

 就增量式PID的函数进行编写
就增量式PID的函数进行编写
描述
首先,就增量式PID的函数进行编写:
头文件,全局变量与宏定义如下:
#include "stdio.h"
#include "math.h"
void pid_init();//PID参数初始化
float pid_realise(float speed);//实现PID算法
#define value 1400.0
首先定义结构体pid的相关内容,后面将根据PID里面的相关参数进行修改调整,观察波形情况。
struct {
float set_speed;//设定速度
float actual_speed;//实际速度
float error;//偏差
float error_next;//上一个偏差
float error_last;//上上一个偏差
float kp,ki,kd;//定义比例,积分,微分参数
}pid;
将PID结构体中的参数进行初始化设置,其中的参数是我经过调整后的参数
void pid_init()
{
pid.set_speed = 0;
pid.actual_speed = 10000.0;//原始值0.0
pid.error = 0.0;
pid.error_next = 0.0;
pid.error_last = 0.0;
//可调节PID 参数。使跟踪曲线慢慢接近阶跃函数200.0 //
pid.kp = 0.33333;//原始值0.2
pid.ki = 0.2111;//原始值0.1
pid.kd = 0.1;//原始值0.3
}
接下来实现PID实现的过程函数:
float pid_realise(float speed)//实现pid
{ float increment_speed;//增量
pid.set_speed = speed;//设置目标速度
pid.error = pid.set_speed - pid.actual_speed;
increment_speed = pid.kp*(pid.error-pid.error_next)+pid.ki*pid.error+\
pid.kd*(pid.error-2*pid.error_next+pid.error_last);//增量计算公式
pid.actual_speed+= increment_speed;
pid.error_last = pid.error_next;//下一次迭代
pid.error_next = pid.error;
return pid.actual_speed;
}
接着就是主函数,主函数这里将进行设置,逻辑如下:初始化参数,进行运算,运算次数设置为400次,可以提高,因为调整后的参数,后面又有break可以跳出while循环因此不需要在意这里,接下来就是不断判断期望值与实际值误差书否在5以内
int main()
{ int count = 1;
int num = 0;
int type;
pid_init();
while(count<400)//进行400次 PID 运算可以提高,使初始值从0开始接近200.0
{
float speed = pid_realise(value);//设定值设定为200.0
type=abs(speed-value);
printf("%f\n",speed);//
if( type <= 5) ///判断每次的误差是否在5以内
{
num++;
if(num==6)
{
printf("run number is %d\r\n",count);
break;
}
else count++;
}
else count++;
}
}
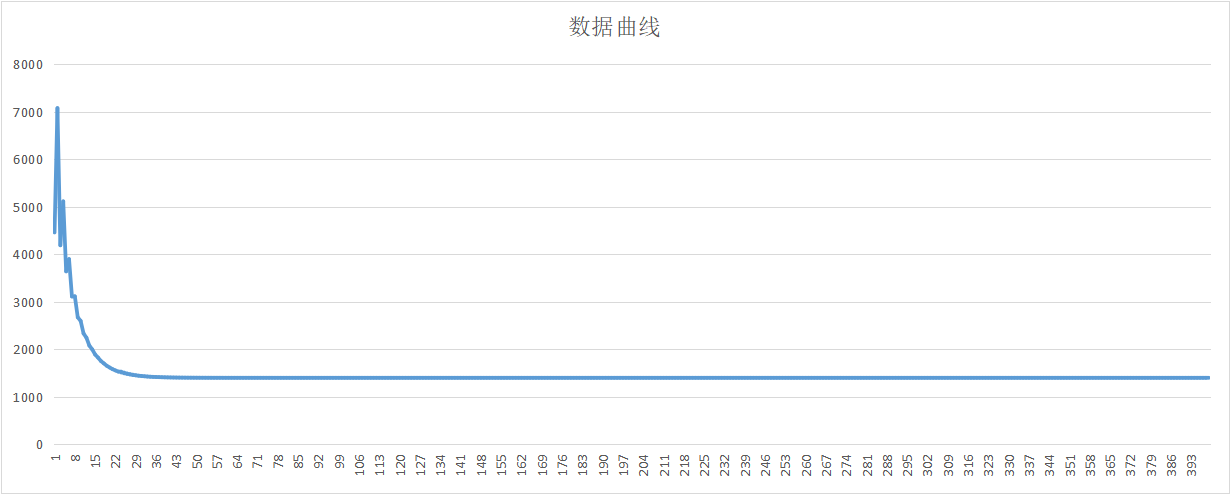
运行函数之后得到如下图所示的曲线,可以看到,假设单位阶跃相应的过程中期望值发生改变,假设初始值为7000,要调整到理想值按照当前参数大约需要47次变换。

审核编辑:汤梓红
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
-
浅析位置式PID与增量式PID算法2016-01-15 8876
-
教你用C语言实现位置式PID和增量式PID2019-05-30 4536
-
位置式PID与增量式PID的区别在哪?2021-07-13 4108
-
什么是增量式PID2021-09-13 2570
-
位置式PID与增量式PID简介2022-01-20 3301
-
位置式PID和增量式PID区别是什么?2023-10-26 544
-
请问如何调节增量式pid?2023-11-09 629
-
增量式PID控制算法2016-04-01 919
-
增量式pid分析及参数整定2017-11-24 17009
-
增量与位置PID2017-11-25 1943
-
增量式pid参数调整公式及策略2018-02-26 58292
-
使用单片机和Arduino实现增量式PID位置式PID算法和PID库免费下载2020-05-28 1990
-
增量式PID控制算法程序设计方案下载2021-03-29 943
-
PID:智能小车入门(位置式和增量式)2022-01-14 3973
-
位置式PID与增量式PID的区别2024-06-05 10438
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

