

Linux内存映射的原理
描述
一、物理地址空间
- 物理地址是处理器在系统总线上看到的地址。使用RISC的处理器通常只实现一个物理地址空间,外围设备和物理内存使用统一的物理地址空间。有些处理器架构把分配给外围设备的物理地址区域称为设备内存。
- 处理器通过外围设备控制器的寄存器访问外围设备,寄存器分为控制器,状态寄存器和数据寄存器三大类。外围设备的寄存器通常被连续地编址,处理器对外围设备寄存编址方式分为:i/o映射方式(i/o-mapped),内存映射方式(memory-mapped)。
- 应用程序只能通过虚拟地址访问外设寄存器,内核提供API函数来把外设寄存器的物理地址映射到虚拟地址空间。
- ARM64(物理地址宽度最大支持48位)架构分为两种内存类型:
- 正常内存(Noramal Memory):包括物理内存和只读存储器(ROM);
- 设备内存(Device Memory):指分配给外围设备寄存器的物理地址区域;
- 设备内存共享属性总是外部共享,缓存属性总是不可缓存(必须绕过处理器的缓存)
- 二、内存映射原理
“内存映射即在进程的虚拟地址空间中创建一个映射,分为两种:
”
- 文件映射:文件支持的内存映射,把文件的一个区间映射到进程的虚拟地址空间,数据源是存储设备上的文件。
- 匿名映射:没有文件支持的内存映射,把物理内存映射到进程的虚拟地址空间,没有数据源。
【原理】:创建内存映射时,在进程的用户虚拟地址空间中分配一个虚拟内存区域。内核采用延迟分配物理内存的策略,在进程第一次访问虚拟页的时候,产生缺页异常。==如果是文件映射,那么分配物理页,把文件指定区间的数据读到物理页中,然后在页表中把虚拟页映射到物理页。如果是匿名映射,就分配物理页,然后在页表中把虚拟页映射到物理页。==(1)两个进程可以使用共享的文件映射实现共享内存。匿名映射通常是私有映射,共享的匿名映射只可能出现父进程和子进程之间。在进程的虚拟地址空间中,代码段和数据段是私有的文件映射,未初始化数据段、堆栈是私有的匿名映射。(2)修改过的脏页面不会立即更新到文件中,可以调用msync来强制同步写入文件。
flowchart LR
task_struct --> mm_struct --> vm_area_struct
三、虚拟内存源码分析
3.1 相关数据结构
struct vm_area_struct {
/* The first cache line has the info for VMA tree walking. */
// 这两个成员分别用来保存该虚拟内存空间的首地址和末地址后第一个字节的地址
unsigned long vm_start; /* Our start address within vm_mm. */
unsigned long vm_end; /* The first byte after our end address within vm_mm. */
/* linked list of VM areas per task, sorted by address */
struct vm_area_struct *vm_next, *vm_prev;
// 如果采用链表组织化,会影响它搜索速度问题,解决此问题采用红黑树(每个进程结构体mm_struct中都
// 创建一颗红黑树,将VMA作为一个节点加入红黑树给中,这样可以提升搜索速度)
struct rb_node vm_rb;
/*
* Largest free memory gap in bytes to the left of this VMA.
* Either between this VMA and vma->vm_prev, or between one of the
* VMAs below us in the VMA rbtree and its ->vm_prev. This helps
* get_unmapped_area find a free area of the right size.
*/
unsigned long rb_subtree_gap;
/* Second cache line starts here. */
struct mm_struct *vm_mm; /* The address space we belong to. */
pgprot_t vm_page_prot; /* Access permissions of this VMA. */
unsigned long vm_flags; /* Flags, see mm.h. */
/*
* For areas with an address space and backing store,
* linkage into the address_space->i_mmap interval tree.
*/
struct {
struct rb_node rb;
unsigned long rb_subtree_last;
} shared;
/*
* A file's MAP_PRIVATE vma can be in both i_mmap tree and anon_vma
* list, after a COW of one of the file pages. A MAP_SHARED vma
* can only be in the i_mmap tree. An anonymous MAP_PRIVATE, stack
* or brk vma (with NULL file) can only be in an anon_vma list.
*/
struct list_head anon_vma_chain; /* Serialized by mmap_sem &
* page_table_lock */
struct anon_vma *anon_vma; /* Serialized by page_table_lock */
/* Function pointers to deal with this struct. */
const struct vm_operations_struct *vm_ops;
/* Information about our backing store: */
unsigned long vm_pgoff; /* Offset (within vm_file) in PAGE_SIZE units, *not* PAGE_CACHE_SIZE */
struct file * vm_file; // 文件,如果是私有的匿名映射,该成员为空指针
void * vm_private_data; /* 指向内存的私有数据 */
#ifndef CONFIG_MMU
struct vm_region *vm_region; /* NOMMU mapping region */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
struct mempolicy *vm_policy; /* NUMA policy for the VMA */
#endif
struct vm_userfaultfd_ctx vm_userfaultfd_ctx;
};
3.2 虚拟内存操作集合
struct vm_operations_struct {
void (*open)(struct vm_area_struct * area); // 在创建虚拟内存区域时调用open方法
void (*close)(struct vm_area_struct * area); // 在删除虚拟内存区域时调用close方法
int (*mremap)(struct vm_area_struct * area); // 使用系统调用mremap移动虚拟内存区域时调用
int (*fault)(struct vm_area_struct *vma, struct vm_fault *vmf); // 访问文件映射的虚拟页时,如果没有映射到物理页,生成
// 缺页异常,异常处理程序调用fault方法来把文件的数据读到文件页缓存当中
int (*pmd_fault)(struct vm_area_struct *, unsigned long address,
pmd_t *, unsigned int flags); // 与fault类似,区别是该方法针对使用透明巨型页的文件映射
/* 读文件映射的虚拟页时,如果没有映射到物理页,生成缺页异常,异常处理程序除了读入正在访问的文件页
还会预读后续文件页,调用map_pages方法在文件的页缓存中分配物理页 */
void (*map_pages)(struct vm_area_struct *vma, struct vm_fault *vmf);
/* notification that a previously read-only page is about to become
* writable, if an error is returned it will cause a SIGBUS */
/* 第一次写私有的文件映射时,生成页错误异常,异常处理程序执行写时复制,调用page_mkwrite方法以
通知文件系统页即将变成可写,以便文件系统检查是否允许写,或者等待页进入合适的状态*/
int (*page_mkwrite)(struct vm_area_struct *vma, struct vm_fault *vmf);
/* same as page_mkwrite when using VM_PFNMAP|VM_MIXEDMAP */
int (*pfn_mkwrite)(struct vm_area_struct *vma, struct vm_fault *vmf);
/* called by access_process_vm when get_user_pages() fails, typically
* for use by special VMAs that can switch between memory and hardware
*/
int (*access)(struct vm_area_struct *vma, unsigned long addr,
void *buf, int len, int write);
/* Called by the /proc/PID/maps code to ask the vma whether it
* has a special name. Returning non-NULL will also cause this
* vma to be dumped unconditionally. */
const char *(*name)(struct vm_area_struct *vma);
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
/*
* set_policy() op must add a reference to any non-NULL @new mempolicy
* to hold the policy upon return. Caller should pass NULL @new to
* remove a policy and fall back to surrounding context--i.e. do not
* install a MPOL_DEFAULT policy, nor the task or system default
* mempolicy.
*/
int (*set_policy)(struct vm_area_struct *vma, struct mempolicy *new);
/*
* get_policy() op must add reference [mpol_get()] to any policy at
* (vma,addr) marked as MPOL_SHARED. The shared policy infrastructure
* in mm/mempolicy.c will do this automatically.
* get_policy() must NOT add a ref if the policy at (vma,addr) is not
* marked as MPOL_SHARED. vma policies are protected by the mmap_sem.
* If no [shared/vma] mempolicy exists at the addr, get_policy() op
* must return NULL--i.e., do not "fallback" to task or system default
* policy.
*/
struct mempolicy *(*get_policy)(struct vm_area_struct *vma,
unsigned long addr);
#endif
/*
* Called by vm_normal_page() for special PTEs to find the
* page for @addr. This is useful if the default behavior
* (using pte_page()) would not find the correct page.
*/
struct page *(*find_special_page)(struct vm_area_struct *vma,
unsigned long addr);
};
四、系统调用
“”
- 应用程序通常使用C标准库提供的函数malloc()申请内存。glibc库的内存分配器ptmalloc使用brk或mmap向内核以页为单位申请虚拟内存,然后把页划分成小内存块分配给应用程序。默认的阈值是128kb,如果应用程序申请的内存长度小于阈值,ptmalloc分配器使用brk向内核申请虚拟内存,否则ptmalloc分配器使用mmap向内核申请虚拟内存。
- 应用程序可以直接使用mmap向内核申请虚拟内存。
【回顾mmap内存映射原理三个阶段】:
- 进程启动映射过程,并且在虚拟地址空间中为映射创建虚拟映射区域;
- 调用内核空间的系统调用函数mmap(不同于用户空间函数),实现文件物理地址和进程虚拟地址的一一映射关系;
- 进程发起对这片映射空间的访问,引发缺页异常,实现文件内容到物理内存(主存)的拷贝。
内存管理子系统提供以下常用系统调用函数:
- mmap() ---->创建内存映射
“#include
”void *mmap(void *addr, size_t length, int prot, int flags, int fd, off_t offset);
- 系统调用mmap():进程创建匿名的内存映射,把内存的物理页映射到进程的虚拟地址空间。进程把文件映射到进程的虚拟地址空间,可以像访问内存一样访问文件,不需要调用系统调用read()/write()访问文件,从而避免用户模式和内核模式之间的切换,提高读写文件速度。两个进程针对同一个文件创建共享的内存映射,实现共享内存。
- munmap() ---->删除内存映射
“#include
”int munmap(void *addr, size_t len);
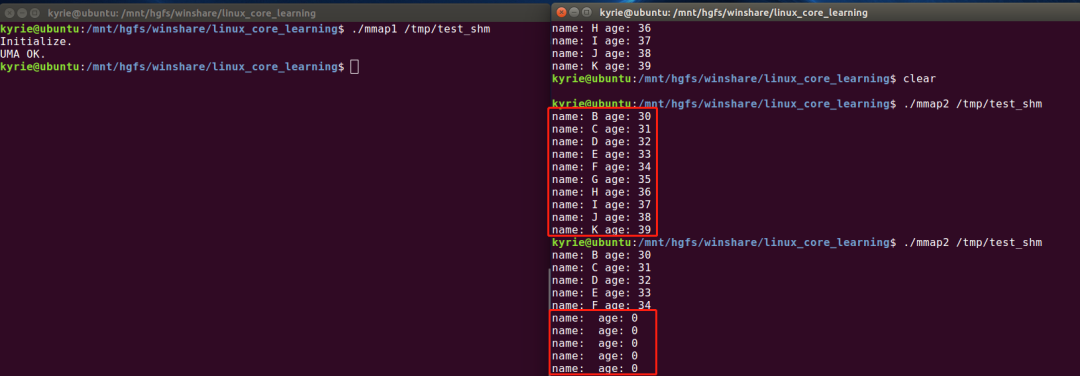
代码实践
#include
#include
运行结果
审核编辑:陈陈
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
-
拆解mmap内存映射的本质!2024-01-24 3134
-
Linux 内存管理总结2023-11-10 1174
-
关于Linux内存管理的详细介绍2023-03-06 1391
-
[4.5.1]--4.5动手实践-Linux内存映射基础(上)jf_75936199 2023-02-25
-
Linux内存映射与页表详解2022-08-18 1472
-
Linux内核之内存映射原理分析2022-07-21 2808
-
浅析linux内存映射原理2019-08-24 1932
-
RTOS和Linux中的内存映射及移植方法2019-07-03 2683
-
Linux内核地址映射模型与Linux内核高端内存详解2018-05-08 3770
-
从史前文明到女娲补天:Linux内存逆向映射(reverse mapping)技术的前世今生2017-09-06 11002
-
Linux的mmap文件内存映射机制2017-03-08 3021
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

