

Python中的排序
电子说
描述
Python 中的排序
在 Python 中,常用的排序就是 sorted ,对于列表这种数据结构来说,还有 sort 方法
列表的排序
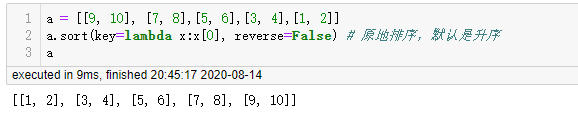
使用 sort 方法进行排序,以第二个值进行升序排序,列表的 sort 方法是原地排序
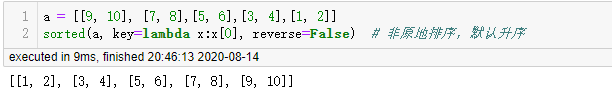
另外一种排序方法是 sorted ,此方法不是原地排序,以第一个值进行排序,同样也是默认升序排序
字典排序
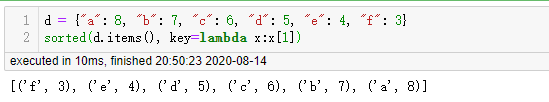
有时候我们也需要对字典进行排序,也是使用 sorted 函数,不过对字典排序后返回的是列表,列表中是元组(tuple)
C++ 中的排序
对 vector 排序
要对 vector 容器中的元素排序,可以使用 algorithm 算法库中的 sort 函数
#include
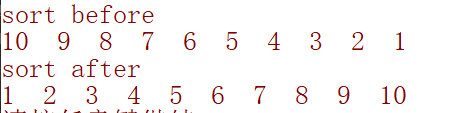
对 2 维vector 排序
类似于 Python ,我们也可以指定根据哪个元素进行排序
#include
对结构体进行排序
模拟一个学生管理系统,依次创建学生信息,然后加入到 vector 中,接着对学生的年龄进行排序
#include
排序前
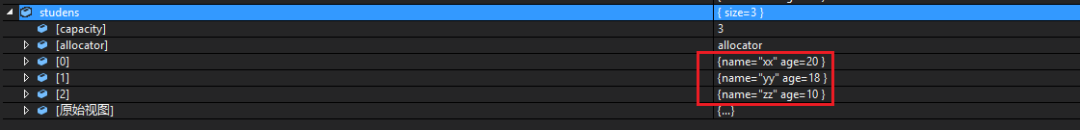
排序后

-
快速学习Python的技巧2018-07-27 3316
-
VHDL中的排序算法怎么实现?2019-03-29 2641
-
python排序得出序号各类的方法2020-06-13 1732
-
外部排序2009-08-13 835
-
常用的非比较排序算法:计数排序,基数排序,桶排序的详细资料概述2018-06-18 7704
-
各种排序算法的分析及java&python实现2019-02-28 2135
-
Linux系统中sort排序命令的使用教程2019-04-02 687
-
Python最简单实现快速排序的办法2020-01-01 2567
-
实用的排序算法 - 交换排序2020-03-20 2274
-
C语言排序中快速排序的技巧2021-07-29 2922
-
Python实现的常见内部排序算法2023-07-06 543
-
FPGA排序-冒泡排序介绍2023-07-17 1610
-
python升序和降序排序代码2023-11-21 4246
-
python中text的用法2023-11-23 5670
-
TimSort:一个在标准函数库中广泛使用的排序算法2025-01-03 1025
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

