

怎么用OpenResty搭建高性能服务端
描述
Socket编程
Linux Socket编程领域为了处理大量连接请求场景,需要使用非阻塞I/O和复用,select、poll、epoll是Linux API提供的I/O复用方式,自从Linux2.6中加入了epoll之后,高性能服务器领域得到广泛的应用,Nignx就是使用epoll来实现I/O复用支持高并发。
对于“高性能”服务端而言,我们所关注的并不是语言的性能,而是缓存和语言支持异步非阻塞。
缓存
针对缓存要明白通信速度的快慢顺序
内存》SSD》机械磁盘
本机》网络
进程内 》 进程间
缓存系统的目标是希望在进程内的命中率是最高的,那么此时缓存系统整体的效率也是最高的。
异步非阻塞
希望访问数据库、访问网络,访问一些比较慢的IO设备时,不要在等待上耗费大量时间。而是使用事件驱动的方式,当系统完成某项任务后再来通知我们。这样就可以将服务器CPU的空闲资源,用来服务客户端连接。
OpenResty
OpenResty是基于Ngnix和Lua的高性能web平台,内部集成精良的LUa库、第三方模块、依赖项。用于方便搭建能够处理高并发、扩展性极高的动态web应用、web服务、动态网关。可以使用Lua脚本调用Ngnix支持的C以及Lua模块,快速构建10K~1000K单机并发连接的高性能web应用系统。OpenResty的目标是让web服务直接运行在Nginx服务内部,利用Ngnix的非阻塞IO模型,对HTTP客户端请求和后端DB进行一致的高性能响应。
OpenResty的出现可以说是颠覆了高性能服务端的开发模式。OpenResty实际上是Nginx+LuaJIT的完美组合。
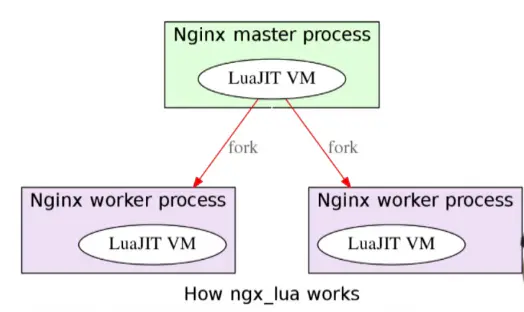
OpenResty工作方式
由于Nginx采用的是master-worker模型,也就是一个master主进程管理多个worker进程,基本的事件处理都是放在worker中,master仅负责一些全剧初始化,以及对worker的管理。在OpenResty中,每个worker使用一个LuaVM,每个请求被分配到worker时,将在这个LuaVM中创建一个coroutine协程。协程之间数据隔离,每个协程具有独立的全局变量_G。
Lua中的协程和多线程下的线程类似,都有自己的堆栈、局部变量、指令指针。。。,但是和其他协程程序共享全局变量等信息。线程和协程主要不同在于:多处理器的情况下,概念上来说多线程是同时运行多个线程,而协程是通过代码来完成协程的切换,任何时刻只有一个协程程序在运行。并且这个在运行的协程只有明确被要求挂起时才会被挂起。
根据实际测试,OpenResty性能接近于Nginx 性能之王c module,甚至超过。
OpenResty 架构
负载均衡
LVS+HAProxy将流量转发给核心Nginx1和Nginx2,即实现了流量的负载均衡。
单机闭环
所有想要的数据都能从本服务器直接获取,大多数时候无需通过网络或去其他服务器获取。
分布式闭环
单机闭环会遇到2个主要问题
1.数据不一致
例如没有主从架构导致不同服务器数据不一致
2.遇到存储瓶颈
磁盘或内存遇到天花板
解决数据不一致比较好的办法是采用主从或分布式集中存储,而遇到存储瓶颈就需要进行按业务键进行分片,将数据分散到多台服务器。
接入网关
接入网关又叫接入层,即接收流量的入口,在入口处做如下事情:
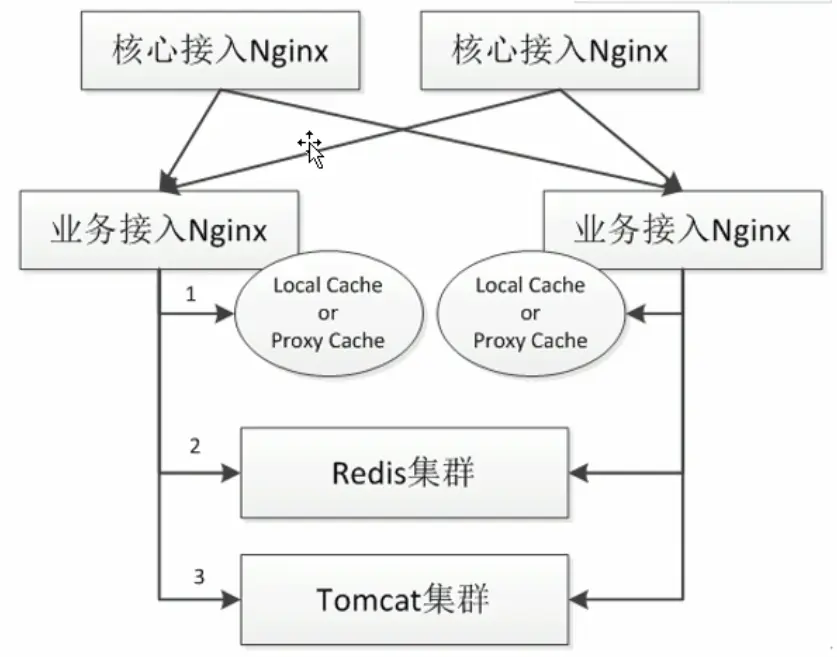
接入网关
OpenResty环境搭建
http://openresty.org
http://openresty.org/cn/download.html
安装前准备,必须安装perl、libpcre、libssl库。
# 从系统路径中查看必备库是否已经安装
$ sudo ldconfig -v
# 安装必备库
$ sudo apt install libpcre3-dev libssl-dev perl make build-essential curl libreadline-dev libncurses5-dev
下载并解压OpenResty后进入其目录
$ wget https://openresty.org/download/ngx_openresty-1.13.6.1.tar.gz
$ tar -zxvf ngx_openresty-1.13.6.1.tar.gz
$ mv openresty-1.13.6.1 openresty
$ cd openresty
$ 。/configure
默认会被安装到/usr/local/openresty目录下
# 编译并安装
$ sudo make && make install
$ cd /usr/local/openresty
启动Nginx
$ sudo /usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx
$ ps -ef | grep nginx
$ service nginx status
Nginx启动若出现
nginx: [emerg] bind() to 0.0.0.0:80 failed (98: Address already in use)
nginx: [emerg] still could not bind()
说明80端口并占用,查看80端口被占用的端口并重启。原因在于nginx先监听了ipv4的80端口之后又监听了ipv6的80端口,于是就重复占用了。
$ sudo netstat -ntlp | grep 80
$ sudo killall -9 nginx
重新编辑Nginx配置文件
$ sudo vim /etc/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
listen 80;
listen [::]:80 ipv6only=on default_server;
使用curl工具或在浏览器访问默认80端口
$ curl 127.0.0.1
浏览器输入http://127.0.0.1/
将Nginx工具配置到当前用户的系统环境变量中
$ sudo vim ~/.bashrc
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin
$ source ~。/bashrc
$ cd ~
$ nginx -s reload
nginx: [alert] kill(12267, 1) failed (1: Operation not permitted)
开发文档
https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/modules/lua/
ubuntu 安装 vcode 或 sublime text 编辑器
content_by_lua
$ vim /usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
location /test {
default_type text/html;
content_by_lua ‘ngx.say(“hello openresty”)’;
}
# 重启Nginx
$ /usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
# 浏览器访问 127.0.0.1/test
content_by_lua_file
$ vim nginx.conf
location /test {
content_by_lua_file ‘html/test.lua’;
}
$ vim 。。/html/test.lua
ngx.say(“hello lua”)
$ sudo /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
$ curl 127.0.0.1/test
hello lua
为避免每次修改都需要重启Nginx,可在Nginx的server选项中配置lua_code_cache选项。
$ vim nginx.conf
server{
lua_code_cache off;
location /test{
content_by_lua_file ‘html/test.lua’;
}
}
$ sudo /usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
nginx: [alert] lua_code_cache is off; this will hurt performance in /usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/nginx.conf:48
注意lua_code_cache off;是会引擎Nginx的性能的,在生产环境中是需要将其开启的。
小节
在OpenResty中开发是分为两步的,第一步是修改Nginx配置,第二步是使用Lua开发自己的脚本。
OpenResty入门
参考资料
OpenResty最佳实践
Nginx Lua
创建工作目录
OpenResty安装之后就有配置文件及相关目录,为了工作目录和安装目录互不干扰,另外创建OpenResty工作目录,并另写配置。
$ mkdir -p ~/openresty/test/logs ~/openresty/test/conf
$ vim ~/openresty/test/conf/nginx.conf
# 设置Nginx worker工作进程数量,即CPU核数。
worker_processes 1;
# 设置错误日志文件路径
error_log logs/error.log;
# 配置Nginx服务器与用户的网络连接
events{
# 设置每个工作进程的最大连接数
worker_connections 10224;
}
http{
# 虚拟机主机块定义
server{
# 监听端口
listen 8001;
# 配置请求的路由
location /{
default_type text/html;
content_by_lua_block{
ngx.say(“hello world”);
}
}
}
}
$ nginx -p ~/openresty/test
$ curl 127.0.0.1:8001
hello world
$ vim nginx.conf
location /test{
content_by_lua_file “lua/test.lua”;
}
$ cd 。。 && mkdir lua && cd lua
$ vim test.lua
local args = ngx.req.get_uri_args()
local salt = args.salt
if not salt then
ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_BAD_REQUEST)
end
local md5str = ngx.md5(ngx.time()。.salt)
ngx.say(md5str)
$ sudo /usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
$ curl -i 127.0.0.1/test?salt=lua
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: openresty/1.13.6.2
Date: Sun, 27 Jan 2019 1017 GMT
Content-Type: application/octet-stream
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Connection: keep-alive
b55b77f75e46b96b11778ca7edfe8d55
若代码中出现错误则需要直接查看Nginx的错误日志进行查看
$ vim nginx/logs/error.log
2019/01/27 1715 [error] 15764#0: *6 failed to load external Lua file “/usr/local/openresty/nginx/test.lua”: cannot open /usr/local/openresty/nginx/test.lua: No such file or.。。
Windows系统下查看Nginx进程
λ tasklist /fi “imagename eq nginx.exe”
映像名称 PID 会话名 会话# 内存使用
========================= ======== ================ =========== ============
nginx.exe 9072 Console 1 7,840 K
nginx.exe 7692 Console 1 12,304 K
nginx.exe 8120 Console 1 7,840 K
nginx.exe 4552 Console 1 12,188 K
nginx.exe 9588 Console 1 7,828 K
nginx.exe 6256 Console 1 12,216 K
nginx.exe 7308 Console 1 7,828 K
nginx.exe 10192 Console 1 12,212 K
λ taskkill /im nginx.exe /f
成功: 已终止进程 “nginx.exe”,其 PID 为 9072。
ngx lua API
参考资料
NGINX API for Lua
编辑:jq
-
服务端的测试主要是测什么内容2024-05-30 6023
-
MQTT中服务端和客户端2023-07-30 3553
-
在远程服务器上搭建一个OpenVPN服务端2023-05-26 11512
-
监控系统客户端及服务端设计2021-12-21 1699
-
TCP服务端测试工具2020-06-29 2054
-
TCP通信时服务端如何接收客户端的数据?2020-04-14 3022
-
TCP服务端的实现2019-09-26 992
-
从服务端视角看高并发难题2018-11-02 2478
-
SSRF服务端请求伪造攻击2017-09-07 590
-
Android 仿QQ客户端及服务端源码2017-03-19 1172
-
Delphi教程之建立基本MTS服务端2016-04-11 666
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

