

Spring多线程异步上传图片、处理水印、缩略图
电子说
描述
使用环境
- SpringBoot+FastDfs+thumbnailator
- fdfs环境自己搞吧
基于 Spring Boot + MyBatis Plus + Vue & Element 实现的后台管理系统 + 用户小程序,支持 RBAC 动态权限、多租户、数据权限、工作流、三方登录、支付、短信、商城等功能
- 项目地址:https://github.com/YunaiV/ruoyi-vue-pro
- 视频教程:https://doc.iocoder.cn/video/
thumbnailator
maven依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>net.coobirdgroupId>
<artifactId>thumbnailatorartifactId>
<version>0.4.8version>
dependency>
工具类:
import net.coobird.thumbnailator.Thumbnails;
import net.coobird.thumbnailator.geometry.Positions;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
@Component
public class PictureUtil {
/**
* 水印图片
*/
private static File markIco = null;
//开机静态加载水印图片
static {
try {
markIco = new File(new File("").getCanonicalPath() + "/icon.png");
LogUtil.info(PictureUtil.class, "水印图片加载" + (markIco.exists() ? "成功" : "失败"));
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
/**
* 加水印
*/
public void photoMark(File sourceFile, File toFile) throws IOException {
Thumbnails.of(sourceFile)
.size(600, 450)//尺寸
.watermark(Positions.BOTTOM_CENTER/*水印位置:中央靠下*/,
ImageIO.read(markIco), 0.7f/*质量,越大质量越高(1)*/)
//.outputQuality(0.8f)
.toFile(toFile);//保存为哪个文件
}
/**
* 生成图片缩略图
*/
public void photoSmaller(File sourceFile, File toFile) throws IOException {
Thumbnails.of(sourceFile)
.size(200, 150)//尺寸
//.watermark(Positions.CENTER, ImageIO.read(markIco), 0.1f)
.outputQuality(0.4f)//缩略图质量
.toFile(toFile);
}
/**
* 生成视频缩略图(这块还没用到呢)
*/
public void photoSmallerForVedio(File sourceFile, File toFile) throws IOException {
Thumbnails.of(sourceFile)
.size(440, 340)
.watermark(Positions.BOTTOM_CENTER, ImageIO.read(markIco), 0.1f)
.outputQuality(0.8f)
.toFile(toFile);
}
}
这个插件很好用,只需集成调用即可,我记得我还试过另外几个,需要另外在linux下配置.so文件的依赖等等,查了半天也没弄明白,很麻烦,这个方便。
这个插件又很不好用,必须要先调整尺寸,才能加水印,而且调整尺寸简直是负压缩。压了分辨率图片还能变大那种。但是简单嘛,这块不是重点。
基于 Spring Cloud Alibaba + Gateway + Nacos + RocketMQ + Vue & Element 实现的后台管理系统 + 用户小程序,支持 RBAC 动态权限、多租户、数据权限、工作流、三方登录、支付、短信、商城等功能
- 项目地址:https://github.com/YunaiV/yudao-cloud
- 视频教程:https://doc.iocoder.cn/video/
线程池
使用springboot线程池,方便易用,只需配置和加注解即可。
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.task.TaskExecutor;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class PoolConfig {
@Bean//return new AsyncResult<>(res);
public TaskExecutor taskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.initialize(); // 设置核心线程数
executor.setCorePoolSize(4); // 设置最大线程数
executor.setMaxPoolSize(32); // 设置队列容量
executor.setQueueCapacity(512); // 设置线程活跃时间(秒)
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60); // 设置默认线程名称
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("ThreadPool-"); // 设置拒绝策略
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()); // 等待所有任务结束后再关闭线程池
executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
return executor;
}
}
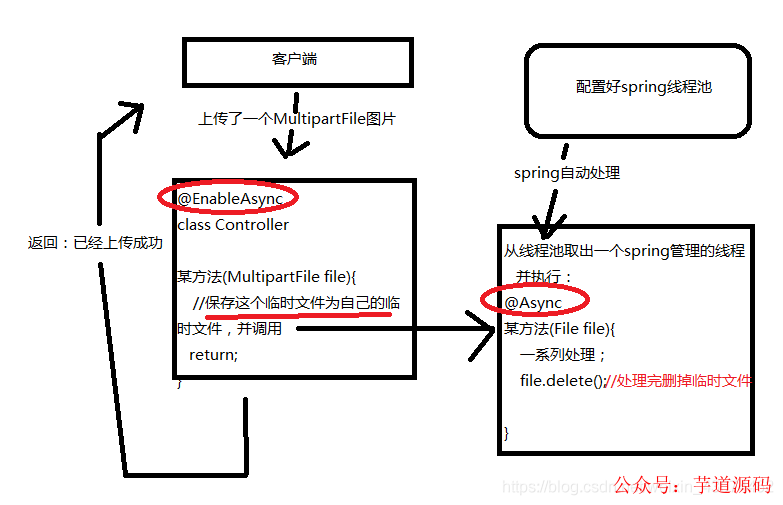
避坑知识点:配置springboot线程池,类上需要
@Configuration、@EnableAsync这两个注解,实际调用时,需要遵守一个规则,即在调用的方法的类上必须使用注解@EnableAsync,调用一个带有@Async的方法。
比如A类使用了注解@EnableAsync 在A类中调用B类的有@Async的方法,只有这样多线程才生效,A类内调用A类的@Async方法不生效。可以理解为Controller层使用@EnableAsync注解,Service层方法上标注@Async。这样在Controller层调用的Service方法会从线程池调用线程来执行。
异步逻辑:为什么要用多线程?
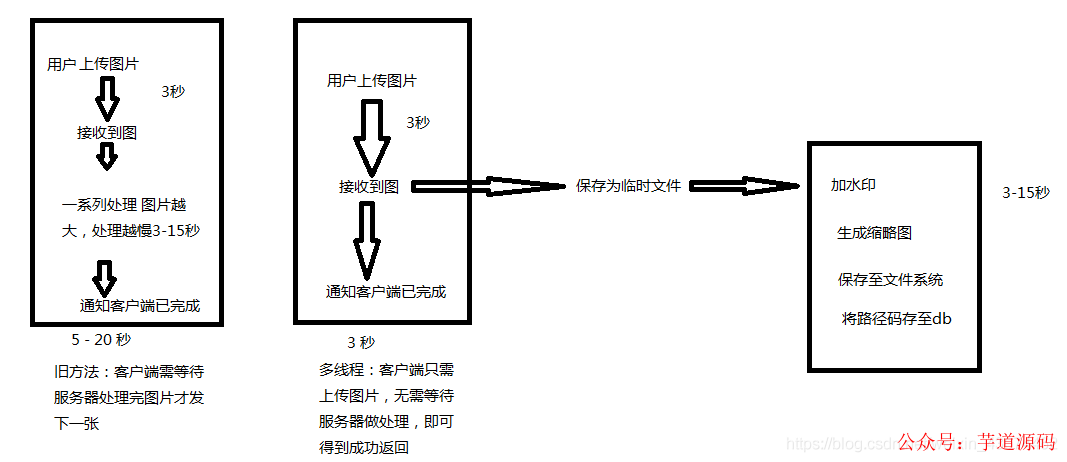
我画了一张简单的示意图,在这个项目中,客户端一次上传10多张图片,每个图片单独上传,等待所有图片上传返回200后,继续执行操作,如果一步一步处理,客户端需等待服务器处理完所有逻辑,这样浪费没必要的时间。顾使用异步操作,客户端只需上传图片,无需等待服务器处理(我们服务器很辣鸡,一个10M的图可能要搞10多秒,见笑)
业务代码
@ApiOperation("上传业务图片")
@PostMapping("/push/photo/{id}/{name}")
public R pushHousingPhotoMethod(
@ApiParam("SourceId") @PathVariable Integer id,
@ApiParam("图片名称不约束,可不填则使用原名,可使用随机码或原名称,但必须带扩展名") @PathVariable(required = false) String name,
@RequestParam MultipartFile file) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, IOException {
String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename();
String ext = StringUtils.substring(fileName, fileName.lastIndexOf('.'),fileName.length());
File tempPhoto = File.createTempFile(UUIDUtil.make32BitUUID(), ext);
file.transferTo(tempPhoto);//转储临时文件
service.pushPhoto(id, name, tempPhoto);
return new R();
}
业务代码里隐藏了一些项目相关的信息,就是某些名改了,嗯。
可以看到,使用StringUtils.substring(fileName, fileName.lastIndexOf(’.’),fileName.length());这句代码,调用apache.common.lang3工具类获取出了扩展名,因为扩展名对图片处理工具类有用,他通过扩展名识别图片格式,所以这个必须有,如代码,生成了一个使用随机码命名,但带有.png扩展名的临时文件,保存在默认临时路径以供处理。File.createTempFile(UUIDUtil.make32BitUUID(), ext);是生成临时文件的方法,UUIDUtil也很简单,我贴出来吧,省着还要找
注意:controller类上需要标注注解@EnableAsync
/**
* 生成一个32位无横杠的UUID
*/
public synchronized static String make32BitUUID(){
return UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-","");
}
避坑知识点:Spring使用MultipartFile接收文件,但不能直接把MultipartFile传下去处理,而是保存为临时文件,并不是多此一举。因为MultipartFile也是临时文件,他的销毁时间是你这个Controller层方法return的时候。
如果不使用异步,是可以在调用的方法里去处理MultipartFile文件的,但如果使用异步处理,肯定是这边线程还没处理完,那边Controller层已经return了,这个MultipartFile就被删除了,于是你的异步线程就找不到这张图了。那还处理个啥,对吧。所以需要手动保存为自己创建的临时文件,再在线程中处理完把他删掉。
贴Service层Impl实现类代码
@Async
public void pushHousingPhoto(Integer id,String name,File file) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, IOException {
//存储FDFS表id
Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Integer[] numb = fastDfsService.upLoadPhoto(StringUtils.isBlank(name) ? file.getName() : name, file).get();
SourcePhotosContext context = new SourcePhotosContext();
context.setSourceId(id);
context.setNumber(numb[0]);
context.setNumber2(numb[1]);
//保存图片关系
sourcePhotosContextService.insertNew(context);
Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
LogUtil.info(this.getClass(),"source [ "+id+" ] 绑定图片 [ "+name+" ] 成功,内部处理耗时 ["+ (endTime-startTime) +"ms ]");
//return new R();
}
这里的number和number2分别是带水印的原图和缩略图,context是个表,用来存图片和缩略图对应fdfs路径的,就不贴了。可见这个方法上带有注解@Async 所以整个方法会异步执行。
加水印处理写到fdfs的service里了,这样不算规范,可以不要学我:
@Override
public Future upLoadPhoto(String fileName, MultipartFile file) throws IOException {
String ext = StringUtils.substring(fileName, fileName.lastIndexOf('.'));
//创建临时文件
File sourcePhoto = File.createTempFile(UUIDUtil.make32BitUUID(), ext);
file.transferTo(sourcePhoto);
return upLoadPhoto(fileName, sourcePhoto);
}
@Override
public Future upLoadPhoto(String fileName, File sourcePhoto) throws IOException {
String ext = StringUtils.substring(fileName, fileName.lastIndexOf('.'));
//创建临时文件
File markedPhoto = File.createTempFile(UUIDUtil.make32BitUUID(), ext);
File smallerPhoto = File.createTempFile(UUIDUtil.make32BitUUID(), ext);
//加水印 缩图
pictureUtil.photoMark(sourcePhoto, markedPhoto);
pictureUtil.photoSmaller(markedPhoto, smallerPhoto);
//上传
Integer markedPhotoNumber = upLoadPhotoCtrl(fileName, markedPhoto);
Integer smallerPhotoNumber = upLoadPhotoCtrl("mini_" + fileName, smallerPhoto);
//删除临时文件
sourcePhoto.delete();
markedPhoto.delete();
smallerPhoto.delete();
Integer[] res = new Integer[]{markedPhotoNumber, smallerPhotoNumber};
return new AsyncResult(res);
}
使用了方法重载,一个调用了另一个,方便以后处理MultipartFile和File格式的图片都能使用,可以见到使用了Future这个东西作为返回值,完全可以不这么做,正常返回就行。我懒得改了,这也是不断探索多线程处理图片的过程中,遗留下来的东西。
在service中fastDfsService.upLoadPhoto(StringUtils.isBlank(name) ? file.getName() : name, file).get()这句就是得到了这个future的内容,可以去掉.get() 和Future<>。可见这一个小小的异步功能,其实走过了很多弯路。future其实是异步调用方法时,从.get()等待异步处理的结果,等待得到结果后获取内容并执行。现在使用spring线程池处理,已经不需要这样做了。
以上,希望你在实现这个功能时可以少走弯路。
附总体示意图:
审核编辑 :李倩
-
Spring 的线程池应用2023-10-13 1326
-
Java多线程永动任务 多线程异步任务项目解读2022-10-19 1653
-
电脑不显示缩略图的解决办法2022-09-28 2521
-
如何使用多线程和异步操作等并发设计方法来最大化程序的性能2022-08-23 5697
-
Atari 2600/7800 RF复合修改的缩略图板2022-07-28 655
-
发烧友资料库后台缩略图链接:请勿删除2021-01-06 4561
-
FPGA+CPU助力数据中心实现图像处理应用体验与服务成本新平衡2020-03-06 1291
-
基于SpringMVC的图片处理系统的研究与设计2017-12-22 825
-
一种面向即时通讯的图片管理方法及其在税务通讯软件上的实现2017-11-23 738
-
基于社交关系的图片缓存替换算法2017-11-22 651
-
C#教程之图片缩略图2016-04-20 335
-
关于文件夹内的图片显示问题2012-10-23 2886
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

