

词法分析-Antlr-1
描述
在上一节中我们提到了,我们可以根据一种叫 有限自动机 的东西将字符串分割成多个Token。
下面是一段swift代码,其中实现了一些基础Token的解析,原理就是: 有限自动机
//
// ScriptLexer.swift
// MyScriptCompiler
//
// Created by legendry on 2019/8/21.
// Copyright © 2019 legendry. All rights reserved.
//
import Foundation
/// 脚本语言词法分析器
public class ScriptLexer {
public enum ScriptLexer: Error {
/// 源码为空
case SourceCodeEmpty
/// 语法错误
case SyntaxError(reason: String)
}
/// 词法分析器的有限状态机状态
var fsmType = FSMType.Initial
/// 默认token为nil
var token: ScriptToken? = nil
var _tmpTokens = [ScriptToken]()
/// 初始化新的token
/// 将状态机迁移到新的状态
private func initToken(_ c: UInt8) throws -> FSMType {
var _fsmType = FSMType.Unknow
if let _t = token {
/// 将解析到的token保存起来
_tmpTokens.append(_t)
token = nil
}
if c.isLetter {
/// 当我们解析到字符i时,当前认为他是一个标识符
token = ScriptToken(type: .Identifier)
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
if c.char == "i" {
/// 状态机状态切换至标识符i,如果后续是nt并以空格结束,则解析成int
/// 否则解析成标识符
_fsmType = .Identifier_Int_i
} else {
_fsmType = .Identifier
}
} else if c.char == "=" {
token = ScriptToken(type: .EQ)
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
_fsmType = .EQ
} else if c.isDigit {
token = ScriptToken(type: .IntLiteral)
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
_fsmType = .IntLiteral
} else if c.char == ">" {
token = ScriptToken(type: .GT)
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
_fsmType = .GT
} else if c.char == "<" {
token = ScriptToken(type: .LT)
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
_fsmType = .LT
} else if c.char == "-" {
token = ScriptToken(type: .Minus)
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
_fsmType = .Minus
} else if c.char == "*" {
token = ScriptToken(type: .Star)
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
_fsmType = .Star
} else if c.char == "+" {
token = ScriptToken(type: .Plus)
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
_fsmType = .Plus
} else if c.char == "/" {
token = ScriptToken(type: .Slash)
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
_fsmType = .Slash
} else if c.char == "(" {
token = ScriptToken(type: .LeftBracket)
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
_fsmType = .LeftBracket
} else if c.char == ")" {
token = ScriptToken(type: .RightBracket)
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
_fsmType = .RightBracket
} else {
if c.isValid {
_fsmType = .Initial
} else {
throw ScriptLexer.SyntaxError(reason: "不支持: \\(c.char)")
}
}
return _fsmType
}
/// 解析脚本,生成Token
/// 利用有限状态自动机在不同状态之间迁移得到不同的Token
/// int age = 45
/// age >= 3
public func analysis(script: String) throws -> ScriptTokenReader {
_tmpTokens.removeAll()
fsmType = FSMType.Initial
token = nil
guard script.count > 0 else {
throw ScriptLexer.SourceCodeEmpty
}
let charReader = CharReader(script)
/// 开始分析源码
while let c = charReader.read() {
switch fsmType {
case .Initial:
self.fsmType = try initToken(c)
case .Identifier_Int_i:
/// 第一个字母是i,如果第二个字母是n则状态机迁移至Identifier_Int_n
/// 否则状态机迁移至Identifier
if c.char == "n" {
self.fsmType = .Identifier_Int_n
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
} else if c.isTail {
/// 当前token标识完成
/// 状态机重置
self.fsmType = try initToken(c)
} else {
/// 状态机迁移至标识符状态,继续解析标识符token
self.fsmType = .Identifier
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
}
case .Identifier_Int_n:
if c.char == "t" {
self.fsmType = .IntLiteral
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
/// 这里暂时将类型切换成Int,如果后面还有字符则表式是一个标识符,再切换类型
token?.type = .Int
} else if c.isTail {
/// 当前token标识完成
/// 状态机重置
self.fsmType = try initToken(c)
} else {
/// 状态机迁移至标识符状态,继续解析标识符token
self.fsmType = .Identifier
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
}
case .IntLiteral:
if c.isTail {
/// 当前token标识完成
/// 状态机重置
self.fsmType = try initToken(c)
} else if c.char == "+" || c.char == "-" || c.char == "*" || c.char == "/" /*|| c.char == "(" || c.char == ")"*/ {
self.fsmType = try initToken(c)
} else if c.isLetter {
throw ScriptLexer.SyntaxError(reason: "非数字字面量")
} else {
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
}
case .Identifier:
if c.isTail {
self.fsmType = try initToken(c)
} else {
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
}
case .EQ:
if c.isTail {
token?.type = .Assignment
self.fsmType = try initToken(c)
} else {
throw ScriptLexer.SyntaxError(reason: "语法异常")
}
case .GE, .LE:
if c.isTail {
self.fsmType = try initToken(c)
} else {
throw ScriptLexer.SyntaxError(reason: "语法异常")
}
case .LeftBracket, .RightBracket:
self.fsmType = try initToken(c)
case .GT:
if c.isTail {
self.fsmType = try initToken(c)
} else if c.char == "=" {
self.fsmType = .GE
token?.type = .GE
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
} else {
throw ScriptLexer.SyntaxError(reason: "语法异常")
}
case .LT:
if c.isTail {
self.fsmType = try initToken(c)
} else if c.char == "=" {
self.fsmType = .LE
token?.type = .LE
token?.appendTokenText(c: c)
} else {
throw ScriptLexer.SyntaxError(reason: "语法异常")
}
case .Minus, .Plus, .Star, .Slash:
if c.isTail || c.isDigit {
self.fsmType = try initToken(c)
} else {
throw ScriptLexer.SyntaxError(reason: "语法异常")
}
default: break
}
}
if let _t = token {
/// 将解析到的token保存起来
_tmpTokens.append(_t)
token = nil
}
let tokenReader = ScriptTokenReader.init(_tmpTokens)
return tokenReader
}
}
如果要快速落地一个DSL原型Demo,全部都自己去写似乎有点慢。所以我们需要借助于工具来帮我们解析Token, 这个工具叫做: Antlr https://www.antlr.org/
这个工具支持很多语言,C++,Swift,Java....,常用的编码语言都可以。你可以选择一个合适你的语言来实现DSL了。
下载并配置好Antlr,Antlr本身是Java实现的,所以你的环境要运行Antlr需要有Java运行时环境。
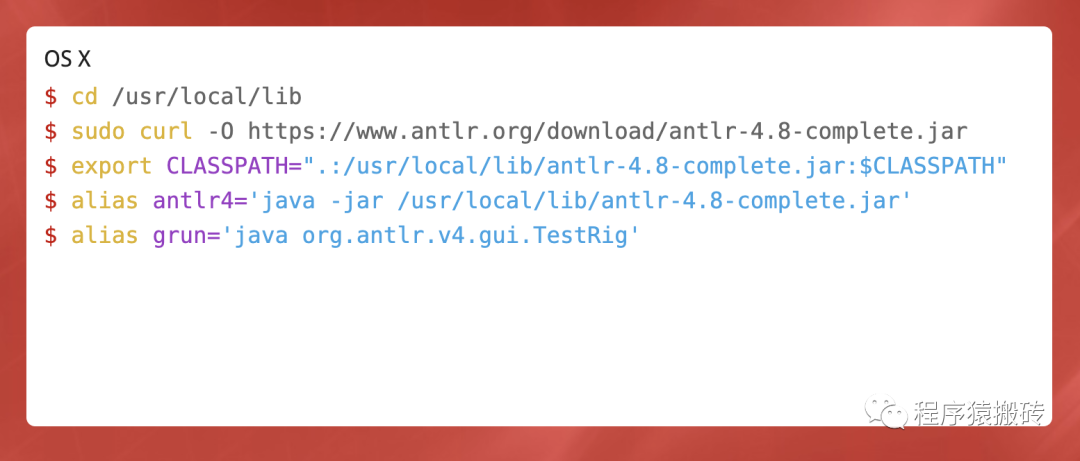
配置好Antlr之后,我们就可以借助Antlr来实现我们的词法分析了。Antlr通过解析规则文件来分析我们要分割的Token的规则,规则则是用正则表达式来书写。
lexer grammar FlexDSLLexer;
//关键字
If: 'if';
FOR: 'for';
WHILE: 'while';
IN: 'in';
/// 基础数据类型
Int: 'int';
Double: 'double';
Float: 'float';
True: 'true';
False: 'false';
//字面量
IntLiteral: [0-9]+;
DoubleLiteral: [0-9] . [0-9]*;
StringLiteral: '"' .*? '"'; //字符串字面量
//操作符
AssignmentOP: '=';
RelationalOP: '>' | '>=' | '<' | '<=';
Star: '*';
Plus: '+';
Sharp: '#';
SemiColon: ';';
Dot: '.';
Comm: ',';
LeftBracket: '[';
RightBracket: ']';
LeftBrace: '{';
RightBrace: '}';
LeftParen: '(';
RightParen: ')';
//标识符
Id: [a-zA-Z_] ([a-zA-Z_] | [0-9])*;
//空白字符,抛弃
Whitespace: [ \\t]+ -> skip;
Newline: ( '\\r' '\\n'? | '\\n') -> skip;
以上的规则文件内容指定了我们要从字符串中解析出来的Token,每一个Token都有一个名字,后面对应的则是这个Token的规则。把这个文件保存到FlexDSLLexer.g4
然后通过命令来编译
antlr4 FlexDSLLexer.g4
编译完成得到如下文件
 然后使用
然后使用
javac *.java
编译完成之后,通过运行grun命令来解析并输出对应的Token(s)
grun FlexDSLLexer tokens -tokens Hello.play
其中Hello.play内容如下
int name = "人\\n字";
true
false
最后得到如下输出,不仅成功的解析出来了我们指定的Token,还把对应的行列都输出了。这样当我们在解析出错时也可以报具体的错误信息了。 到此,我们的词法解析就完成了,接下来我们将进行语法分析。
到此,我们的词法解析就完成了,接下来我们将进行语法分析。
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
-
手写词法分析器2023-05-23 1161
-
语法分析-Antlr2023-03-03 1476
-
#硬声创作季 4.2.1 词法分析器的结构Mr_haohao 2022-09-01
-
语言与编译器设计课程之词法分析程序源程序2020-07-01 763
-
手写SQL编译器词法分析2020-05-26 2033
-
词法作用域和闭包2019-05-20 1994
-
postgreSQL命令的词法分析和语法分析2019-05-16 1493
-
Hanlp分词之CRF中文词法分析详解2019-02-18 3438
-
关于antlr词法分析器的使用2014-11-12 3543
-
基于ANTLR的试卷识别和导入系统2011-04-27 741
-
借助Lex和Yacc进行词法语法分析2011-04-18 1788
-
C语言词法分析器的代码2010-10-10 545
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

