

 【RT-Thread学习笔记】使用scons命令生成静态库
【RT-Thread学习笔记】使用scons命令生成静态库
描述
1 问题来源
本问题来源于RT-Thread的技术论坛的一个常见问题,当时我回答了这个问题,很荣幸拿了一个最佳答案,为了能够再次消化并进行知识点沉淀,我把这个问题再次抛到这里。 原问题,请戳这里:scons 命令buildlib使用方法
2 实践分析
2.1 不懂就要问
既然不知道怎么用scons,那么我们先看到它的帮助信息,以下命令在scons的主目录执行,即可以找到Sconscript的目录下执行:
-
rt-thread/bsp/qemu-vexpress-a9$ scons -h -
scons: Reading SConscript files ... -
drivers/SConscript -
applications/SConscript -
[, , ] -
scons: done reading SConscript files. -
usage: scons [OPTION] [TARGET] ... -
SCons Options: -
-b, -d, -e, -m, -S, -t, -w, --environment-overrides, --no-keep-going, -
--no-print-directory, --print-directory, --stop, --touch -
Ignored for compatibility. -
-c, --clean, --remove Remove specified targets and dependencies. -
-C DIR, --directory=DIR Change to DIR before doing anything. -
--cache-debug=FILE Print CacheDir debug info to FILE. -
--cache-disable, --no-cache -
Do not retrieve built targets from CacheDir. -
--cache-force, --cache-populate -
Copy already-built targets into the CacheDir. -
--cache-readonly Do not update CacheDir with built targets. -
--cache-show Print build actions for files from CacheDir. -
--config=MODE Controls Configure subsystem: auto, force, -
cache. -
-D Search up directory tree for SConstruct, -
build all Default() targets. -
--debug=TYPE Print various types of debugging information: -
count, duplicate, explain, findlibs, includes, -
memoizer, memory, objects, pdb, prepare, -
presub, stacktrace, time, action-timestamps. -
--diskcheck=TYPE Enable specific on-disk checks. -
--duplicate=DUPLICATE Set the preferred duplication methods. Must be -
one of hard-soft-copy, soft-hard-copy, -
hard-copy, soft-copy, copy -
--enable-virtualenv Import certain virtualenv variables to SCons -
-f FILE, --file=FILE, --makefile=FILE, --sconstruct=FILE -
Read FILE as the top-level SConstruct file. -
-h, --help Print defined help message, or this one. -
-H, --help-options Print this message and exit. -
-i, --ignore-errors Ignore errors from build actions. -
-I DIR, --include-dir=DIR Search DIR for imported Python modules. -
--ignore-virtualenv Do not import virtualenv variables to SCons -
--implicit-cache Cache implicit dependencies -
--implicit-deps-changed Ignore cached implicit dependencies. -
--implicit-deps-unchanged Ignore changes in implicit dependencies. -
--interact, --interactive Run in interactive mode. -
-j N, --jobs=N Allow N jobs at once. -
-k, --keep-going Keep going when a target can't be made. -
--max-drift=N Set maximum system clock drift to N seconds. -
--md5-chunksize=N Set chunk-size for MD5 signature computation to -
N kilobytes. -
-n, --no-exec, --just-print, --dry-run, --recon -
Don't build; just print commands. -
--no-site-dir Don't search or use the usual site_scons dir. -
--profile=FILE Profile SCons and put results in FILE. -
-q, --question Don't build; exit status says if up to date. -
-Q Suppress "Reading/Building" progress messages. -
--random Build dependencies in random order. -
-s, --silent, --quiet Don't print commands. -
--site-dir=DIR Use DIR instead of the usual site_scons dir. -
--stack-size=N Set the stack size of the threads used to run -
jobs to N kilobytes. -
--taskmastertrace=FILE Trace Node evaluation to FILE. -
--tree=OPTIONS Print a dependency tree in various formats: all, -
derived, prune, status, linedraw. -
-u, --up, --search-up Search up directory tree for SConstruct, -
build targets at or below current directory. -
-U Search up directory tree for SConstruct, -
build Default() targets from local SConscript. -
-v, --version Print the SCons version number and exit. -
--warn=WARNING-SPEC, --warning=WARNING-SPEC -
Enable or disable warnings. -
-Y REPOSITORY, --repository=REPOSITORY, --srcdir=REPOSITORY -
Search REPOSITORY for source and target files. -
Local Options: -
--dist make distribution -
--dist-strip make distribution and strip useless files -
--dist-ide make distribution for RT-Thread Studio IDE -
--project-path=PROJECT-PATH -
set dist-ide project output path -
--project-name=PROJECT-NAME -
set project name -
--reset-project-config reset the project configurations to default -
--cscope Build Cscope cross reference database. Requires -
cscope installed. -
--clang-analyzer Perform static analyze with Clang-analyzer. -
Requires Clang installed. It is recommended to -
use with scan-build like this: `scan-build -
scons --clang-analyzer` If things goes well, -
scan-build will instruct you to invoke -
scan-view. -
--buildlib=BUILDLIB building library of a component -
--cleanlib clean up the library by --buildlib -
--target=TARGET set target project: mdk/mdk4/mdk5/iar/vs/vsc/ua/ -
cdk/ses/makefile/eclipse/codelite/cmake -
--stackanalysis thread stack static analysis -
--genconfig Generate .config from rtconfig.h -
--useconfig=USECONFIG make rtconfig.h from config file. -
--verbose print verbose information during build -
--menuconfig make menuconfig for RT-Thread BSP -
--pyconfig Python GUI menuconfig for RT-Thread BSP -
--pyconfig-silent Don`t show pyconfig window
精准匹配下:
-
rt-thread/bsp/qemu-vexpress-a9$ scons -h | grep buildlib -
--buildlib=BUILDLIB building library of a component -
--cleanlib clean up the library by --buildlib
2.2 实践出整理
从上面的帮助信息,我们已经找到关键信息了,我们来实践下:
-
rt-thread/bsp/qemu-vexpress-a9$ scons --buildlib=BUILDLIB -
scons: Reading SConscript files ... -
b'' -
drivers/SConscript -
applications/SConscript -
[, , ] -
scons: done reading SConscript files. -
scons: Building targets ... -
scons: building associated VariantDir targets: build -
scons: `.' is up to date. -
scons: done building targets.
发现并没有生成,仔细一看,这个buildlib=后面跟的名称不是乱填的,是需要填写你当前目录下,已经使用scons语法配置好的组件,这个东西在scons里面是叫Group。 通俗来说,就是使用buildlib,一个Gourp就可以生成一个库。 我们再来实践下,以bsp/qemu-vexpress-a9的Application这个Group为例,在其applications目录有定义Sconsript:
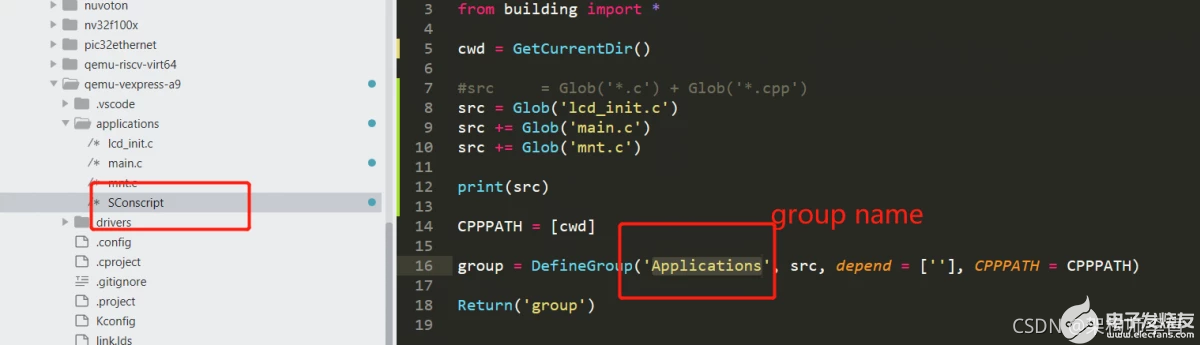
那么就可以输入scons--buildlib=Applications
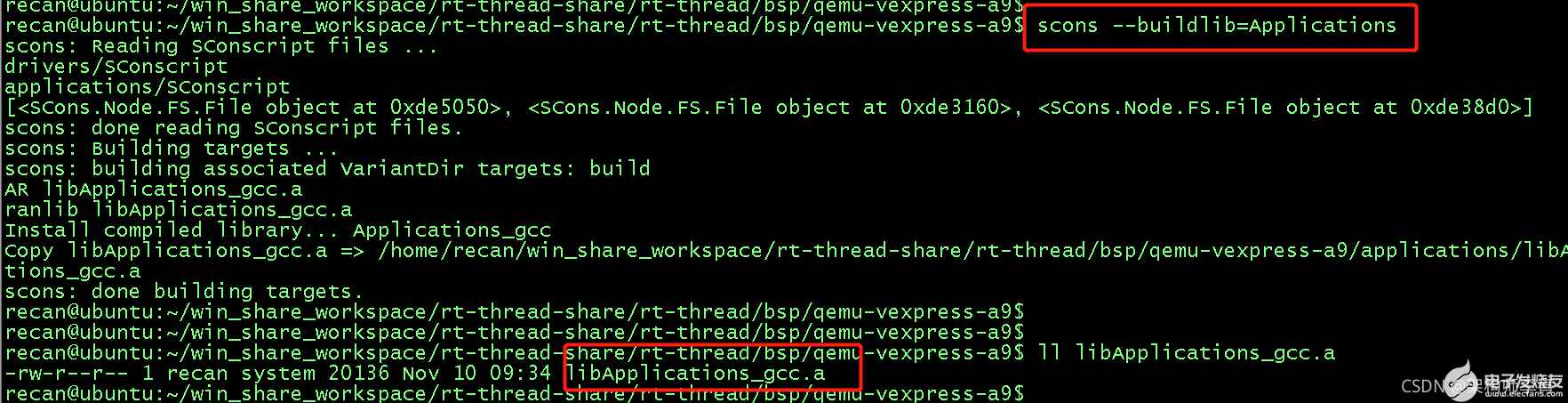
就可以将Applications那个group定义的C文件编译打包成一个静态库,输出也是位于bsp的目录中。
3 经验总结
- 任何命令行指令,千万不要放过它的help信息
-
scons 使用
--buildlib=xxx轻松生存库文件,库名称为libxxx.a
4 更多分享
架构师李肯
一个专注于嵌入式IoT领域的架构师。有着近10年的嵌入式一线开发经验,深耕IoT领域多年,熟知IoT领域的业务发展,深度掌握IoT领域的相关技术栈,包括但不限于主流RTOS内核的实现及其移植、硬件驱动移植开发、网络通讯协议开发、编译构建原理及其实现、底层汇编及编译原理、编译优化及代码重构、主流IoT云平台的对接、嵌入式IoT系统的架构设计等等。拥有多项IoT领域的发明专利,热衷于技术分享,有多年撰写技术博客的经验积累,连续多月获得RT-Thread官方技术社区原创技术博文优秀奖,荣获CSDN博客专家、CSDN物联网领域优质创作者、2021年度CSDN&RT-Thread技术社区之星、RT-Thread官方嵌入式开源社区认证专家、RT-Thread 2021年度论坛之星TOP4、华为云云享专家(嵌入式物联网架构设计师)等荣誉。坚信【知识改变命运,技术改变世界】!
欢迎关注我的github仓库01workstation,日常分享一些开发笔记和项目实战,欢迎指正问题。
同时也非常欢迎关注我的专栏:有问题的话,可以跟我讨论,知无不答,谢谢大家。
-
ENV的scons能生成RT-Thread studio工程吗?2025-10-13 127
-
基于RT-Thread Studio学习2023-05-15 6058
-
【RT-Thread学习笔记】Makefile的FORCE2022-07-30 3608
-
RT-Thread学习笔记 RT-Thread的架构概述2022-07-09 5571
-
RT-Thread全球技术大会:关于SCons构建引擎的主要部分介绍2022-05-27 1432
-
RT-Thread 4.1.0的CMake构建教程2022-05-25 4332
-
RT-Thread系统中的Scons构建工具资料推荐2022-05-07 4001
-
RT-Thread 内核学习笔记 - 理解defunct僵尸线程2022-01-25 724
-
RT-Thread Nano入门学习笔记2021-11-26 939
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

