

 RT-Thread操作系统打印函数概述
RT-Thread操作系统打印函数概述
描述
在设计之初我们希望通过调试程序完成我们需要的代码设计,这些都需要我们进行调试,进入degug模式,往往系统运行起来我们无法判断程序运行哪一步因此需要通过打印功能显示关键步骤的程序运行节点,同样在rt-thread操作系统中依然可以进行此过程 的代码实现。下面就此进行讨论。
作为打印函数它提供了我们对应的函数接口,我们调用时其实与printf是相同的用法,但是看底层的函数描述我们就知道其实还是存在差异的。
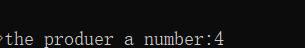
首先粘贴出函数的实际项目中的用法:
rt_kprintf("the producer generates a number: %d\n", array[set%MAXSEM]);
运行起来我们看到相应的打印结果
相比于之前我们接触到的重定义函数,rt_kprintf定义为:void rt_kprintf(const char *fmt, ...)
下面我们看一下具体函数的描述(看注释):
void rt_kprintf(const char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list args;
rt_size_t length;
static char rt_log_buf[RT_CONSOLEBUF_SIZE];
va_start(args, fmt);
/* the return value of vsnprintf is the number of bytes that would be
* written to buffer had if the size of the buffer been sufficiently
* large excluding the terminating null byte. If the output string
* would be larger than the rt_log_buf, we have to adjust the output
* length. */
length = rt_vsnprintf(rt_log_buf, sizeof(rt_log_buf) - 1, fmt, args); //计算长度
if (length > RT_CONSOLEBUF_SIZE - 1)
length = RT_CONSOLEBUF_SIZE - 1;
#ifdef RT_USING_DEVICE
if (_console_device == RT_NULL) //判断控制台设备是否为空
{
rt_hw_console_output(rt_log_buf);
}
else
{
rt_uint16_t old_flag = _console_device->open_flag;
_console_device->open_flag |= RT_DEVICE_FLAG_STREAM;
rt_device_write(_console_device, 0, rt_log_buf, length); //设备写线程
_console_device->open_flag = old_flag; //控制台设备状态
}
#else
rt_hw_console_output(rt_log_buf); 0 //控制台输出buf
#endif
va_end(args);
}
RTM_EXPORT(rt_kprintf);
其中包含的几个线程大家可以自行观看官方文件库。
审核编辑:汤梓红
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
-
RT-Thread操作系统应用开发寒假师资培训2024-12-06 987
-
RT-Thread内部机制大揭秘,带你深入操作系统内核2024-08-01 5805
-
新书发布——《实时操作系统应用技术:RT-Thread与ARM编程实践》2024-05-11 1963
-
RT-Thread荣获“最具影响力IoT操作系统奖”2024-04-12 919
-
RT-Thread操作系统的FreeRTOS兼容层2023-01-14 3065
-
RT-Thread操作系统已经成功部署至芯驰E32022-09-09 2068
-
RT-Thread学习笔记 RT-Thread的架构概述2022-07-09 5597
-
基于RT-Thread操作系统衍生rt-smart实时操作系统简介2022-06-22 5455
-
2022 RT-Thread全球技术大会:实时嵌入式操作系统概述2022-05-27 1925
-
RT-Thread实时操作系统安装向导2022-04-02 697
-
国民技术携手RT-Thread共同推进MCU与RT-Thread操作系统广泛适配2021-12-16 2961
-
RT-Thread Smart微内核操作系统发布!2020-09-09 3342
-
RT Thread操作系统教程及资料2016-05-11 1277
-
RT-Thread编程指南2015-11-26 2192
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

