

SystemVerilog语言中的Upcasting和Downcasting概念解析
描述
要想理解清楚SystemVerilog语言中的Upcasting和Downcasting概念,最好的方式从内存分配的角度理解。
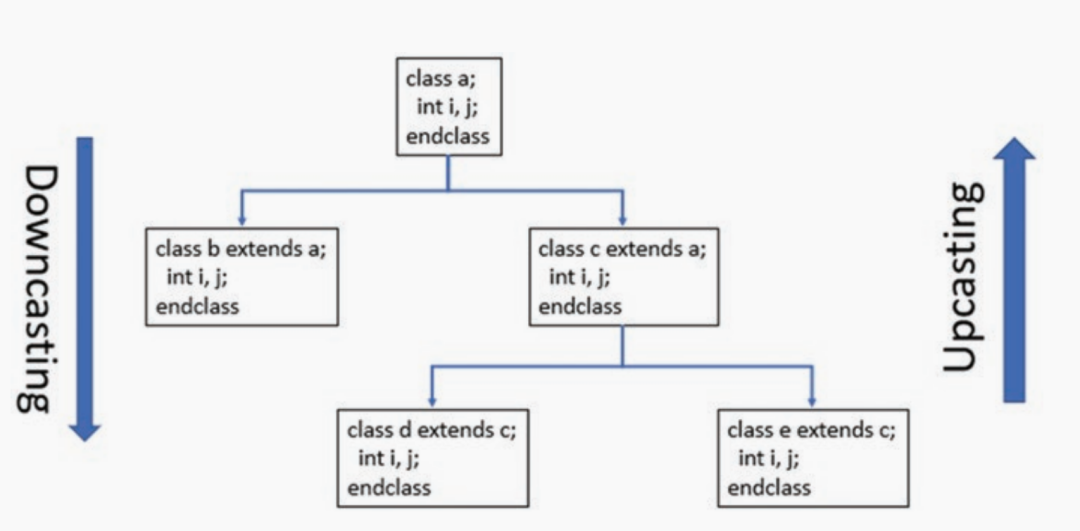
class “e”扩展自class “c”,class “c”又继承自class “a”。同时,class “b”扩展自class “a.”
如果我们执行了下面的代码:
a a1; //base class variable e e1; e1 = new; a1 = e1; //assigning extended object handle 'e1' to base class variable 'a1'
当我们实例化'e1 = new()'时,同时我们实例化了class e, class c和class a。
将扩展对象句柄“e1”赋值给基类句柄a1,就是一个“upcast”。
这意味着,如果你此时你访问“a1.i”,实际上访问到的就是上面class a所占用的内存空间。
换句话说,“a1.i”、“c1.i”和“e1.i”实际上是不同的内容。
SystemVerilog支持Upcasting,即将扩展类句柄直接赋值给基类句柄。
a a1; e e1; a1 = new; e1 = a1; //ILLEGAL
在上面的例子中,我们实例化了对象a1,此时会为对象a1分配内存空间,但是此时并没有为对象c1和对象e1分配内存空间。
所以,如果此时我们赋值“e1 = a1”是不允许的,因为e1并没有一个合适的物理空间去指向。
这种就是downcasting的概念,只能通过$cast()进行检查之后(如果a1确实指向了一个足够的内存空间e1就可以赋值)才能完成赋值。
$cast(e1,a1); //dynamic casting
首先看一个将子类句柄赋值给父类的示例:
class p_class;
bit [31:0] p_Var;
function void display();
$display("p_Var = %0d",p_Var);
endfunction
endclass
class c_class extends p_class;
bit [31:0] c_Var;
function void display( );
super.display( );
$display("c_Var = %0d",c_Var);
endfunction
endclass
module top;
initial begin
p_class p;
c_class c = new( );
c.p_Var = 10;
c.c_Var = 20;
//assigning child class handle to parent class variable
p = c;
c.display( );
end
endmodule
在这个例子中,我们声明了一个父类“p_class”和其扩展类“c_class.”
然后赋值c_class中的属性 c.p_Var和c.c_Var,最后进行upcasting,打印信息如下:
p_Var = 10 c_Var = 20 V C S S i m u l a t i o n R e p o r t
因为我们在实例化c_class时,同样为其父类p_class分配了内存空间。
相反,如果我们将父类句柄赋值给子类句柄
c = p
会得到一个编译错误
Error-[SV-ICA] Illegal class assignment testbench.sv, 32 "c = p;" Expression 'p' on rhs is not a class or a compatible class and hence cannot be assigned to a class handle on lhs. Please make sure that the lhs and rhs expressions are compatible.
我们再看一个upcast的示例:
class animals;
string color = "white";
function void disp;
$display("color = %s", color);
endfunction
endclass
class bufalo extends animals;
string color = "black";
function void disp;
$display("color = %s", color);
endfunction
endclass
program tb;
initial begin
animals p;
bufalo c;
c = new( ); //allocate memory for c
//this will allocate memory for both 'c' and 'p'
p = c; //upcasting
p.disp;
c.disp;
end
endprogram
仿真log:
color = white color = black $fnish at simulation time 0 V C S S i m u l a t i o n R e p o r t
在上面的例子中,虽然我们只是实例化了扩展类bufalo,但是同时也为父类animals分配的内存空间,所以打印了
color = white color = black
审核编辑:刘清
- 相关推荐
- 热点推荐
- Verilog语言
-
基于Rust语言中的生命周期2023-09-19 1449
-
C语言中指针的基本概念和用法2023-08-17 1392
-
C语言中多级指针的概念和使用方法2023-08-16 1829
-
简述C语言中指针重点2023-03-10 1041
-
FPGA学习-SystemVerilog语言简介2022-12-08 3019
-
Systemverilog event的示例2022-10-17 2200
-
go语言中怎么使用HTTP代理2022-09-01 2903
-
IEEE SystemVerilog标准:统一的硬件设计规范和验证语言2022-08-25 676
-
带你了解go语言中的闭包2021-11-02 2901
-
详细介绍go语言中的闭包的实现2021-10-20 2274
-
SystemVerilog语言介绍汇总2021-10-11 3019
-
基于SystemVerilog语言的验证方法学介绍2011-05-09 1056
-
SystemVerilog设计语言2010-09-07 1377
-
SystemVerilog 3.1a语言参考手册2009-07-22 1811
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

