

异质锂合金界面实现稳定的锂电锡箔负极
描述
研究背景
锡基箔材负极具有容量高、成本低、加工容易等优势,是一种理想的高能量密度锂离子电池负极材料。然而,锡箔负极面临着循环过程中活性锂损失多、活性材料/电解液之间副反应严重以及电极电化学反应不均匀等问题,导致了全电池实际能量密度低以及循环寿命差,限制了锡箔负极在锂电池中应用。
因此,亟需开发简单有效的方法解决以上问题,并且开展其在实际全电池中的应用研究。
成果简介
近日,华中科技大学孙永明教授课题组在国际知名储能期刊Energy Storage Materials上发表了题为“Heterogeneous Li-alloy interphase enabling Li compensation during cycling for high energy density batteries”的研究论文。该论文提出通过在锡箔上构建共形的异质锂合金界面(锂化液态合金,Sn/Li-LA),可以有效避免电解液与活性锂锡合金的直接接触,抑制电极循环过程中电解液与活性物质之间的副反应。
同时,该异质合金界面高的离子电导率可以促进界面离子传输,均匀化电化学反应,能有效缓解电极破裂与粉化失效。更为重要的是,该异质锂合金界面具有略高于锂锡合金的脱锂电位,可以在电池长期循环过程中过电位增加时触发锂补偿,延长全电池的循环寿命。
当其与面载量为15.3 mg/cm2的三元(NCM622)正极组装全电池时,电池的容量可达180 mAh/g-1,230次循环容量保持率为96%。而使用纯锡箔负极的对比电池在230次循环后容量仅为22 mAh/g-1。
该工作揭示了箔材电极在高比能锂电池中应用的关键因素,即均匀化电化学反应、界面副反应抑制、界面离子传输及循环过程锂补偿,并提供了一种潜在实际可行的解决方案,为锡箔负极用于高比能锂电池的研究提供了新的思路。
图文解读
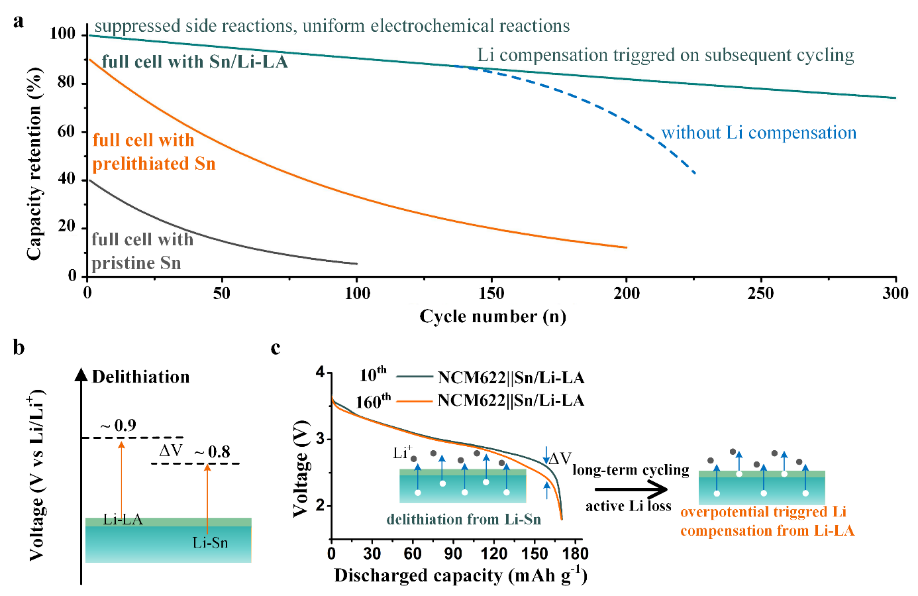
Fig. 1 (a) Schematic of the capacity retention-cycle number curves of full cells paired with pristine Sn foil, prelithiated Sn foil and Sn/Li-LA foil. (b) Design principle of heterogeneous Li-alloy interphase. Delithiation voltage of the Li-LA should be slightly higher than the active Li-Sn alloy. (c) The comparison of voltage-capacity curves of the NCM622||Sn/Li-LA at the 10th and 160th cycles. The insets showed Li compensation from Li-LA would be triggered once the overpotential after long-term cycling increased to ΔV in full cells.
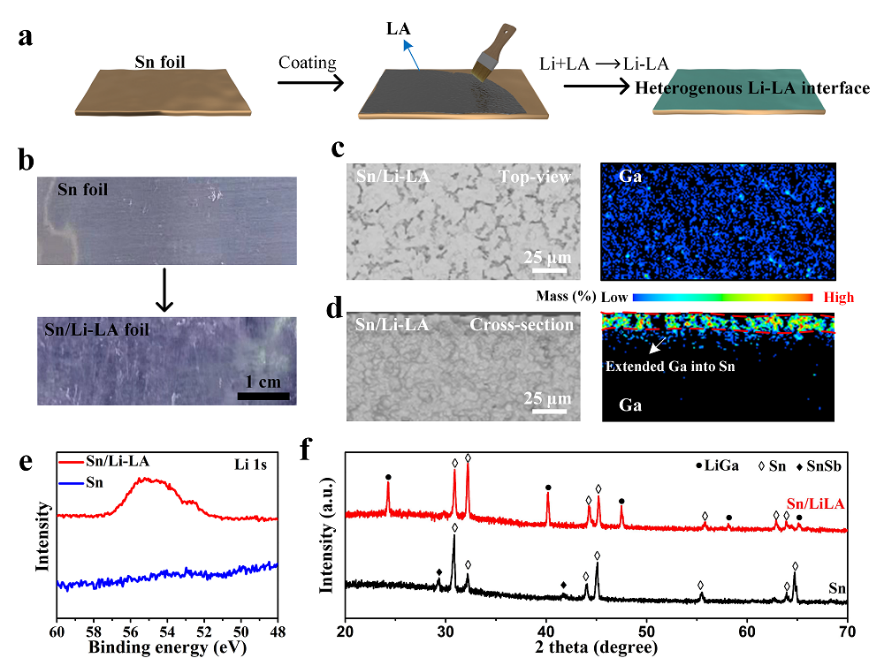
Fig. 2 (a) Schematic of the preparation processes of the Sn/Li-LA foil utilizing the chemical lithiation reaction between the metallic Li foil and LA coating layer. (b) Digital photos of the Sn and Sn/Li-LA foils. (c, d) Top-view and cross-section EPMA images and the corresponding Ga element mapping images of the Sn/Li-LA foil, respectively. (e) High-resolution Li 1s XPS results of the Sn/Li-LA and pristine Sn electrodes. (f) XRD patterns of the Sn (with 5wt% Sb doped) and the Sn/Li-LA foils (Sn: JCPDS#04-0673, SnSb: JCPDS#33-0118, and LiGa: JCPDS #09-0043).
要点:
1. 异质锂合金界面具有略高于锂锡合金的去锂化电位,可以在全电池过电位增加时,触发锂补偿。
2. 均匀的异质锂合金界面可以有效分隔电极活性材料与电解液的直接接触,抑制他们之间的副反应。
3. 异质锂合金界面主要成分为LiGa合金,其高的离子电导率能促进锂离子在界面的快速传输。
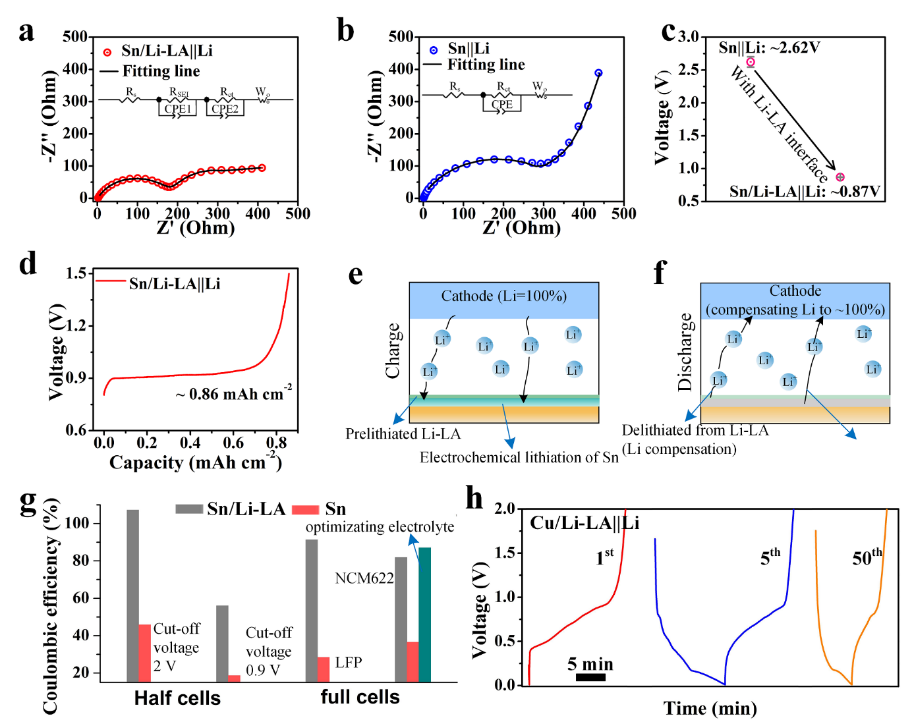
Fig. 3 (a, b) Nyquist plots of the Sn/Li-LA||Li and Sn||Li cells before cycling, respectively. (c) Open-circuit voltages of the Sn/Li-LA||Li and Sn||Li cells. (d) Delithiation capacity of the Sn/Li-LA foil by charging Sn/Li-LA||Li cell to 1.5 V (vs. Li/Li+) at the current density of 0.1 mA cm–2. (e, f) Schematic of the electrochemical behavior of the Sn/Li-LA foil in full cell during the charge /discharge processes. (g) Comparisons of the initial Coulombic efficiency of Sn/Li-LA and Sn electrodes in half and full cells. (h) Charge/discharge curves of the Cu/Li-LA||Li cell for the 1st, 5th and 50th cycles.
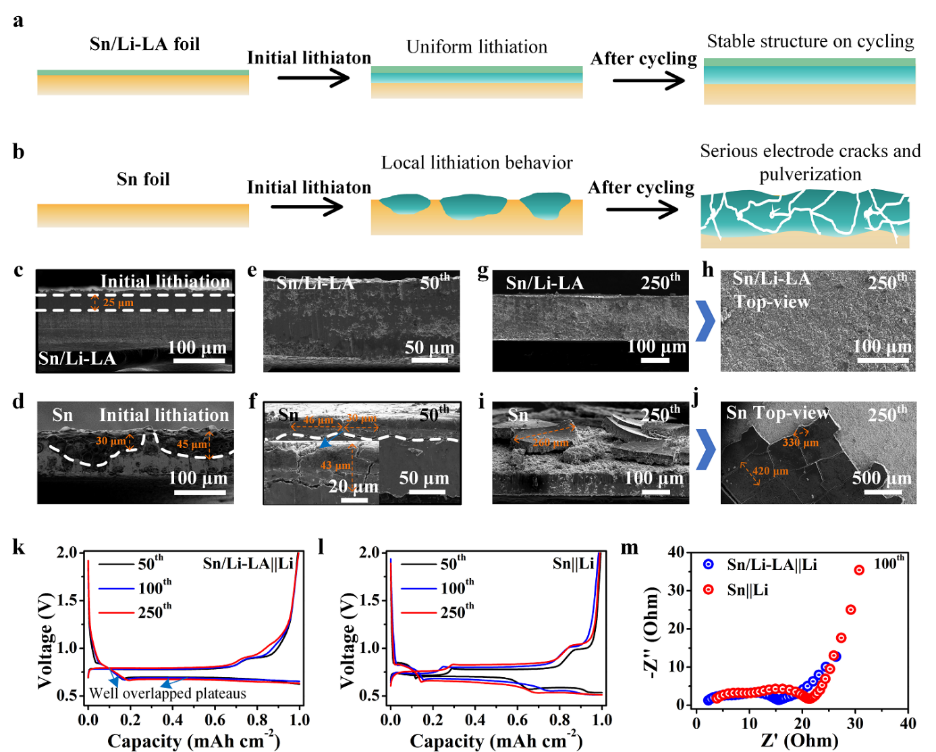
Fig. 4 (a, b) Schematic of the structural evolutions of the Sn/Li-LA and Sn electrodes over lithiation/delithiation cycling. (c, d) Cross-section SEM images of the Sn/Li-LA and Sn electrodes after the initial lithiation at 1 mA cm–2 for 3 hours, respectively. (e, f) Cross-section SEM images of the Sn/Li-LA and Sn electrodes after 50 cycles, respectively. (g, h) Cross-section SEM and top-view images of the Sn/Li-LA electrode after 250 cycles, respectively. (i, j) Cross-section SEM and top-view SEM images of the pristine Sn electrode after 250 cycles. (k, l) Voltage-capacity curves of the Sn/Li-LA and Sn electrodes at the 50th, 100th and 250th cycles, respectively. (m) Nyquist plots of the Sn/Li-LA||Li and Sn||Li cells after 100 cycles.
要点:
1. 异质锂合金界面抑制了初始循环过程中电极界面副反应,减少了首次活性锂损失,与纯锡箔负极相比,首次库伦效率得到了大幅度提升。
2. LiGa合金界面高的离子电导性可以有效均匀化电极的电化学反应,抑制电极的粉化,使Sn/Li-LA电极在循环过程中保持了良好的结构完整性和稳定性。
3. Sn/Li-LA电极充放电曲线在长循环过程中保持高度重合,进一步表明了其在循环过程中能够保持电化学反应均匀性与电极结构稳定性。
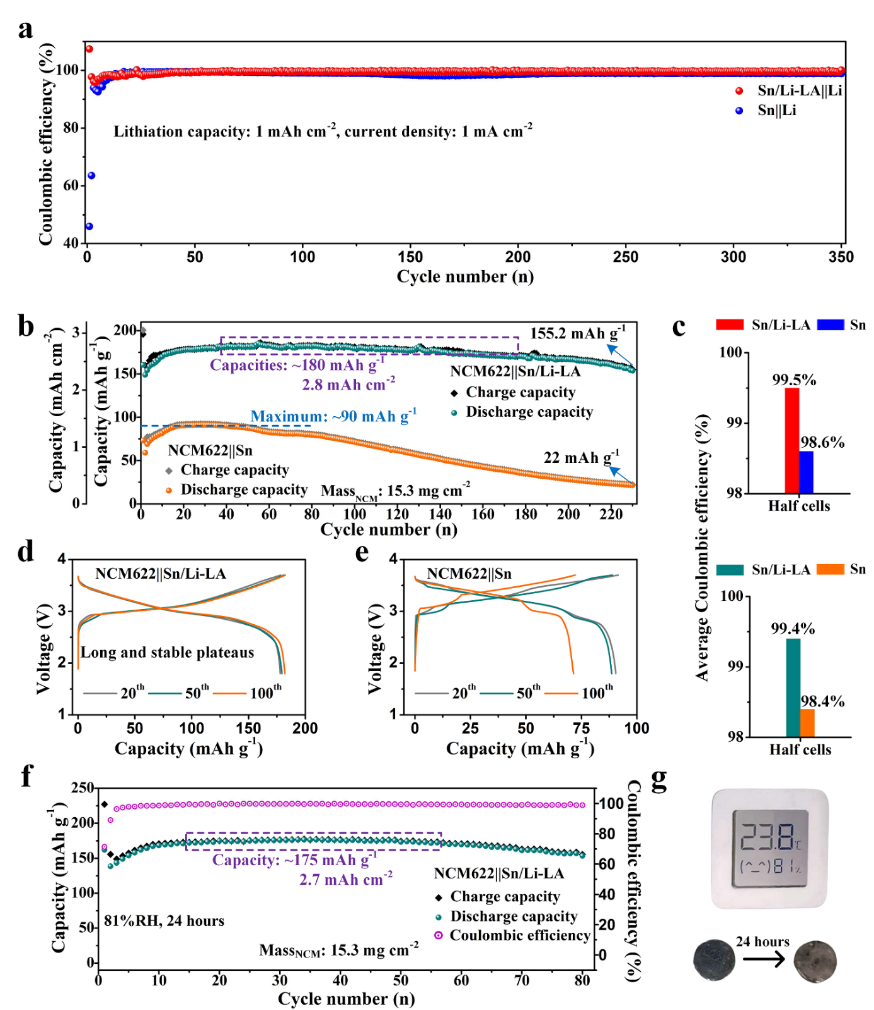
Fig. 5 (a) Coulombic efficiency-cycle number plots of the Sn/Li-LA||Li and Sn||Li cells. (b) Electrochemical performance of NCM622||Sn/Li-LA and NCM622||Sn cells. (c) Average Coulombic efficiency of the Sn/Li-LA and Sn electrodes in half cell corresponding to (a) and full cell corresponding to (b), respectively. (d, e) Charge/discharge curves of NCM622||Sn/Li-LA and NCM622||Sn cells at the 20th, 50th and 100th cycles. (f) Electrochemical cycling of NCM622||Sn/Li-LA full cell using dual-salt electrolyte. The Sn/Li-LA electrode was exposed in ambient condition with the relative humidity of 81% for 24 hours before use. (g) The digital photo of the temperature and humidity indicator to show the test conditions and the corresponding digital photos of the electrodes before and after exposure.
要点:
1. 在使用半电池和全电池进行长循环测试中, Sn/Li-LA电极比纯锡电极展现出了更高的循环过程库伦效率。
2. Sn/Li-LA负极搭配高载量NCM622(15.2 mg/cm2)正极组成的电池可以实现230次稳定循环,其可逆容量相较NCM622||Sn电池显著增加。
3. Sn/Li-LA负极具有极好的空气稳定性,在大于80%的相对湿度下暴露24小时后仍能实现稳定电化学充放电循环。
审核编辑:刘清
-
锂电池与铅酸电池的不同之处2018-03-31 5102
-
锂电池2009-11-09 678
-
锂电池负极材料突破 山东大学攻克金属锂负极应用难题2018-04-20 7487
-
制约锂负极可充性的本质因素有哪些?2018-09-10 5267
-
锂金属负极稳定技术解读2019-02-10 3455
-
锂电池和锂电芯的区别2019-12-02 16858
-
锂电池碳负极界面反应机理2020-10-12 4261
-
磷酸铁锂电池和锂电池的优缺点及应用2021-05-25 27133
-
锂合金的亲锂位点对锂电镀过程的影响2022-10-28 2411
-
金属负极异质界面合金化动力学设计原则2022-11-07 1545
-
工作条件下固态锂金属电池负极界面脱锂空位的形成生长机制2022-12-01 2232
-
解读预锂化对全电池循环稳定性的影响2022-12-19 2131
-
面向高安全锂金属电池的空气稳定负极保护层2023-01-17 1526
-
人工界面修饰助力高性能锂金属电池的最新研究进展与展望!2024-01-02 2541
-
弱溶剂化少层碳界面实现硬碳负极的高首效和稳定循环2024-01-26 3918
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

