

使用matlab产生采样率为44.1khz的1khz的sin波
描述
1 信号的基本概念
信号是表示消息的物理量,如电信号可以通过幅度、频率、相位的变化来表示不同的消息。这种电信号有模拟信号和数字信号两类。
信号是运载消息的工具,是消息的载体。从广义上讲,它包含光信号、声信号和电信号等。按照实际用途区分,信号包括电视信号、广播信号、雷达信号,通信信号等;按照所具有的时间特性区分,则有确定性信号和随机性信号等。
模拟信号是指信号波形模拟着信息的变化而变化,其主要特征是幅度是连续的,可取无限多个值;而在时间上则可连续,也可不连续。
数字信号是指不仅在时间上是离散的,而且在幅度上也是离散的,只能取有限个数值的信号。如电报信号,脉冲编码调制(PCM,Pulse Code Modulation)信号等都属于数字信号。二进制信号就是一种数字信号,它是由“1”和“0”这两位数字的不同的组合来表示不同的信息。
2 matlab产生sin波
使用matlab产生采样率为44.1khz的1khz的sin 波,并量化为32bit写成txt文档(用于FPGA数字信号处理仿真源)。
clc
clear all
close all
%set system parameter
fs = 1000; %The frequency of the local oscillator signal
Fs = 44100; %sampling frequency
L = 226760; %The length of the data 1s =22676
N = 32; %Quantitative bits
%Generating an input signal
t =0:1/Fs:(1/Fs)*(L-1); %Generating the time series of sampling frequencies
sc =sin(2*pi*fs*t); %a sinusoidal input signal that produces a random starting phase
sc_32bit =round(sc*(2^(N-1)-1)); %32bit Quantification
sc_nor =sc_32bit/max(abs(sc_32bit));
sound(sc_32bit,Fs);
audiowrite('sin_1khz.wav',sc_32bit,Fs);
fid = fopen('sin.txt','w');
for k= 1:1024
fprintf(fid,'%d ',sc_32bit(k));
end
fclose(fid);
figure,
subplot(221);plot(t(1:1024),sc(1:1024));
xlabel('时间(s)','fontsize',8); ylabel('幅度(v)','fontsize',8);
title('sc','fontsize',8);
subplot(222);plot(t(1:1024),sc_32bit(1:1024));
xlabel('时间(s)','fontsize',8); ylabel('幅度(v)','fontsize',8);
title('sc_32bit','fontsize',8);
subplot(223);plot(t(1:1024),sc_nor(1:1024));
xlabel('时间(s)','fontsize',8); ylabel('幅度(v)','fontsize',8);
title('sc_nor','fontsize',8);
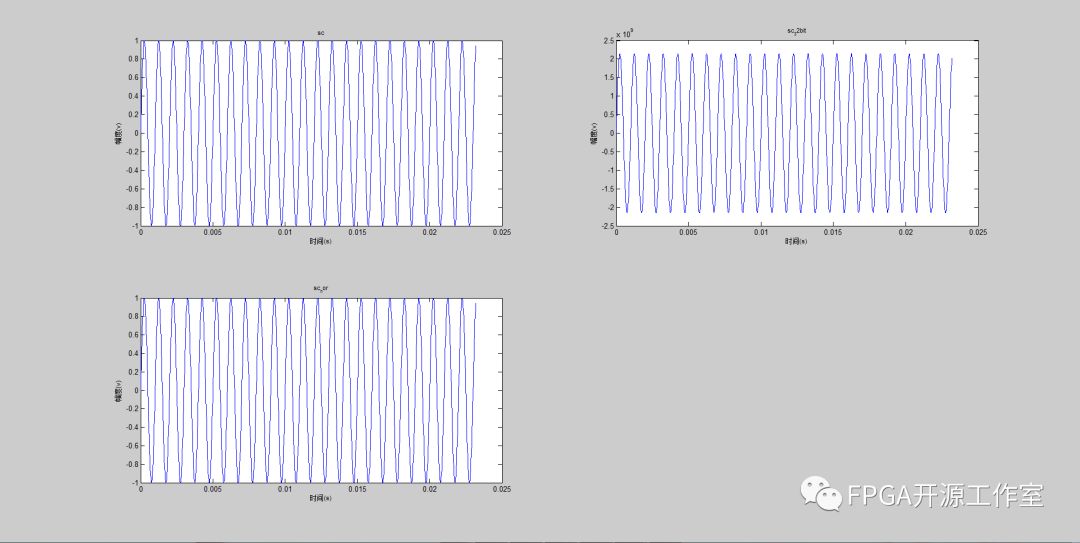
如上图所示,①为量化32bit后生成的txt正玄波数据,用于FPGA数字信号处理仿真源文件。②为生成的音频文件,大家可以使用播放器播放试听。普通人人耳能听到的声音频率范围为20HZ-20KHZ 大家可以产生不同频率的声音试听,也可以产生方波或者三角波。
审核编辑:刘清
-
24bit,192kHz集成数字音频接收接口的异步采样率转换器-MS8422N2025-10-23 235
-
AD7841需要设置为以100KHZ或者1KHZ采样率对连续128点采样时,应该怎么设置采样率?2025-02-07 342
-
请问AFE4400采样率配置成1KHz,LED的时间为250us,能正确采样血氧数据吗?2024-12-20 318
-
请问PPS如何设置采样率?2024-11-01 397
-
请问PCM1754是只支持44.1KHz的采样频率?2024-10-25 209
-
TLV320AIC3100设置DAC采样频率8KHz,但测量结果却是44.1KHz,这是为什么?2024-10-21 614
-
TAS5825M只有48khz及以下采样率可用,为什么?2024-09-30 677
-
常用的语音芯片采样率有哪些呢?2022-12-29 1416
-
AD7841怎么设置为以100KHZ或者1KHZ采样率对连续128点采样2019-05-24 3047
-
如何对dsPIC33E系列器件使用采样率转换库的详细中文资料概述2018-06-08 1484
-
频率范围为1KHZ~100KHZ的自动跟踪90度相位移相器2010-05-11 3802
-
1KHZ正弦波产生电路(文氏电桥振荡器)2009-12-14 7512
-
1KHz的谐波失真测量表2009-09-24 1637
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

