

如何为Raspberry Pi开发一个GUI?
描述
我一直在从事一个项目,通过该项目我可以整理来自 MQ-135 空气质量传感器的空气质量信息,以检测我工作场所空气质量恶化的情况。然而,MQ-135 空气质量传感器的位置在从传感器收集原始信息时具有巨大的重要性。因此,我决定通过开发一个用户友好的界面,通过选定的角度制作一个可移动的传感器底座。为了实现这一目标并添加一些确凿的功能(例如可调节背景光),我使用 Python 中的 guizero 模块为我的 Raspberry Pi 开发了一个 GUI,名为 Air Quality Module。
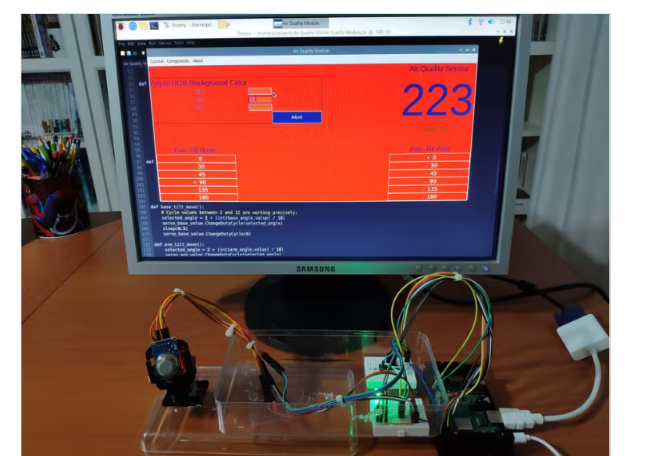
通过空气质量模块,您可以通过选择给定角度之一 - 0、30、45、90、135、180 - 来控制连接到迷你云台套件的两个伺服电机,并以 RGB 格式调整背景光 - 255, 255, 255. 而且,最重要的是,您可以监控 MQ-135 传感器生成的当前空气质量范围:如果空气质量恶化,GUI 会通过警告消息通知您。
本项目中提到的一些产品和组件:
树莓派 3 板壳 3B
树莓派 4B/3B+ SD 卡 32GB
树莓派 3B Micro-HDMI VGA 转换器电缆
补给品:
树莓派 3 型号 B+× 1
DigitSpace Raspberry Pi 3 板壳× 1
SD 卡 32 GB× 1
DigitSpace Raspberry Pi 3B Micro-HDMI VGA 转换线× 1
Adafruit MCP3008× 1
MQ-135 空气质量传感器× 1
Pimoroni Pan-Tilt 帽子× 1
SG90微型伺服电机 × 2
RGB扩散共阳极× 1
SparkFun 可焊接面包板 - 迷你× 2
电阻 220 欧姆 × 3
跳线(通用) × 1
在这个项目中,你将学到:
如何使用 Raspberry Pi 的角度控制伺服电机
如何使用 Raspberry Pi 调整 RGB LED 的颜色
如何使用 MCP3008 和 Raspberry Pi 读取模拟传感器
如何使用 guizero 模块开发 GUI
如何编写范围函数来排列值,如 Arduino 中的 map 函数
第 1 步:使用 MCP3008 读取模拟传感器
与 Arduino 相比,Raspberry Pi 没有内置的 ADC(模数转换器),我们可以通过它轻松地从模拟传感器收集信息。因此,我们需要在我们的电路中实现一个外部 ADC,以整理来自模拟传感器(如 MQ-135 空气质量传感器)的数据。我使用了 MCP3008 8 通道 ADC,因为它效率高且使用简单。
我使用 Raspberry Pi 上的 Adafruit CircuitPython MCP3xxx 库来读取带有 MCP3008 的模拟传感器。
但是,您需要安装在 Python 中提供 CircuitPython 支持的 Adafruit_Blinka 库才能使用上述库。
sudo pip3 install adafruit-blinka
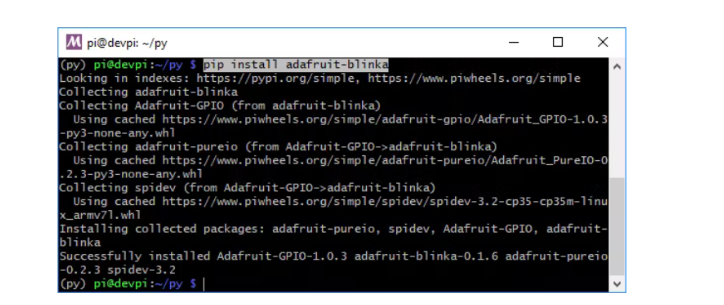
如果需要,您必须在执行命令之前在 Raspberry Pi Configuration Settings 上启用 SPI。
完成后,从命令行运行以下命令来安装 Adafruit CircuitPython MCP3xxx 库。
sudo pip3 install adafruit-circuitpython-mcp3xxx
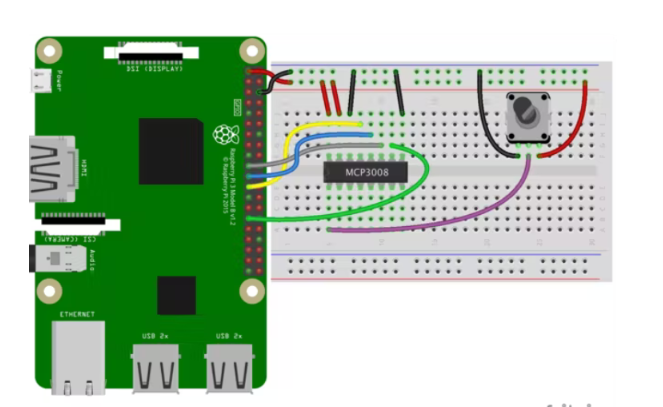
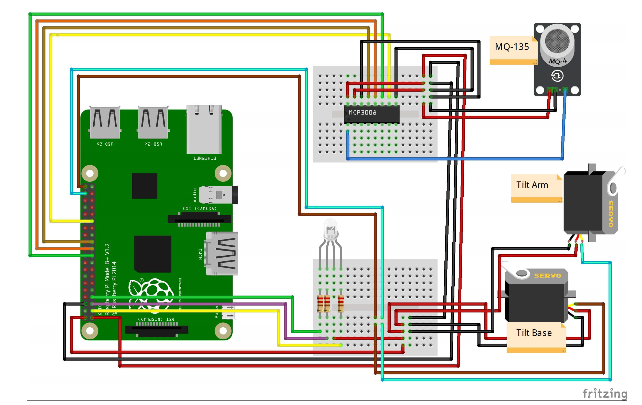
然后,按如下方式进行引脚连接。尽管在项目原理图和代码中对引脚连接进行了很好的解释,但除此之外,我将保留 MCP3008 的以下引脚连接原理图。
MCP3008 CLK 转 Pi SCLK
MCP3008 DOUT 转 Pi MISO
MCP3008 DIN 转 Pi MOSI
MCP3008 CS 转 Pi D5
MCP3008 VDD 至 Pi 3.3V
MCP3008 VREF 至 Pi 3.3V
MCP3008 AGND 到 Pi GND
MCP3008 DGND 到 Pi GND
MCP3008 CH0 到模拟传感器的信号引脚
CH0 指的是 MCP3008 上的第一个输入引脚 - 从 0 到 7。
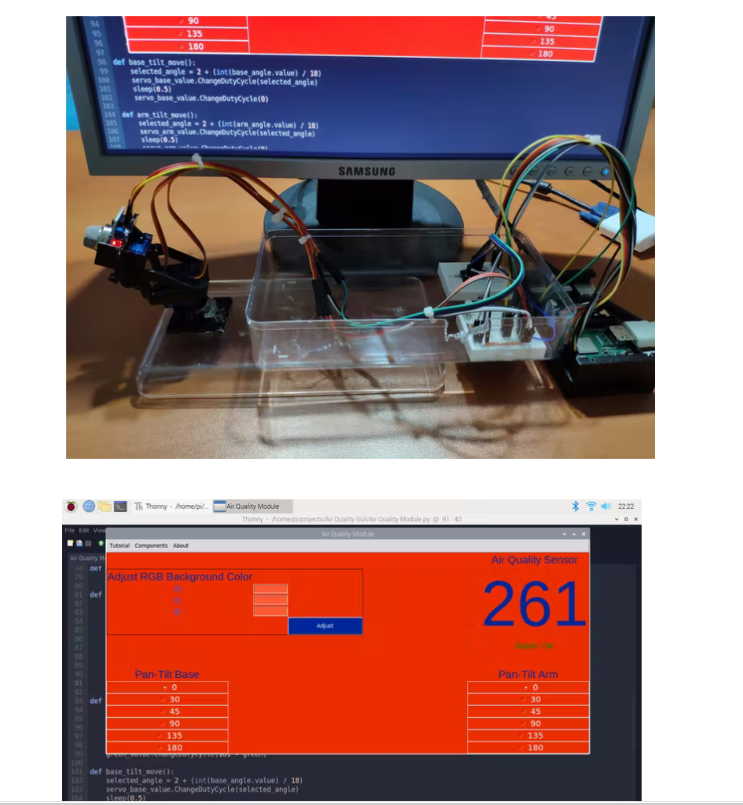
第 2 步:开发 GUI(空气质量模块)和编程 Raspberry Pi
为了能够在 Python 中创建 GUI,您需要在 Raspberry Pi 上安装 guizero 模块。然后,您可以使用模块提供的所有小部件和事件。
从您的命令行运行以下命令来安装 guizero 模块。
sudo pip3 install guizero
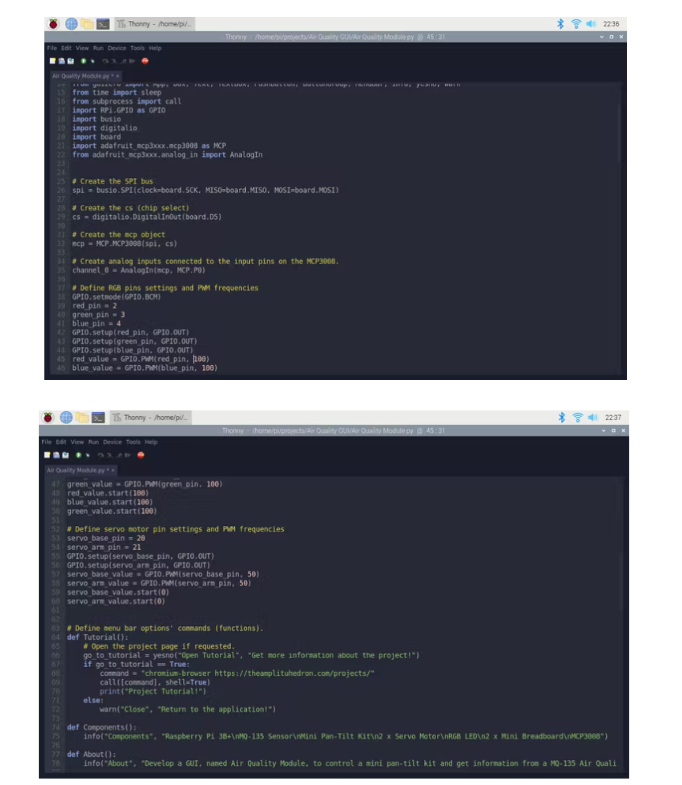
导入所需的库和模块。
不要忘记包含所有 GUI 小部件 - App、Box、Text、TextBox、PushButton、ButtonGroup、MenuBar、info、yesno、warn。
创建 SPI 总线、cs(片选)和 mcp 对象。
创建连接到 MCP3008 输入引脚的模拟输入通道——我只使用了通道 0。
定义 GPIO 引脚设置 - GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) 。
定义 RGB 引脚并设置 PWM 频率 - 100。
在 100 - OFF 处启动 RGB PWM 引脚。
定义伺服电机引脚并设置 PWM 频率 - 50。
在 0 - OFF 处启动伺服底座和臂销。
定义菜单栏选项命令(功能):
在Tutorial()函数中,如果需要,打开一个 yesno 消息以转到项目教程页面。
在Components()函数中,打开一条信息消息以显示组件。
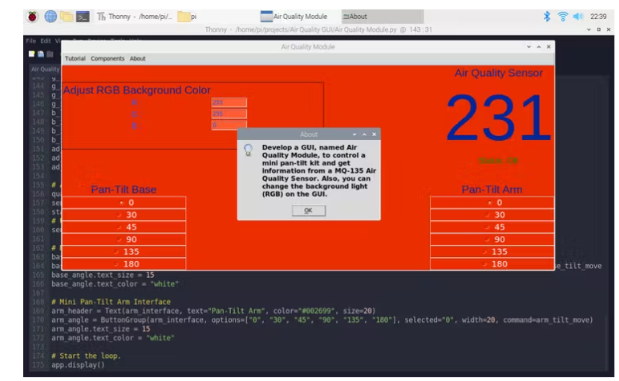
在About()函数中,打开一条信息消息以显示电梯间距。
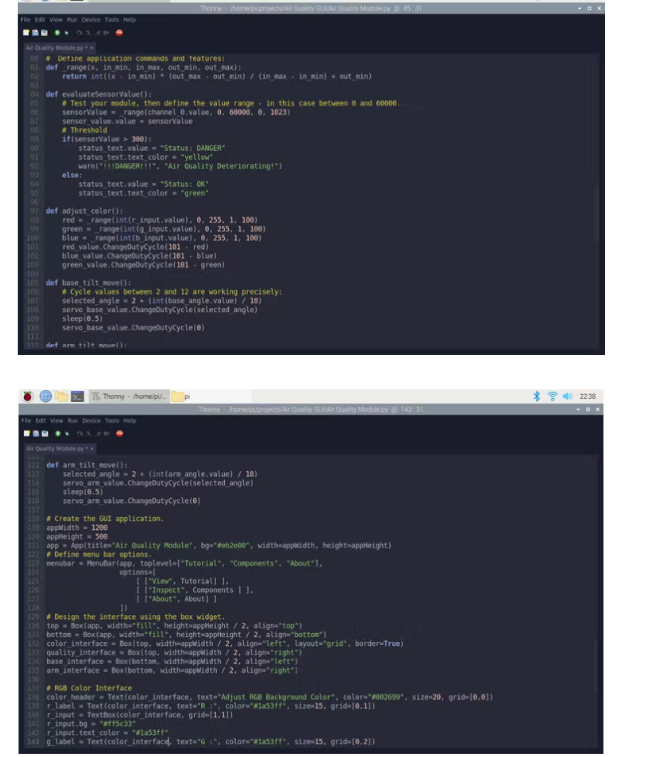
定义小部件命令和功能:
在_range()函数中,复制 Arduino 映射函数以在 Python 中排列给定范围内的值。
在evaluateSensorValue()函数中,从测试范围内的 MQ-135 空气质量中获取空气质量值 - 从 0-60000 到 0-1023。
测试您的模块,然后在本例中定义 0 到 60000 之间的值范围。
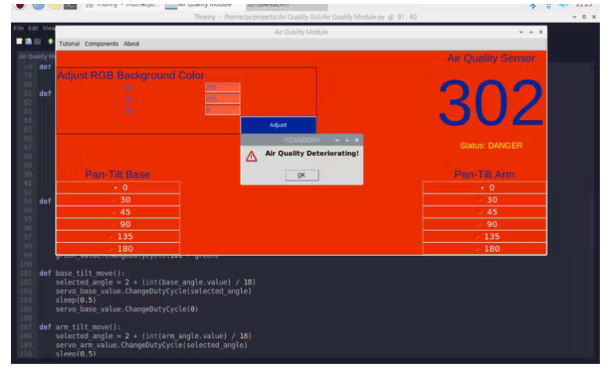
如果超过阈值 (300),则通过警告消息通知 - 空气质量恶化 - 并将状态更改为危险。
在adjust_color()函数中,通过使用ChangeDutyCycle()更改 PWM 频率(在 0 到 100 之间)来调整 RGB LED 的颜色。将输入的颜色值从 0-255 排列到 0-100。
在base_tilt_move()和arm_tilt_move()函数中,通过选择的角度控制伺服电机 - 0, 30, 45, 90, 135, 180 - 运行ChangeDutyCycle(selected_angle) 。2 到 12 之间的循环值精确地适用于 0 到 180 之间的角度。
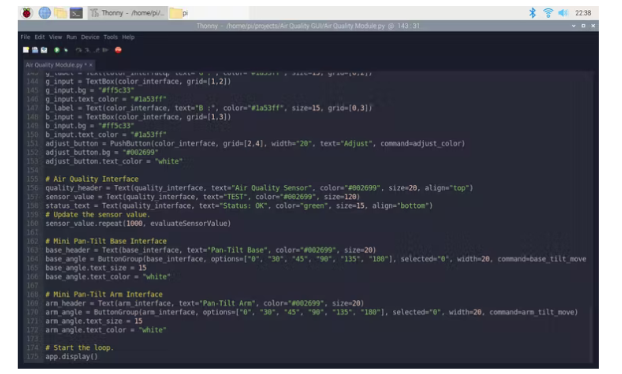
调整伺服电机位置后不要忘记执行以下行以关闭伺服 PWM 引脚。
改变工作周期(0)
创建名为 Air Quality Module 的 GUI 应用程序。
定义菜单栏选项 - 教程、组件、关于。
使用 box 小部件设计界面
RGB 颜色接口
使用布局网格对齐部件。
将相关命令(功能)分配给调整按钮 - adjust_color。
空气质量界面
定义传感器和状态文本变量。
使用repeat()函数每秒更新 MQ-135 空气质量传感器生成的传感器值。
注意:在执行app.display()函数时,While 循环不起作用。
迷你云台底座接口
在按钮组小部件中定义角度 - 0、30、45、90、135、180。
分配相关命令(函数) - base_tilt_move。
迷你云台臂接口
在按钮组小部件中定义角度 - 0、30、45、90、135、180。
分配相关的命令(函数)——arm_tilt_move。
启动循环 app.display() 。
特征
1) 改变仪器的背景颜色(RGB)。
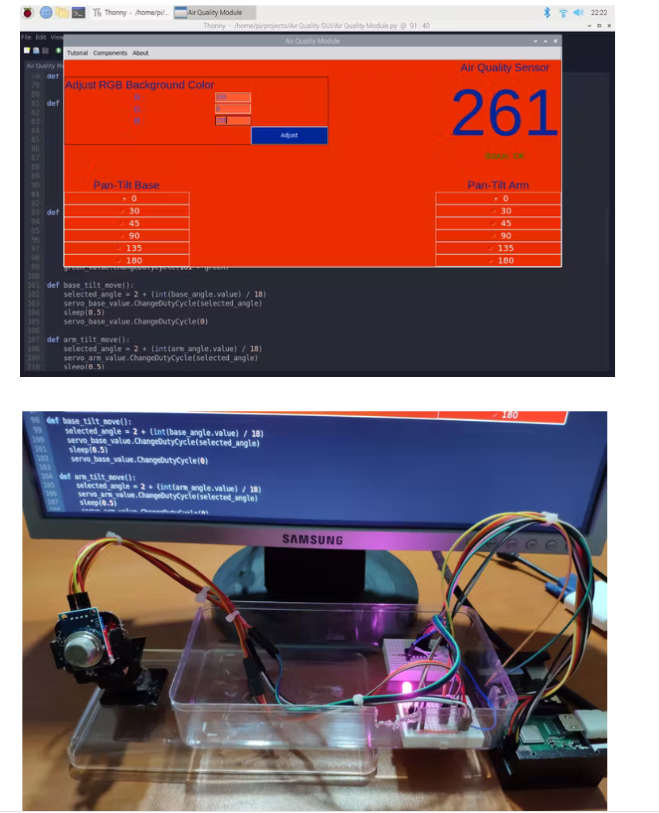
2) 通过选择中间角度 - 0、30、45、90、135、180 来调整迷你云台套件上伺服电机的位置。
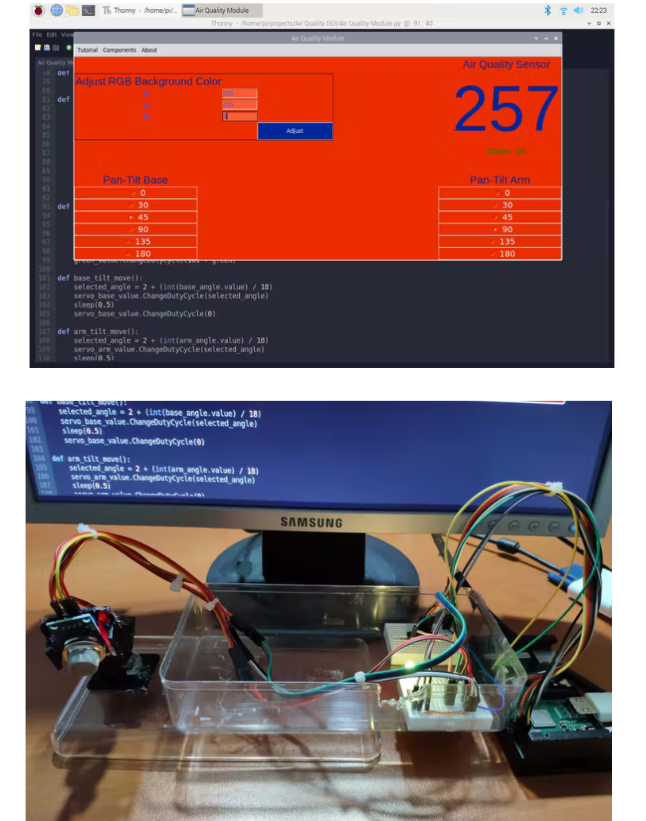
3) 当传感器 (MQ-135) 检测到空气质量恶化时收到通知 - 状态:危险。
在菜单栏上:
4) 进入教程页面。
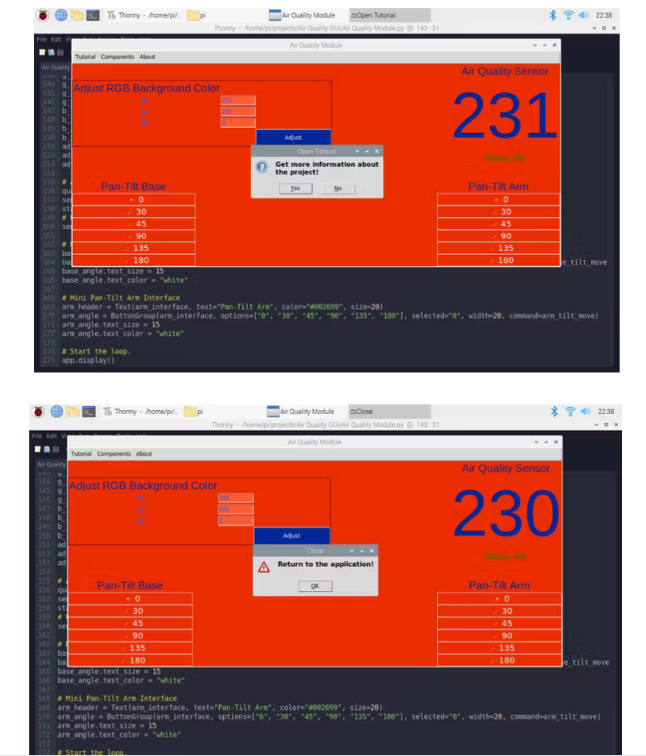
5) 检查组件。
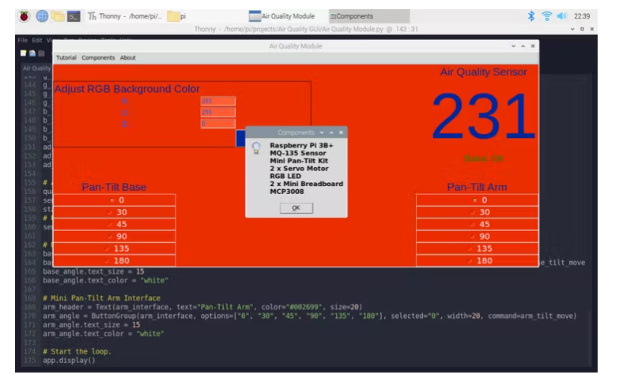
6) 显示电梯间距。
连接
引脚连接在代码和下面的项目示意图中得到了很好的解释。
将树莓派连接到屏幕。
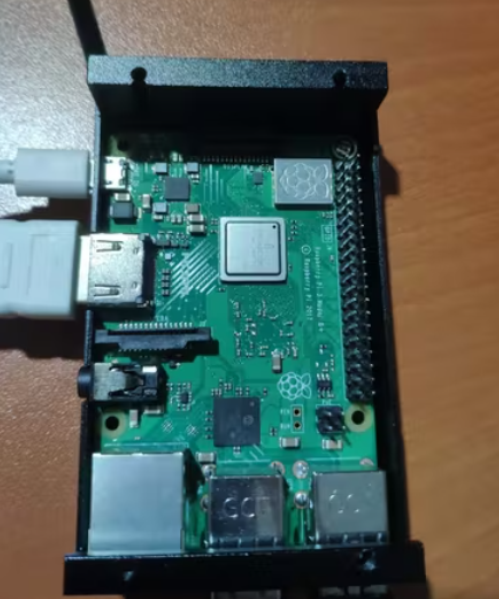

将 MCP3008 和 RGB LED 连接到迷你面包板上。在将 MCP3008 连接到 Raspberry Pi 之前,我使用了一个电位器来测试值范围。
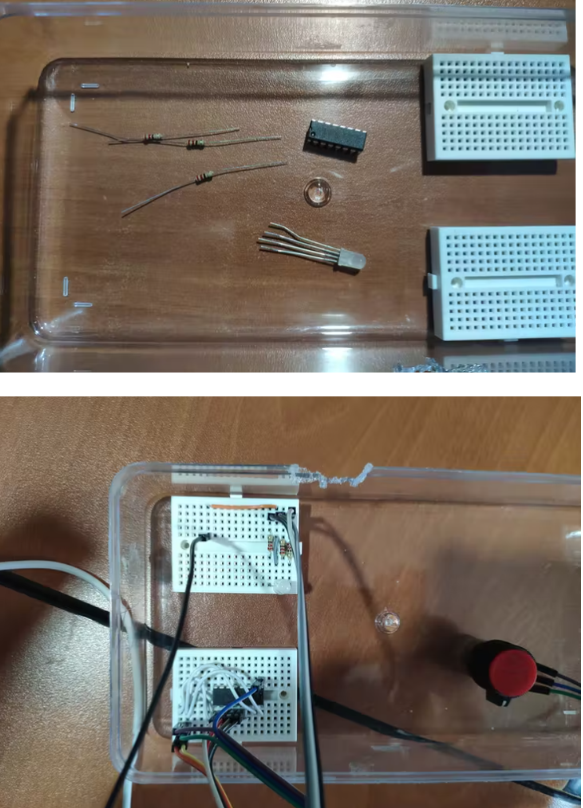
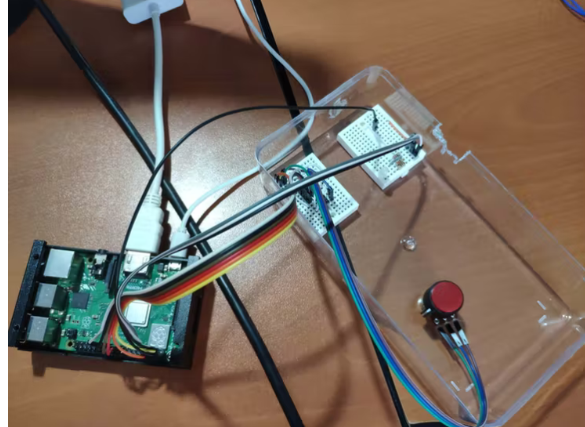
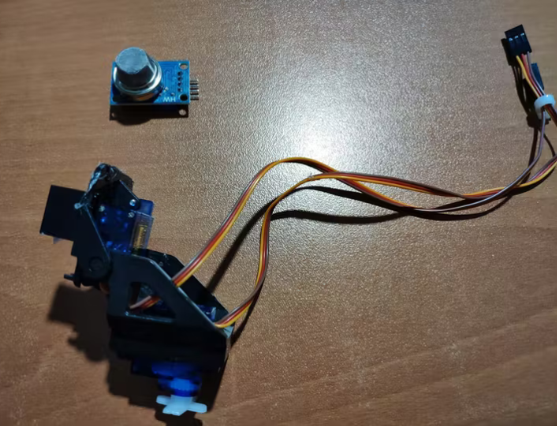
组装迷你云台套件并将 MQ-135 空气质量传感器粘在迷你云台套件(臂)上。

总结
完成所有步骤后,我将所有部件固定在一个旧塑料盒上,并将设备放在我的桌子上,以收集空气质量数据并使用树莓派上的空气质量模块 (GUI) 调整其背景颜色
示意图
代码
# Raspberry Pi Adjustable Air Quality Detector Controlled via GUI
#
# Raspberry Pi 3B+
#
# By Kutluhan Aktar
#
# Learn how to develop a GUI, named Air Quality Module, to control a mini pan-tilt kit and get information from an MQ-135 Air Quality Sensor.
# Also, you can change the background light (RGB) via the GUI.
#
# Get more information on the project page:
# https://theamplituhedron.com/projects/Raspberry-Pi-Adjustable-Air-Quality-Detector-Controlled-via-GUI/
from guizero import App, Box, Text, TextBox, PushButton, ButtonGroup, MenuBar, info, yesno, warn
from time import sleep
from subprocess import call
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import busio
import digitalio
import board
import adafruit_mcp3xxx.mcp3008 as MCP
from adafruit_mcp3xxx.analog_in import AnalogIn
# Create the SPI bus
spi = busio.SPI(clock=board.SCK, MISO=board.MISO, MOSI=board.MOSI)
# Create the cs (chip select)
cs = digitalio.DigitalInOut(board.D5)
# Create the mcp object
mcp = MCP.MCP3008(spi, cs)
# Create analog inputs connected to the input pins on the MCP3008.
channel_0 = AnalogIn(mcp, MCP.P0)
# Define RGB pins settings and PWM frequencies
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
red_pin = 2
green_pin = 3
blue_pin = 4
GPIO.setup(red_pin, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(green_pin, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(blue_pin, GPIO.OUT)
red_value = GPIO.PWM(red_pin, 100)
blue_value = GPIO.PWM(blue_pin, 100)
green_value = GPIO.PWM(green_pin, 100)
red_value.start(100)
blue_value.start(100)
green_value.start(100)
# Define servo motor pin settings and PWM frequencies
servo_base_pin = 20
servo_arm_pin = 21
GPIO.setup(servo_base_pin, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(servo_arm_pin, GPIO.OUT)
servo_base_value = GPIO.PWM(servo_base_pin, 50)
servo_arm_value = GPIO.PWM(servo_arm_pin, 50)
servo_base_value.start(0)
servo_arm_value.start(0)
# Define menu bar options' commands (functions).
def Tutorial():
# Open the project page if requested.
go_to_tutorial = yesno("Open Tutorial", "Get more information about the project!")
if go_to_tutorial == True:
command = "chromium-browser https://theamplituhedron.com/projects/"
call([command], shell=True)
print("Project Tutorial!")
else:
warn("Close", "Return to the application!")
def Components():
info("Components", "Raspberry Pi 3B+\nMQ-135 Sensor\nMini Pan-Tilt Kit\n2 x Servo Motor\nRGB LED\n2 x Mini Breadboard\nMCP3008")
def About():
info("About", "Develop a GUI, named Air Quality Module, to control a mini pan-tilt kit and get information from an MQ-135 Air Quality Sensor. Also, you can change the background light (RGB) on the GUI.")
# Define application commands and features:
def _range(x, in_min, in_max, out_min, out_max):
return int((x - in_min) * (out_max - out_min) / (in_max - in_min) + out_min)
def evaluateSensorValue():
# Test your module, then define the value range - in this case between 0 and 60000.
sensorValue = _range(channel_0.value, 0, 60000, 0, 1023)
sensor_value.value = sensorValue
# Threshold
if(sensorValue > 300):
status_text.value = "Status: DANGER"
status_text.text_color = "yellow"
warn("!!!DANGER!!!", "Air Quality Deteriorating!")
else:
status_text.value = "Status: OK"
status_text.text_color = "green"
def adjust_color():
red = _range(int(r_input.value), 0, 255, 1, 100)
green = _range(int(g_input.value), 0, 255, 1, 100)
blue = _range(int(b_input.value), 0, 255, 1, 100)
red_value.ChangeDutyCycle(101 - red)
blue_value.ChangeDutyCycle(101 - blue)
green_value.ChangeDutyCycle(101 - green)
def base_tilt_move():
# Cycle values between 2 and 12 are working precisely:
selected_angle = 2 + (int(base_angle.value) / 18)
servo_base_value.ChangeDutyCycle(selected_angle)
sleep(0.5)
servo_base_value.ChangeDutyCycle(0)
def arm_tilt_move():
selected_angle = 2 + (int(arm_angle.value) / 18)
servo_arm_value.ChangeDutyCycle(selected_angle)
sleep(0.5)
servo_arm_value.ChangeDutyCycle(0)
# Create the GUI application.
appWidth = 1200
appHeight = 500
app = App(title="Air Quality Module", bg="#eb2e00", width=appWidth, height=appHeight)
# Define menu bar options.
menubar = MenuBar(app, toplevel=["Tutorial", "Components", "About"],
options=[
[ ["View", Tutorial] ],
[ ["Inspect", Components ] ],
[ ["About", About] ]
])
# Design the interface using the box widget.
top = Box(app, width="fill", height=appHeight / 2, align="top")
bottom = Box(app, width="fill", height=appHeight / 2, align="bottom")
color_interface = Box(top, width=appWidth / 2, align="left", layout="grid", border=True)
quality_interface = Box(top, width=appWidth / 2, align="right")
base_interface = Box(bottom, width=appWidth / 2, align="left")
arm_interface = Box(bottom, width=appWidth / 2, align="right")
# RGB Color Interface
color_header = Text(color_interface, text="Adjust RGB Background Color", color="#002699", size=20, grid=[0,0])
r_label = Text(color_interface, text="R :", color="#1a53ff", size=15, grid=[0,1])
r_input = TextBox(color_interface, grid=[1,1])
r_input.bg = "#ff5c33"
r_input.text_color = "#1a53ff"
g_label = Text(color_interface, text="G :", color="#1a53ff", size=15, grid=[0,2])
g_input = TextBox(color_interface, grid=[1,2])
g_input.bg = "#ff5c33"
g_input.text_color = "#1a53ff"
b_label = Text(color_interface, text="B :", color="#1a53ff", size=15, grid=[0,3])
b_input = TextBox(color_interface, grid=[1,3])
b_input.bg = "#ff5c33"
b_input.text_color = "#1a53ff"
adjust_button = PushButton(color_interface, grid=[2,4], width="20", text="Adjust", command=adjust_color)
adjust_button.bg = "#002699"
adjust_button.text_color = "white"
# Air Quality Interface
quality_header = Text(quality_interface, text="Air Quality Sensor", color="#002699", size=20, align="top")
sensor_value = Text(quality_interface, text="TEST", color="#002699", size=120)
status_text = Text(quality_interface, text="Status: OK", color="green", size=15, align="bottom")
# Update the sensor value.
sensor_value.repeat(1000, evaluateSensorValue)
# Mini Pan-Tilt Base Interface
base_header = Text(base_interface, text="Pan-Tilt Base", color="#002699", size=20)
base_angle = ButtonGroup(base_interface, options=["0", "30", "45", "90", "135", "180"], selected="0", width=20, command=base_tilt_move)
base_angle.text_size = 15
base_angle.text_color = "white"
# Mini Pan-Tilt Arm Interface
arm_header = Text(arm_interface, text="Pan-Tilt Arm", color="#002699", size=20)
arm_angle = ButtonGroup(arm_interface, options=["0", "30", "45", "90", "135", "180"], selected="0", width=20, command=arm_tilt_move)
arm_angle.text_size = 15
arm_angle.text_color = "white"
# Start the loop.
app.display()
-
如何使用Raspberry Pi 3进行快速开发2019-02-25 7721
-
适用于Raspberry Pi 4的Raspberry Pi Pico开发板2022-07-22 1754
-
一篇比较 BeagleBone 和 Raspberry Pi 个方面配置的文章2014-10-22 7808
-
Raspberry Pi 开发板优化设计2018-07-16 3643
-
黑科技!使用Raspberry Pi和Python GUI控制伺服电机(原理图、源码、项目教程)2019-10-16 16175
-
使用raspberry pi Pico的原因2022-02-07 1656
-
Raspberry Pi 4/3B的Pico开发板2022-07-26 1596
-
一个Raspberry Pi扩展板2022-07-29 1419
-
使用Raspberry Pi 3 快速开发(相较于稀缺的 Raspberry Pi Zero)2017-05-04 1362
-
raspberry pi官网2020-03-07 6896
-
使用Raspberry Pi构建一个OpenCV人群计数装置2022-08-12 4137
-
使用Raspberry Pi构建一个智能车库开门器2022-09-07 3034
-
使用带有Raspberry Pi的超声波测距模块构建超声波测距仪GUI2022-12-26 621
-
寻找实用的Raspberry Pi项目? 制作一个智能伞架!2023-02-24 1580
-
使用Raspberry Pi Pico W和MicroPython开发物联网应用2023-07-21 3415
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

