

8个常用的option配置选项
电子说
描述
通过pandas的使用,我们经常要交互式地展示表格(dataframe)、分析表格。而表格的格式就显得尤为重要了,因为大部分时候如果我们直接展示表格,格式并不是很友好。
其实呢,这些痛点都可以通过pandas的option来解决。短短几行代码,只要提前配置好,一次设置好,全局生效,perfect!
# 使用方法 import pandas as pd pd.set_option() pd.get_option() # 使用属性,例如展示的最大行数 pd.option.display.max_rows
东哥整理了8个常用的配置选项,供大家参考。记住这8个option代码,下次直接粘贴进去,效率可以提高很多,爽歪歪。
显示更多行
显示更多列
改变列宽
设置float列的精度
数字格式化显示
更改绘图方法
配置info()的输出
打印出当前设置并重置所有选项
1. 显示更多行
默认情况下,pandas 是不超出屏幕的显示范围的,如果表的行数很多,它会截断中间的行只显示一部分。我们可以通过设置display.max_rows来控制显示的最大行数,比如我想设置显示200行。
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', 200)
# pd.options.display.max_rows = 200
如果行数超过了display.max_rows,那么display.min_rows将确定显示的部分有多少行。因为display.min_rows的默认行数为5,,下面例子只显示前5行和最后5行,中间的所有行省略。
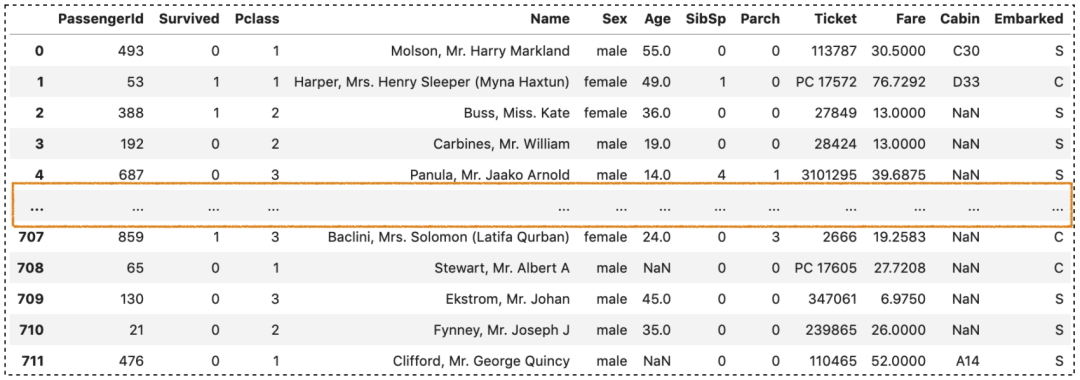
同理,也可根据自己的习惯显示可显示的行数,比如10, 20..
pd.set_option('display.min_rows', 10)
# pd.options.display.min_rows = 10
还可以直接重置。
# 重置
pd.reset_option('display.max_rows')
2. 显示更多列
行可以设置,同样的列也可以设置,display.max_columns控制着可显示的列数,默认值为20。
pd.get_option('display.max_columns')
# pd.options.display.max_columns
20
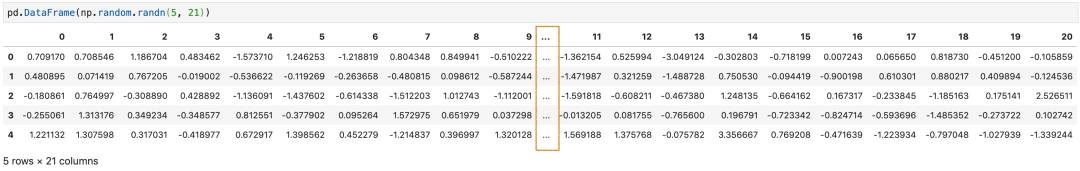
3. 改变列宽
pandas对列中显示的字符数有一些限制,默认值为50字符。所以,有的值字符过长就会显示省略号。如果想全部显示,可以设置display.max_colwidth,比如设置成500。
pd.set_option ('display.max_colwidth',500)
# pd.options.display.max_colwidth = 500
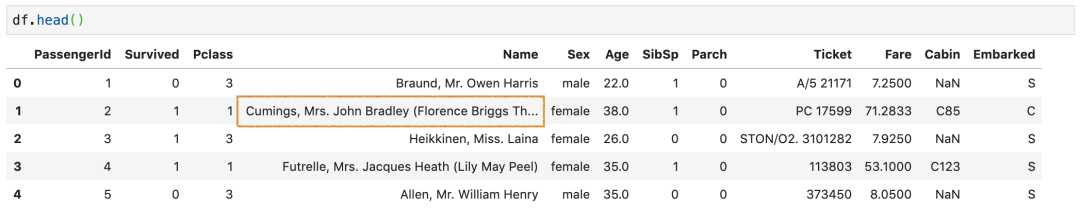
4. 设置float列的精度
对于float浮点型数据,pandas默认情况下只显示小数点后6位。我们可以通过预先设置display.precision让其只显示2位,避免后面重复操作。
pd.set_option( 'display.precision',2) # pd.options.display.precision = 2
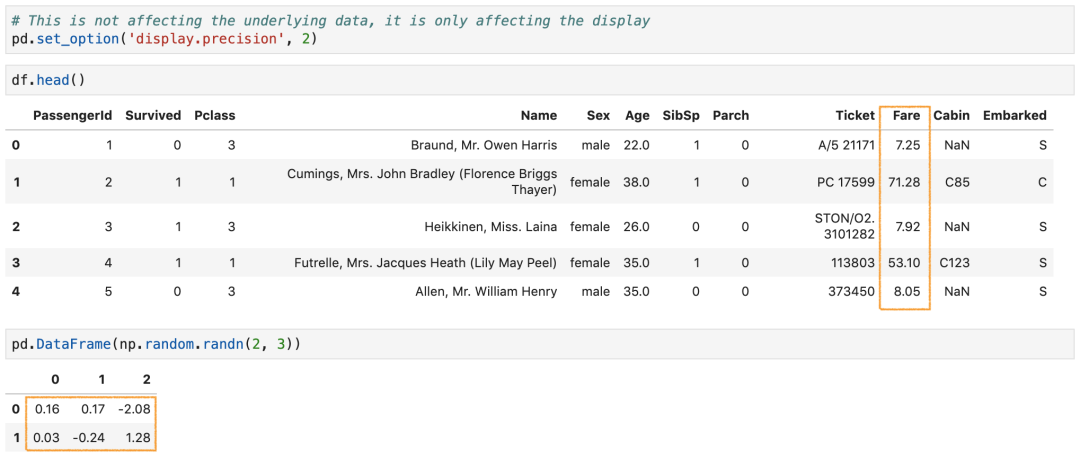
这个设置不影响底层数据,它只影响浮动列的显示。
5. 数字格式化显示
pandas中有一个选项display.float_formatoption可以用来格式化任何浮点列。这个仅适用于浮点列,对于其他数据类型,必须将它们转换为浮点数才可以。
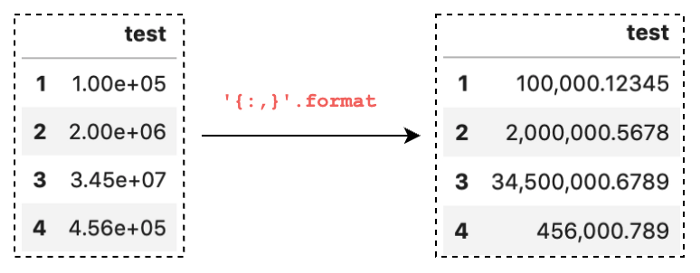
用逗号格式化大值数字
例如 1200000 这样的大数字看起来很不方便,所以我们用逗号进行分隔。
pd.set_option('display.float_format','{:,}'.format)
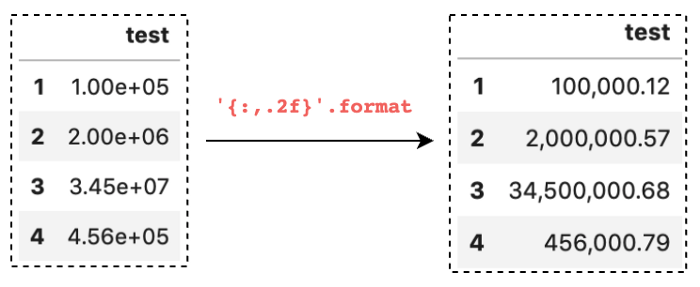
设置数字精度
和上面display.precision有点类似,假如我们只关心小数点后的2位数字,我们可以这样设置格式化:
pd.set_option('display.float_format', '{:,.2f}'.format)
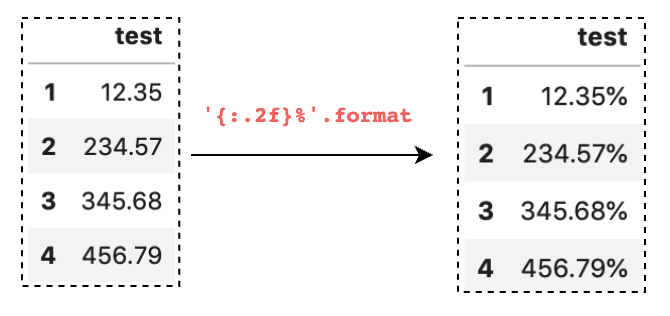
百分号格式化
如果我们要显示一个百分比的列,可以这样设置。
pd.set_option('display.float_format', '{:.2f}%'.format)
或者其它币种的符号等均可,只需要在大括号{}前后添加即可。
6. 更改绘图方法
默认情况下,pandas使用matplotlib作为绘图后端。从 0.25 版本开始,pandas提供了使用不同后端选择,比如plotly,bokeh等第三方库,但前提是你需要先安装起来。
设置很简单,只要安装好三方库后,同样只需要一行。
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
pd.set_option('plotting.backend', 'altair')
data = pd.Series(np.random.randn(100).cumsum())
data.plot()
7. 配置info()的输出
pandas中我们经常要使用info()来快速查看DataFrame的数据情况。但是,info这个方法对要分析的最大列数是有默认限制的,并且如果数据集中有null,那么在大数据集计数统计时会非常慢。
pandas提供了两种选择:
display.max_info_columns: 设置要分析的最大列数,默认为100。
display.max_info_rows: 设置计数null时的阈值,默认为1690785。
比如,在分析有 150 个特征的数据集时,我们可以设置display.max_info_columns为涵盖所有列的值,比如将其设置为 200:
pd.set_option('display.max_info_columns', 200)
在分析大型数据集时,df.info()由于要计算所有null,导致速度很慢。因此我们可以简单地设置display.max_info_rows为一个小的值来避免计数,例如只在行数不超过5时才计数null:
pd.set_option('display.max_info_rows', 5)
8. 打印出当前设置并重置所有选项
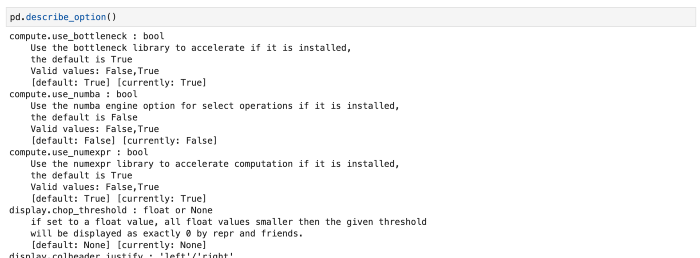
pd.describe_option()将打印出设置的描述及其当前值。
pd.describe_option()
还可以打印特定的选项,例如,行显示。
# 具体的搜索
pd.describe_option('rows')
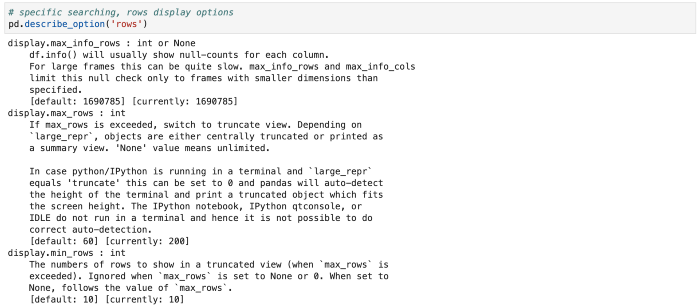
最后,我们还可以直接全部重置。
pd.reset_option('all')
以上就是8个常用set_option的使用,下面进行了汇总,方便大家粘贴使用。
pd.set_option('display.max_rows',xxx) # 最大行数
pd.set_option('display.min_rows',xxx) # 最小显示行数
pd.set_option('display.max_columns',xxx) # 最大显示列数
pd.set_option ('display.max_colwidth',xxx) #最大列字符数
pd.set_option( 'display.precision',2) # 浮点型精度
pd.set_option('display.float_format','{:,}'.format) #逗号分隔数字
pd.set_option('display.float_format', '{:,.2f}'.format) #设置浮点精度
pd.set_option('display.float_format', '{:.2f}%'.format) #百分号格式化
pd.set_option('plotting.backend', 'altair') # 更改后端绘图方式
pd.set_option('display.max_info_columns', 200) # info输出最大列数
pd.set_option('display.max_info_rows', 5) # info计数null时的阈值
pd.describe_option() #展示所有设置和描述
pd.reset_option('all') #重置所有设置选项
-
STM8S103K3 option配置target下面有code和Data,这两个的模式应该怎么选择?2024-04-28 767
-
STM8S配置字节OPTION BYTE2023-10-10 708
-
STM8S的配置字节Option Byte2023-10-07 635
-
Option的基础用法2023-09-20 3847
-
我的keil新建工程后为什么在option中没有c/c++的选项配置呢2022-04-07 5830
-
详解tcpdump命令的六个常用选项2022-03-16 3645
-
IO口配置常用的8个寄存器 1.62021-11-29 2695
-
常用的一些Linux内核配置选项有哪些?2021-07-22 1387
-
Capital功能选项Option的实际设置实例2021-01-12 1238
-
MDK-ARM工程中各目标(Targets)之间选项(Option)配置有什么区别 ?2020-03-14 7404
-
IAR中IDE Options 的Project配置选项2020-03-07 5249
-
STM8S BLDC电机第六章工程的stm8选项字节配置2018-03-05 1265
-
关于stm8,option byte的问题。2016-12-16 3216
-
ad使用中的常用选项2016-01-21 542
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

