

virtio I/O通信流程及设备框架的实现
描述
virtio 是一种通用的半虚拟化的 I/O 通信协议,提供了一套前后端 I/O 通信的的框架协议和编程接口。根据该协议实现的设备通过前后端的配合,相比全模拟设备可以大幅减少陷入陷出以及内存拷贝的次数,使 guest 获得高效的 I/O 性能。作为目前虚拟化标准的通用协议规范,经历了 0.95、1.0、1.1 三个版本的演进。根据 0.95 版本实现的称为传统 virtio 设备,1.0 版本修改了一些 PCI 配置空间的访问方式和 virtioqueue 的优化和特定设备的约定,1.1 版本则增加了 packed virtqueue 的支持,详细可以参考官方发布的 virtio 协议规范。
之所以称 virtio 是一种半虚拟化的解决方案,是因为其首先需要在主机侧通过软件创建 virito 的后端设备,其次在 Guest 要有对应的设备前端驱动,前后端通过共享内存进行通信。virtio 规范定义了设备的控制和数据面接口,控制面接口包括设备状态、feature 的协商等,数据面则包括共享内存的数据布局定义以及前后端的通知方式。基于 virtio 协议,目前已衍生出了 virtio-blk、virtio-net、virtio-scsi、virtio-mem 等各种各样的半虚拟化设备。virtio 设备可以支持多种传输层协议,既可以挂载到 MMIO 总线,也可以作为 PCI 设备,另外还可以支持基于标准 I/O 通道机制的 S/390 设备。
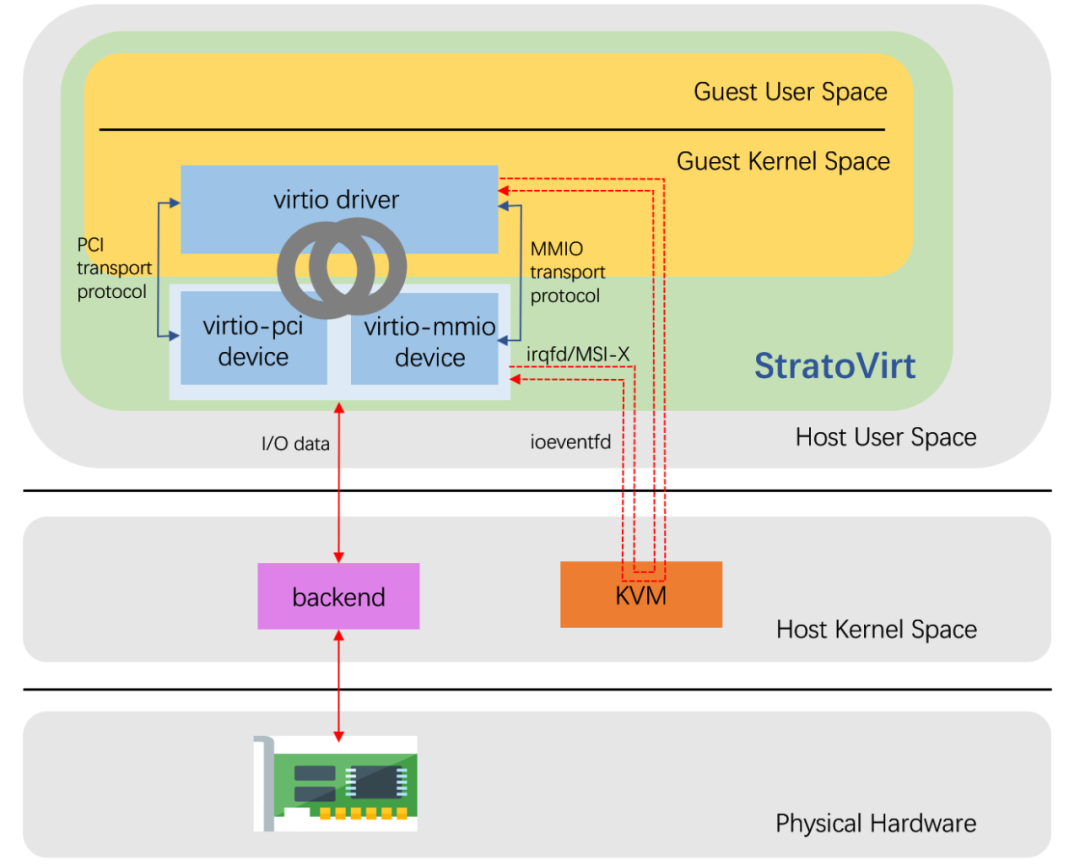
鉴于 virtio 设备具备较好的性能及通用性,StratoVirt 自然也支持,StratoVirt 中 virtio 设备的实现架构以及 I/O 通信流程如上图所示。下面就基于目前最新的代码,探究一下 StratoVirt 中 virtio 设备的代码实现框架。
VirtioDevice Trait
StratoVirt 的 virtio crate 提供了 virtio 设备的通用接口以及所有 virtio 设备的相关实现。其中,lib.rs 中定义了为所有 virtio 设备定义的 VirtioDevice Trait。每种 virtio 设备都需要实现自定义的 VirtioDevice 接口。
/// The trait for virtio device operations.
pub trait VirtioDevice: Send {
/// Realize low level device.
fn realize(&mut self) -> Result<()>;
/// Unrealize low level device
fn unrealize(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
bail!("Unrealize of the virtio device is not implemented");
}
/// Get the virtio device type, refer to Virtio Spec.
fn device_type(&self) -> u32;
/// Get the count of virtio device queues.
fn queue_num(&self) -> usize;
/// Get the queue size of virtio device.
fn queue_size(&self) -> u16;
/// Get device features from host.
fn get_device_features(&self, features_select: u32) -> u32;
/// Set driver features by guest.
fn set_driver_features(&mut self, page: u32, value: u32);
/// Read data of config from guest.
fn read_config(&self, offset: u64, data: &mut [u8]) -> Result<()>;
/// Write data to config from guest.
fn write_config(&mut self, offset: u64, data: &[u8]) -> Result<()>;
/// Activate the virtio device, this function is called by vcpu thread when frontend
/// virtio driver is ready and write `DRIVER_OK` to backend.
///
/// # Arguments
///
/// * `mem_space` - System mem.
/// * `interrupt_evt` - The eventfd used to send interrupt to guest.
/// * `interrupt_status` - The interrupt status present to guest.
/// * `queues` - The virtio queues.
/// * `queue_evts` - The notifier events from guest.
fn activate(
&mut self,
mem_space: Arc,
interrupt_cb: Arc,
queues: &[Arc>],
queue_evts: Vec,
) -> Result<()>;
/// Deactivate virtio device, this function remove event fd
/// of device out of the event loop.
fn deactivate(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
bail!(
"Reset this device is not supported, virtio dev type is {}",
self.device_type()
);
}
/// Reset virtio device.
fn reset(&mut self) -> Result<()> {
Ok(())
}
/// Update the low level config of MMIO device,
/// for example: update the images file fd of virtio block device.
///
/// # Arguments
///
/// * `_file_path` - The related backend file path.
fn update_config(&mut self, _dev_config: Optiondyn ConfigCheck>>) -> Result<()> {
bail!("Unsupported to update configuration")
}
}
- realize()/unrealize(): 这一组接口用于具现化/去具现化具体的 virtio 设备。具现化做的一些具体操作包括设置支持的 features、设备特有的属性(如网卡的 mac)、初始化连接 Host 后端设备等。
- set_driver_features():将前端驱动支持的 features 与后端模拟设备支持的 features 进行协商后,设置最终实现的 features。
- read_config()/write_config():virtio 协议规范为每种 virtio 设备定义了自定义的配置空间,这组接口就是用来读写这部分配置数据。
- activate()/deactivate(): 激活/去激活设备,负责绑定/解绑后端、加入/移除 I/O 循环。
- reset():虚拟机重启时某些设备需要重置。
- update_config():支持轻量机型下的 virtio-mmio 设备动态绑定/解绑后端,实现 virtio-mmio 设备的模拟热插拔。
virtqueue
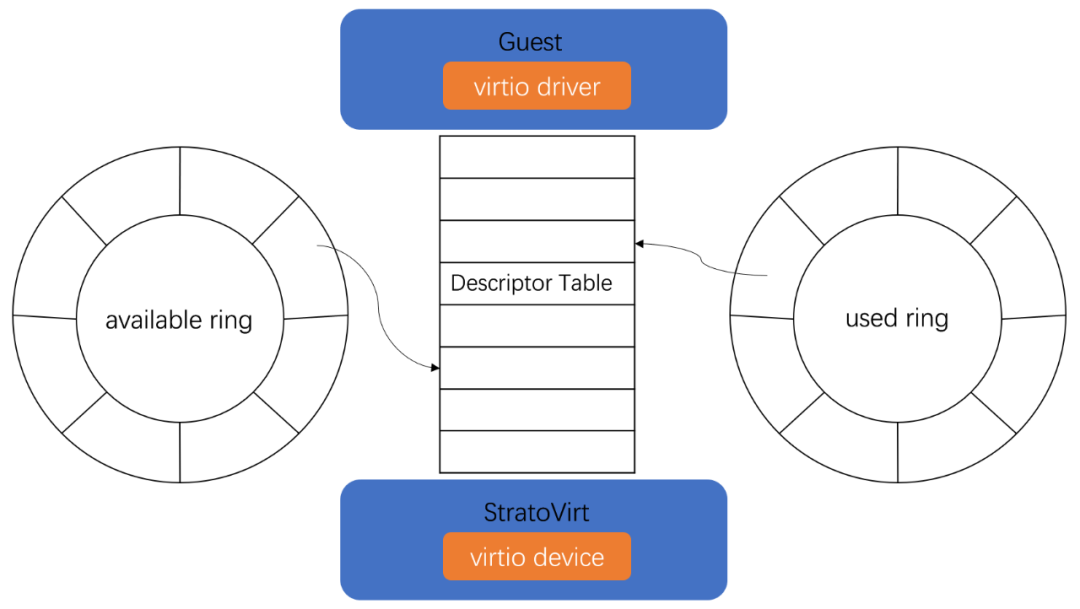
virtio 设备可以有一个或多个队列,每个队列有描述符表、available ring、used ring 三个部分。当前 StratoVirt 的 virtio 设备均遵循 1.0 规范,队列的内存布局仅支持 Split Vring 的方式。queue.rs 中定义了一系列针对队列操作及查询的接口。所有的 I/O 请求数据信息以描述符的形式存放在描述符表中,前端准备好数据后更新 available ring 告诉后端还有哪些 I/O 待发送,后端执行完 I/O 更新 used ring 通知前端。不同设备的 I/O 处理不尽相同,但是核心的 virtqueue 操作是一样的。
pub struct SplitVring {
/// Region cache information.
pub cache: Option,
/// Guest physical address of the descriptor table.
/// The table is composed of descriptors(SplitVringDesc).
pub desc_table: GuestAddress,
/// Guest physical address of the available ring.
/// The ring is composed of flags(u16), idx(u16), ring[size](u16) and used_event(u16).
pub avail_ring: GuestAddress,
/// Guest physical address of the used ring.
/// The ring is composed of flags(u16), idx(u16), used_ring[size](UsedElem) and avail_event(u16).
pub used_ring: GuestAddress,
/// Host address cache.
pub addr_cache: VirtioAddrCache,
/// Indicate whether the queue configuration is finished.
pub ready: bool,
/// The maximal size in elements offered by the device.
pub max_size: u16,
/// The queue size set by frontend.
pub size: u16,
/// Interrupt vector index of the queue for msix
pub vector: u16,
/// The next index which can be popped in the available vring.
next_avail: Wrapping<u16>,
/// The next index which can be pushed in the used vring.
next_used: Wrapping<u16>,
/// The index of last descriptor used which has triggered interrupt.
last_signal_used: Wrapping<u16>,
}
virtio-mmio 设备
StratoVirt 目前提供两种机型:轻量机型和标准机型。轻量机型由于需要追求极致的启动速度以及内存底噪开销,因此只支持挂载数量有限的 virtio-mmio 设备。而标准机型面向传统的标准云化场景,对于 I/O 设备的性能要求较高,且需要支持热插拔满足资源弹性,因此标准机型支持将 virtio 设备以 PCI 设备挂载在模拟的 PCI 总线上。目前标准机型只支持配置 virtio-pci 设备,不支持 virtio-mmio 设备。
结构体 VirtioMmioDevice 定义了一个通用的 virtio-mmio 设备,其中的 device 即为实现了 VirtioDevice 这个 trait 的具体的 virtio 设备结构,可以是网卡、磁盘等。VirtioMmioState 结构体中存放了 virtio-mmio 设备的控制寄存器,并且为其实现了对应的读写接口 read_common_config()/write_common_config()。virtio-mmio 设备的配置空间布局如下图所示:

interrupt_evt 通过 irqfd 向虚拟机注入中断,host_notify_info 则为每个队列创建了一个 eventfd,虚拟机利用 ioeventfd 机制陷出到 StratoVirt 执行后端的 I/O 处理。
pub struct VirtioMmioDevice {
// The entity of low level device.
pub device: Arcdyn VirtioDevice>>,
// EventFd used to send interrupt to VM
interrupt_evt: EventFd,
// Interrupt status.
interrupt_status: Arc,
// HostNotifyInfo used for guest notifier
host_notify_info: HostNotifyInfo,
// The state of virtio mmio device.
state: VirtioMmioState,
// System address space.
mem_space: Arc,
// Virtio queues.
queues: Vec>>,
// System Resource of device.
res: SysRes,
}
VirtioMmioDevice 实现了 realize 接口完成设备的具现化:
- 调用各设备实现的 VirtioDevice trait 的具现化接口。
- virtio-mmio 设备挂载在了系统总线上,StratoVirt 为每个设备分配 512 字节的配置空间。除此之外,需要为其注册 irqfd 以便后续 I/O 完成后向虚拟机注入中断。这些信息都保存在 SysRes 数据结构中。
- 添加内核启动参数,通过内核启动参数将设备的内存区间及中断号信息直接告诉 Guest。
pub fn realize(
mut self,
sysbus: &mut SysBus,
region_base: u64,
region_size: u64,
#[cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")] bs: &Arc>,
) -> ResultSelf>>> {
self.device
.lock()
.unwrap()
.realize()
.chain_err(|| "Failed to realize virtio.")?;
if region_base >= sysbus.mmio_region.1 {
bail!("Mmio region space exhausted.");
}
self.set_sys_resource(sysbus, region_base, region_size)?;
let dev = Arc::new(self));
sysbus.attach_device(&dev, region_base, region_size)?;
#[cfg(target_arch = "x86_64")]
bs.lock().unwrap().kernel_cmdline.push(Param {
param_type: "virtio_mmio.device".to_string(),
value: format!(
"{}@0x{:08x}:{}",
region_size,
region_base,
dev.lock().unwrap().res.irq
),
});
Ok(dev)
}
前端驱动加载过程中会读写设备的配置空间,前后端完成 feature 的协商,一切 OK 后前端驱动将向配置空间写状态,后端设备将会调用 activate 方法激活设备。当触发激活时,前端已为这三个部分分配了内存空间,Guest 物理地址(GPA)已写入设备的配置空间,后端需要将 GPA 地址转化为 Host 虚拟地址(HVA)。随后,就可以根据队列配置创建队列,并将 I/O 的 eventfd 加入事件循环激活设备开始 I/O 通信。
virtio-pci 设备
如上所述,virtio 设备也可以作为一个 PCI 类设备挂载到 PCI 总线上。类似的,在 StratoVirt 中用结构体 VirtioPciDevice 来表示一个 virtio-pci 设备。既然是作为一个 PCI 设备,virtio-pci 就需要拥有符合 PCI 规范拥有 PCI 设备的配置空间,Guest 启动后通过 PCI 设备树枚举来发现设备,而不是像 virtio-mmio 设备一样直接通过内核启动参数告诉 Guest。
pub struct VirtioPciDevice {
/// Name of this device
name: String,
/// The entity of virtio device
device: Arcdyn VirtioDevice>>,
/// Device id
dev_id: Arc,
/// Devfn
devfn: u8,
/// If this device is activated or not.
device_activated: Arc,
/// Memory AddressSpace
sys_mem: Arc,
/// Pci config space.
config: PciConfig,
/// Virtio common config refer to Virtio Spec.
common_config: Arc>,
/// Primary Bus
parent_bus: Weak>,
/// Eventfds used for notifying the guest.
notify_eventfds: NotifyEventFds,
/// The function for interrupt triggering
interrupt_cb: Option>,
/// Virtio queues. The vector and Queue will be shared acrossing thread, so all with Arc> wrapper.
queues: ArcVec>>>>,
/// Multi-Function flag.
multi_func: bool,
}
VirtioPciDevice 通过实现 PciDevOps trait 的 realize()方法完成设备的具现化:
- 初始化 PCI 配置寄存器。
- 将 virtio 协议规定的 common configuration、notifications、ISR status、Device-specific configuration 作为四个 PCI 设备的 capability, 对应数据的内存空间则映射到第 3 个 BAR 空间的不同部分。配置空间布局如下图所示:
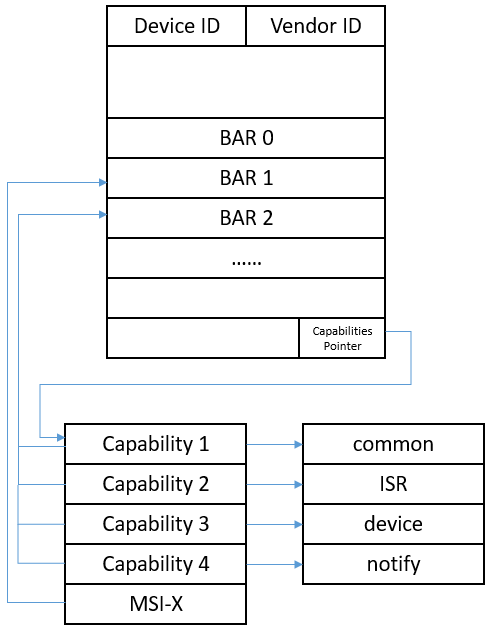
- 前端驱动对于各空间的访问的回调函数由 modern_mem_region_init()注册,当前端读写这部分内存区间时会陷出到 StratoVirt 执行注册的回调接口。每个队列在 notification cap 指向的空间中占据 4 个字节,StratoVirt 为每个队列的 4 个字节空间注册 ioeventfd。前端驱动准备好某个队列后,就会写对应队列的这 4 个字节的地址空间,后端借助 ioeventfd 机制收到通知后陷出进行 host 侧的 I/O 下发。
- 中断机制采用 MSI-X,向量表和 pending 位图则位于第 2 个 BAR 空间。
审核编辑:郭婷
-
Linux I/O 接口的类型及处理流程2023-11-08 2022
-
RT-Thread设备驱动开发之二I/O设备框架2023-10-12 969
-
VirtIO Networking虚拟网络设备实现架构2023-05-08 2078
-
探究I/O虚拟化及Virtio接口技术(上)2023-04-04 5039
-
RT-Tread设备驱动开发之I/O设备框架简析2023-03-15 1001
-
I/O虚拟化及Virtio接口介绍2022-10-26 5747
-
StratoVirt 中的虚拟网卡是如何实现的?2022-08-10 20802
-
StratoVirt 的 virtio-blk 设备是如何实现的?2022-06-29 1825
-
请问怎样设计并实现闪存设备I/O软件?2021-04-27 1771
-
linux设备中virtio组织关系及设备初始化调用流程2020-09-25 5626
-
如何减少器件间通信所用的I/O引脚数实现双向通信2018-04-27 1253
-
输入输出设备I/O设备总结2017-11-24 4184
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

