

怎么查看嵌入式Linux开发中各个线程的运行情况
嵌入式技术
1412人已加入
描述
在嵌入式Linux开发中,有时候为了定位问题,需要查看某个进程的各个线程的运行情况。
例子
multi_thread.c:
左右滑动查看全部代码>>>
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include
我们可以通过top命令来查看,具体做法就是要在top输出中开启线程查看,请调用top命令的“-H”选项,该选项会列出所有Linux线程。
这里我们指定查看multi_thread进程的各线程运行情况,命令:
top -H -p `pidof multi_thread`
注意:这里的 `号并不是单引号!!!
这个符号在键盘上感叹号!键的左边。
我们先运行程序,再使用top命令查看,比如:
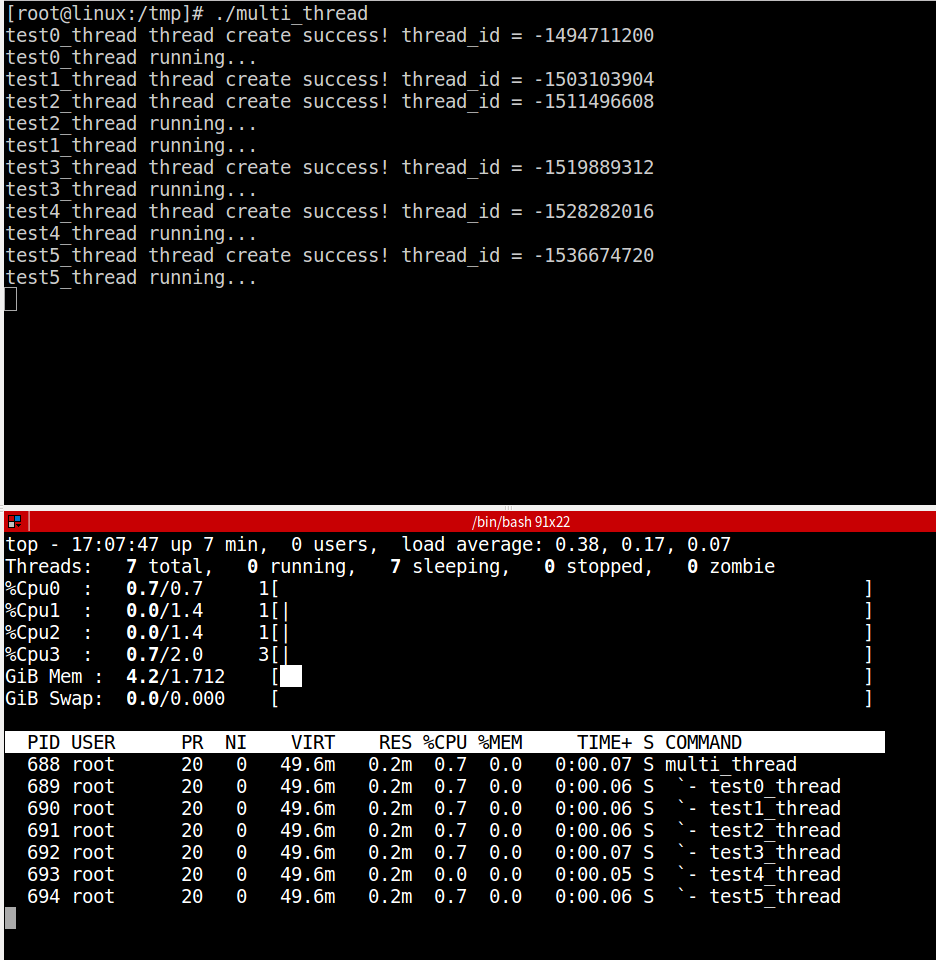
注意:我们创建线程的时候需要使用 pthread_setname_np 函数设置线程的名字,否则top -H显示不出来具体的线程。
假如我们把上例中的pthread_setname_np屏蔽掉,结果如下:
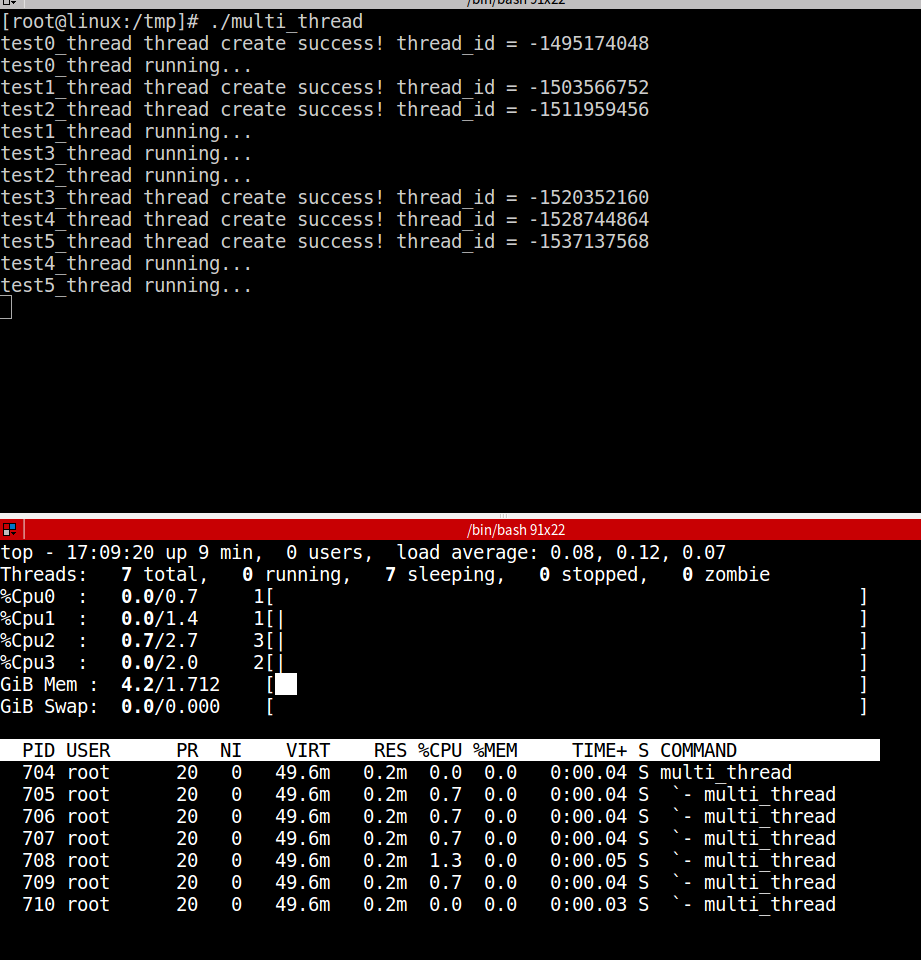
可见,不调用pthread_setname_np设置线程名称的话,top -H查看得到的各线程名称就是进程名。
以上就是本次的分享,期待大家的三连支持!
审核编辑:汤梓红
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
-
Linux中如何查看系统运行信息2022-11-25 4368
-
嵌入式Linux多线程编程2021-11-05 1061
-
嵌入式Linux开发流程中的各个步骤2021-11-04 992
-
嵌入式Linux路线2021-11-02 1045
-
嵌入式Linux下线程CPU消耗查看2021-11-01 592
-
linux的线程状态怎么查看2019-07-22 1623
-
嵌入式LINUX开发基础知识2011-07-31 1085
-
嵌入式Linux系统开发基础2008-09-10 689
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

