

状态机常见的3种类型 状态机案例设计
电子说
描述
1、状态机设计
Mealy 机方框图
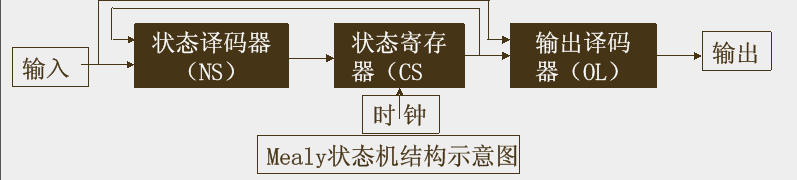
状态寄存器输出当前的信号,用来控制下一个状态是什么,和当前状态下的输出是什么。
Moore机方框图
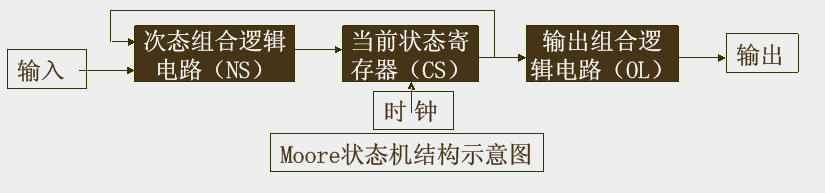
2、状态机---3种类型
二元的:(CPLD与阵列扇入比较多,寄存器比较少)
S1 = 001, S2 = 010, S3 = 011, S3 = 100,etc。。。
枚举的:
S1 = 100, S2 = 110, S3 = 101, S4 = 111,etc。。。
One Hot:每1 个状态机只有1个寄存器(FPGA触发器比较多)
S1 = 00000001, S2 =00000010,S3 = 00000100,etc。。。
3、对生剩余状态的处理
1、在CASE 语句中增加语句,对每个非法状态明确地给出状态轮换的指示;
2、用OTHERS语句来对未提及的状态做统一处理。
Moore 型状态机设计
摩尔型的有限状态机的输出只与当前状态有关,而与输入信号的当前值无关,且仅丰时钟信号边沿到来时才发生变化。
要实现这种结构,必须使用暂存信号(如 temp)来存储电路的输出值,当今信号在时钟边沿出现时才能够更新输出。
例:
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
entity s_machine2 is
port(
clk, reset : in std_logic;
x : in std_logic;
z : out std_logic
);
architecture behav of s_machine2 is
type m_state is(s0, s1, s2);
signal present_state, next_state : m_state;
signal temp : std_logic;
begin
-----------------------时序进程---------------------------
reg : process(reset, clk)
begin
if reset = ‘1’ then present_state 《= s0;
elsif clk = ‘1’ and clk‘event then
z 《=temp; --只有在时钟的上升沿时,输出才会发生变化。是同步输出。
prsent_state 《=nxet_state;
end if;
end process;
-------------------------组合进程-----------------------------
com : process(present_state, x)
begin
case prsent_state is
when s0 =》
if x = ’0‘ then next_state 《= s0;
else next_state 《= s1;
end if;
temp 《= ’0‘;
when s1 =》
if x = ’0‘ then next_state 《= s0;
else next_state 《= s2;
end if;
temp 《= ’0‘;
when s2 =》
if x = ’0‘; then next_state 《= s0; temp 《= ’1‘;
else next_state 《= s2; temp 《= ’0‘;
end if
end case;
end process;
end behv;
Mearly 型的有限状态机设计
米立状态机的输出信号是当前状态和输出信号的函数,它的输出在输入变化后立即发生变化,
不依赖时钟信号的同步。是异步输出。
例:
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
entity s_machine1 is
port(
clk, reset : in std_logic;
x : in std_logic;
z : out std_logic
);
end s_machine1;
architecture behav of s_machine2 is
type m_state is(s0, s1, s2);
signal present_state, next_state : m_state;
begin
-----------------------时序进程---------------------------
reg : process(reset, clk)
begin
if reset = ’1‘ then present_state 《= s0;
elsif clk = ’1‘ and clk’event then
prsent_state 《=nxet_state;
end if;
end process;
-------------------------组合进程-----------------------------
com : process(present_state, x)
begin
case prsent_state is
when s0 =》
if x = ‘0’ then next_state 《= s0;
else next_state 《= s1;
end if;
z 《= ‘0’;
when s1 =》
if x = ‘0’ then next_state 《= s0;
else next_state 《= s2;
end if;
z 《= ‘0’;
when s2 =》
if x = ‘0’; then next_state 《= s0; z 《= ‘1’;
else next_state 《= s2; z《= ‘0’;
end if
end case;
end process;
end behv;
可以看到在该程序中,只要输入有变化,输出z就会有变化,它并不依赖于时钟的上升沿。
怎样确保一个进程是组合进程:
1、不出现带沿的语句,即组合进程中决不能出现用时钟沿控制的敏感信号;
2、在组合电路的进程中,给出输出端口的缺省值,这样可以防止锁存器的生成;
3、在敏感清单中包含所有的输入量,防止锁存器的生成。
敏感清单不全的话综合时可能出现敬告。
例:下例敏感清单中输入端口不全,可能出现锁存器
p0 : process (a)
begin
q 《= a and b;
end process p0;
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
下面是一个实例,洗衣机的工作过程:
TYPE state_type IS(idle, fill, heat_w, wash, drain);
entity wm is
port(
clk, reset, door_closed, full : in std_logic;
heat_demand, done, empty : in std_logic;
water, spin, heat, pump : out std_logic
);
end wm;
architecture behave of wm is
------------------------说明部分--------------------------
--说明部分用枚举数据类型来字义状态机中的状态;并把状态变量(如现态和次态)定义为信号。
type state_type is (
idle, fill, heat_w, wash, drain);
signal state : state_type;
begin
process (clk, reset)
begin
if reset = ‘1’ then
state 《= idle;
elsif clk‘event and clk= ’1‘ then
case state is
when idle =》
if door_closed = ’1‘ then
state 《= fill;
else
state 《= idle;
end if
when fill =》
if full =’1‘; then
state 《= neat_w;
else
state 《= fill;
。
。
。
when others =》
state 《= idle;
end case
end if;
end process;
----------------------------------------------
利用两个进程(纯组合逻辑措施一)
--------------时序进程----------------------------
--时序进程是指在时钟驱动下负责状态转换的进程,只表示次态和现态的关系
process(clk, reset)
begin
if reset =’1‘ then
state 《= idle;
elsif clk’event and clk = ‘1’ then
state 《= next_state;
end if;
end process;
------------------组合进程---------------------
组合进程的任务是根据输入信号和现态对输出端口赋值以及确定状态机的下一个状态,由于没有任何信号
的赋值是通过其他某个信号的跳变来触发的,所以不会产生寄存器。一般用CASE 或IF语句来实现
process(state, door_closed, full,
heat_demand, done, empty)
begin
case state is
when idle =》
if door_closed =‘1’ then
next_state 《= fill;
else
next_state 《= idle;
end if;
when fill =》
if full = ‘1’ then
next_state 《= heat_w;
else
next_state 《= fill;
。
。
。
end case;
end if;
end process;
process(state)
begin
water_i 《= ‘0’;
spin_i 《= ‘0’;
heat_i 《= ‘0’;
pump_i 《= ‘0’;
case state is
when idle =》
when fill =》
water_i 《= ‘1’;
when heat_w =》
spin_i 《=‘1’;
heat_i 《= ‘1’;
when wash =》
spin_i 《= ‘1’;
when drain =》
spin_i 《= ‘1’;
pump_i 《= ‘i’;
end case;
end process;
--------------寄存输出---------------------
process (clk)
begin
if rising_edge(clk) then
water 《= water_i;
spin 《= spin_i;
heat 《= heat_i;
pump 《= pump_i;
end if;
end process
-
Verilog状态机+设计实例2024-02-12 6016
-
玩转Spring状态机2024-06-25 1585
-
有限状态机有什么类型?2020-04-06 4191
-
状态机是什么?什么是消息触发类型的状态机?2021-04-19 2277
-
如何写好状态机2009-06-14 934
-
状态机举例2009-03-28 1183
-
状态机代码生成工具2015-11-19 824
-
状态机原理及用法2016-03-15 1582
-
状态机概述 如何理解状态机2019-01-02 11188
-
什么是状态机 状态机的描述三种方法2020-11-16 27918
-
FPGA:状态机简述2020-11-05 8717
-
什么是状态机?状态机5要素2021-07-27 21879
-
状态模式(状态机)2021-12-16 872
-
Verilog状态机的类型2023-06-01 2717
-
什么是状态机?状态机的种类与实现2023-10-19 12746
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

