

Linux系统中标准输入设备的控制方法
嵌入式技术
描述
大家好,我是ST。
今天主要和大家聊一聊,如何使用标准输入设备,进行控制信息的识别。
第一:按键应用编程方法
编写一个应用程序,获取按键状态,判断按键当前是按下,松开或长按状态。
#以字母A键为例 KEY_A //上报KEY_A事件 SYN_REPORT //同步
如果是按下,则上报KEY_A事件时,value=1;如果是松开,则value=0;如果长按,则value=2。接下来编写按钮应用程序,读取按键状态并将结果打印出来,代码如下所示。
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { struct input_event in_ev = {0}; int fd = -1; int value = -1; /* 校验传参 */ if (2 != argc) { fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s ", argv[0]); exit(-1); } /* 打开文件 */ if (0 > (fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY))) { perror("open error"); exit(-1); } for ( ; ; ) { /* 循环读取数据 */ if (sizeof(struct input_event) != read(fd, &in_ev, sizeof(struct input_event))) { perror("read error"); exit(-1); } if (EV_KEY == in_ev.type) { //按键事件 switch (in_ev.value) { case 0: printf("code<%d>: 松开 ", in_ev.code); break; case 1: printf("code<%d>: 按下 ", in_ev.code); break; case 2: printf("code<%d>: 长按 ", in_ev.code); break; } } } }
在for循环中,调用read()读取输入设备上报的数据,当按键按下或松开(以及长按)动作发生时,read()会读取到输入设备上报的数据,首先判断此次上报的事件是否是按键类事件(EV_KEY),如果是按键类事件,接着根据value值来判断按键当前的状态是松开、按下还是长按。
将编译得到的可执行文件复制到开发板Linux系统的家目录下:
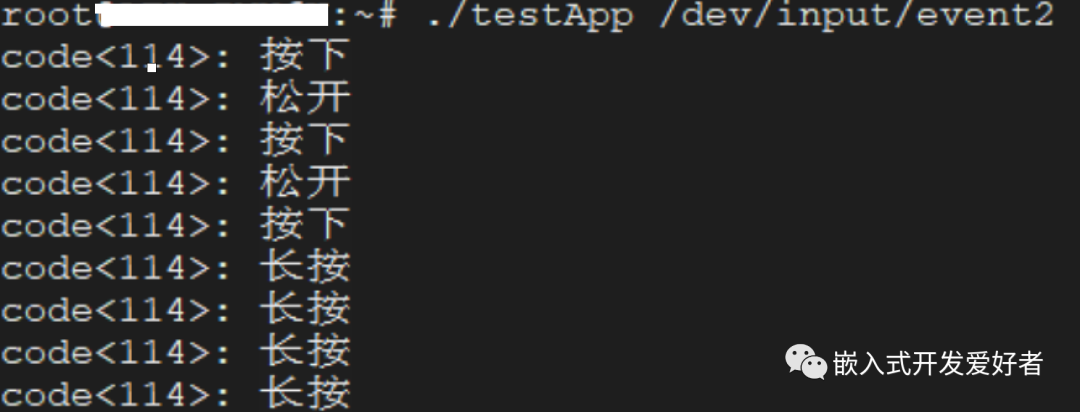
注意:除了能够测试KEY0按键之外,还可以测试键盘上的按键,可以找到一个USB键盘连接到开发板的USB HOST接口上,当键盘插入之后,终端将会打印出相应的驱动加载信息。
驱动加载成功之后,可以查看下该键盘设备对应的设备节点,使用命令"cat /proc/bus/input/devices",在打印信息中找到键盘设备的信息:
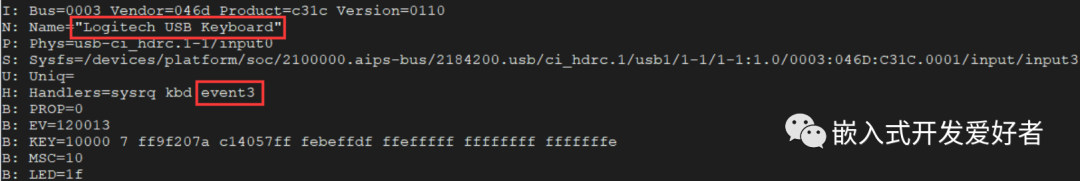
操作的时候,可以对应相应的设备节点/dev/input/event3,运行测试程序并按下、松开键盘上的按键;
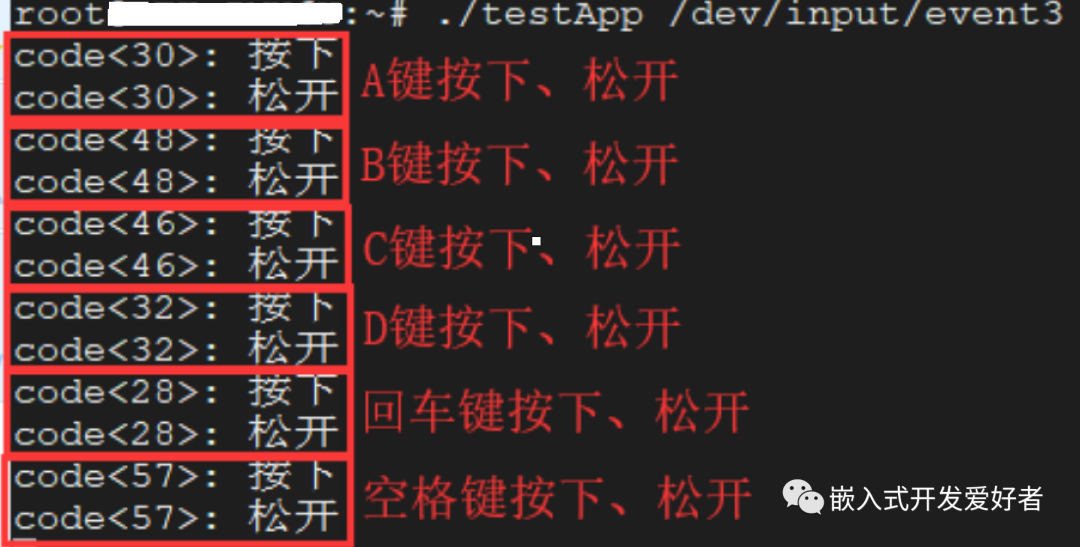
大家可以根据code值查询对应的按键,譬如code=30对应的键盘上的字母A键,code=48对应的字母B键。
第二:单点触摸应用程序实现
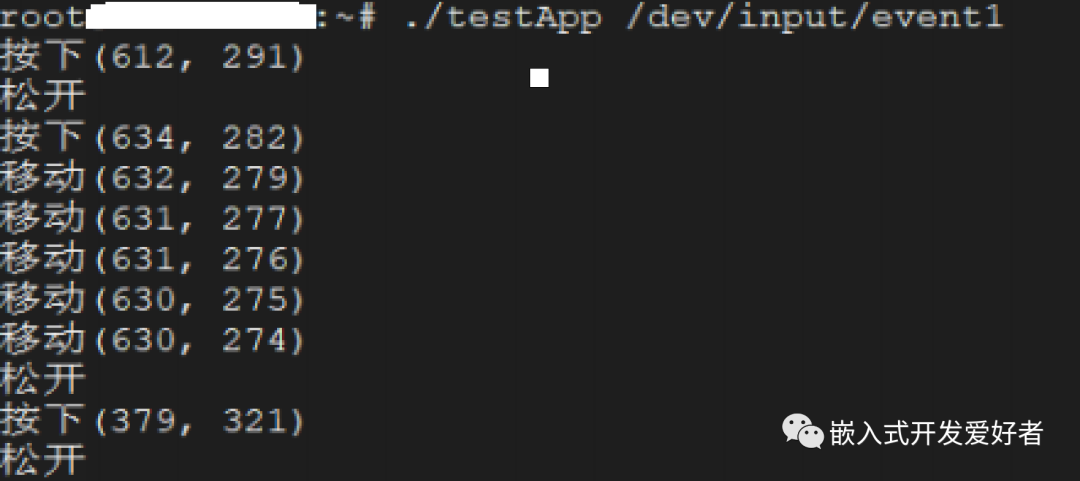
通过上面的详细介绍,大家应该知道如何编写一个触摸屏的应用程序了,接下来我们编写一个单点触摸屏应用程序,获取一个触摸点的坐标信息,并将其打印出来。具体代码实现如下:
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { struct input_event in_ev; int x, y; //触摸点 x 和 y 坐标 int down; //用于记录 BTN_TOUCH 事件的 value,1 表示按下,0 表示松开,-1 表示移动 int valid; //用于记录数据是否有效(我们关注的信息发生更新表示有效,1 表示有效,0 表示无效) int fd = -1; /* 校验传参 */ if (2 != argc) { fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s ", argv[0]); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } /* 打开文件 */ if (0 > (fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY))) { perror("open error"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } x = y = 0; //初始化 x 和 y 坐标值 down = -1; //初始化<移动> valid = 0;//初始化<无效> for ( ; ; ) { /* 循环读取数据 */ if (sizeof(struct input_event) != read(fd, &in_ev, sizeof(struct input_event))) { perror("read error"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } switch(in_ev.type) { case EV_KEY: //按键事件 if (BTN_TOUCH == in_ev.code) { down = in_ev.value; valid = 1; } break; case EV_ABS: //绝对位移事件 switch (in_ev.code) { case ABS_X: //X 坐标 x = in_ev.value; valid = 1; break; case ABS_Y: //Y 坐标 y = in_ev.value; valid = 1; break; } break; case EV_SYN: //同步事件 if (SYN_REPORT == in_ev.code) { if (valid) {//判断是否有效 switch (down) {//判断状态 case 1: printf("按下(%d, %d) ", x, y); break; case 0: printf("松开 "); break; case -1: printf("移动(%d, %d) ", x, y); break; } valid = 0; //重置 valid down = -1; //重置 down } } break; } } }
分析:程序中先传入参数,main()函数中定义了4个变量;
⑴、变量 x 表示触摸点的 X 坐标;
⑵、变量 y 表示触摸点的 Y 坐标;
⑶、变量 down 表示手指状态时候按下、松开还是滑动,down=1 表示手指按下、down=0 表示手指松开、down=-1 表示手指滑动;
⑷、变量 valid 表示数据是否有效,valid=1 表示有效、valid=0 表示无效;有效指的是我们检测的信息发生了更改,譬如程序中只检测了手指的按下、松开动作以及坐标值的变化。接着调用 open()打开触摸屏设备文件得到文件描述符 fd;在 for 循环之前,首先对 x、y、down、valid这 4 个变量进行初始化操作。在 for 循环读取触摸屏上报的数据,将读取到的数据存放在 struct input_event数据结构中。在 switch…case 语句中对读取到的数据进行解析,获取 BTN_TOUCH 事件的 value 数据,判断触摸屏是按下还是松开状态,获取 ABS_X 和 ABS_Y 事件的 value 变量,得到触摸点的 X 轴坐标和 Y 轴坐标。
当上报同步事件时,表示数据已上传完整,接着对得到的数据进行分析,打印坐标信息。
第三:多点触摸应用程序实现
实现了单点触摸应用程序之后,可以再来实现多点触摸屏应用程序该如何实现。
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include /* 用于描述 MT 多点触摸每一个触摸点的信息 */ struct ts_mt { int x; //X 坐标 int y; //Y 坐标 int id; //对应 ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID int valid; //数据有效标志位(=1 表示触摸点信息发生更新) }; /* 一个触摸点的 x 坐标和 y 坐标 */ struct tp_xy { int x; int y; }; static int ts_read(const int fd, const int max_slots, struct ts_mt *mt) { struct input_event in_ev; static int slot = 0;//用于保存上一个 slot static struct tp_xy xy[12] = {0};//用于保存上一次的 x 和 y 坐标值,假设触摸屏支持的最大触摸点数不会超 过 12 int i; /* 对缓冲区初始化操作 */ memset(mt, 0x0, max_slots * sizeof(struct ts_mt)); //清零 for (i = 0; i < max_slots; i++) mt[i].id = -2;//将 id 初始化为-2, id=-1 表示触摸点删除, id>=0 表示创建 for ( ; ; ) { if (sizeof(struct input_event) != read(fd, &in_ev, sizeof(struct input_event))) { perror("read error"); return -1; } switch (in_ev.type) { case EV_ABS: switch (in_ev.code) { case ABS_MT_SLOT: slot = in_ev.value; break; case ABS_MT_POSITION_X: xy[slot].x = in_ev.value; mt[slot].valid = 1; break; case ABS_MT_POSITION_Y: xy[slot].y = in_ev.value; mt[slot].valid = 1; break; case ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID: mt[slot].id = in_ev.value; mt[slot].valid = 1; break; } break; //case EV_KEY://按键事件对单点触摸应用比较有用 // break; case EV_SYN: if (SYN_REPORT == in_ev.code) { for (i = 0; i < max_slots; i++) { mt[i].x = xy[i].x; mt[i].y = xy[i].y; } } return 0; } } } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { struct input_absinfo slot; struct ts_mt *mt = NULL; int max_slots; int fd; int i; /* 参数校验 */ if (2 != argc) { fprintf(stderr,"usage: %s ", argv[0]); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } /* 打开文件 */ fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY); if (0 > fd) { perror("open error"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } /* 获取触摸屏支持的最大触摸点数 */ if (0 > ioctl(fd, EVIOCGABS(ABS_MT_SLOT), &slot)) { perror("ioctl error"); close(fd); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } max_slots = slot.maximum + 1 - slot.minimum; printf("max_slots: %d ", max_slots); /* 申请内存空间并清零 */ mt = calloc(max_slots, sizeof(struct ts_mt)); /* 读数据 */ for ( ; ; ) { if (0 > ts_read(fd, max_slots, mt)) break; for (i = 0; i < max_slots; i++) { if (mt[i].valid) {//判断每一个触摸点信息是否发生更新(关注的信息发生更新) if (0 <= mt[i].id) printf("slot<%d>, 按下(%d, %d) ", i, mt[i].x, mt[i].y); else if (-1 == mt[i].id) printf("slot<%d>, 松开 ", i); else printf("slot<%d>, 移动(%d, %d) ", i, mt[i].x, mt[i].y); } } } /* 关闭设备、退出 */ close(fd); free(mt); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); }
示例代码中申明了 struct ts_mt 数据结构,用于描述多点触摸情况下每一个触摸点的信息。
首先来看下 main()函数,定义了 max_slots 变量,用于指定触摸屏设备的支持的最大触摸点数,通过:
ioctl(fd, EVIOCGABS(ABS_MT_SLOT), &slot)
获取到触摸屏该信息。
接着根据 max_slots 变量的值,为 mt 指针申请内存:
mt = calloc(max_slots, sizeof(struct ts_mt));
for( ; ; )循环中调用 ts_read()函数,该函数是自定义函数,用于获取触摸屏上报的数据,第一个参数表示文件描述符 fd、第二个参数表示触摸屏支持的最大触摸点数、第三个参数则是 struct ts_mt 数组,ts_read()函数会将获取到的数据存放在数组中,mt[0]表示 slot<0>数据、mt[1]表示 slot<1>的数据依次类推!
在内部的 for 循环中,则对获取到的数据进行分析,判断数据是否有效,并根据 id 判断手指的动作,在单点触摸应用程序中,我们是通过 BTN_TOUCH 事件来判断手指的动作;而在多点触摸应用中,我们需要通过 id 来判断多个手指的动作。
关于自定义函数 ts_read()就不再介绍了,代码的注释已经描述很清楚了!
接着编译应用程序,将编译得到的可执行文件拷贝到开发板 Linux 系统的用户家目录下,执行应用程序,接着可以用多个手指触摸触摸屏、松开、滑动等操作。
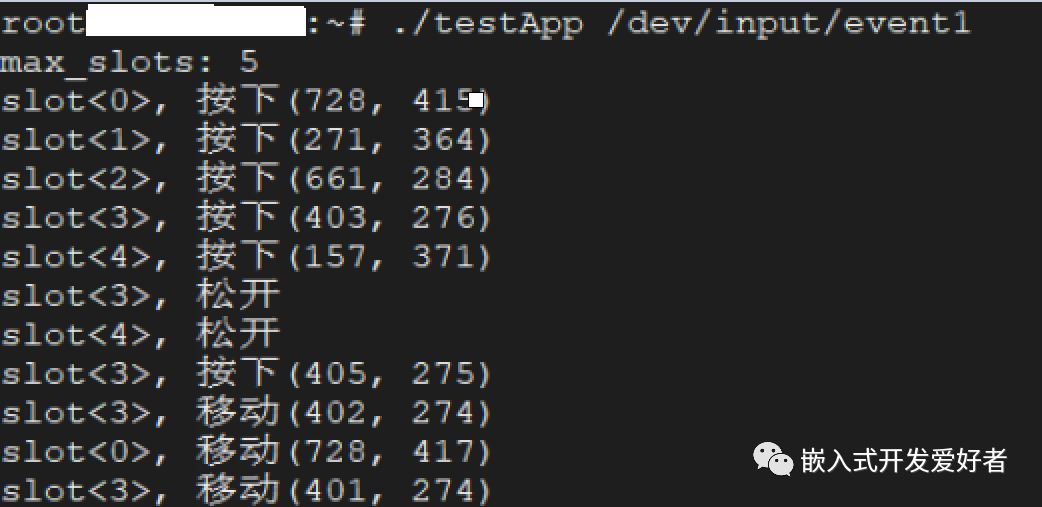
总结:每一个不同的slot表示不同的触摸点,譬如 slot<0>表示触摸点 0、slot<1>表示触摸点 1 以此类推!
-
Linux下输入子系统上报触摸屏坐标2022-09-25 3606
-
家庭影院中标准的THX系统2012-11-26 2610
-
linux中标准的看门狗程序讲解2019-07-08 2670
-
中标麒麟操作系统的串口怎么调试?2019-08-23 8027
-
基于Linux的USB设备驱动方法有什么优点?2019-11-07 2772
-
嵌入式LINUX应用程序开发标准教程2021-11-04 1009
-
怎么实现嵌入式MCU中标准的三重中断控制设计?2021-11-29 921
-
在Android系统中的linux下控制GPIO的方法2022-10-12 3798
-
关于WinAVR-20060421中的标准输入/输出2010-07-02 907
-
基于Linux内核输入子系统的驱动研究2012-09-12 742
-
《Linux设备驱动开发详解》第5章、Linux文件系统与设备文件系统2017-10-27 1015
-
Linux内核输入子系统的驱动研究2017-10-31 980
-
详细了解Linux设备模型中的input子系统2019-05-12 1298
-
嵌入式linux应用程序开发标准教程pdf,嵌入式LINUX应用程序开发标准教程-华清远见.PDF...2021-11-01 1209
-
如何使用Linux系统下的输入设备进行应用编程2022-11-10 2187
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

