

浅谈Linux系统的管理系统
嵌入式技术
1412人已加入
描述
也许你配置过Windows开机启动的服务,其中有些服务在日常的管理工作中用不到,我们就要把它停止,一来可以节省资源,二来可以减少安全隐患。在Linux上同样也有相关的工具来管理系统的服务。
14.6.1 chkconfig服务管理工具
早期的CentOS 6上的服务管理工具为chkconfig,Linux系统所有的预设服务都可以通过查看/etc/init.d/目录得到,如下所示:
# ls /etc/init.d/ functions README只有屈指可数的几个文件,这是因为从CentOS 7起开始已经不再延续CentOS 6版本的服务管理方案了。但是我们依然可以继续使用chkconfig这个命令。系统的预设服务都可以通过这样的命令实现:service 服务名 start|stop|restart。这里的服务名就是/etc/init.d/目录下的这些文件了。使用chkconfig启动某服务除了可以使用命令service xxx start外,还可以使用命令/etc/init.d/xxx start。 我们可以使用命令chkconfig --list列出所有的服务及其每个级别的开启状态,如下所示:
# chkconfig --list注:该输出结果只显示 SysV 服务,并不包含原生 systemd 服务。SysV 配置数据可能被原生 systemd 配置覆盖。要列出 systemd 服务,请执行 'systemctl list-unit-files'。查看在具体 target 启用的服务请执行
'systemctl list-dependencies [target]'。在这里也会看到一个提示,它提示我们该命令输出的内容并没有包含Rocky 8的原生systemd服务,而这里仅仅列出来SysV服务。这也是/etc/init.d/目录下面只有一两个启动脚本的根本原因。也就是说,早期CentOS版本(7之前)采用的服务管理都是SysV,而从7开始换成了systemd。 Chkconfig列出来的服务,有7个运行级别(数字0~6),其为系统启动级别(CentOS 7之前版本的用法,而从CentOS 7开始已经不再严格区分级别的概念了)。其中0作为shutdown动作,1作为重启至单用户模式,6为重启。在一般的Linux系统实现中,都使用了2、3、4、5几个级别。在CentOS系统中,2表示无NFS支持的多用户模式,3表示完全多用户模式(也是最常用的级别),4保留给用户自定义,5表示图形登录方式。现在我们只是看到了各服务在每个级别下的开启状态,那么如何去更改某级别下的开启状态呢?
# chkconfig --level 3 xxx off这里用--level指定级别,后面xxx是服务名,然后是off或者on。选项--level后面还可以指定多个级别,如下所示:
# chkconfig --level 345 xxx off另外还可以省略级别,默认是针对级别2、3、4和5操作的,如下所示:
# chkconfig xxx onChkconfig还有一个功能,就是可以把某个服务加入系统服务或者删除,即可以使用“chkconfig --add 服务名“或者“chkconfig --del 服务名“这样的形式,并且可以在chkconfig --list的结果中查找到。
# chkconfig --del xxx # chkconfig --add xxx这个功能常用于把自定义的启动脚本加入到系统服务当中。关于chkconfig工具,阿铭就先介绍这么多,毕竟systemd才是本书的主角。 14.6.2 systemd服务管理 上一节阿铭提到过,从CentOS 7开始不使用SysV而改为systemd了,这是因为systemd支持多个服务并发启动,而SysV只能一个一个地启动,这样最终导致的结果是systemd方式启动会快很多。但毕竟阿铭使用CentOS很多年,突然这样一变化还是有点不太习惯,接下来的知识点也会让你觉得systemd有点复杂。我们不妨对比着chkconfig工具来学习一下systemd。首先是列出系统所有的服务,如下所示:
# systemctl list-units --all --type=service UNIT LOAD ACTIVE SUB DESCRIPTION atd.service loaded active running Job spooling tools auditd.service loaded active running Security Auditing Service chronyd.service loaded active running NTP client/server ● cloud-init-local.service not-found inactive dead cloud-init-local.service cpupower.service loaded inactive dead Configure CPU power relat> crond.service loaded active running Command Scheduler dbus.service loaded active running D-Bus System Message Bus ● display-manager.service not-found inactive dead display-manager.service dnf-makecache.service loaded inactive dead dnf makecache dracut-cmdline.service loaded inactive dead dracut cmdline hook dracut-initqueue.service loaded inactive dead dracut initqueue hook dracut-mount.service loaded inactive dead dracut mount hook dracut-pre-mount.service loaded inactive dead dracut pre-mount hook dracut-pre-pivot.service loaded inactive dead dracut pre-pivot and clea> dracut-pre-trigger.service loaded inactive dead dracut pre-trigger hook dracut-pre-udev.service loaded inactive dead dracut pre-udev hook dracut-shutdown.service loaded active exited Restore /run/initramfs on> ebtables.service loaded inactive dead Ethernet Bridge Filtering> emergency.service loaded inactive dead Emergency Shell firewalld.service loaded active running firewalld - dynamic firew> getty@tty1.service loaded active running Getty on tty1 import-state.service loaded active exited Import network configurat> initrd-cleanup.service loaded inactive dead Cleaning Up and Shutting > initrd-parse-etc.service loaded inactive dead Reload Configuration from> initrd-switch-root.service loaded inactive dead Switch Root initrd-udevadm-cleanup-db.service loaded inactive dead Cleanup udevd DB ip6tables.service loaded inactive dead IPv6 firewall with ip6tab>太多了,阿铭仅仅列出来一部分。那这些服务对应的启动脚本文件在哪里呢?
# ls /usr/lib/systemd/system/ arp-ethers.service multi-user.target.wants sysinit.target.wants atd.service NetworkManager-dispatcher.service sys-kernel-config.mount auditd.service NetworkManager.service sys-kernel-debug.mount autovt@.service NetworkManager-wait-online.service syslog.socket basic.target network-online.target syslog.target.wants basic.target.wants network-pre.target systemd-ask-password-console.path bluetooth.target network.target systemd-ask-password-console.service文件同样很多,阿铭仅仅列出来一部分。你会发现这个目录下面的文件有点奇怪,有的是目录,有的是文件,有的以.service为后缀,有的以.target为后缀,当然还有其他的格式,这些东西到底是什么?有没有不知所以的感觉?其实阿铭和你一样,有点晕晕的,还是先来看与服务相关的知识点吧,下面是阿铭整理的一些常用命令:
# systemctl enable crond.service #让某个服务开机启动(.service可以省略) # systemctl disable crond.service #不让开机启动 # systemctl status crond.service #查看服务状态 # systemctl start crond.service #启动某个服务 # systemctl stop crond.service #停止某个服务 # systemctl restart crond.service #重启某个服务 # systemctl is-enabled crond #查看某个服务是否开机启动其实关于服务的用法还有不少,但阿铭认为有上面这些就够用了。下面再介绍两个概念,等你看完这部分内容,对于上面不知所以的文件就会有些眉目了。我们先来说一个很重要的概念——unit。刚刚阿铭执行命令ls /usr/lib/systemd/system的时候,下面有很多文件,其实可以把它们归类为下面这几大类。
service:系统服务。
target:多个unit组成的组。
device:硬件设备。
mount:文件系统挂载点。
automount:自动挂载点。
path:文件或路径。
scope:不是由systemd启动的外部进程。
slice:进程组。
snapshot:systemd快照。
socket:进程间通信的套接字。
swap:swap文件。
timer:定时器。
以上每种类型的文件都为一个unit,正是这些unit才组成了系统的各个资源(各个服务、各个设备等)。下面阿铭给大家介绍几个和unit相关的命令:
# systemctl list-units # 列出正在运行(active)的unit # systemctl list-units --all # 列出所有的unit(包括失败的、inactive的) # systemctl list-units --all --state=inactive # 列出所有inactive的unit # systemctl list-units --all --type=service #列出所有状态的service # systemctl list-units --type=service #列出状态为active的service # systemctl is-active crond.service #查看某个unit是否active关于unit,阿铭不再多解释,毕竟我们平时在工作中几乎用不到它。下面再来看另外一个概念——target。target类似于CentOS 6里面的启动级别,但target支持多个target同时启动。target其实是多个unit的组合,系统启动说白了就是启动多个unit,为了管理方便,就使用target来管理这些unit。查看当前系统的所有 target:
# systemctl list-unit-files --type=target // 注意和前面命令的区分 UNIT FILE STATE basic.target static bluetooth.target static cryptsetup-pre.target static cryptsetup.target static ctrl-alt-del.target disabled default.target indirect emergency.target static exit.target disabled final.target static getty-pre.target static getty.target static graphical.target static halt.target disabled hibernate.target static hybrid-sleep.target static initrd-fs.target static查看一个 target 包含的所有 unit,如下所示:
# systemctl list-dependencies multi-user.target multi-user.target ● ├─atd.service ● ├─auditd.service ● ├─chronyd.service ● ├─crond.service ● ├─dbus.service ● ├─dnf-makecache.timer ● ├─firewalld.service ● ├─irqbalance.service ● ├─kdump.service ● ├─NetworkManager.service ● ├─plymouth-quit-wait.service ● ├─plymouth-quit.service ● ├─rsyslog.service ● ├─sshd.service ● ├─sssd.service因为内容太长,阿铭并没有全部列出来,你可以在自己的CentOS 8上全部列出来,显示效果还是很不错的,它以树形的方式列出来,一目了然。下面还有几个关于target的命令:
# systemctl get-default #查看系统默认的target multi-user.target # systemctl set-default multi-user.target #设置默认的target上面提到的multi-user.target等同于CentOS 6的运行级别3,其实还有其他几个target对应0~6运行级别,如下表所示。
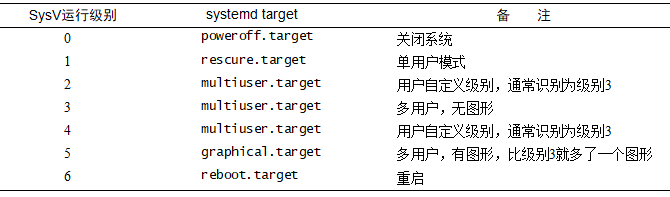
介绍完了unit和target,阿铭再带着你一起梳理一下service、unit以及target之间的联系: (1) 一个service属于一种unit; (2) 多个unit一起组成了一个target; (3) 一个target里面包含了多个service,你可以查看文件/usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service里面[install]部分的内容,它就定义了该service属于哪一个target。
编辑:黄飞
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
- 相关推荐
- 热点推荐
- Linux
-
浅谈ARM嵌入式系统如何学习与入门2019-03-15 4611
-
浅谈Android与Linux系统之间的差异2019-07-05 1918
-
Linux系统中磁盘管理是什么2020-05-11 1765
-
linux系统进程存在状态及管理2020-05-21 1333
-
企业级的LInux系统日志管理2020-05-29 1638
-
Linux电源管理的系统架构和驱动2022-01-03 1998
-
Linux系统管理命令2009-01-18 939
-
Linux系统管理技术手册—奈米斯2011-08-10 610
-
Linux系统管理命令整理及使用方法介绍2018-09-23 7366
-
Linux操作系统实用教程之如何Linux系统的远程管理2018-10-31 1344
-
Linux操作系统实用教程之如何进行Linux系统下的编程管理2018-11-01 1228
-
Linux应用基础教程之Linux如何进行系统管理2018-11-28 965
-
浅谈嵌入式Linux系统2021-06-12 3549
-
Linux系统进程管理入门指南2025-04-22 905
-
Linux系统管理的核心概念2025-05-15 532
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

