

整理一些实用的Linux Shell脚本案例
电子说
描述
今天给大家整理一些实用的 Linux Shell 脚本案例
希望可以帮到大家,让大家更熟悉 shell 编程
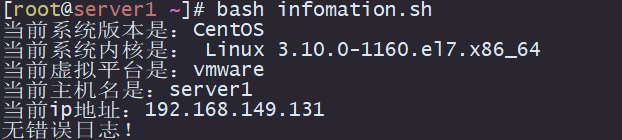
1.显示系统一些基本信息
显示信息如下:
系统版本
系统内核
虚拟平台
主机名
ip地址
开机信息有没有报错,有的话输出到屏幕
可以将该脚本加入到开机自启动里面,这样开机就会输出基本信息
#!/bin/bash
info(){
system=$(hostnamectl | grep System | awk '{print $3}')
kernel_release=$(hostnamectl | grep Kernel | awk -F : '{print $2}')
Virtualization=$(hostnamectl | grep Virtualization | awk '{print $2}')
server_name=$(hostname)
ipaddr=$(hostname -I)
echo "当前系统版本是:${system}"
echo "当前系统内核是:${kernel_release}"
echo "当前虚拟平台是:${Virtualization}"
echo "当前主机名是:${server_name}"
echo "当前ip地址:${ipaddr}"
}
checkerrror(){
error_info=$(dmesg | grep error)
if [ -e ${error_info} ]
then
echo "无错误日志!"
else
ehcho ${error_info}
fi
}
info
checkerrror
2.关闭系统防火墙和SELinux
检查防火墙状态,是否安装防火墙,如果安装则关闭 关闭SELinux 清空iptables规则
#!/bin/bash
close_firewalld(){
code=$(systemctl status firewalld)
if [ ${code} -eq 0 ]
then
systemctl stop firewalld
fi
}
close_selinux(){
sed -i '/^SELINUX/s/=.*/=disabled/' /etc/selinux/config
setenforce 0
}
close_iptables(){
iptables -F
service iptables save
service iptables restart
}
close_firewalld
close_selinux
close_iptables
3.定时任务计划:归档备份
打包压缩/var/log/nginx目录下所有内容,存放在/tmp/nginx目录里
压缩文件命名规范:yymmdd_logs.tar.gz,只保存七天内的文件,超过七天的文件会进行清理
#!bin/bash
date="$(date +%Y%m%d)"
dir='/tmp/nginx'
backupfile='yymmdd_logs.tar.gz'
#查看/tmp/nginx是否存在,不存在则创建
checkbak(){
if [ ! -e ${dir} ]
then
mkdir ${dir}
fi
}
#压缩文件
backup(){
tar -zcvf ${dir}/${backupfile} /var/log/nginx/ > /dev/null 2>&1
echo "${backupfile} Compressed and packaged successfully !"
}
#清除七天过期文件
cleanup(){
find ${dir} -type f -mtime +7 | xagrs rm -rf
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
echo "Cleaned up successfully!"
else
echo "data cleaning failed error, please pay attention in time"
fi
}
checkbak
backup
cleanup
4.自动批量创建用户
批量创建user1、user2、user3.....
#!/bin/bash
#检查用户是否存在,不存在则创建
checkuser(){
for i in $(seq 1 20)
do
id user${i} > /dev/null 2>&1
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
echo "user${i} 已存在!"
else
useradd user${i} && echo "user${i}" | passwd --stdin user${i} > /dev/null 2>&1
fi
done
}
checkuser
5.通过位置参数创建用户
$1 是执行脚本的第一个参数
$2 是执行脚本的第二个参数
#!/bin/bash
checkuser(){
id ${1} > /dev/null 2>&1
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
echo "${1} 已存在!"
else
useradd "$1"
echo "$2" | passwd ‐‐stdin "$1"
fi
}
6.批量删除用户
批量删除user1...user20
#!/bin/bash
#检查用户是否存在,存在则删除
checkuser(){
for i in $(seq 1 20)
do
id user${i} > /dev/null 2>&1
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
userdel -r user${i}
else
echo "user${i} 不存在!"
fi
done
}
checkuser
7.更新系统时间,并写入硬件时间里
查看是否安装ntpdate工具
创建上海时区文件的软链接
更新时间并写入到硬件时间里
#!/bin/bash
package="ntpdate"
info=$(rpm -q ${package})
check_pkgs(){
if [ ! -e ${info} ]
then
echo "ntpdate already exists!"
else
echo "start installation!"
yum clean all > /dev/null 2>&1
fi
yum update -y && yum install -y ${package} > /dev/null 2>&1
fi
}
modify_time(){
echo "开始修改时间"
rm -rf /etc/localtime && ln -s /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
/usr/sbin/ntpdate cn.pool.ntp.org > /dev/null 2>&1 && hwclock -w
}
check_pkgs
modify_time
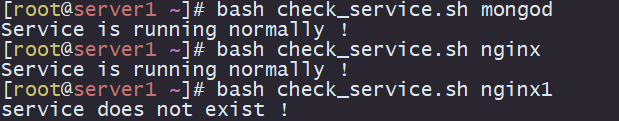
8.检查服务运行状态
检查某一服务是否正常运行,执行脚本的时候第一个参数为服务名
#!/bin/bash
result=$(pidof $1 | wc -l)
echo ${result}
if [ ${result} -eq 0 ]
then
echo "service does not exist !"
else
echo "Service is running normally !"
fi
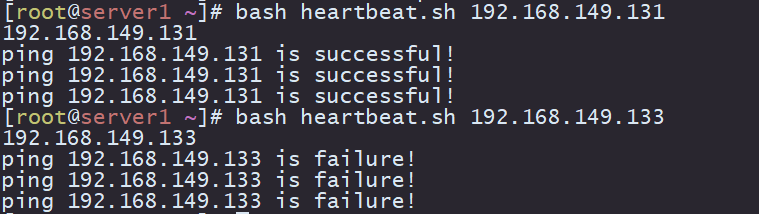
9.对目标主机进行心跳检测
ping目标主机看是否ping得通,三次ping通表示主机正常运行
将目标主机的ip地址作为第一个参数传进去
#!/bin/bash
ipaddr=$1
echo ${ipaddr}
ping_status(){
if ping -c 1 ${ipaddr} > /dev/null 2>&1
then
echo "ping ${ipaddr} is successful!"
continue
fi
}
for i in $(seq 1 3)
do
ping_status
echo "ping ${ipaddr} is failure!"
done
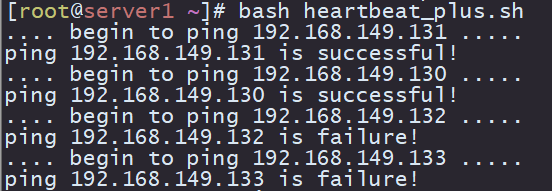
进阶版:对ip地址池里的主机分别进行心跳检测
ipaddr=(192.168.149.131 192.168.149.130 192.168.149.132 192.168.149.133)
for i in ${ipaddr[*]}
do
echo ".... begin to ping ${i} ....."
if ping -c 3 ${i} > /dev/null 2>&1
then
echo "ping ${i} is successful!"
else
echo "ping ${i} is failure!"
fi
done
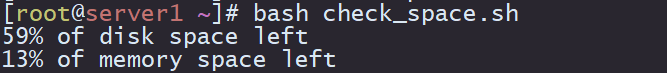
10.系统磁盘内存容量告警
根分区剩余空间小于20%(即使用空间大于80%) 输出告警信息 内存使用空间大于80% 输出告警信息 配合crond每5分钟检查一次
#!/bin/bash
disk_letfspace=$(df -Th | grep -w / | awk '{print$6}' | cut -d % -f 1)
mem_used=$(free -m | grep Mem | awk '{print$3}')
mem_total=$(free -m | grep Mem | awk '{print$2}')
mem_letfspace=$[${mem_used}*100/${mem_total}]
if [ ${disk_letfspace} -gt 80 ]
then
echo "Disk free space is less than 20%!"
else
echo "${disk_letfspace}% of disk space left"
fi
if [ ${mem_letfspace} -gt 80 ]
then
echo "memory space is less than 20%!"
else
echo "${mem_letfspace}% of memory space left"
fi
crontab -l */5 * * * * /root/check_space.sh
审核编辑:刘清
-
如何使用Shell脚本在 Linux 服务器寻找攻击证据2022-10-09 1428
-
一步一步了解并搞懂shell脚本2022-12-06 892
-
Linux Shell脚本入门到实战详解2023-02-17 993
-
Linux shell脚本分享2023-07-18 838
-
Linux中常用的Shell脚本示例2023-09-08 920
-
如何利用Shell脚本掩藏Linux服务器使用痕迹2018-02-13 3801
-
如何创建和执行一个简单的Linux shell脚本2019-11-06 13829
-
Linux shell脚本经验分享2020-04-04 2190
-
Linux系统命令及shell脚本实践指南2021-06-01 996
-
34个Linux Shell脚本汇总2023-01-06 1835
-
Linux命令行与shell脚本编写2023-01-11 615
-
通过Shell脚本掩盖Linux系统上的操作痕迹2023-04-03 959
-
使用Shell脚本掩盖Linux上的操作痕迹2023-05-23 1118
-
Linux Shell脚本经典案例分享2023-06-16 1014
-
Linux从零到精通:最简单的Shell脚本入门教程2024-12-05 2409
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

