

图像清晰度的评价方法
描述
图像清晰度是衡量图像质量的一个重要指标,对于相机来说,其一般工作在无参考图像的模式下,所以在拍照时需要进行对焦的控制。对焦不准确,图像就会变得比较模糊不清晰。相机对焦时通过一些清晰度评判指标,控制镜头与CCD的距离,使图像成像清晰。一般对焦时有一个调整的过程,图像从模糊到清晰,再到模糊,确定清晰度峰值,再最终到达最清晰的位置。
常见的图像清晰度评价一般都是基于梯度的方法,本文将介绍五种简单的评价指标,分别是Brenner梯度法、Tenegrad梯度法、laplace梯度法、方差法、能量梯度法。
Brenner梯度法:
计算相差两个单元的两个像素点的灰度差:
FBrenner=∑M∑N(f(x+2,y)−f(x,y))2 式中 (f(x+2,y)−f(x,y))2>Threshold算法准确性取决于阈值的选取。
Tenegrad梯度法:
采用sobel算子分别提取水平和竖直方向的梯度: FTenegrad=∑M∑N|G(x,y)| G(x,y)>Threshold
G(x,y)=Gx(x,y)2+Gy(x,y)2
sobel算子模板如下:
Gx=14⎡⎣⎢−1−2−1000121⎤⎦⎥∗I
Gy=14⎡⎣⎢−101−202−101⎤⎦⎥∗I
Laplace梯度法:
laplace梯度函数与Tenegrad基本一致,只需要用Laplace算子替代sobel算子即可:L=16⎡⎣⎢1414204141⎤⎦⎥∗I
方差法:
聚焦清晰的图像比模糊图像有更大的灰度差异,可用方差函数作为评价:Fvariance=∑M∑N(f(x,y)−E2)
式中E为整幅图像的平均灰度值,该函数对噪声敏感。
能量梯度法:
能量梯度函数适合实时评价图像清晰度:
FBrenner=∑M∑N((f(x+1,y)−f(x,y))2+(f(x,y+1)−f(x,y))2)
实例代码:
//方差法 region_to_mean(ImageReduced, Image, ImageMean) convert_image_type(ImageMean, ImageMean, 'real') convert_image_type(Image, Image, 'real') sub_image(Image, ImageMean, ImageSub, 1, 0) mult_image(ImageSub, ImageSub, ImageResult, 1, 0) intensity(ImageResult, ImageResult, Value, Deviation) //拉普拉斯梯度函数 laplace(Image, ImageLaplace4, 'signed', 3, 'n_4') laplace(Image, ImageLaplace8, 'signed', 3, 'n_8') add_image(ImageLaplace4, ImageLaplace4, ImageResult1, 1, 0) add_image(ImageLaplace4, ImageResult1, ImageResult1, 1, 0) add_image(ImageLaplace8, ImageResult1, ImageResult1, 1, 0) mult_image(ImageResult1, ImageResult1, ImageResult, 1, 0) intensity(ImageResult, ImageResult, Value, Deviation) //能量梯度函数 crop_part(Image, ImagePart00, 0, 0, Width-1, Height-1) crop_part(Image, ImagePart01, 0, 1, Width-1, Height-1) crop_part(Image, ImagePart10, 1, 0, Width-1, Height-1) convert_image_type(ImagePart00, ImagePart00, 'real') convert_image_type(ImagePart10, ImagePart10, 'real') convert_image_type(ImagePart01, ImagePart01, 'real') sub_image(ImagePart10, ImagePart00, ImageSub1, 1, 0) mult_image(ImageSub1, ImageSub1, ImageResult1, 1, 0) sub_image(ImagePart01, ImagePart00, ImageSub2, 1, 0) mult_image(ImageSub2, ImageSub2, ImageResult2, 1, 0) add_image(ImageResult1, ImageResult2, ImageResult, 1, 0) intensity(ImageResult, ImageResult, Value, Deviation) //Brenner梯度法 crop_part(Image, ImagePart00, 0, 0, Width, Height-2) convert_image_type(ImagePart00, ImagePart00, 'real') crop_part(Image, ImagePart20, 2, 0, Width, Height-2) convert_image_type(ImagePart20, ImagePart20, 'real') sub_image(ImagePart20, ImagePart00, ImageSub, 1, 0) mult_image(ImageSub, ImageSub, ImageResult, 1, 0) intensity(ImageResult, ImageResult, Value, Deviation) //Tenegrad梯度法 sobel_amp(Image, EdgeAmplitude, 'sum_sqrt', 3) min_max_gray(EdgeAmplitude, EdgeAmplitude, 0, Min, Max, Range) threshold(EdgeAmplitude, Region1, 20, 255) region_to_bin(Region1, BinImage, 1, 0, Width, Height) mult_image(EdgeAmplitude, BinImage, ImageResult4, 1, 0) mult_image(ImageResult4, ImageResult4, ImageResult, 1, 0) intensity(ImageResult, ImageResult, Value, Deviation)
结果分析:
处理图像为一组对焦从模糊到清晰再到模糊的标定板图像,如下为其中三幅图像:

中间为最清晰的图像。
采用五种评价函数,对一百多幅图像进行计算,并将结果进行归一化,得到如图所示结果:
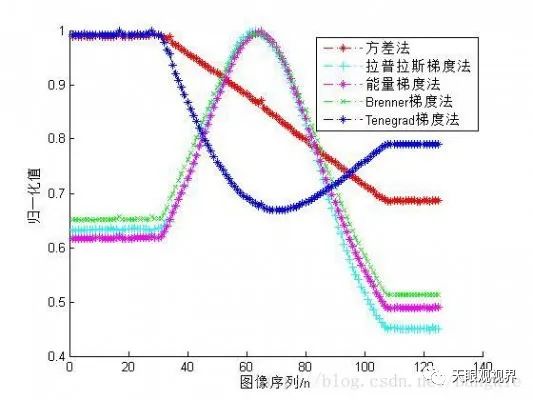
一个好的评价函数需要具有单峰性,无偏性,灵敏性,在本实例中,采用Laplace、能量梯度和Brenner梯度法较好,而方差法效果较差,Tenegrad梯度法反向了。
审核编辑:汤梓红
-
如何提高uvc相机的清晰度?2025-04-28 268
-
labview图像清晰度评价怎么做?自动聚焦怎样实现?2016-09-03 7894
-
高清晰度电视广播概述2009-08-01 768
-
等离子数字电视动态图像清晰度测量方法 CVIA–PDP01-2009-05-24 1699
-
OmniVision公司推出给手机带来高清晰度视频的图像传感2009-11-04 1575
-
什么是液晶电视的动态清晰度/分辨率2010-03-27 2617
-
基于小波频带划分及HVS特性的图像清晰度评价2012-06-04 1095
-
一种结合点锐度和平方梯度的图像清晰度评价方法2017-11-01 1100
-
基于四元数小波变换QWT的图像清晰度评价方法2017-12-15 1089
-
OpenCV 图像清晰度评价(相机自动对焦)2018-01-17 16935
-
Zyla具有突破精度和清晰度的动态图像单元的sCMOS相机介绍2019-05-14 1458
-
常见的图像清晰度评价方法2022-10-10 11400
-
红外热成像的清晰度详解2023-08-11 2752
-
影响LED透明屏清晰度的因素有哪些?怎样提高LED透明屏的清晰度?2023-12-11 1642
-
led屏幕清晰度级别2024-10-09 7263
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

