

使用CUDA PCL 1.0加速Jetson的点云处理
描述
很多Jetson用户在自动化解决方案中选择激光雷达进行定位和感知。激光雷达使用3D点云描绘周围的空间环境。点云可以高精度长距离采样物体表面信息以便于上层应用的障碍感知、绘图、定位和路径规划算法。
使用CUDA-PCL处理点云
CUDA PCL 1.0是基于CUDA开发的点云处理库,在本文中,我们将介绍目前所有的三个库:ICP,segmentation 和 filter。
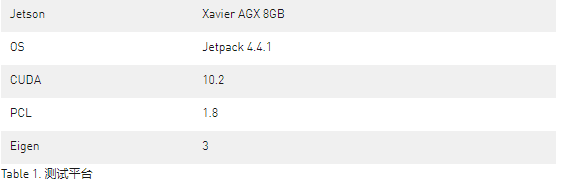
CUDA-ICP
迭代最近点算法(Iterative Closest Point,ICP) 用于计算两帧点云数据之间的坐标变换矩阵,从而能够使不同的坐标下的点云数据合并到同一个坐标系统中。ICP算法 通过计算两帧点云的距离误差从而修正变换矩阵(平移和旋转)以便最小化距离误差,通常两帧点云之间的距离误差是通过匹配点的距离计算得来。ICP算法应用广泛,能够获得很高的匹配结果且有很高的鲁棒性,同时会耗费大量的计算资源。为了改进ICP算法在Jetson上的性能,我们推荐使用基于CUDA加速的CUDA-ICP。
使用CUDA-ICP
以下是CUDA ICP的使用实例
我们仅仅需要初始化相关的类对象,并调用接口函数即可。
cudaICP icpTest(nPCountM, nQCountM, stream);
icpTest.icp(cloud_source, nPCount,
float *cloud_target, int nQCount,
int Maxiterate, double threshold,
Eigen::Matrix4f &transformation_matrix, stream);
CUDA-ICP 计算的输出是 transformation_matrix,代表的含义如下:
源点云(P)* transformation = 目标坐标系的点云(Q)
因为激光类型的输出点云的数量为固定值,所以CUDA-ICP在输出化的时候,要求输入两帧点云的最大数量,从而分配计算资源。
class cudaICP
{
public:
/*
nPCountM and nQCountM are the maximum of count for input clouds
They are used to pre-allocate memory.
*/
cudaICP(int nPCountM, int nQCountM, cudaStream_t stream = 0);
~cudaICP(void);
/*
cloud_target = transformation_matrix *cloud_source
When the Epsilon of transformation_matrix is less than threshold,
the function will return transformation_matrix.
Input:
cloud_source, cloud_target: data pointer for points cloud
nPCount: the points number of cloud_source
nQCount: the points number of cloud_target
Maxiterate: the threshold for iterations
threshold: When the Epsilon of transformation_matrix is less than
threshold, the function will return transformation_matrix.
Output:
transformation_matrix
*/
void icp(float *cloud_source, int nPCount,
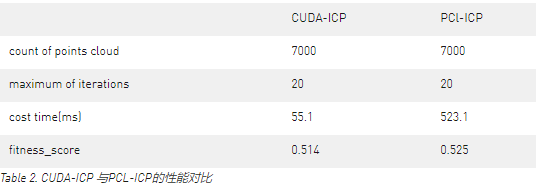

Figure 1. 执行ICP之前的两帧点云。

Figure 2. 经过ICP匹配后的两帧点云。
CUDA-Segmentation
点云地图包含大量的地面点,不仅会使得地图变的杂乱,也会干扰之后的点云的分类和识别。因此在实际处理中,我们会首先使用点云分割移除点云中的地面。CUDA-Segmentation 使用随机样本一致性算法(random sample consensus, Ransac)进行点云的分割。
使用CUDA- Segmentation
以下代码是CUDA Segmentation的使用实例。
我们直接初始化对象并调用相关的接口函数即可。

//Now Just support: SAC_RANSAC + SACMODEL_PLANE
std::vector indexV;
cudaSegmentation cudaSeg(SACMODEL_PLANE, SAC_RANSAC, stream);
segParam_t setP;
setP.distanceThreshold = 0.01;
setP.maxIterations = 50;
setP.probability = 0.99;
setP.optimizeCoefficients = true;
cudaSeg.set(setP);
cudaSeg.segment(input, nCount, index, modelCoefficients);
for(int i = 0; i < nCount; i++)
{
if(index[i] == 1)
indexV.push_back(i);
}
CUDA Segmentation分割拥有nCount个的点云,并输出索引表index用于指示输入点云中的被分割掉的点和modelCoefficients用于指示寻找的平面公式。
typedef struct {
double distanceThreshold;
int maxIterations;
double probability;
bool optimizeCoefficients;
} segParam_t;
class cudaSegmentation
{
public:
//Now Just support: SAC_RANSAC + SACMODEL_PLANE
cudaSegmentation(int ModelType, int MethodType, cudaStream_t stream = 0);
~cudaSegmentation(void);
/*
Input:
cloud_in: data pointer for points cloud
nCount: count of points in cloud_in
Output:
Index: data pointer which has the index of points in a plane from input
modelCoefficients: data pointer which has the group of coefficients of the plane
*/
int set(segParam_t param);
void segment(float *cloud_in, int nCount,
int *index, float *modelCoefficients);
private:
void *m_handle = NULL;
};
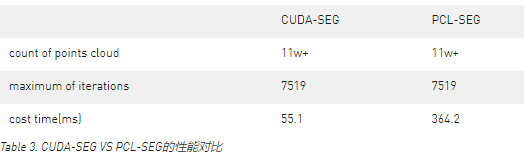
让我们查看下面的实例,第一张图是原始的点云,第二张图是经过算法寻找到的平面。这是一个非常典型的平面移除的应用。

Figure 3. cuda-segmentaion处理之前的点云。

Figure 4. cuda-segmentaion找到的点云平面。
CUDA-Filter
滤波器是在分割,检测和识别之前,点云数据中最重要的处理。
带通点云滤波是最简单的方法,仅仅是过滤X,Y和Z轴方向的点云。
目前CUDA-Filter仅支持带通操作,更多的滤波器会在后续加入。
使用CUDA- Filter
这个是CUDA Filter的使用实例。
我们仅仅需要初始化对象并调用相关的接口函数即可。
我们仅仅需要初始化对象并调用相关的接口函数即可。
cudaFilter filterTest(stream);
FilterParam_t setP;
FilterType_t type = PASSTHROUGH;
setP.type = type;
setP.dim = 2;
setP.upFilterLimits = 1.0;
setP.downFilterLimits = 0.0;
setP.limitsNegative = false;
filterTest.set(setP);
filterTest.filter(output, &countLeft, input, nCount);
CUDA-Filter使用指定的参数过滤nCount有个点的点云数据,过滤后输出的点云数量为countLeft。
typedef struct {
FilterType_t type;
//0=x,1=y,2=z
int dim;
float upFilterLimits;
float downFilterLimits;
bool limitsNegative;
} FilterParam_t;
class cudaFilter
{
public:
cudaFilter(cudaStream_t stream = 0);
~cudaFilter(void);
int set(FilterParam_t param);
/*
Input:
source: data pointer for points cloud
nCount: count of points in cloud_in
Output:
output: data pointer which has points filtered by CUDA
countLeft: count of points in output
*/
int filter(void *output, unsigned int *countLeft, void *source, unsigned int nCount);
void *m_handle = NULL;
};
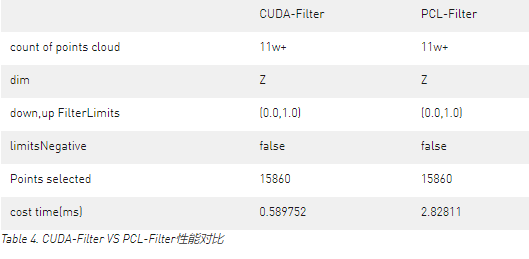
让我们看下X轴方向的带通滤波实例。

Figure 5. 原始点云。

Figure 6. X周过滤后的数据。
开始使用 CUDA-PCL
我们希望通过本文介绍使用CUDA-PCL从而获得更好的点云处理性能。
因为PCL在Jetson上无法使用CUDA进行点云的加速处理,所以我们开发了基于CUDA的点云处理库CUDA-PCL。
关于作者
范磊是英伟达高级CUDA软件工程师,在TSE China 小组致力于CUDA软件方案的开发和优化。
李雨倩负责基于Jetson的自主机器解决方案和生态发展建设,让开发者在Jetson上开发机器人应用获得更好更全面的体验和支持。
审核编辑:郭婷
-
有没有大佬知道NI vision 有没有办法通过gpu和cuda来加速图像处理2024-10-20 8194
-
cuda可以和特斯拉M10一起使用吗?2018-09-26 4838
-
华为FPGA加速云服务器如何加速让硬件应用高效上云?2019-10-22 3940
-
PCL点云库介绍及项目配置方式2021-07-02 1487
-
NVIDIA Jetson介绍2021-12-14 3042
-
使用NVIDIA CUDA-Pointpillars检测点云中的对象2022-04-13 2600
-
用于工业AI的Jetson AGX Xavier模块2022-06-08 2887
-
OpenCV+CUDA编译实现YOLOv5能加速2022-07-18 3291
-
如何在OpenCV中实现CUDA加速2022-09-05 6007
-
CV-CUDA 高性能图像处理加速库发布 Alpha 版本,正式向全球开发者开源2022-12-21 2096
-
CUDA与Jetson Nano:并行Pollard Rho测试2023-06-15 651
-
CV-CUDA 助力腾讯云音视频 PaaS 平台实现视频增强 AI 全流程 GPU 加速2023-07-28 1447
-
PCL中基础下采样介绍2023-11-21 2002
-
激光雷达点云预处理介绍2023-11-27 1697
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

