

机器学习在各领域的广泛应用以及促生其在材料领域的应用
电子说
描述
机器学习的在各领域的广泛应用也促生其在材料领域的应用。它提供了一种革命性的工具,即能从高维数据中发现数据间的规律。有助于减少计算量从而加速对新材料的探索。对于复杂的数据集,如晶体化合物的数据集,一个至关重要的问题是如何从化学视角为晶体结构构建低维特征。糟糕的特征无法减低数据的复杂性或无法提取晶体的关键信息从而导致巨大的预测误差。为了满足覆盖绝大多数晶体结构和组成,特征需要满足旋转、平移和尺度不变性。因此完整、精确地数字化描述晶体材料是一项具有挑战性的任务。
来自北京大学深圳研究生院新材料学院的潘锋教授和密歇根州立大学数学系的魏国卫教授等提出,原子特殊的持续同调(ASPH)可作为机器学习预测材料形成能的特征,取得了较好的预测效果。不同于传统拓扑的高级抽象,ASPH能将多尺度几何信息嵌入拓扑不变量中,能有效地提取几何空间中的独立元件、环、空腔等独特特征。
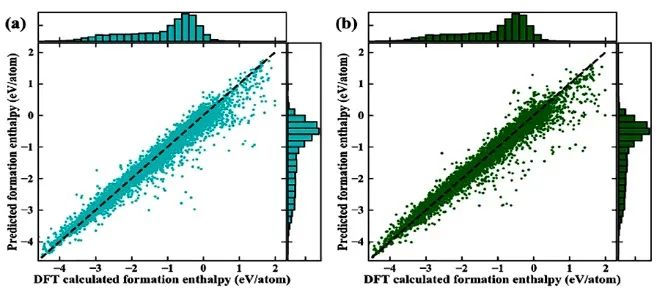
更具体来说,独立元件由化学键彼此连接,而环和空腔则为多体相互作用。这一发现证明了代数拓扑理论在研究晶体材料中可发挥重要作用。值得注意的是,相比于暨往方法,ASPH对晶体材料形成能的模拟计算有更准确的预测能力,它的适用性可扩展到所有空间群和绝大多数元素。这不仅提供了一种新型的晶体结构描述方法,而且有助于利用计算机辅助设计和新材料发现。
该文近期发表于npj Computational Materials 7: 28 (2021),英文标题与摘要如下,。
Topological representations of crystalline compounds for the machine-learning prediction of materials properties
Yi Jiang, Dong Chen, Xin Chen, Tangyi Li, Guo-Wei Wei & Feng Pan
Accurate theoretical predictions of desired properties of materials play an important role in materials research and development. Machine learning (ML) can accelerate the materials design by building a model from input data. For complex datasets, such as those of crystalline compounds, a vital issue is how to construct low-dimensional representations for input crystal structures with chemical insights.
In this work, we introduce an algebraic topology-based method, called atom-specific persistent homology (ASPH), as a unique representation of crystal structures. The ASPH can capture both pairwise and many-body interactions and reveal the topology-property relationship of a group of atoms at various scales.
Combined with composition-based attributes, ASPH-based ML model provides a highly accurate prediction of the formation energy calculated by density functional theory (DFT). After training with more than 30,000 different structure types and compositions, our model achieves a mean absolute error of 61 meV/atom in cross-validation, which outperforms previous work such as Voronoi tessellations and Coulomb matrix method using the same ML algorithm and datasets.
Our results indicate that the proposed topology-based method provides a powerful computational tool for predicting materials properties compared to previous works.
图1:以BaTiO3为例,构建晶体拓扑特征的过程
编辑:jq
-
激光技术在材料加工领域的发展及应用2010-04-24 2749
-
机器视觉在焊接领域大展身手2015-09-10 4054
-
POGO PIN 产品广泛应用到的领域有哪些?2016-07-06 2622
-
机器视觉在交通中有哪些应用?2019-09-30 3865
-
区块链技术在金融领域的 开发搭建的广泛应用2019-12-23 2506
-
关于各领域的电机驱动系统的详细概述2021-02-25 2623
-
激光熔覆在材料加工领域获得广泛应用2010-05-05 1952
-
基于Modicon M340在各领域中的应用介绍2017-09-23 789
-
FPGA、ASIC有望在机器学习领域中崛起2017-12-26 1414
-
机器人行业发展迅速 广泛应用于各个领域2019-05-17 6029
-
如何让Transformer在多种模态下处理不同领域的广泛应用?2021-03-08 3326
-
机器学习在故障检测与诊断领域中的应用综述2021-06-24 1036
-
IGBT在电力领域的广泛应用2023-09-07 1762
-
蓝牙设备在嵌入式领域的广泛应用2023-10-19 620
-
环氧树脂在各领域的应用2025-09-11 664
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

