

YOLOv5在OpenCV上的推理程序
描述
测试与发现
YOLOv5官方给出的YOLOv5在OpenCV上推理的程序相对来说是比较通俗易懂的,条理清晰,有基本的封装,直接可用!但是我也发现,模型的推理时间跟前后处理的时间相差无几,特别是当视频流有多个检测到的对象时候,整个帧率会有明显下降!官方推荐的参考示例代码链接为:
https://github.com/doleron/yolov5-opencv-cpp-python/blob/main/python/yolo-tiny.py最后发现推理时间没有明显变化,主要是前后处理,有两个函数耗时比较高!从输入图像转换到模型输入数据的函数:
cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(input_image , 1/255.0, (640, 640), swapRB=True)推理之后的重叠目标框非最大抑制函数:
indexes = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, 0.25, 0.45)特别是非最大抑制函数,随着图像中目标数目增多,导致帧率成明显下降趋势!
修改输入转换
cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(input_image , 1/255.0, (640, 640), swapRB=True)
可以通过下面的代码等价替换:
rgb = cv.cvtColor(image, cv.COLOR_BGR2RGB) input_image = cv.resize(src=rgb, dsize=(INPUT_WIDTH, INPUT_HEIGHT)) blob_img = np.float32(input_image) / 255.0 input_x = blob_img.transpose((2, 0, 1)) input_blob = np.expand_dims(input_x, 0)
修改之后测试发现该替代降低了执行时间,说明替代有效!
修改非最大抑制
indexes = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, 0.25, 0.45)
输入的box格式x, y,w,h,我参考了网上的代码,修改实现一个基于并交比最简单的NMS抑制算法,基于矩阵计算,保证不会因为对象变得多了,增加计算耗时,然后把它们封装成一个单独的方法,导入该方法直接替换之前的代码行为:
class_ids, boxes = non_max_suppression_fast(np.asarray(class_ids), np.asarray(boxes), 0.75)
该函数完整的实现代码如下:
import numpy as np
def non_max_suppression_fast(class_ids, boxes, nms_threshold):
# if there are no boxes, return
if len(boxes) == 0:
return [], []
if boxes.dtype.kind == "i":
boxes = boxes.astype("float")
# initialize the list of picked indexes
pick = []
# grab the coordinates of the bounding boxes
x1 = boxes[:,0]
y1 = boxes[:,1]
x2 = boxes[:,2]
y2 = boxes[:,3]
# compute the area of the bounding boxes and sort the bounding
# boxes by the bottom-right y-coordinate of the bounding box
area = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
idxs = np.argsort(y2)
# keep looping while some indexes still remain in the indexes
# list
while len(idxs) > 0:
# grab the last index in the indexes list and add the
# index value to the list of picked indexes
last = len(idxs) - 1
i = idxs[last]
pick.append(i)
# find the largest (x, y) coordinates for the start of
# the bounding box and the smallest (x, y) coordinates
# for the end of the bounding box
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[idxs[:last]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[idxs[:last]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[idxs[:last]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[idxs[:last]])
# compute the width and height of the bounding box
w = np.maximum(0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
# compute the ratio of overlap
overlap = (w * h) / area[idxs[:last]]
# delete all indexes from the index list that have
idxs = np.delete(idxs, np.concatenate(([last],
np.where(overlap > nms_threshold)[0])))
# return only the bounding boxes that were picked using the
# integer data type
return class_ids[pick], boxes[pick].astype("int")
if __name__ == "__main__":
boxes = []
boxes.append((163, 0, 27+163, 41))
boxes.append((164, 0, 28+164, 43))
boxes.append((165, 0, 29+165, 42))
res = non_max_suppression_fast(None, np.asarray(boxes), 0.25)
print(res)
对比测试
两处都修改完成之后,其它输入条件与代码不变,硬件相同条件下对比测试效果如下:修改之前 Python版本OpenCV与OpenVINO上推理速度:
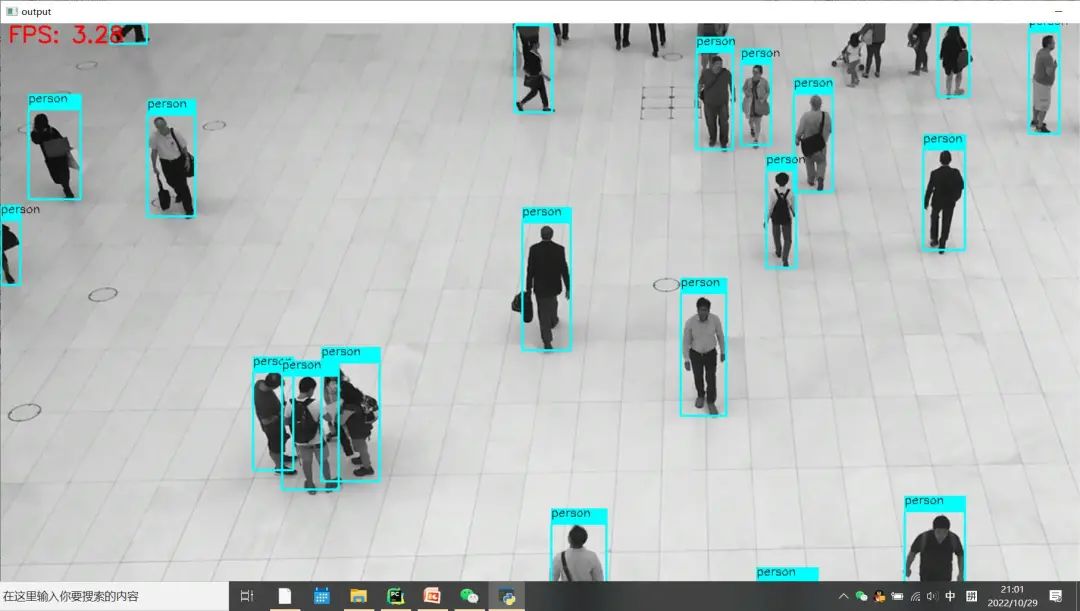
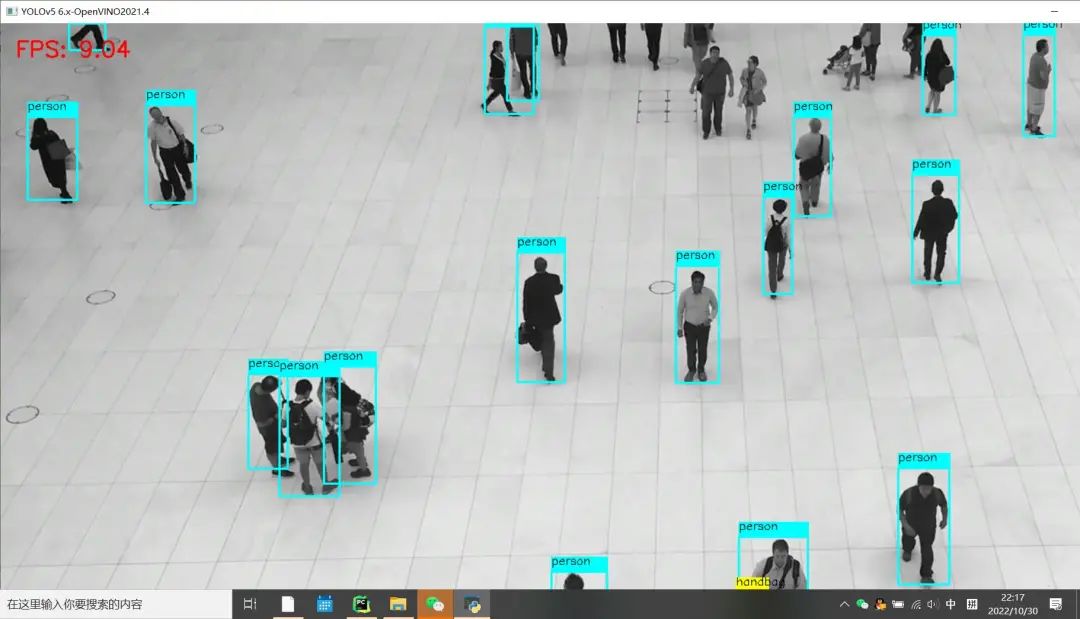
修改之后 Python版本OpenCV与OpenVINO上推理速度:
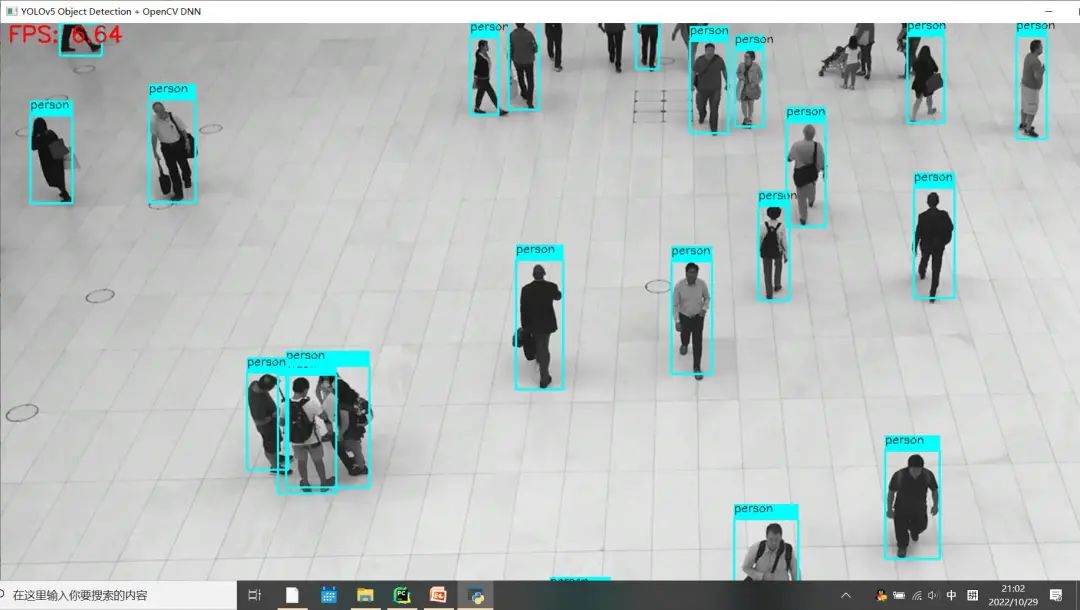
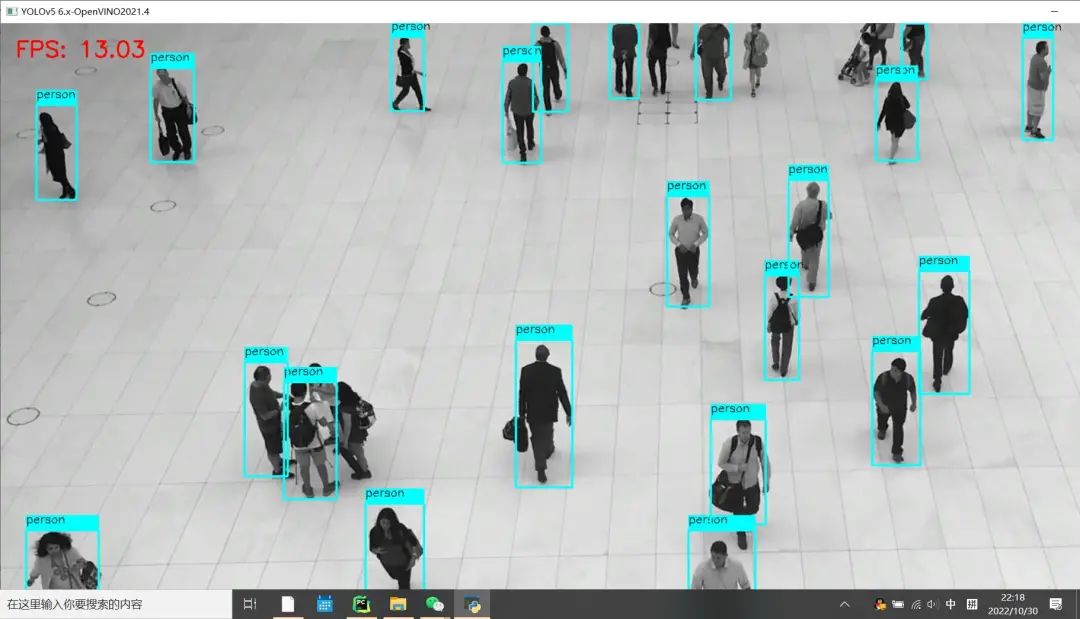
可以看到FPS较之前有明显的提升!
审核编辑:彭静
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
-
在Jetson Nano上使用TensorRT C++实现YOLOv5模型推理2022-11-17 5605
-
【YOLOv5】LabVIEW+YOLOv5快速实现实时物体识别(Object Detection)含源码2023-03-13 3158
-
Yolov5算法解读2023-05-17 13886
-
【YOLOv5】LabVIEW+TensorRT的yolov5部署实战(含源码)2023-08-21 2090
-
在C++中使用OpenVINO工具包部署YOLOv5-Seg模型2023-12-21 3830
-
在RK3568教学实验箱上实现基于YOLOV5的算法物体识别案例详解2024-12-03 2036
-
怎样使用PyTorch Hub去加载YOLOv5模型2022-07-22 3446
-
OpenCV C++程序编译与演示2022-11-10 1722
-
使用Yolov5 - i.MX8MP进行NPU错误检测是什么原因?2023-03-31 879
-
yolov5模型onnx转bmodel无法识别出结果如何解决?2023-09-15 713
-
使用旭日X3派的BPU部署Yolov52023-04-26 1718
-
yolov5和YOLOX正负样本分配策略2023-08-14 3908
-
OpenCV4.8+YOLOv8对象检测C++推理演示2023-09-27 2396
-
yolov5训练部署全链路教程2025-07-25 1495
-
基于瑞芯微RK3576的 yolov5训练部署教程2025-09-11 2528
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

