

OpenCV中积分图函数与应用
描述
OpenCV中积分图函数与应用
一:图像积分图概念
积分图像是Crow在1984年首次提出,是为了在多尺度透视投影中提高渲染速度。随后这种技术被应用到基于NCC的快速匹配、对象检测和SURF变换中、基于统计学的快速滤波器等方面。积分图像是一种在图像中快速计算矩形区域和的方法,这种算法主要优点是一旦积分图像首先被计算出来我们可以计算图像中任意大小矩形区域的和而且是在常量时间内。这样在图像模糊、边缘提取、对象检测的时候极大降低计算量、提高计算速度。第一个应用积分图像技术的应用是在Viola-Jones的对象检测框架中出现。
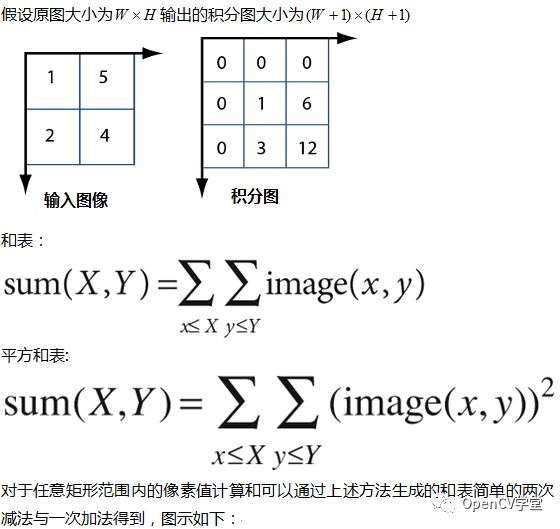
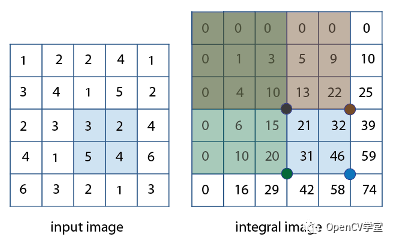
上图左侧四个点的矩形区域像素求和,只要根据每个点左上方所有像素和表值,进行两次减法与一次加法即可=》46 – 22 – 20 + 10 = 14
二:OpenCV中积分图函数
OpenCV中通过integral()函数可以很容易的计算图像的积分图,该函数支持和表积分图、平方和表积分图、瓦块和表积分图计算。integral函数与参数解释如下:
-
void cv::integral( -
InputArray src, // 输入图像 -
OutputArray sum, // 和表 -
OutputArray sqsum, // 平方和表 -
OutputArray tilted, // 瓦块和表 -
int sdepth = -1, // 和表数据深度常见CV_32S -
int sqdepth = -1 // 平方和表数据深度 常见 CV_32F -
)
三:使用积分图函数
通过代码演示计算积分图实现任意窗口大小的盒子模糊与垂直边缘提取,完整的代码实现如下:
-
#include -
#include -
-
using namespace cv; -
using namespace std; -
-
void blur_demo(Mat &image, Mat &sum); -
void edge_demo(Mat &image, Mat &sum); -
int getblockSum(Mat &sum, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int i); -
int main(int argc, char** argv) { -
Mat src = imread("D:/vcprojects/images/yuan_test.png"); -
if (src.empty()) { -
printf("could not load image... "); -
return -1; -
} -
namedWindow("input", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); -
imshow("input", src); -
-
namedWindow("output", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); -
-
// 计算积分图 -
Mat sum, sqrsum; -
integral(src, sum, sqrsum, CV_32S, CV_32F); -
-
// 积分图应用 -
int type = 0; -
while (true) { -
char c = waitKey(100); -
if (c > 0) { -
type = (int)c; -
printf("c : %d ", type); -
} -
-
if (c == 27) { -
break; // ESC -
} -
if (type == 49) { // 数字键 1 -
blur_demo(src, sum); -
} -
else if (type == 50) { // 数字键 2 -
edge_demo(src, sum); -
} -
else { -
blur_demo(src, sum); -
} -
} -
-
waitKey(0); -
return 0; -
} -
-
void blur_demo(Mat &image, Mat &sum) { -
int w = image.cols; -
int h = image.rows; -
Mat result = Mat::zeros(image.size(), image.type()); -
int x2 = 0, y2 = 0; -
int x1 = 0, y1 = 0; -
int ksize = 5; -
int radius = ksize / 2; -
int ch = image.channels(); -
int cx = 0, cy = 0; -
for (int row = 0; row < h + radius; row++) { -
y2 = (row + 1)>h ? h : (row + 1); -
y1 = (row - ksize) < 0 ? 0 : (row - ksize); -
for (int col = 0; col < w + radius; col++) { -
x2 = (col + 1)>w ? w : (col + 1); -
x1 = (col - ksize) < 0 ? 0 : (col - ksize); -
cx = (col - radius) < 0 ? 0 : col - radius; -
cy = (row - radius) < 0 ? 0 : row - radius; -
int num = (x2 - x1)*(y2 - y1); -
for (int i = 0; i < ch; i++) { -
// 积分图查找和表,计算卷积 -
int s = getblockSum(sum, x1, y1, x2, y2, i); -
result.at<Vec3b>(cy, cx)[i] = saturate_cast(s / num); -
} -
} -
} -
imshow("output", result); -
imwrite("D:/result.png", result); -
} -
-
/** -
* 3x3 sobel 垂直边缘检测演示 -
*/ -
void edge_demo(Mat &image, Mat &sum) { -
int w = image.cols; -
int h = image.rows; -
Mat result = Mat::zeros(image.size(), CV_32SC3); -
int x2 = 0, y2 = 0; -
int x1 = 0, y1 = 0; -
int ksize = 3; // 算子大小,可以修改,越大边缘效应越明显 -
int radius = ksize / 2; -
int ch = image.channels(); -
int cx = 0, cy = 0; -
for (int row = 0; row < h + radius; row++) { -
y2 = (row + 1)>h ? h : (row + 1); -
y1 = (row - ksize) < 0 ? 0 : (row - ksize); -
for (int col = 0; col < w + radius; col++) { -
x2 = (col + 1)>w ? w : (col + 1); -
x1 = (col - ksize) < 0 ? 0 : (col - ksize); -
cx = (col - radius) < 0 ? 0 : col - radius; -
cy = (row - radius) < 0 ? 0 : row - radius; -
int num = (x2 - x1)*(y2 - y1); -
for (int i = 0; i < ch; i++) { -
// 积分图查找和表,计算卷积 -
int s1 = getblockSum(sum, x1, y1, cx, y2, i); -
int s2 = getblockSum(sum, cx, y1, x2, y2, i); -
result.at<Vec3i>(cy, cx)[i] = saturate_cast(s2 - s1); -
} -
} -
} -
Mat dst, gray; -
convertScaleAbs(result, dst); -
normalize(dst, dst, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX); -
cvtColor(dst, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY); -
imshow("output", gray); -
imwrite("D:/edge_result.png", gray); -
} -
-
int getblockSum(Mat &sum, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int i) { -
int tl = sum.at<Vec3i>(y1, x1)[i]; -
int tr = sum.at<Vec3i>(y2, x1)[i]; -
int bl = sum.at<Vec3i>(y1, x2)[i]; -
int br = sum.at<Vec3i>(y2, x2)[i]; -
int s = (br - bl - tr + tl); -
return s; -
}
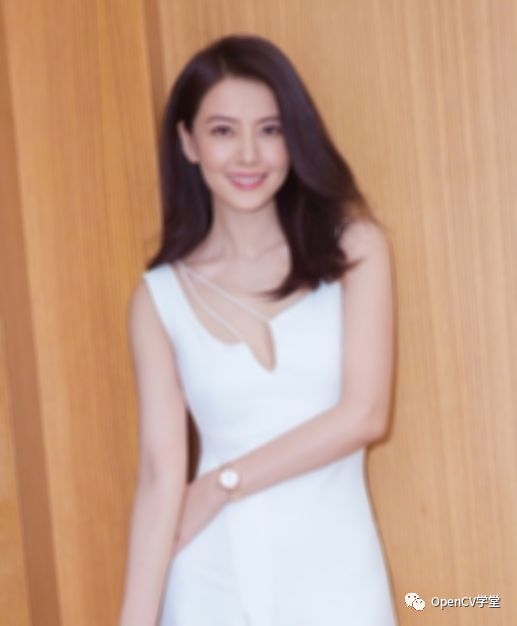
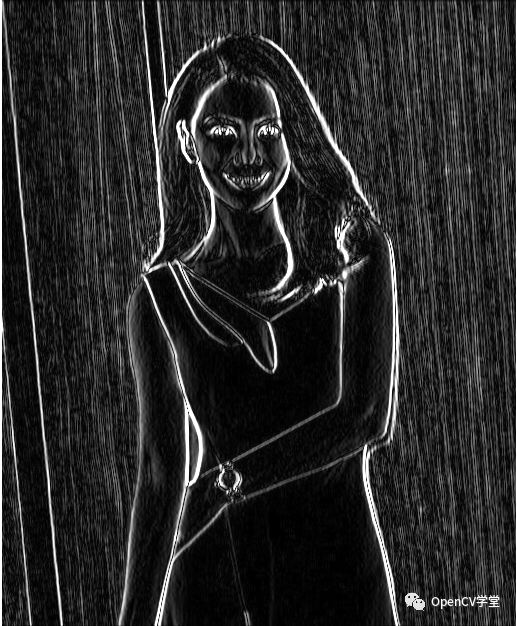
这里最重要的是要注意到上面的图示,积分图对象的Mat(1,1)对应实际图像Mat(0,0),如果不加处理的话会导致结果有明显的中心迁移。edge_demo实现了积分图查找提取图像边缘、blur_demo函数实现积分图查找图像均值模糊,getblockSum函数实现和表查找功能,运行显示:
原图:
模糊效果

边缘效果

审核编辑 :李倩
-
为什么电路中有积分电路和微分电路,Python中无法对某个函数直接求导?2023-10-26 1154
-
如何使用Python中的OpenCV模块检测颜色2023-02-09 1731
-
OpenCV-Python中的函数说明2022-07-08 1344
-
复变函数与积分变换练习题及解答2021-06-27 992
-
Vivado设计流程分析 Vivado HLS实现OpenCV的开发流程2021-04-23 6322
-
OpenCV中色彩空间的转换函数2020-11-02 3178
-
OpenCV的小波变换函数代码免费下载2019-11-14 1131
-
OpenCV函数图像处理目录说明2019-10-29 1072
-
人脸识别历程中的opencv库是1.0还是emcv版本?2019-10-28 3398
-
OpenCV3编程入门-源码例程全集-pyrUp函数用法示例2016-09-18 771
-
OpenCV_1.02015-11-24 583
-
利用RBF神经网络实现高斯型函数积分2009-03-29 573
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

