

贪心算法:分发饼干
描述
贪心的第一道题目,快看看你够不够贪心
455.分发饼干
力扣题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/assign-cookies
假设你是一位很棒的家长,想要给你的孩子们一些小饼干。但是,每个孩子最多只能给一块饼干。
对每个孩子 i,都有一个胃口值 g[i],这是能让孩子们满足胃口的饼干的最小尺寸;并且每块饼干 j,都有一个尺寸 s[j] 。如果 s[j] >= g[i],我们可以将这个饼干 j 分配给孩子 i ,这个孩子会得到满足。你的目标是尽可能满足越多数量的孩子,并输出这个最大数值。
示例 1:
- 输入: g = [1,2,3], s = [1,1]
- 输出: 1 解释:你有三个孩子和两块小饼干,3个孩子的胃口值分别是:1,2,3。虽然你有两块小饼干,由于他们的尺寸都是1,你只能让胃口值是1的孩子满足。所以你应该输出1。
示例 2:
- 输入: g = [1,2], s = [1,2,3]
- 输出: 2
- 解释:你有两个孩子和三块小饼干,2个孩子的胃口值分别是1,2。你拥有的饼干数量和尺寸都足以让所有孩子满足。所以你应该输出2.
提示:
- 1 <= g.length <= 3 * 10^4
- 0 <= s.length <= 3 * 10^4
- 1 <= g[i], s[j] <= 2^31 - 1
思路
为了了满足更多的小孩,就不要造成饼干尺寸的浪费。
大尺寸的饼干既可以满足胃口大的孩子也可以满足胃口小的孩子,那么就应该优先满足胃口大的。
这里的局部最优就是大饼干喂给胃口大的,充分利用饼干尺寸喂饱一个,全局最优就是喂饱尽可能多的小孩。
可以尝试使用贪心策略,先将饼干数组和小孩数组排序。
然后从后向前遍历小孩数组,用大饼干优先满足胃口大的,并统计满足小孩数量。
如图:
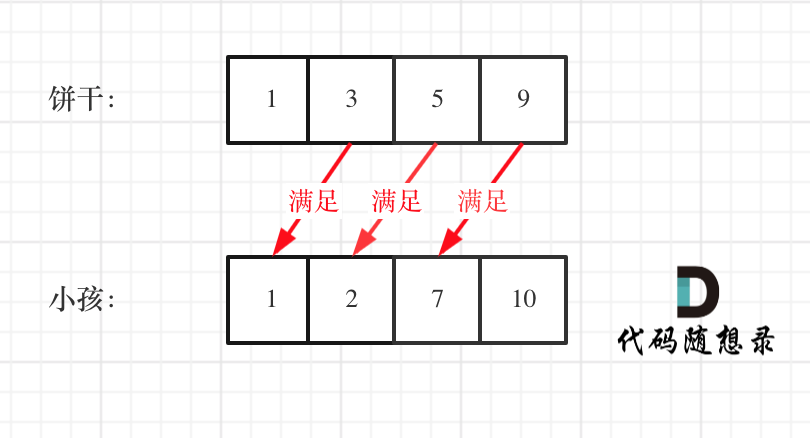 455.分发饼干
455.分发饼干这个例子可以看出饼干9只有喂给胃口为7的小孩,这样才是整体最优解,并想不出反例,那么就可以撸代码了。
C++代码整体如下:
// 时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
// 空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int findContentChildren(vector<int>& g, vector<int>& s) {
sort(g.begin(), g.end());
sort(s.begin(), s.end());
int index = s.size() - 1; // 饼干数组的下表
int result = 0;
for (int i = g.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (index >= 0 && s[index] >= g[i]) {
result++;
index--;
}
}
return result;
}
};
从代码中可以看出我用了一个index来控制饼干数组的遍历,遍历饼干并没有再起一个for循环,而是采用自减的方式,这也是常用的技巧。
有的同学看到要遍历两个数组,就想到用两个for循环,那样逻辑其实就复杂了。
也可以换一个思路,小饼干先喂饱小胃口
代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int findContentChildren(vector<int>& g, vector<int>& s) {
sort(g.begin(),g.end());
sort(s.begin(),s.end());
int index = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < s.size();++i){
if(index < g.size() && g[index] <= s[i]){
index++;
}
}
return index;
}
};
总结
这道题是贪心很好的一道入门题目,思路还是比较容易想到的。
文中详细介绍了思考的过程,想清楚局部最优,想清楚全局最优,感觉局部最优是可以推出全局最优,并想不出反例,那么就试一试贪心。
其他语言版本
Java
class Solution {
// 思路1:优先考虑饼干,小饼干先喂饱小胃口
public int findContentChildren(int[] g, int[] s) {
Arrays.sort(g);
Arrays.sort(s);
int start = 0;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length && start < g.length; i++) {
if (s[i] >= g[start]) {
start++;
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
}
class Solution {
// 思路2:优先考虑胃口,先喂饱大胃口
public int findContentChildren(int[] g, int[] s) {
Arrays.sort(g);
Arrays.sort(s);
int count = 0;
int start = s.length - 1;
// 遍历胃口
for (int index = g.length - 1; index >= 0; index--) {
if(start >= 0 && g[index] <= s[start]) {
start--;
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
}
Python
class Solution:
# 思路1:优先考虑胃饼干
def findContentChildren(self, g: List[int], s: List[int]) -> int:
g.sort()
s.sort()
res = 0
for i in range(len(s)):
if res = g[res]: #小饼干先喂饱小胃口
res += 1
return res
class Solution:
# 思路2:优先考虑胃口
def findContentChildren(self, g: List[int], s: List[int]) -> int:
g.sort()
s.sort()
start, count = len(s) - 1, 0
for index in range(len(g) - 1, -1, -1): # 先喂饱大胃口
if start >= 0 and g[index] <= s[start]:
start -= 1
count += 1
return count
Go
//排序后,局部最优
func findContentChildren(g []int, s []int) int {
sort.Ints(g)
sort.Ints(s)
// 从小到大
child := 0
for sIdx := 0; child < len(g) && sIdx < len(s); sIdx++ {
if s[sIdx] >= g[child] {//如果饼干的大小大于或等于孩子的为空则给与,否则不给予,继续寻找选一个饼干是否符合
child++
}
}
return child
}
审核编辑 :李倩
-
算法设计:8.1 贪心算法(2)#硬声创作季学习电子 2022-12-21
-
贪心算法学习2019-09-04 3963
-
基于BitTorrent种子的内容分发算法2009-03-29 945
-
基于贪心算法的云计算资源调度策略2017-01-07 971
-
一种混合进化算法提高仓库货物平台的作业效率2017-11-13 760
-
动态规划算法和贪心算法的区别与联系2017-11-30 76285
-
基于贪心算法的非一致决策表的决策树分析方法2017-12-05 826
-
一种基于贪心算法的紧急控制策略优化搜素方法2018-03-06 930
-
使用模拟退火与贪心策略的平衡聚类算法的介绍2018-11-28 1224
-
清华毕业计算机教授遭持枪劫车!靠“贪心算法”追回秒杀美国警察2019-01-19 4383
-
关于贪心算法详解2022-04-07 2170
-
贪心算法的基础知识2022-09-14 3819
-
C语言最常用的贪心算法2022-10-31 849
-
基于贪心算法的智能RGV的动态调度策略2023-04-11 548
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

