

riscv64裸机编程实践与分析
描述
riscv64 裸机编程实践与分析
-
1.概述
-
2.最小工程的构成
-
3. 链接脚本
-
4.可执行的程序源代码分析
-
5.编译与运行
-
5.1 编译
-
5.2 运行
-
5.3 调试
-
-
6.总结
1.概述
任何芯片在启动之前都需要有一段汇编代码,从这段汇编代码上就可以体现一些架构设计的特点。往往做嵌入式底层开发都需要关注这段汇编代码的含义,这样在使用的时候才能全面的了解启动时做了什么事情,在后续的程序中遇到问题也能复盘推演。
本文就针对riscv64的最开始的启动部分代码进行分析,从最小的一个裸机代码开始分析,彻底的弄清楚riscv启动的流程。
本次使用的环境是riscv64 qemu,而编译器是通过下面的地址进行下载:
https://www.sifive.com/software
2.最小工程的构成
一个最小的工程包含两个东西:链接脚本以及源代码。
源代码就是可以让cpu执行的代码,通过交叉编译工具链编译生成可执行的二进制程序。
链接脚本文件则可以告诉程序的布局,比如代码段,函数的入口等等。有了这两个文件将编译出来的程序loader到板子上运行即可。
3. 链接脚本
下面看一下hello.ld文件。
OUTPUT_ARCH( "riscv" )
OUTPUT_FORMAT("elf64-littleriscv")
ENTRY( _start )
SECTIONS
{
/* text: test code section */
. = 0x80000000;
.text : { *(.text) }
/* data: Initialized data segment */
.gnu_build_id : { *(.note.gnu.build-id) }
.data : { *(.data) }
.rodata : { *(.rodata) }
.sdata : { *(.sdata) }
.debug : { *(.debug) }
. += 0x8000;
stack_top = .;
/* End of uninitalized data segement */
_end = .;
}
对于链接脚本(linker script),往往都是规定如何把输入的文件按照特定的地址放到内存中。
其中就上面的脚本而言:
OUTPUT_ARCH("riscv"):表示输入文件的架构是riscv。
OUTPUT_FORMAT("elf64-littleriscv"):表示elf64小端。一般arm,riscv,x86都是小端,小端是比较主流的。
ENTRY( _start ):表示函数入口是_start。
然后开始进行代码段的布局,起始地址开始处为0x80000000。然后依次放代码段、数据段、只读数据段、全局数据段,debug段等等。
这里需要注意:
. += 0x8000;
stack_top = .;
这里说明,栈顶预留了0x8000个字节空间作为程序的栈空间,因为栈是向上增长的,所以这里预留了一些栈空间。
通过反汇编来查看生成程序的布局情况
# riscv64-unknown-elf-objdump -d hello
hello: file format elf64-littleriscv
Disassembly of section .text:
0000000080000000 <_start>:
80000000: f14022f3 csrr t0,mhartid
80000004: 00029c63 bnez t0,8000001c
80000008: 00008117 auipc sp,0x8
8000000c: 04410113 addi sp,sp,68 # 8000804c <_end>
80000010: 00000517 auipc a0,0x0
80000014: 03450513 addi a0,a0,52 # 80000044
000000008000001c :
8000001c: 0000006f j 8000001c
0000000080000020 :
80000020: 100102b7 lui t0,0x10010
80000024: 00054303 lbu t1,0(a0)
80000028: 00030c63 beqz t1,80000040
8000002c: 0002a383 lw t2,0(t0) # 10010000
80000034: 0062a023 sw t1,0(t0)
80000038: 00150513 addi a0,a0,1
8000003c: fe9ff06f j 80000024
80000040: 00008067 ret
对于qemu来说,sifive_u的起始地址为0x80000000,将代码段的入口放在此处。
4.可执行的程序源代码分析
前面已经描述了链接脚本的布局,也就是给程序指定了执行的地址,每个函数以及函数入口在什么地址都已经规划好了,那么具体的入口函数该如何写呢?
看看hello.s的编程代码:
.align 2
.equ UART_BASE, 0x10010000
.equ UART_REG_TXFIFO, 0
.section .text
.globl _start
_start:
csrr t0, mhartid # read hardware thread id (`hart` stands for `hardware thread`)
bnez t0, halt # run only on the first hardware thread (hartid == 0), halt all the other threads
la sp, stack_top # setup stack pointer
la a0, msg # load address of `msg` to a0 argument register
jal puts # jump to `puts` subroutine, return address is stored in ra regster
halt: j halt # enter the infinite loop
puts: # `puts` subroutine writes null-terminated string to UART (serial communication port)
# input: a0 register specifies the starting address of a null-terminated string
# clobbers: t0, t1, t2 temporary registers
li t0, UART_BASE # t0 = UART_BASE
1: lbu t1, (a0) # t1 = load unsigned byte from memory address specified by a0 register
beqz t1, 3f # break the loop, if loaded byte was null
# wait until UART is ready
2: lw t2, UART_REG_TXFIFO(t0) # t2 = uart[UART_REG_TXFIFO]
bltz t2, 2b # t2 becomes positive once UART is ready for transmission
sw t1, UART_REG_TXFIFO(t0) # send byte, uart[UART_REG_TXFIFO] = t1
addi a0, a0, 1 # increment a0 address by 1 byte
j 1b
3: ret
.section .rodata
msg:
.string "Hello.
"
根据汇编语言的规则
.align 2
表示入口程序以2^2也就是4字节对齐。
.equ UART_BASE, 0x10010000
.equ UART_REG_TXFIFO, 0
定义了UART的寄存器的基地址。
接着主要从_start:开始分析。
csrr t0, mhartid # read hardware thread id (`hart` stands for `hardware thread`)
bnez t0, halt # run only on the first hardware thread (hartid == 0), halt all the other threads
根据riscv的设计,如果一个部件包含一个独立的取指单元,那么该部件被称为核心(core)。
一个RiscV兼容的核心能够通过多线程技术(或者说超线程技术)支持多个RiscV兼容硬件线程(harts),harts这儿就是指硬件线程, hardware thread的意思。
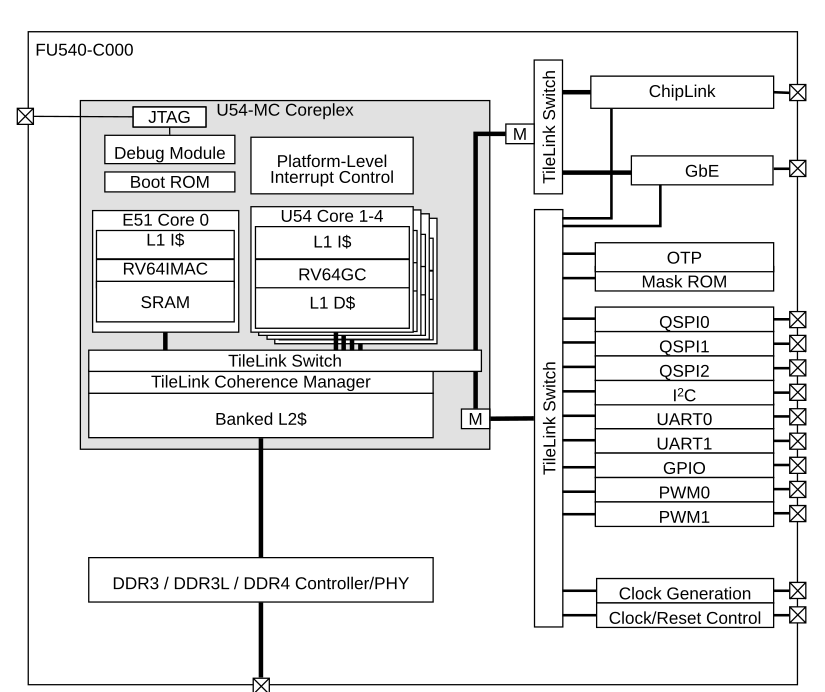
上面的就包含一个E51的核和4个U54的核。
而这段汇编就是将其他的核挂起,只运行hartid == 0的核。
紧接着
la sp, stack_top # setup stack pointer
这里将栈指针sp赋值,sp此时指向栈顶。
la a0, msg # load address of `msg` to a0 argument register
jal puts # jump to `puts` subroutine, return address is stored in ra regster
对于riscv 架构来说,a0寄存器表示第一个参数赋值,接着跳转到puts函数中。
此时传递过去的参数为a0,也就是
.section .rodata
msg:
.string "Hello.
"
指向一个只读的字符串结构的数据。
puts的实现
通过汇编来描述一个串口驱动程序的编写是比较重要的。
puts: # `puts` subroutine writes null-terminated string to UART (serial communication port)
# input: a0 register specifies the starting address of a null-terminated string
# clobbers: t0, t1, t2 temporary registers
li t0, UART_BASE # t0 = UART_BASE
1: lbu t1, (a0) # t1 = load unsigned byte from memory address specified by a0 register
beqz t1, 3f # break the loop, if loaded byte was null
# wait until UART is ready
2: lw t2, UART_REG_TXFIFO(t0) # t2 = uart[UART_REG_TXFIFO]
bltz t2, 2b # t2 becomes positive once UART is ready for transmission
sw t1, UART_REG_TXFIFO(t0) # send byte, uart[UART_REG_TXFIFO] = t1
addi a0, a0, 1 # increment a0 address by 1 byte
j 1b
3: ret
首先刚才通过a0寄存器将参数传递过来,然后从1:开始,读取字符串,beqz t1, 3f表示当t1 == 0时,跳转到3:之前。此时会跳出2:循环。
2:则是向串口FIFO送数的过程。
到这里一个字符串输出就可以正常的执行了。
5.编译与运行
5.1 编译
上述程序分析完成会,可以将其进行编译。
riscv64-unknown-elf-gcc -march=rv64g -mabi=lp64 -static -mcmodel=medany -fvisibility=hidden -nostdlib -nostartfiles -Thello.ld -Isifive_u hello.s -o hello
上述编译过程可以生成hello程序。
#readelf -h hello
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF64
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: EXEC (Executable file)
Machine: RISC-V
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0x80000000
Start of program headers: 64 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 4680 (bytes into file)
Flags: 0x0
Size of this header: 64 (bytes)
Size of program headers: 56 (bytes)
Number of program headers: 1
Size of section headers: 64 (bytes)
Number of section headers: 7
Section header string table index: 6
可以分析一下gcc携带的参数。
-march:可以指定编译出来的架构,比如rv32或者rv64等等。
-static:表示静态编译。
-mabi=lp64:数据模型和浮点参数传递规则
数据模型:
| - | int字长 | long字长 | 指针字长 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ilp32/ilp32f/ilp32d | 32bits | 32bits | 32bits |
| lp64/lp64f/lp64d | 32bits | 64bits | 64bits |
浮点传递规则
| - | 需要浮点扩展指令? | float参数 | double参数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ilp32/lp64 | 不需要 | 通过整数寄存器(a0-a1)传递 | 通过整数寄存器(a0-a3)传递 |
| ilp32f/lp64f | 需要F扩展 | 通过浮点寄存器(fa0-fa1)传递 | 通过整数寄存器(a0-a3)传递 |
| ilp32d/lp64d | 需要F扩展和D扩展 | 通过浮点寄存器(fa0-fa1)传递 | 通过浮点寄存器(fa0-fa1)传递 |
-mcmodel=medany:对于-mcmodel=medlow与-mcmodel=medany。
-mcmodel=medlow
使用 LUI 指令取符号地址的高20位。LUI 配合其它包含低12位立即数的指令后,可以访问的地址空间是 -2GiB ~ 2GiB。
对于 RV64 而言,能访问的就是 0x0000000000000000 ~ 0x000000007FFFFFFF,以及 0xFFFFFFFF800000000 ~ 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF 这两个区域,前一个区域即 +2GiB 的地址空间,后一个区域即 -2GiB 的地址空间。其它地址空间就访问不到了。
-mcmodel=medany
使用 AUIPC 指令取符号地址的高20位。AUIPC 配合其它包含低12位立即数的指令后,可以访问当前 PC 的前后2GiB (PC - 2GiB ~ PC + 2GiB)的地址空间。
对于RV64,取决于当前 PC 值,能访问到是 PC - 2GiB 到 PC + 2GiB 这个地址空间。假设当前 PC 是 0x1000000000000000,那么能访问的地址范围是 0x0000000080000000 ~ 0x100000007FFFFFFF。假设当前 PC 是 0xA000000000000000,那么能访问的地址范围是0x9000000080000000~0xA00000007FFFFFFF。
-fvisibility=hidden:动态库部分需要对外显示的函数接口显示出来。
-nostdlib:不连接系统标准启动文件和标准库文件,只把指定的文件传递给连接器。
-nostartfiles:不带main函数的入口程序。
-Thello.ld:加载链接地址。
5.2 运行
输入下面的命令即可看到Hello.字符串输出。
# qemu-system-riscv64 -nographic -machine sifive_u -bios none -kernel hello
Hello.
5.3 调试
调试过程比较只需在运行的后面加-s -S,即
qemu-system-riscv64 -nographic -machine sifive_u -bios none -kernel hello -s -S
另外再开一个终端输入
riscv64-unknown-elf-gdb hello
接着输入target remote localhost:1234即可。
通过b _start打断点,并且通过si进行单步跳转可实现程序的单步运行。
6.总结
riscv64最小裸机程序的运行很好理解,主要梳理清楚其启动地址与链接文件即可。还有就是注意gcc的编译参数,这些对于riscv的启动来说也是非常关键的部分。
责任编辑:xj
原文标题:riscv64 裸机编程实践与分析
文章出处:【微信公众号:嵌入式IoT】欢迎添加关注!文章转载请注明出处。
-
【CIE全国RISC-V创新应用大赛】+MUSE Pi Pro RiscV UEFI固件开发2025-11-13 305
-
全志D1开发板(哪吒 RISCV64)开箱评测2025-10-31 148
-
【M-K1HSE开发板免费体验】超高性能与颜值RISCV64位8核视美泰M-K1HSE开发板2025-06-26 1012
-
请问Openvino是否支持 Risc-V (riscv64) 架构?2025-06-24 227
-
【「RISC-V体系结构编程与实践」阅读体验】-- SBI及NEMU环境2024-11-26 985
-
全志D1开发板RISCV64开箱评测2023-08-16 1261
-
RT-Thread BSP qemu-virt64-riscv的编译环境搭建2023-05-16 1391
-
RT-Smart riscv64汇编注释2023-02-08 2027
-
如何一键生成支持riscv64的Debian rootfs?2021-12-28 1897
-
全志D1哪吒 RISCV64开发板上手评测2021-05-27 10973
-
riscv64上运行完整Linux的流程2021-05-23 9297
-
opensbi下的riscv64裸机编程:中断与异常2021-01-07 3619
-
opensbi下的riscv64裸机系列编程1(串口输出)2020-12-31 10713
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

