

跨机房ES同步实战
描述
背景众所周知单个机房在出现不可抗拒的问题(如断电、断网等因素)时,会导致无法正常提供服务,会对业务造成潜在的损失。所以在协同办公领域,一种可以基于同城或异地多活机制的高可用设计,在保障数据一致性的同时,能够最大程度降低由于机房的仅单点可用所导致的潜在高可用问题,最大程度上保障业务的用户体验,降低单点问题对业务造成的潜在损失显得尤为重要。同城双活,对于生产的高可用保障,重大的意义和价值是不可言喻的。表面上同城双活只是简单的部署了一套生产环境而已,但是在架构上,这个改变的影响是巨大的,无状态应用的高可用管理、请求流量的管理、版本发布的管理、网络架构的管理等,其提升的架构复杂度巨大。结合真实的协同办公产品:京办(为北京市政府提供协同办公服务的综合性平台)生产环境面对的复杂的政务网络以及京办同城双活架构演进的案例,给大家介绍下京办持续改进、分阶段演进过程中的一些思考和实践经验的总结。本文仅针对 ES 集群在跨机房同步过程中的方案和经验进行介绍和总结。
架构
1. 部署 Logstash 在金山云机房上,Logstash 启动多个实例(按不同的类型分类,提高同步效率),并且和金山云机房的 ES 集群在相同的 VPC2. Logstash 需要配置大网访问权限,保证 Logstash 和 ES 原集群和目标集群互通。3. 数据迁移可以全量迁移和增量迁移,首次迁移都是全量迁移后续的增加数据选择增量迁移。4. 增量迁移需要改造增加识别的增量数据的标识,具体方法后续进行介绍。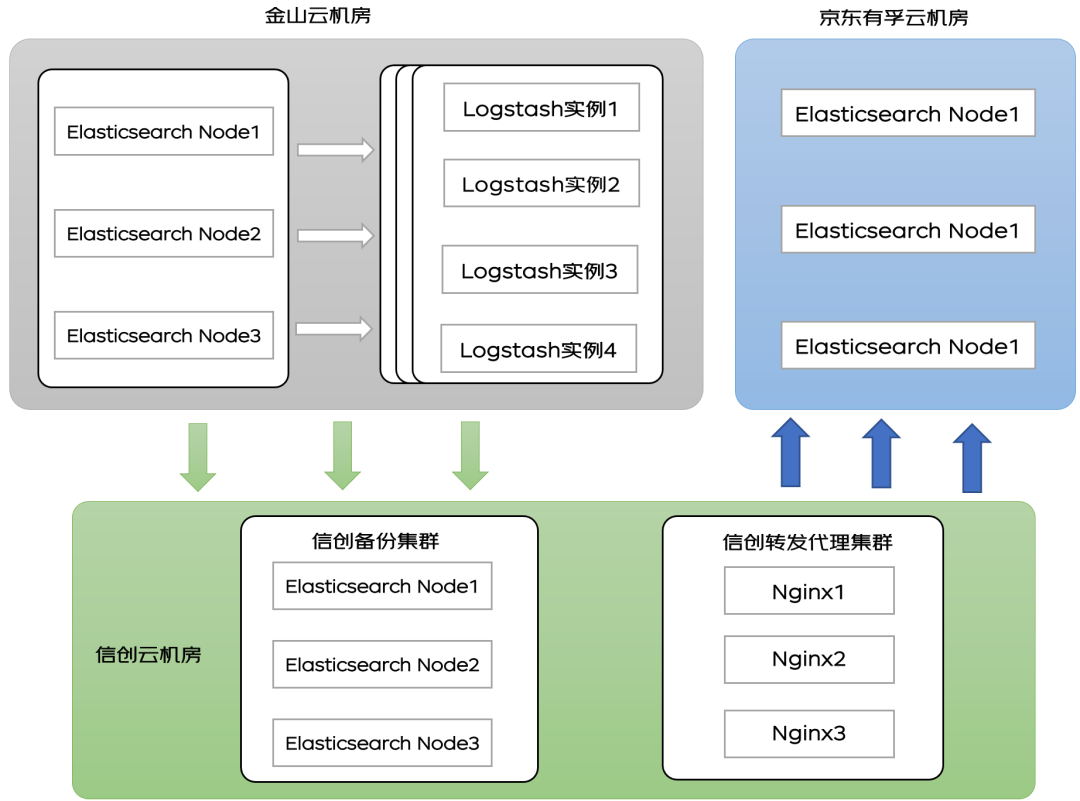 原理
原理Logstash 工作原理
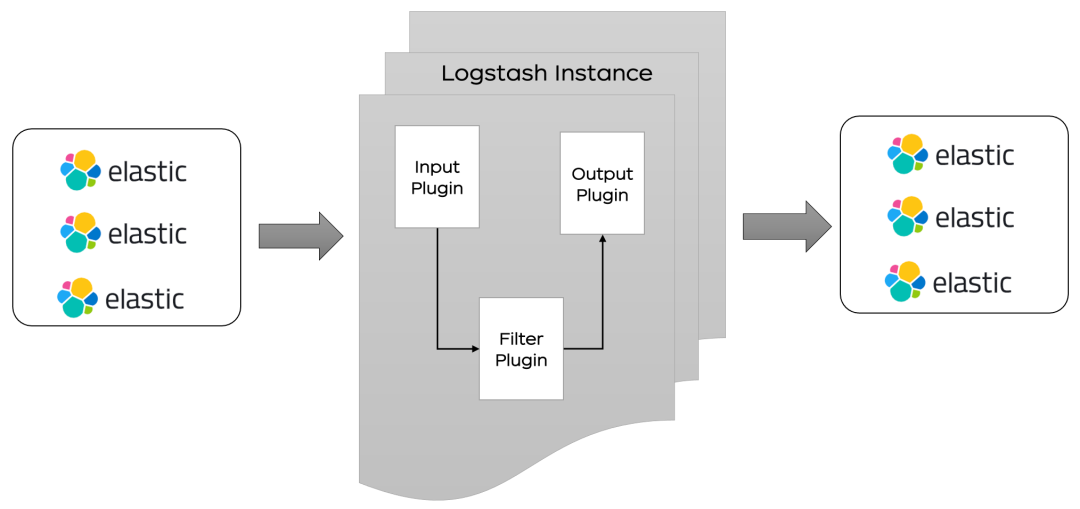 Logstash 分为三个部分 input 、filter、ouput:1. input 处理接收数据,数据可以来源 ES,日志文件,kafka 等通道.2. filter 对数据进行过滤,清洗。3. ouput 输出数据到目标设备,可以输出到 ES,kafka,文件等。
Logstash 分为三个部分 input 、filter、ouput:1. input 处理接收数据,数据可以来源 ES,日志文件,kafka 等通道.2. filter 对数据进行过滤,清洗。3. ouput 输出数据到目标设备,可以输出到 ES,kafka,文件等。增量同步原理
1. 对于 T 时刻的数据,先使用 Logstash 将 T 以前的所有数据迁移到有孚机房京东云 ES,假设用时∆T2. 对于 T 到 T+∆T 的增量数据,再次使用 logstash 将数据导入到有孚机房京东云的 ES 集群3. 重复上述步骤 2,直到∆T 足够小,此时将业务切换到华为云,最后完成新增数据的迁移适用范围:ES 的数据中带有时间戳或者其他能够区分新旧数据的标签流程
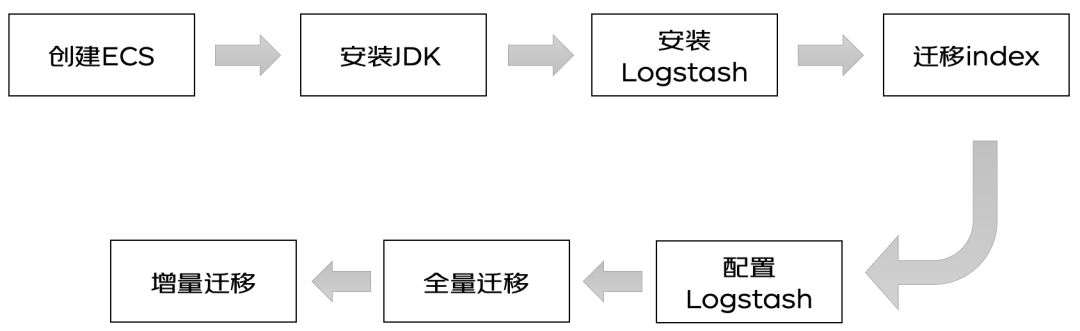
准备工作
1. 创建 ECS 和安装 JDK 忽略,自行安装即可2. 下载对应版本的 Logstash,尽量选择与 Elasticsearch 版本一致,或接近的版本安装即可https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/logstash1) 源码下载直接解压安装包,开箱即用
2)修改对内存使用,logstash 默认的堆内存是 1G,根据 ECS 集群选择合适的内存,可以加快集群数据的迁移效率。

3. 迁移索引
Logstash 会帮助用户自动创建索引,但是自动创建的索引和用户本身的索引会有些许差异,导致最终数据的搜索格式不一致,一般索引需要手动创建,保证索引的数据完全一致。
以下提供创建索引的 python 脚本,用户可以使用该脚本创建需要的索引。
create_mapping.py 文件是同步索引的 python 脚本,config.yaml 是集群地址配置文件。
注:使用该脚本需要安装相关依赖
yum install -y PyYAML
yum install -y python-requests
拷贝以下代码保存为 create_mapping.py:
import yaml
import requests
import json
import getopt
import sys
defhelp():
print
"""
usage:
-h/--help print this help.
-c/--config config file path, default is config.yaml
example:
python create_mapping.py -c config.yaml
"""
defprocess_mapping(index_mapping, dest_index):
print(index_mapping)
# remove unnecessary keys
del index_mapping["settings"]["index"]["provided_name"]
del index_mapping["settings"]["index"]["uuid"]
del index_mapping["settings"]["index"]["creation_date"]
del index_mapping["settings"]["index"]["version"]
# check alias
aliases = index_mapping["aliases"]
for alias inlist(aliases.keys()):
if alias == dest_index:
print(
"source index "+ dest_index +" alias "+ alias +" is the same as dest_index name, will remove this alias.")
del index_mapping["aliases"][alias]
if index_mapping["settings"]["index"].has_key("lifecycle"):
lifecycle = index_mapping["settings"]["index"]["lifecycle"]
opendistro ={"opendistro":{"index_state_management":
{"policy_id": lifecycle["name"],
"rollover_alias": lifecycle["rollover_alias"]}}}
index_mapping["settings"].update(opendistro)
# index_mapping["settings"]["opendistro"]["index_state_management"]["rollover_alias"] = lifecycle["rollover_alias"]
del index_mapping["settings"]["index"]["lifecycle"]
print(index_mapping)
return index_mapping
defput_mapping_to_target(url, mapping, source_index, dest_auth=None):
headers ={'Content-Type':'application/json'}
create_resp = requests.put(url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(mapping), auth=dest_auth)
if create_resp.status_code !=200:
print(
"create index "+ url +" failed with response: "+str(create_resp)+", source index is "+ source_index)
print(create_resp.text)
withopen(source_index +".json","w")as f:
json.dump(mapping, f)
defmain():
config_yaml ="config.yaml"
opts, args = getopt.getopt(sys.argv[1:],'-h-c:',['help','config='])
for opt_name, opt_value in opts:
if opt_name in('-h','--help'):
help()
exit()
if opt_name in('-c','--config'):
config_yaml = opt_value
config_file =open(config_yaml)
config = yaml.load(config_file)
source = config["source"]
source_user = config["source_user"]
source_passwd = config["source_passwd"]
source_auth =None
if source_user !="":
source_auth =(source_user, source_passwd)
dest = config["destination"]
dest_user = config["destination_user"]
dest_passwd = config["destination_passwd"]
dest_auth =None
if dest_user !="":
dest_auth =(dest_user, dest_passwd)
print(source_auth)
print(dest_auth)
# only deal with mapping list
if config["only_mapping"]:
for source_index, dest_index in config["mapping"].iteritems():
print("start to process source index"+ source_index +", target index: "+ dest_index)
source_url = source +"/"+ source_index
response = requests.get(source_url, auth=source_auth)
if response.status_code !=200:
print("*** get ElasticSearch message failed. resp statusCode:"+str(
response.status_code)+" response is "+ response.text)
continue
mapping = response.json()
index_mapping = process_mapping(mapping[source_index], dest_index)
dest_url = dest +"/"+ dest_index
put_mapping_to_target(dest_url, index_mapping, source_index, dest_auth)
print("process source index "+ source_index +" to target index "+ dest_index +" successed.")
else:
# get all indices
response = requests.get(source +"/_alias", auth=source_auth)
if response.status_code !=200:
print("*** get all index failed. resp statusCode:"+str(
response.status_code)+" response is "+ response.text)
exit()
all_index = response.json()
for index inlist(all_index.keys()):
if"."in index:
continue
print("start to process source index"+ index)
source_url = source +"/"+ index
index_response = requests.get(source_url, auth=source_auth)
if index_response.status_code !=200:
print("*** get ElasticSearch message failed. resp statusCode:"+str(
index_response.status_code)+" response is "+ index_response.text)
continue
mapping = index_response.json()
dest_index = index
if index in config["mapping"].keys():
dest_index = config["mapping"][index]
index_mapping = process_mapping(mapping[index], dest_index)
dest_url = dest +"/"+ dest_index
put_mapping_to_target(dest_url, index_mapping, index, dest_auth)
print("process source index "+ index +" to target index "+ dest_index +" successed.")
if __name__ =='__main__':
main()
配置文件保存为 config.yaml:
# 源端ES集群地址,加上http://
source: http://ip:port
source_user: "username"
source_passwd: "password"
# 目的端ES集群地址,加上http://
destination: http://ip:port
destination_user: "username"
destination_passwd: "password"
# 是否只处理这个文件中mapping地址的索引
# 如果设置成true,则只会将下面的mapping中的索引获取到并在目的端创建
# 如果设置成false,则会取源端集群的所有索引,除去(.kibana)
# 并且将索引名称与下面的mapping匹配,如果匹配到使用mapping的value作为目的端的索引名称
# 如果匹配不到,则使用源端原始的索引名称
only_mapping: true
# 要迁移的索引,key为源端的索引名字,value为目的端的索引名字
mapping:
source_index: dest_index
以上代码和配置文件准备完成,直接执行 python create_mapping.py 即可完成索引同步。
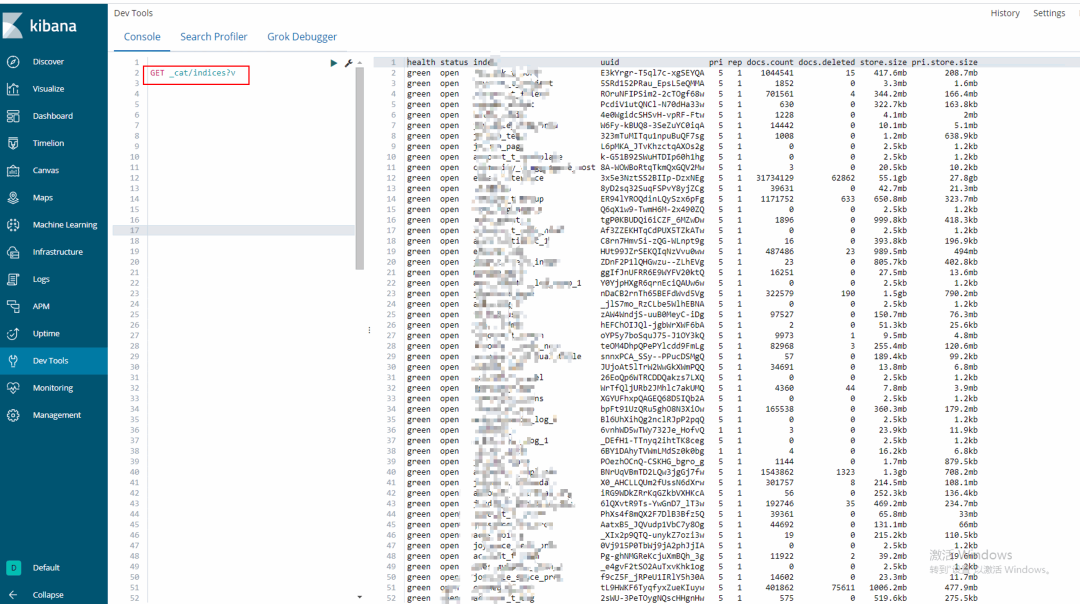
索引同步完成可以取目标集群的 kibana 上查看或者执行 curl 查看索引迁移情况:
GET _cat/indices?v
input{
elasticsearch{
# 源端地址
hosts => ["ip1:port1","ip2:port2"]
# 安全集群配置登录用户名密码
user => "username"
password => "password"
# 需要迁移的索引列表,以逗号分隔,支持通配符
index => "a_*,b_*"
# 以下三项保持默认即可,包含线程数和迁移数据大小和logstash jvm配置相关
docinfo=>true
slices => 10
size => 2000
scroll => "60m"
}
}
filter {
# 去掉一些logstash自己加的字段
mutate {
remove_field => ["@timestamp", "@version"]
}
}
output{
elasticsearch{
# 目的端es地址
hosts => ["http://ip:port"]
# 安全集群配置登录用户名密码
user => "username"
password => "password"
# 目的端索引名称,以下配置为和源端保持一致
index => "%{[@metadata][_index]}"
# 目的端索引type,以下配置为和源端保持一致
document_type => "%{[@metadata][_type]}"
# 目标端数据的_id,如果不需要保留原_id,可以删除以下这行,删除后性能会更好
document_id => "%{[@metadata][_id]}"
ilm_enabled => false
manage_template => false
}
# 调试信息,正式迁移去掉
stdout { codec => rubydebug { metadata => true }}
}
增量迁移
预处理:
1. @timestamp 在 elasticsearch2.0.0beta 版本后弃用
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/2.4/mapping-timestamp-field.html
2. 本次对于京办从金山云机房迁移到京东有孚机房,所涉及到的业务领域多,各个业务线中所代表新增记录的时间戳字段不统一,所涉及到的兼容工作量大,于是考虑通过 elasticsearch 中预处理功能 pipeline 进行预处理添加统一增量标记字段:gmt_created_at,以减少迁移工作的复杂度(各自业务线可自行评估是否需要此步骤)。
PUT _ingest/pipeline/gmt_created_at
{
"description":"Adds gmt_created_at timestamp to documents",
"processors":[
{
"set":{
"field":"_source.gmt_created_at",
"value":"{{_ingest.timestamp}}"
}
}
]
}
3. 检查 pipeline 是否生效
GET _ingest/pipeline/*
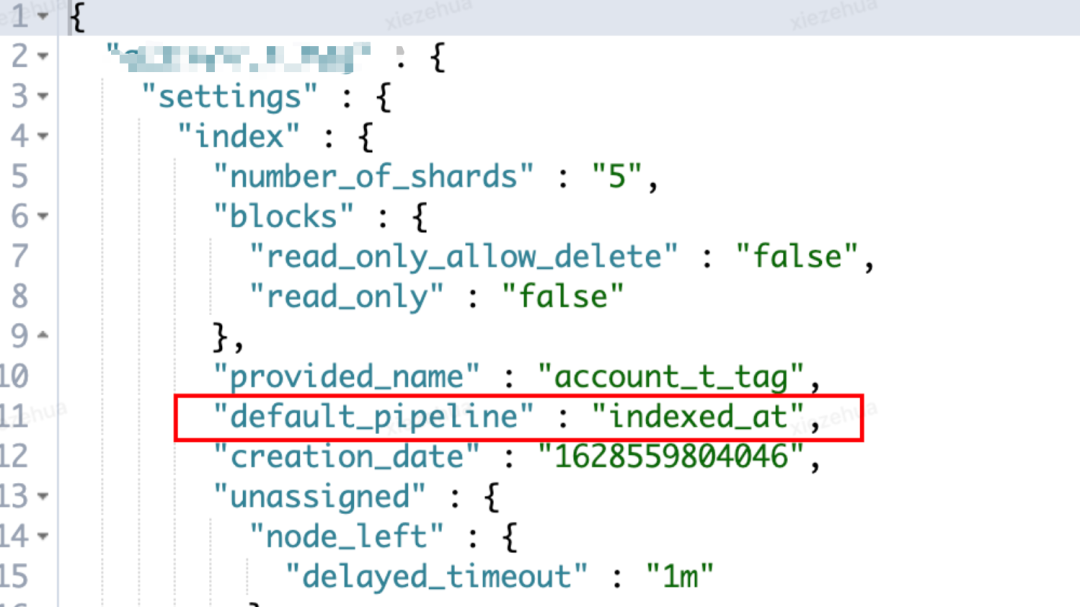
4. 各个 index 设置对应 settings 增加 pipeline 为默认预处理
PUT index_xxxx/_settings
{
"settings": {
"index.default_pipeline": "gmt_created_at"
}
}
5. 检查新增 settings 是否生效
GET index_xxxx/_settings
增量迁移脚本
schedule-migrate.conf
index:可以使用通配符的方式
query: 增量同步的 DSL,统一 gmt_create_at 为增量同步的特殊标记
schedule: 每分钟同步一把,"* * * * *"
input {
elasticsearch {
hosts =>["ip:port"]
# 安全集群配置登录用户名密码
user =>"username"
password =>"password"
index =>"index_*"
query =>'{"query":{"range":{"gmt_create_at":{"gte":"now-1m","lte":"now/m"}}}}'
size =>5000
scroll =>"5m"
docinfo =>true
schedule =>"* * * * *"
}
}
filter {
mutate {
remove_field =>["source", "@version"]
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
# 目的端es地址
hosts =>["http://ip:port"]
# 安全集群配置登录用户名密码
user =>"username"
password =>"password"
index =>"%{[@metadata][_index]}"
document_type =>"%{[@metadata][_type]}"
document_id =>"%{[@metadata][_id]}"
ilm_enabled =>false
manage_template =>false
}
# 调试信息,正式迁移去掉
stdout { codec => rubydebug { metadata =>true}}
}
问题:
mapping 中存在 join 父子类型的字段,直接迁移报 400 异常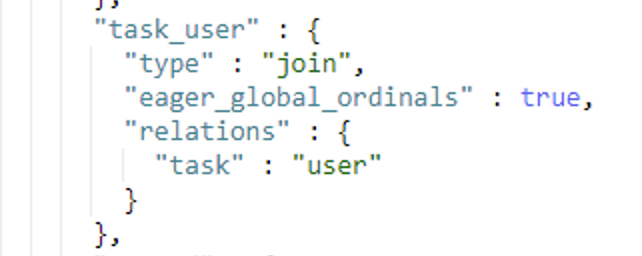
[2022-09-20T20:02:16,404][WARN ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] Could not index event to Elasticsearch. {:status=>400,
:action=>["index", {:_id=>"xxx", :_index=>"xxx", :_type=>"joywork_t_work", :routing=>nil}, #],
:response=>{"index"=>{"_index"=>"xxx", "_type"=>"xxx", "_id"=>"xxx", "status"=>400,
"error"=>{"type"=>"mapper_parsing_exception", "reason"=>"failed to parse",
"caused_by"=>{"type"=>"illegal_argument_exception", "reason"=>"[routing] is missing for join field [task_user]"}}}}}
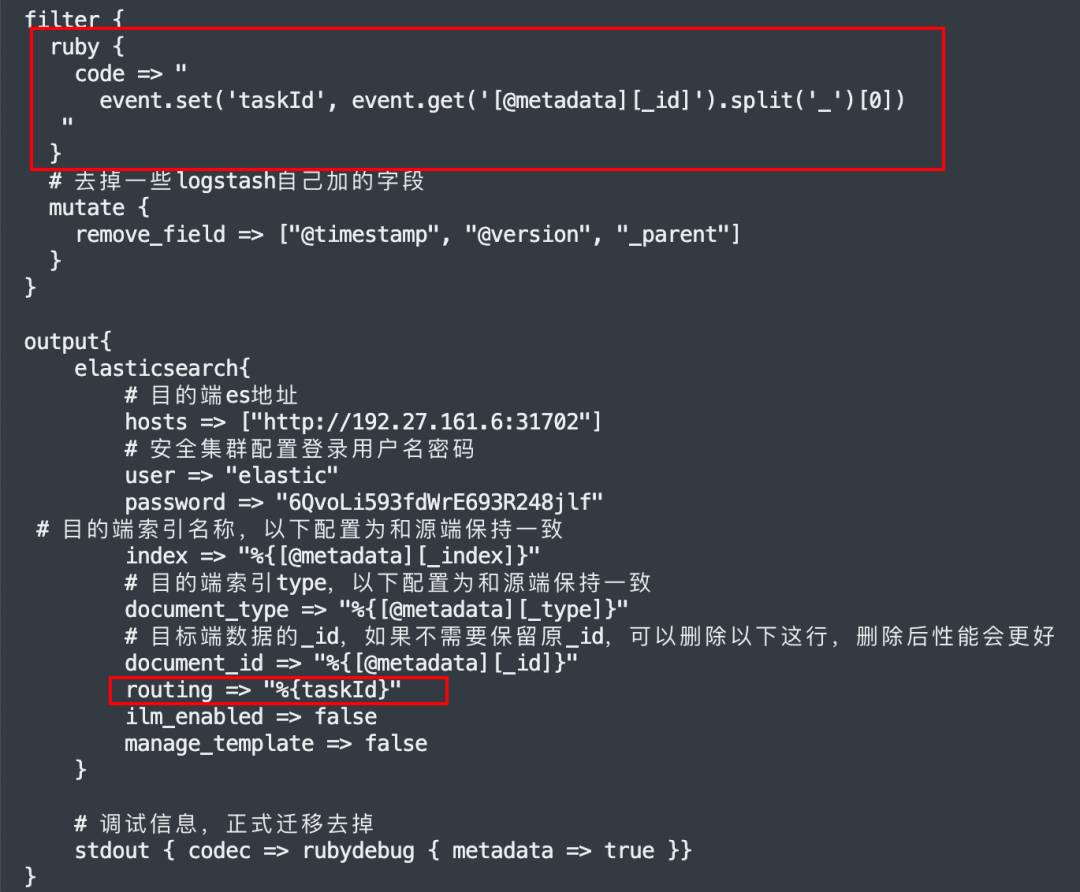
解决方法:
https://discuss.elastic.co/t/an-routing-missing-exception-is-obtained-when-reindex-sets-the-routing-value/155140 https://github.com/elastic/elasticsearch/issues/26183
结合业务特征,通过在 filter 中加入小量的 ruby 代码,将_routing 的值取出来,放回 logstah event 中,由此问题得以解决。
示例:
审核编辑 :李倩
-
MySQL到ES的4种常用数据同步方案2023-08-09 1135
-
从处理单bit跨时钟域信号同步问题来入手2023-06-27 2631
-
深度解读ES+Redis+MySQL的高可用架构设计2023-06-01 1263
-
智慧机房是什么机房?智慧机房解决方案包括这些!2023-04-06 6239
-
机房动环监控系统应用建设2023-03-24 863
-
模块化机房和传统机房有哪些不同2022-09-15 10128
-
HarmonyOS测试技术与实战-声画同步测试标准及来源2021-10-23 1603
-
计算机机房布线方案与机房的环境要求2021-09-10 2221
-
跨时钟域为什么要双寄存器同步2020-08-20 3589
-
机房监控分类_机房监控用途范围2020-05-19 2870
-
如何利用FPGA设计一个跨时钟域的同步策略?2018-09-01 6014
-
计算机机房2016-04-17 4107
-
跨时钟域信号的几种同步方法研究2012-05-09 1264
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

