

EAST模型结构
描述
EAST模型
EAST( An Efficient and Accurate Scene Text Detector)是标题的英文首字母缩写,模型出自旷视科技。相比其他几种场景文字检测模型,表现开挂。在ICDAR 2015数据集上表现优异,见下图:

可以看到红色点标记EAST模型的速度与性能超过之前的模型。EAST模型是一个全卷积神经网络(FCN)它会预测每个像素是否是TEXT或者WORDS,对比之前的一些卷积神经网络剔除了区域候选、文本格式化等操作,简洁明了,后续操作只需要根据阈值进行过滤以及通过非最大抑制(NMS)得到最终的文本区域即可,EAST模型结构如下:
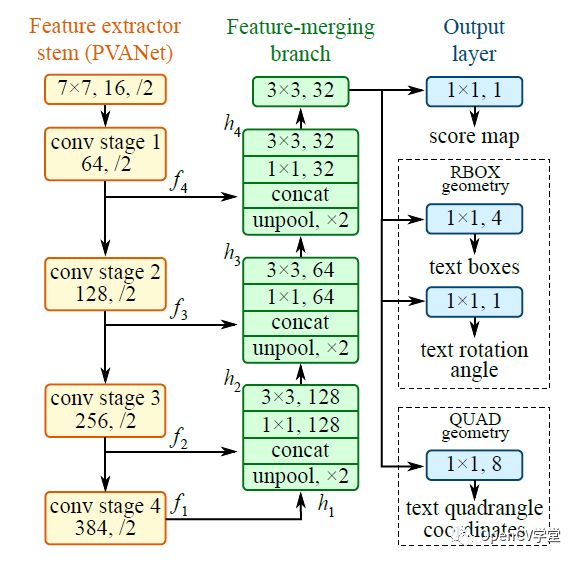
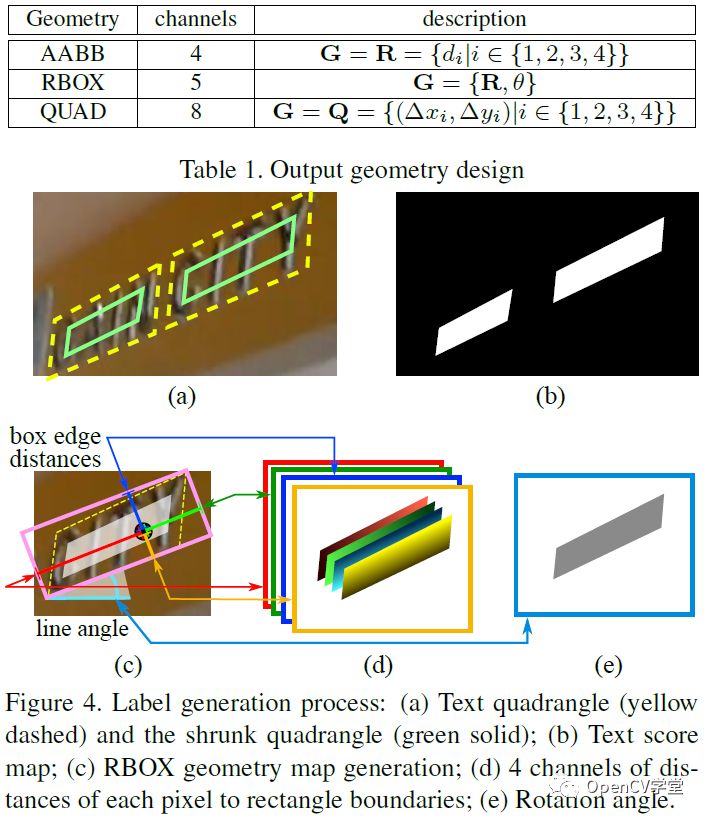
其中stem网络是一个基于ImageNet预训练的卷积神经网络(CNN)比如VGG-16,剩下的分别是通过卷积不断降低尺度大小,再通过不同层的反卷积进行合并,这个有点像UNet图像分割网络,最后输出层,通过1x1的卷积分别得到score、RBOX、QUAD,输出参数的解释如下:
OpenCV DNN使用
OpenCV4.0 的深度神经网络(DNN)模块能力大大加强,不仅支持常见的图像分类、对象检测、图像分割网络,还实现了自定义层与通用网络模型支持,同时提供了非最大抑制相关API支持,使用起来十分方便。EAST模型的tensorflow代码实现参见如下:
https://github.com/argman/EAST
下载预训练模型,生成pb文件,OpenCV DNN中导入tensorflow模型的API如下:
Net cv::readNet( const String & model, const String & config = "", const String & framework = "" ) model表示模型路径 config表示配置文件,缺省为空 framework表示框架,缺省为空,根据导入模型自己决定
OpenCV DNN已经实现非最大抑制算法,支持的API调用如下:
void cv::NMSBoxes( const std::vector< Rect > & bboxes, const std::vector< float > & scores, const float score_threshold, const float nms_threshold, std::vector< int > & indices, const float eta = 1.f, const int top_k = 0 ) Bboxes表示输入的boxes Score表示每个box得分 score_threshold表示score的阈值 nms_threshold表示非最大抑制阈值 indices表示输出的结果,是每个box的索引index数组 eta表示自适应的阈值nms阈值方式 top_k表示前多少个,为0表示忽略
代码实现
首先加载模型,然后打开摄像头,完成实时检测,C++的代码如下:
#include> #include using namespace cv; using namespace cv::dnn; void decode(const Mat& scores, const Mat& geometry, float scoreThresh, std::vector & detections, std::vector & confidences); int main(int argc, char** argv) { float confThreshold = 0.5; float nmsThreshold = 0.4; int inpWidth = 320; int inpHeight = 320; String model = "D:/python/cv_demo/ocr_demo/frozen_east_text_detection.pb"; // Load network. Net net = readNet(model); // Open a camera stream. VideoCapture cap(0); static const std::string kWinName = "EAST: An Efficient and Accurate Scene Text Detector"; namedWindow(kWinName, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); std::vector outs; std::vector outNames(2); outNames[0] = "feature_fusion/Conv_7/Sigmoid"; outNames[1] = "feature_fusion/concat_3"; Mat frame, blob; while (waitKey(1) < 0) { cap >> frame; if (frame.empty()) { waitKey(); break; } blobFromImage(frame, blob, 1.0, Size(inpWidth, inpHeight), Scalar(123.68, 116.78, 103.94), true, false); net.setInput(blob); net.forward(outs, outNames); Mat scores = outs[0]; Mat geometry = outs[1]; // Decode predicted bounding boxes. std::vector boxes; std::vector confidences; decode(scores, geometry, confThreshold, boxes, confidences); // Apply non-maximum suppression procedure. std::vector indices; NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, confThreshold, nmsThreshold, indices); // Render detections. Point2f ratio((float)frame.cols / inpWidth, (float)frame.rows / inpHeight); for (size_t i = 0; i < indices.size(); ++i) { RotatedRect& box = boxes[indices[i]]; Point2f vertices[4]; box.points(vertices); for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) { vertices[j].x *= ratio.x; vertices[j].y *= ratio.y; } for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) line(frame, vertices[j], vertices[(j + 1) % 4], Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1); } // Put efficiency information. std::vector layersTimes; double freq = getTickFrequency() / 1000; double t = net.getPerfProfile(layersTimes) / freq; std::string label = format("Inference time: %.2f ms", t); putText(frame, label, Point(0, 15), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, Scalar(0, 255, 0)); imshow(kWinName, frame); } return 0; } void decode(const Mat& scores, const Mat& geometry, float scoreThresh, std::vector & detections, std::vector & confidences) { detections.clear(); CV_Assert(scores.dims == 4); CV_Assert(geometry.dims == 4); CV_Assert(scores.size[0] == 1); CV_Assert(geometry.size[0] == 1); CV_Assert(scores.size[1] == 1); CV_Assert(geometry.size[1] == 5); CV_Assert(scores.size[2] == geometry.size[2]); CV_Assert(scores.size[3] == geometry.size[3]); const int height = scores.size[2]; const int width = scores.size[3]; for (int y = 0; y < height; ++y) { const float* scoresData = scores.ptr (0, 0, y); const float* x0_data = geometry.ptr (0, 0, y); const float* x1_data = geometry.ptr (0, 1, y); const float* x2_data = geometry.ptr (0, 2, y); const float* x3_data = geometry.ptr (0, 3, y); const float* anglesData = geometry.ptr (0, 4, y); for (int x = 0; x < width; ++x) { float score = scoresData[x]; if (score < scoreThresh) continue; // Decode a prediction. // Multiple by 4 because feature maps are 4 time less than input image. float offsetX = x * 4.0f, offsetY = y * 4.0f; float angle = anglesData[x]; float cosA = std::cos(angle); float sinA = std::sin(angle); float h = x0_data[x] + x2_data[x]; float w = x1_data[x] + x3_data[x]; Point2f offset(offsetX + cosA * x1_data[x] + sinA * x2_data[x], offsetY - sinA * x1_data[x] + cosA * x2_data[x]); Point2f p1 = Point2f(-sinA * h, -cosA * h) + offset; Point2f p3 = Point2f(-cosA * w, sinA * w) + offset; RotatedRect r(0.5f * (p1 + p3), Size2f(w, h), -angle * 180.0f / (float)CV_PI); detections.push_back(r); confidences.push_back(score); } } }
python的代码实现如下:
if __name__ == "__main__":
text_detector = TextAreaDetector("D:/python/cv_demo/ocr_demo/frozen_east_text_detection.pb")
frame = cv.imread("D:/txt.png")
start = time.time()
text_detector.detect(frame)
end = time.time()
print("[INFO] text detection took {:.4f} seconds".format(end - start))
# show the output image
cv.imshow("Text Detection", frame)
cv.waitKey(0)
cap = cv.VideoCapture(0)
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if ret is not True:
break
text_detector.detect(frame)
cv.imshow("east text detect demo", frame)
c = cv.waitKey(5)
if c == 27:
break
cv.destroyAllWindows()
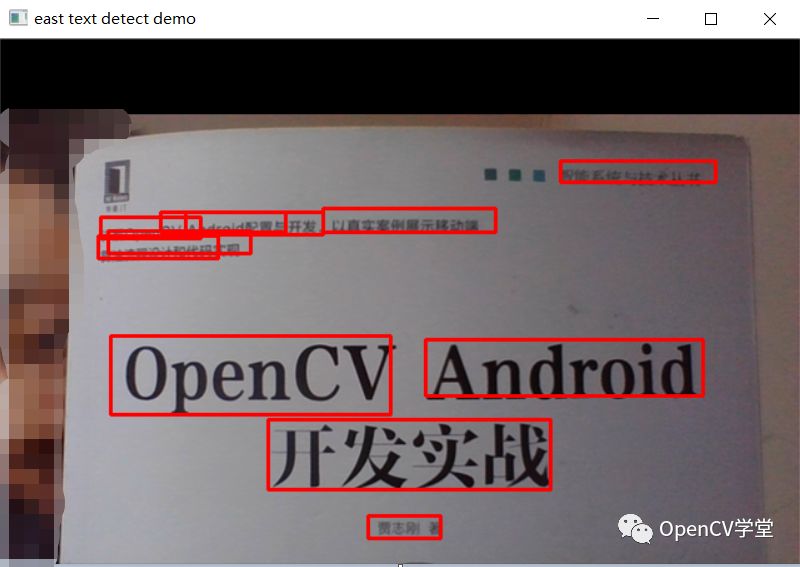
运行结果
图书封面 – 图像检测
视频场景中文字检测
手写文本检测
-
PROFIBUS协议结构及协议模型与ISO/OSI协议模型的关系2009-11-17 6713
-
如何对双母线结构模型进行仿真2021-09-24 2379
-
EAST技术诊断系统监控子系统分析和设计2009-04-21 725
-
DCS 在EAST 低温系统中的设计与应用The Desig2009-05-25 545
-
小型分布式定时触发系统在EAST中的应用2009-07-07 619
-
EAST低温历史数据可视化软件设计与实现2010-02-22 1282
-
基于PLC与WINCC的EAST快控电源远控网络设计2010-07-20 676
-
UMTS的物理结构模型2009-09-18 1735
-
MPOA的模型结构,MPOA的模型结构是什么?2010-04-07 675
-
EAST快控电源远程监控系统的实现_管子平2017-03-19 851
-
基于富因特网应用的EAST数据采集管理系统_杨育2017-03-17 776
-
利用符合AUTOSAR的架构描述语言EAST-ADL2开发汽车产品2017-11-30 990
-
基于AUTOSAR的架构描述语言EAST-ADL2开发汽车产品2017-12-01 1060
-
golang的调度模型-GPM 模型的源码结构2021-07-06 2820
-
手工优化ncnn模型结构2022-01-26 471
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

