def larsen_set(index, color):
if index 《 0:
return
else:
pixels[index] = color
def larsen(delay):
global pos
global direction
color_dark = (int(user_color[0]/8), int(user_color[1]/8),
int(user_color[2]/8))
color_med = (int(user_color[0]/2), int(user_color[1]/2),
int(user_color[2]/2))
larsen_set(pos - 2, color_dark)
larsen_set(pos - 1, color_med)
larsen_set(pos, user_color)
larsen_set(pos + 1, color_med)
if (pos + 2) 《 NUM_PIXELS:
# Dark red, do not exceed number of pixels
larsen_set(pos + 2, color_dark)
pixels.write()
time.sleep(delay)
# Erase all and draw a new one next time
for j in range(-2, 2):
larsen_set(pos + j, (0, 0, 0))
if (pos + 2) 《 NUM_PIXELS:
larsen_set(pos + 2, (0, 0, 0))
# Bounce off ends of strip
pos += direction
if pos 《 0:
pos = 1
direction = -direction
elif pos 》= (NUM_PIXELS - 1):
pos = NUM_PIXELS - 2
direction = -direction
def solid(new_color):
pixels.fill(new_color)
pixels.show()
def map_value(value, in_min, in_max, out_min, out_max):
out_range = out_max - out_min
in_range = in_max - in_min
return out_min + out_range * ((value - in_min) / in_range)
speed = 6.0
wait = 0.097
def change_speed(mod, old_speed):
new_speed = constrain(old_speed + mod, 1.0, 10.0)
return(new_speed, map_value(new_speed, 10.0, 0.0, 0.01, 0.3))
while True:
# While BLE is *not* connected
if not uart_server.connected:
# OK to call again even if already advertising
uart_server.start_advertising()
# While BLE is connected
else:
if uart_server.in_waiting:
packet = Packet.from_stream(uart_server)
# Received ColorPacket
if isinstance(packet, ColorPacket):
user_color = packet.color
# Received ButtonPacket
elif isinstance(packet, ButtonPacket):
if packet.pressed:
if packet.button == ButtonPacket.UP:
speed, wait = change_speed(1, speed)
elif packet.button == ButtonPacket.DOWN:
speed, wait = change_speed(-1, speed)
elif packet.button == ButtonPacket.BUTTON_1:
mode = 0
elif packet.button == ButtonPacket.BUTTON_2:
mode = 1
elif packet.button == ButtonPacket.BUTTON_3:
mode = 2
elif packet.button == ButtonPacket.BUTTON_4:
mode = 3
# Determine animation based on mode
if mode == 0:
peak = audio_meter(peak)
elif mode == 1:
rainbow_cycle(0.001)
elif mode == 2:
larsen(wait)
elif mode == 3:
solid(user_color)
“”“
LED Disco Tie with Bluetooth
=========================================================
Give your suit an sound-reactive upgrade with Circuit
Playground Bluefruit & Neopixels. Set color and animation
mode using the Bluefruit LE Connect app.
Author: Collin Cunningham for Adafruit Industries, 2019
”“”
# pylint: disable=global-statement
import time
import array
import math
import audiobusio
import board
import neopixel
from adafruit_ble.uart_server import UARTServer
from adafruit_bluefruit_connect.packet import Packet
from adafruit_bluefruit_connect.color_packet import ColorPacket
from adafruit_bluefruit_connect.button_packet import ButtonPacket
uart_server = UARTServer()
# User input vars
mode = 0 # 0=audio, 1=rainbow, 2=larsen_scanner, 3=solid
user_color= (127,0,0)
# Audio meter vars
PEAK_COLOR = (100, 0, 255)
NUM_PIXELS = 10
CURVE = 2
SCALE_EXPONENT = math.pow(10, CURVE * -0.1)
NUM_SAMPLES = 160
# Restrict value to be between floor and ceiling.
def constrain(value, floor, ceiling):
return max(floor, min(value, ceiling))
# Scale input_value between output_min and output_max, exponentially.
def log_scale(input_value, input_min, input_max, output_min, output_max):
normalized_input_value = (input_value - input_min) / \
(input_max - input_min)
return output_min + \
math.pow(normalized_input_value, SCALE_EXPONENT) \
* (output_max - output_min)
# Remove DC bias before computing RMS.
def normalized_rms(values):
minbuf = int(mean(values))
samples_sum = sum(
float(sample - minbuf) * (sample - minbuf)
for sample in values
)
return math.sqrt(samples_sum / len(values))
def mean(values):
return sum(values) / len(values)
def volume_color(volume):
return 200, volume * (255 // NUM_PIXELS), 0
# Set up NeoPixels and turn them all off.
pixels = neopixel.NeoPixel(board.A1, NUM_PIXELS, brightness=0.1, auto_write=False)
pixels.fill(0)
pixels.show()
mic = audiobusio.PDMIn(board.MICROPHONE_CLOCK, board.MICROPHONE_DATA,
sample_rate=16000, bit_depth=16)
# Record an initial sample to calibrate. Assume it’s quiet when we start.
samples = array.array(‘H’, [0] * NUM_SAMPLES)
mic.record(samples, len(samples))
# Set lowest level to expect, plus a little.
input_floor = normalized_rms(samples) + 10
# Corresponds to sensitivity: lower means more pixels light up with lower sound
input_ceiling = input_floor + 500
peak = 0
def wheel(wheel_pos):
# Input a value 0 to 255 to get a color value.
# The colours are a transition r - g - b - back to r.
if wheel_pos 《 0 or wheel_pos 》 255:
r = g = b = 0
elif wheel_pos 《 85:
r = int(wheel_pos * 3)
g = int(255 - wheel_pos*3)
b = 0
elif wheel_pos 《 170:
wheel_pos -= 85
r = int(255 - wheel_pos*3)
g = 0
b = int(wheel_pos*3)
else:
wheel_pos -= 170
r = 0
g = int(wheel_pos*3)
b = int(255 - wheel_pos*3)
return (r, g, b)
def rainbow_cycle(delay):
for j in range(255):
for i in range(NUM_PIXELS):
pixel_index = (i * 256 // NUM_PIXELS) + j
pixels[i] = wheel(pixel_index & 255)
pixels.show()
time.sleep(delay)
def audio_meter(new_peak):
mic.record(samples, len(samples))
magnitude = normalized_rms(samples)
# Compute scaled logarithmic reading in the range 0 to NUM_PIXELS
c = log_scale(constrain(magnitude, input_floor, input_ceiling),
input_floor, input_ceiling, 0, NUM_PIXELS)
# Light up pixels that are below the scaled and interpolated magnitude.
pixels.fill(0)
for i in range(NUM_PIXELS):
if i 《 c:
pixels[i] = volume_color(i)
# Light up the peak pixel and animate it slowly dropping.
if c 》= new_peak:
new_peak = min(c, NUM_PIXELS - 1)
elif new_peak 》 0:
new_peak = new_peak - 1
if new_peak 》 0:
pixels[int(new_peak)] = PEAK_COLOR
pixels.show()
return new_peak
pos = 0 # position
direction = 1 # direction of “eye”
def larsen_set(index, color):
if index 《 0:
return
else:
pixels[index] = color
def larsen(delay):
global pos
global direction
color_dark = (int(user_color[0]/8), int(user_color[1]/8),
int(user_color[2]/8))
color_med = (int(user_color[0]/2), int(user_color[1]/2),
int(user_color[2]/2))
larsen_set(pos - 2, color_dark)
larsen_set(pos - 1, color_med)
larsen_set(pos, user_color)
larsen_set(pos + 1, color_med)
if (pos + 2) 《 NUM_PIXELS:
# Dark red, do not exceed number of pixels
larsen_set(pos + 2, color_dark)
pixels.write()
time.sleep(delay)
# Erase all and draw a new one next time
for j in range(-2, 2):
larsen_set(pos + j, (0, 0, 0))
if (pos + 2) 《 NUM_PIXELS:
larsen_set(pos + 2, (0, 0, 0))
# Bounce off ends of strip
pos += direction
if pos 《 0:
pos = 1
direction = -direction
elif pos 》= (NUM_PIXELS - 1):
pos = NUM_PIXELS - 2
direction = -direction
def solid(new_color):
pixels.fill(new_color)
pixels.show()
def map_value(value, in_min, in_max, out_min, out_max):
out_range = out_max - out_min
in_range = in_max - in_min
return out_min + out_range * ((value - in_min) / in_range)
speed = 6.0
wait = 0.097
def change_speed(mod, old_speed):
new_speed = constrain(old_speed + mod, 1.0, 10.0)
return(new_speed, map_value(new_speed, 10.0, 0.0, 0.01, 0.3))
while True:
# While BLE is *not* connected
if not uart_server.connected:
# OK to call again even if already advertising
uart_server.start_advertising()
# While BLE is connected
else:
if uart_server.in_waiting:
packet = Packet.from_stream(uart_server)
# Received ColorPacket
if isinstance(packet, ColorPacket):
user_color = packet.color
# Received ButtonPacket
elif isinstance(packet, ButtonPacket):
if packet.pressed:
if packet.button == ButtonPacket.UP:
speed, wait = change_speed(1, speed)
elif packet.button == ButtonPacket.DOWN:
speed, wait = change_speed(-1, speed)
elif packet.button == ButtonPacket.BUTTON_1:
mode = 0
elif packet.button == ButtonPacket.BUTTON_2:
mode = 1
elif packet.button == ButtonPacket.BUTTON_3:
mode = 2
elif packet.button == ButtonPacket.BUTTON_4:
mode = 3
# Determine animation based on mode
if mode == 0:
peak = audio_meter(peak)
elif mode == 1:
rainbow_cycle(0.001)
elif mode == 2:
larsen(wait)
elif mode == 3:
solid(user_color)
项目代码一旦保存 到 CIRCUITPY 作为 code.py, 软件已全部设置好了–是时候继续组装硬件。
准备NeoPixels
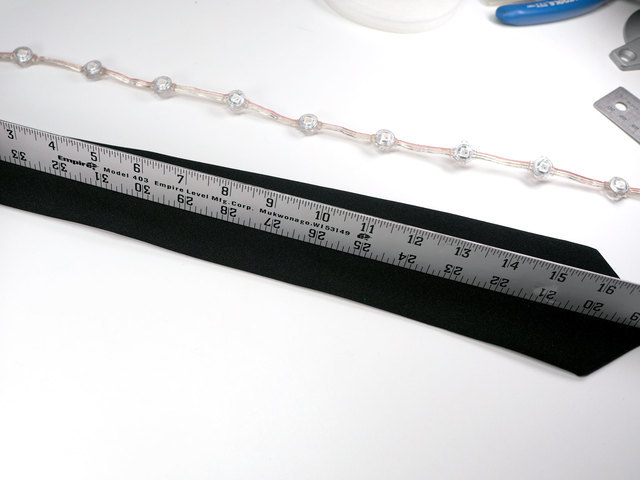
首先要做的是修剪Neopixel LED条以使其与领带的长度相匹配。 20“分离式领带的长度可以为 9 NeoPixels 。如果使用其他领带,请确保在切割前找到合适的长度。
《表类=“ build-table”》

常规剪刀可以被拖拉或损坏,因此请确保使用一对钢丝钳或专为切割金属而设计的剪刀。
我们将在下图中用红色虚线表示的两个点处剪切条。

剪切输入线
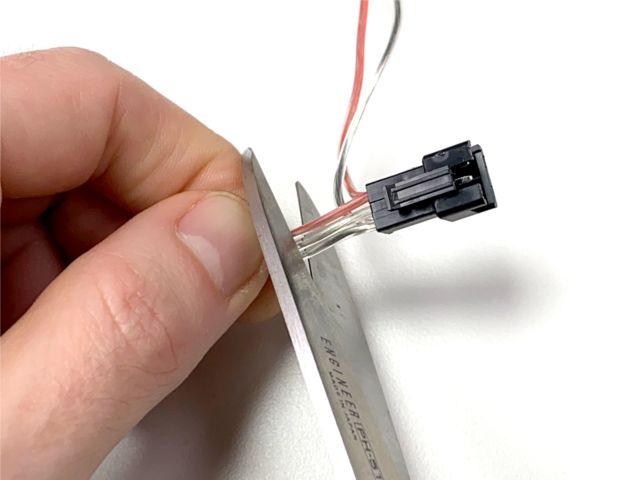



从条形板上剪下公型插针连接器(将2根多余的电线垂到一侧)。切近连接器本身以增加长度。这是将要连接到Circuit Playground蓝果的条带的末端。
使用剥线钳移除大约 15mm 》从每根刚切割的导线的末端开始绝缘。
轻轻地扭曲每捆线束,以防止它们磨损。
删除多余的新像素
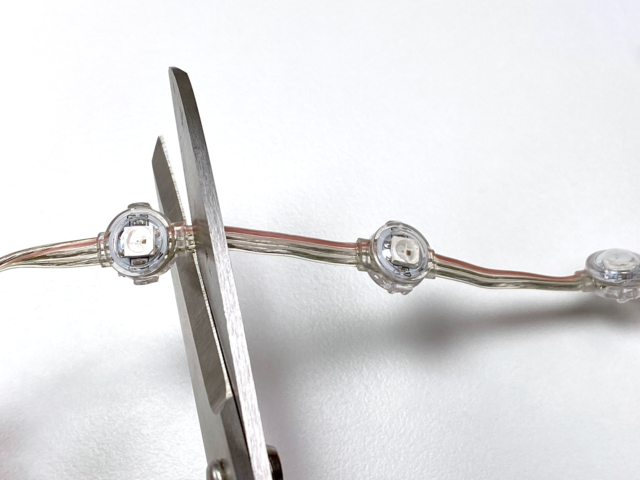



从您刚剪切的一端开始,算出长度为 9 NeoPixels 。
剪切第九个 neopixel之后的条带,并留有尽可能多的尾巴。
不要在此末端剥皮或分开导线。

完成后,完成条应类似于上图。
添加电池袋
为了安全地容纳脂电池,我们将在领带的背面创建一个简单的袋。 p》
此口袋将使用热激活下摆带固定在领带上,但您可以根据需要使用传统缝制轻松地重新制作它。
剪切并排列材料
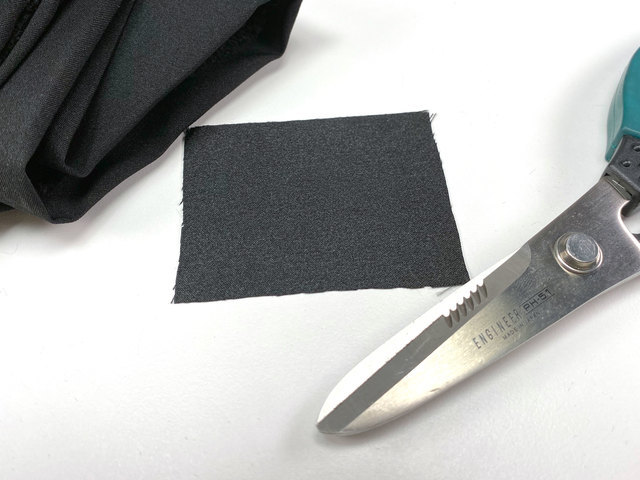





切一块布 60mm 尺寸 x 75mm 。
剪切4条下摆带 2 x 75mm ,和 2 x 15mm
将下摆带的各部分按照领带的底部附近的口袋形状排列后缝。
小心地小心地将放在口袋顶部的中间位置,在口袋底部的中间留出空隙。 。 确保胶带在口袋的外边缘–熨烫后将无法重新放置它。
铁袋就位

轻轻地放置一块在所有物品上刮擦织物,以在熨烫时保护袖珍织物。

用热铁施加确定压力 10次到20秒来回移动熨斗,将口袋均匀地固定到位。

完成后,请检查并确保口袋完全紧贴到领带。
组装和接线
用针和线以及一点点接线组装所有组件。
位置新像素带





找到领带的垂直中心线并标记
将条带沿中心线放置,使大约一英寸的导线悬挂领带的尖端。
塞住靠近脖子的金属丝条的多余的尾巴到领带的结。
缝制NeoPixel s
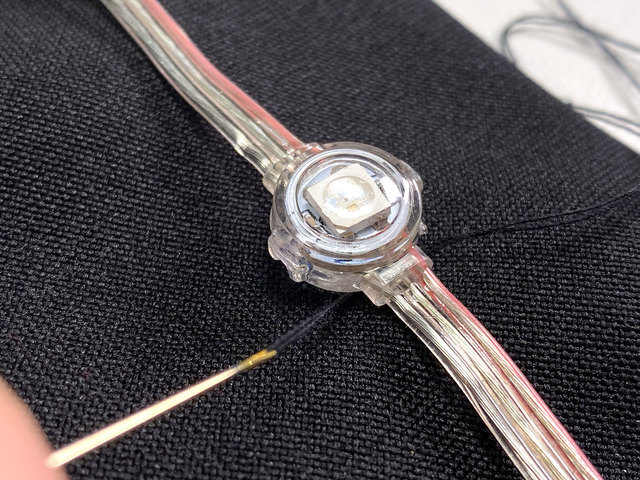



通过将线程穿过织物的顶层并将其包裹起来,将每个NeoPixel缝合到位NeoPixel胶囊的一端。然后对胶囊的另一端进行相同操作。
要在工作时保持条带对齐,请先缝制NeoPixels的顶部,底部和中间。
附加赛道游乐场Bluefruit
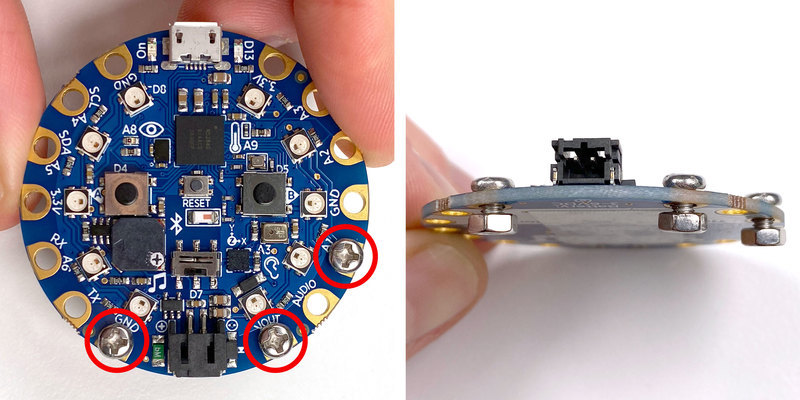
安装螺栓到CPB的 GND , VOUT 和 A1 焊盘。将它们稍稍松动,以便稍后可以轻松地将电线绕在螺钉上。
将CPB放在扎带背面的底部,以便微型USB端口稍微扎在扎带的折线下方。
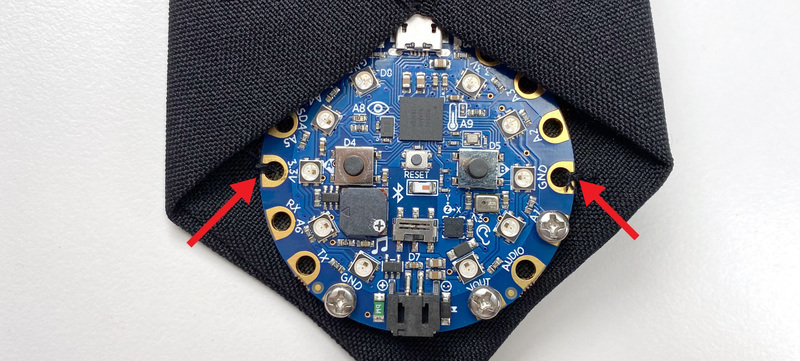
通过将 GND 和 3.3V 焊盘牢固地缝合到织物的顶层,将CPB缝制到位。
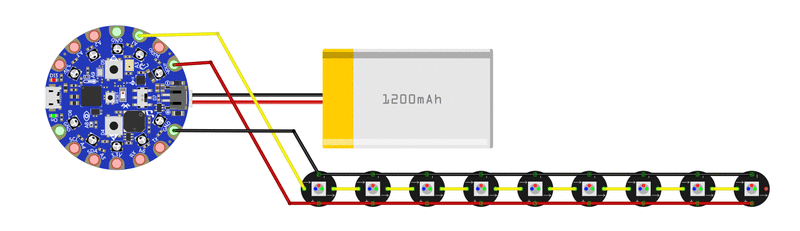
接线图
下面是显示所有需要进行的电气连接。单击图像可查看大图。
连接NeoPixel地带



NeoPixel带中的三根导线连接到CPB上的以下焊盘:
红色导线- 》 VOUT
中间线-》 A1
剩余线-》 GND
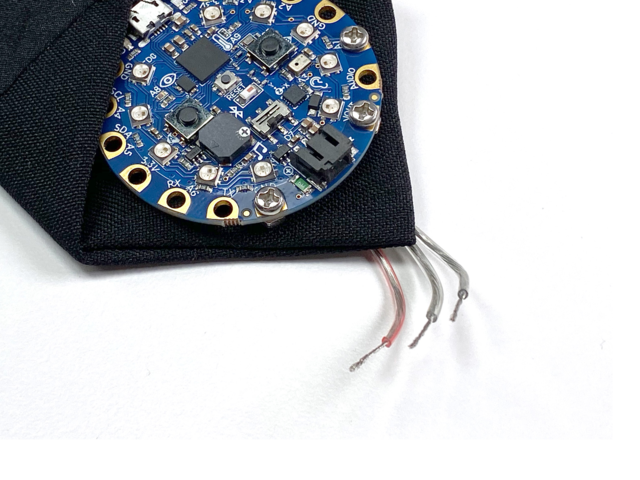
弯曲在绑带底部边缘上的导线,并固定 裸露的导线 》用小螺丝刀拧紧螺栓。

将脂状电池滑入口袋,同时将其电线连接器穿过口袋末端的开口。
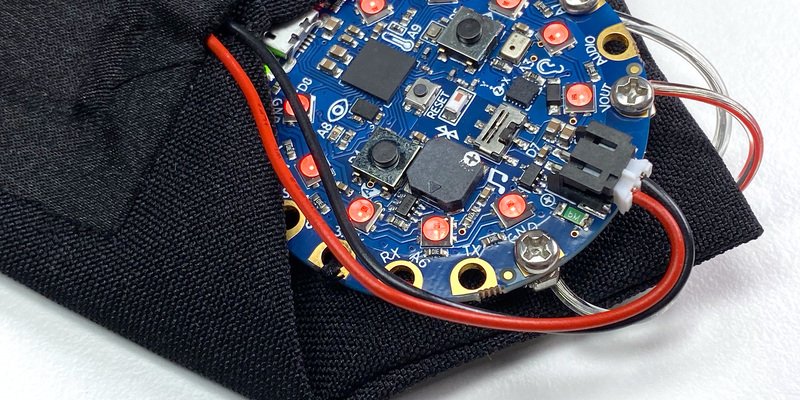

将电池连接到CPB上的黑色JST端口。
祝贺您-您的新领带已经通电并且可以穿了!
使用

下载应用
Adafruit的Bluefruit LE Connect应用是免费的,这是多方面的Bluetooth LE工具包,我们将使用它来控制领带的照明和动画。在以下移动设备上下载并安装该应用:
iOS版下载
Android版下载
通过BLE连接
确保您的移动设备已启用蓝牙,然后启动该应用。启动屏幕将显示该应用可以连接到的附近蓝牙LE设备的列表。
》
查找名称以 CIRCUITPY 开头的设备,然后单击右侧按钮上的连接。
连接后,点击标题为 Controller 的表格行。这是我们用来控制领带的颜色和动画的模块。
更改动画
领带具有4种动画模式:
Audio Meter -CPB检测到的现场声音水平
彩虹周期-所有LED在整个光谱范围内都会褪色
拉森扫描器-LED上下移动,呈“赛隆”风格
单色-全部相同颜色的LED
在 Controller 视图中,点击 Control Pad 。游戏控制器按钮界面将会出现。
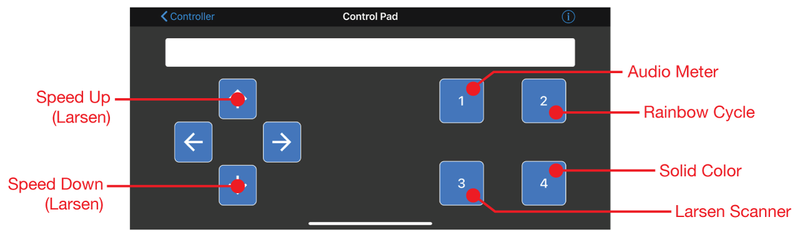
以下是每个控制面板按钮的功能细分:
按钮1 –更改为音频计模式
按钮2 –更改为彩虹周期模式
按钮3 –更改为Larsen Scanner模式
按钮4 –更改为纯色模式
向上箭头按钮-加快Larsen Scanner
向下箭头按钮-放慢Larsen Scanner
更改颜色
在控制器视图中,点击拾色器 –将出现色轮界面。 Color Picker (颜色选择器)可让您更改 Larsen Scanner 和 Solid Color 动画模式的颜色。
触摸色轮上的一个点以选择一种色调,然后拖动下面的滑块来调整颜色亮度。按下发送按钮,将颜色数据发送到领带。
责任编辑:wv
- 相关推荐
- 热点推荐
- l
-
幻彩LED灯带芯片:SM16703SP单点单控 断点续传2023-12-18 1394
-
Arduino WS2812B LED灯带设计方案2022-04-24 14983
-
LED灯带的类型及LED灯带选型2021-12-10 12042
-
LED灯带能用来制作显示屏吗?2021-06-20 4278
-
dfrobot 炫彩LED模块简介2020-01-03 1877
-
dfrobot炫彩WS2812LED灯带3米简介2019-12-25 4453
-
七彩闪光LED灯带控制电路2019-02-07 20554
-
炫彩音乐显示器制作教程2018-09-14 2873
-
led灯带安装接线图_安装led灯带的5种方法2018-01-16 291250
-
led灯带怎么安装_led灯带安装图解_led灯带效果图2017-12-22 56005
-
求炫彩音乐显示器DIY进阶大作:炫酷LED尽显音乐质感2012-10-28 5224
-
LED发光字(炫彩字)2010-09-27 3622
-
led柔性灯带彻底取代玻璃霓虹灯带与光纤灯带2009-11-18 3093
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

