

C++中动态类型的识别
描述
大家好,我是情报小哥~
1、所要解决的问题
在前面的相同专辑文章中,跟大家介绍过虚函数,其中提到了基类的指针可以指向派生类,同时基类的引用也可以成为派生类的别名。
比如是非常经典的例子:
#include class Child: public Parent
{
public:
void print(void)
{
cout<<"child print"<void Test1(Parent *ptr)
{
ptr->print();
}
void Test2(Parent& p)
{
p.print();
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
Child child;
Parent parent;
Test1(&child);
Test1(&parent);
Test2(child);
Test2(parent);
return 0;
}
这样其输出的结果如下:
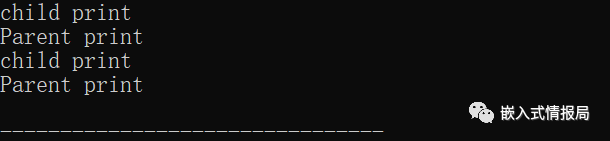
由于存在虚函数的重写,所以其函数调用都是跟随传入的对象类型,这就是多态;当然如果此例子中Parent类中的print没有virtual虚函数标识,则编译器会认为传入的就是父类指针,从而只会调用父类的成员。
而从Test1或者Test2对象内部看来并不能知道传参是子类型还是父类型:
void Test1(Parent *ptr)
{
Child* ptrChild = (Child *)ptr;
ptrChild->dosomething(); //调用派生类成员
}
如上代码如果传入的参数是子类对象,那么函数内部用子类类型指向该对象是正常运行的,但如果此时传入的是父类对象,而强制转化为子类指针来使用,则程序就有可能出现未知错误。
所以这里也引出来两个概念:静态类型与动态类型
静态类型: 即编译期间所确定的变量类型;
动态类型: 在运行过程中指针或者引用所指向对象的实际类型。
基于上面的风险,我们急需有一种手段来识别变量的动态类型,以进行相应的处理,我们通常叫其为:RTTI(Run-Time Type Identification,运行时类型识别)
2、进行动态类型识别的方法
进行动态类型识别的方法挺多的,比如利用多态对派生类进行相应ID的标识等等,不过推荐还是采用typeid的方式。
typeid关键字能够获得任意变量的类型信息,也是C++专门提供用于类型识别的方式。
那么下面我们就用一个例程在看看typeid如何使用的:
#include class Child: public Parent
{
public:
void print(void)
{
cout<<"child print"<void dosomething(void)
{
cout<<"dosomething"<void Test1(Parent *ptr)
{
if( typeid(*ptr) == typeid(Child) ) //具体使用方式 Child
{
Child* ptrChild = dynamic_cast(ptr);
cout<<"**Dynamic Type: "<<"Child"<dosomething();
}
else if( typeid(*ptr) == typeid(Parent) ) //Parent
{
cout<<"**Dynamic Type: "<<"Parent"<print();
}
}
void Test2(Parent& p)
{
if( typeid(p) == typeid(Child) ) //具体使用方式 Child
{
Child& ptrChild = (Child&)p;
cout<<"**Dynamic Type: "<<"Child"<dosomething();
}
else if( typeid(p) == typeid(Parent) ) //Parent
{
cout<<"**Dynamic Type: "<<"Parent"<print();
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
Child child;
Parent parent;
Test1(&child);
Test1(&parent);
cout<Test2(child);
Test2(parent);
cout<const type_info& tparent = typeid(parent);
const type_info& tchild = typeid(child);
cout<name()<name()<return 0;
}
其输出结果如下:

结果看每种指针或者引用的类型均可以动态且正确的获得识别,挺方便的。
最后有几点需要注意下:
1、typeid返回值是名为type_info的标准库类型的对象引用。
2、type_Info的name返回的是一个字符串,且其类名与实际程序中类型不一定是一致的,但是肯定是唯一标识字符串,通过上面输出结果大家也是可以了解到的。
最 后
好了,这里小哥就简单介绍了C++中动态识别机制的使用,本系列文章后续还会更新,记得关注学习哦。
-
C++中实现类似instanceof的方法2024-07-18 1345
-
动态数组和C++ std::vector详解2023-07-19 2110
-
C和C++编写环境下LabVIEW如何调用动态库?2023-06-11 9882
-
C++入门之string2023-03-17 1106
-
现代C++之模板类型推导2023-03-02 1574
-
C++打印类型名称的分析与实现2022-10-20 1864
-
C++中的四种类型转换分别是哪些?C++中析构函数的作用是什么2021-12-24 1432
-
c++ 之布尔类型和引用的学习总结2020-12-24 1125
-
C++语法的外围基础2018-03-15 794
-
关于C++中的函数重载机制2016-10-01 1923
-
labview调用c++中的取地址符对应labview什么数据类型?2016-08-18 5259
-
C++的动态多态和静态多态2011-06-29 708
-
人脸识别C/C++源代码2010-02-09 1496
-
C++静态分析中对泛型构件的识别与表示方法2009-08-17 721
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

