

依赖于尺寸和载体的Ptn/X-石墨烯催化剂(X = C、B、N)减弱CO中毒
描述
【原文摘要】
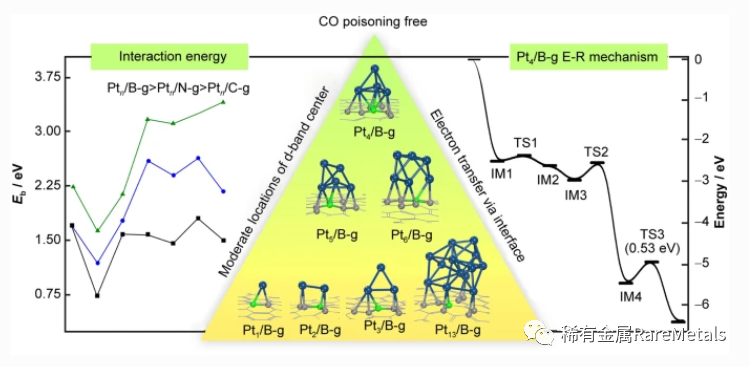
一氧化碳中毒是铂基催化剂应用于电催化过程的主要障碍之一。本文基于DFT+D3 计算,通过B 和N 掺杂石墨 烯并改变团簇尺寸以减弱Pt 催化剂的CO 中毒现象。计算得到了能量上最有利的Ptn/X-石墨烯(X = C, B, N; n = 1‒6, 13)结构,且Ptn 和X-石墨烯之间的结合能依赖于团簇尺寸与载体,顺序为:Ptn/B-g > Ptn/N-g > Ptn/C-g。低 配位及突出的原子作为主要活性位点参与反应。由于d 带中心的位置和界面引起的电子转移,中等大小团簇(n = 4‒6)能有效抑制CO 中毒,具有优异的CO 氧化性能。此外揭示了以第二次CO2 解吸为速控步的E-R 机制主导 的反应路线。Ptn/B-g (n = 4,5,6)对应的活化能垒分别为0.53、0.61 和0.56 eV。这项工作为抗CO 中毒的Ptn/Xg 催化剂在燃料电池中的应用与设计提供了理论指导。
【图文速览】
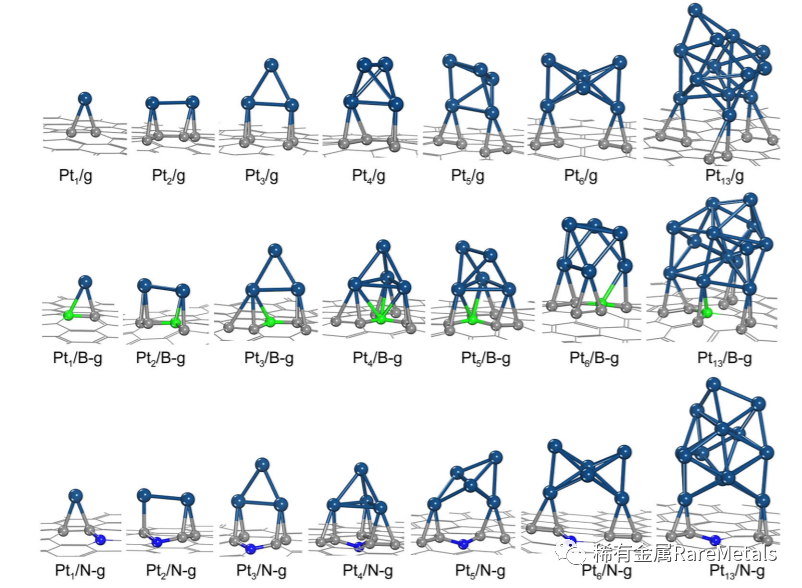
Fig. 1 Configurations of Pt clusters adsorption on pristine and B/N-doped graphenes, where gray, green, blue, and dark bluerepresent C, B, N, and Pt, respectively
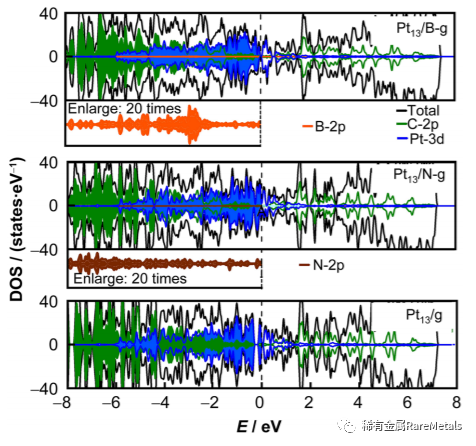
Fig. 2 Normalized total DOS and local DOS of Pt13/X-g X = (C,B, N) with an energy scale from –8.0 to 8.0 eV, wherecontribution from B and N around Fermi level (–8.0 to 0 eV)are energy 20 times in Pt13/B-g and Pt13/N-g, respectively, andFermi level is shift to zero
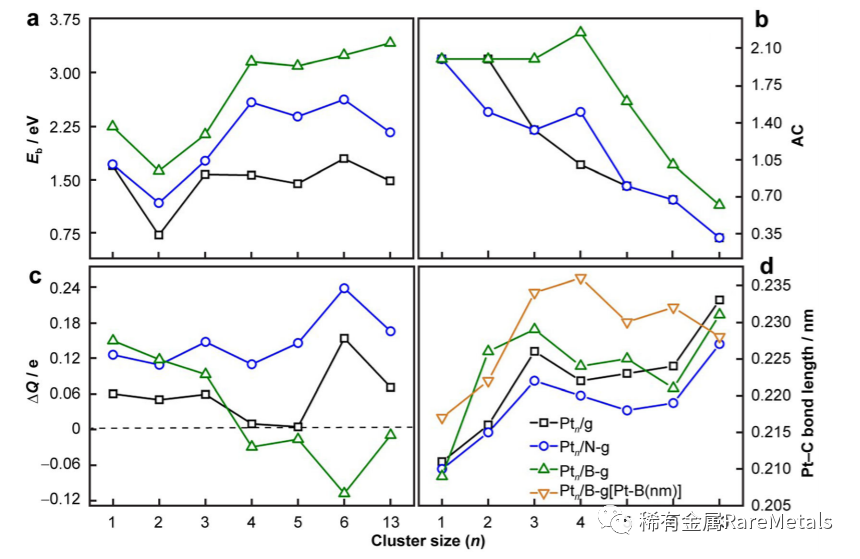
Fig. 3 Interaction between Pt catalyst and doped graphene: a binding energy (Eb); b AC between Pt atom and C/B/N; c average netcharge (DQ(e)) of Pt (± denotes gaining/losing electrons); d geometrical parameters of bond length of Pt-C and Pt-B/N
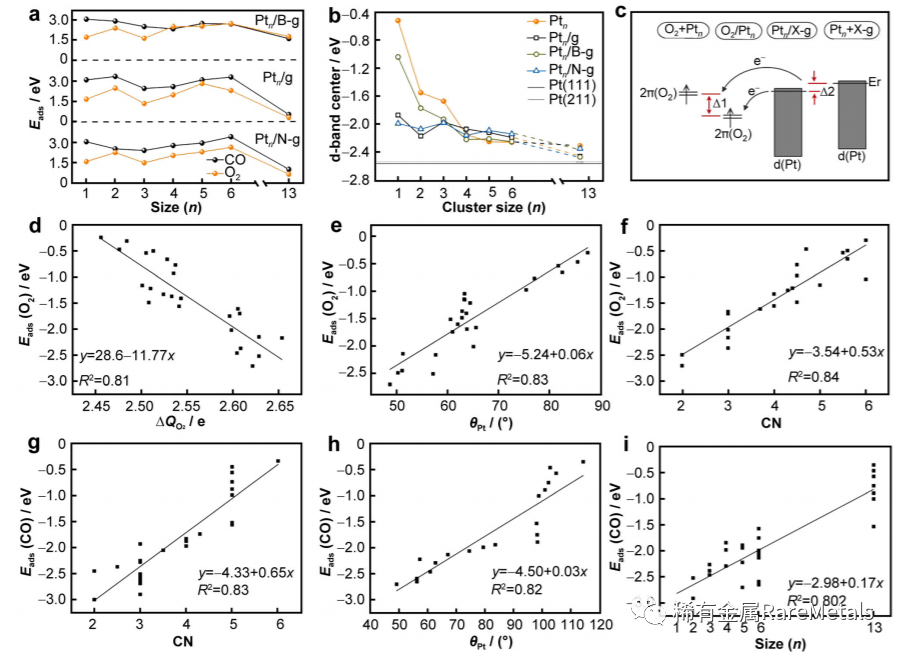
Fig. 4 a Adsorption energy between CO/O2 and Ptn/X-g (X = B, N, and C); b positions of d-band center calculated for Ptn/X-g (X = B,N and C) clusters as a function of cluster size; c illustration of energy level shifts between O2 and Ptn/X-g (X = C, B, N); relationshipbetween O2 adsorption energy and parameters: d QO2, e hPt, and f CN; relationship between CO adsorption energy and parameters:g CN, h hPt, and i n
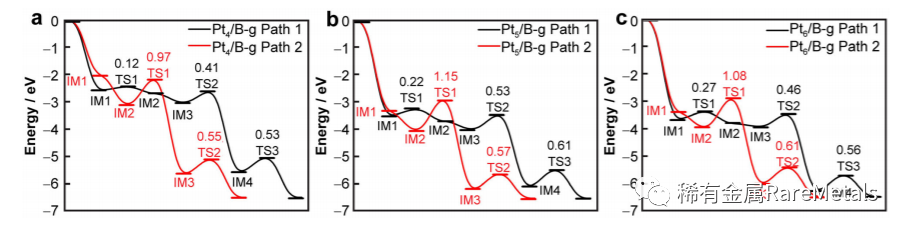
Fig. 5 Potential energy curves for CO oxidation promoted by a Pt4/B-g, b Pt5/B-g, and c Pt6/B-g along Path 1 (black line) and Path 2(red line), respectively, where energies include zero-point energy corrections
审核编辑 :李倩
-
石墨烯负载金属氧化物催化剂的制备方法2023-08-11 2048
-
纳米波纹石墨烯成为强大的催化剂2023-03-31 2013
-
CO2辅助生成富含晶界的Cu催化剂实现高效CO-CO偶联2023-03-17 1774
-
铱酸盐开放骨架衍生的高活性长寿命析氧电催化剂2023-01-31 2038
-
金属簇催化剂的CO2转化反应性和循环性2023-01-09 1346
-
CO2转化为C2产物的高效光催化剂的设计研究2022-11-25 4263
-
“纳米岛”型催化剂突破传统催化剂活性和稳定性的矛盾2022-11-18 1453
-
应变效应对催化剂活性的影响2022-10-26 3190
-
生成CO的催化剂与Cu之间的相互作用2022-08-22 3526
-
一类新的钌基催化剂,采用原位制备技术2022-08-13 2704
-
低结晶和异质结构AuPt-Ru@CNT像高效多功能电催化剂2022-05-31 646
-
高活性生物质碳负载Fe/Pt单原子双功能催化剂开发2021-02-12 3275
-
CH4与CO检测气敏元件中催化剂的制备与反应性能研究2016-12-17 756
-
碱性醇类燃料电池新型催化剂的研究2011-03-11 1905
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

