

使用TRACE_EVENT定义tracepoint的方式
描述
内核的各个子系统已经有大量的跟踪点,如果这些跟踪点无法满足工作中的需求,可以自己手动添加跟踪点。
添加跟踪点有两种方式,一种是仿照events/目录下的跟踪点,使用TRACE_EVENT() 宏添加。另一种是参考内核目录samples/trace_events添加。本文对这两种方式分别进行介绍。
使用 TRACE_EVENT 定义 tracepoint
我们仿照events/timer/timer_start,添加一个timer_stat的跟踪点,获取start_pid和slack参数。
首先,需要在include/trace/events/timer.h头文件种添加名为timer_stat的跟踪点。
/**
* timer_stat - ftrace interface timer_stat
* @timer: pointer to struct timer_list
*/
TRACE_EVENT(timer_stat,
TP_PROTO(struct timer_list *timer),
TP_ARGS(timer),
TP_STRUCT__entry(
__field( void *, timer )
__field( int, start_pid )
__field( int, slack)
),
TP_fast_assign(
__entry->timer = timer;
__entry->start_pid = timer->start_pid;
__entry->slack = timer->slack;
),
TP_printk("ftrace interface timer_stat:timer=%p pid=%d slack=%d
",
__entry->timer,__entry->start_pid,__entry->slack)
);
TRACE_EVENT()宏如下
#define TRACE_EVENT(name, proto, args, struct, assign, print) DEFINE_TRACE(name)
name:表示跟踪点的名字,如上面的timer_stat。
proto:表示跟踪点调用的入参的原型,比如timer类型为struct timer_list *。
args:表示参数。
struct:定义跟踪器内部使用的__entry数据结构。
assign:把参数复制到__entry数据结构中。
print:定义输出的格式。
接着在kernel/kernel/time/timer.c debug_activate()添加trace_timer_stat()。
static inline void
debug_activate(struct timer_list *timer, unsigned long expires)
{
debug_timer_activate(timer);
trace_timer_start(timer, expires, timer->flags);
trace_timer_stat(timer);
}
重新编译内核后,烧写到设备中,即可看到sys节点已经有了新增的跟踪点。
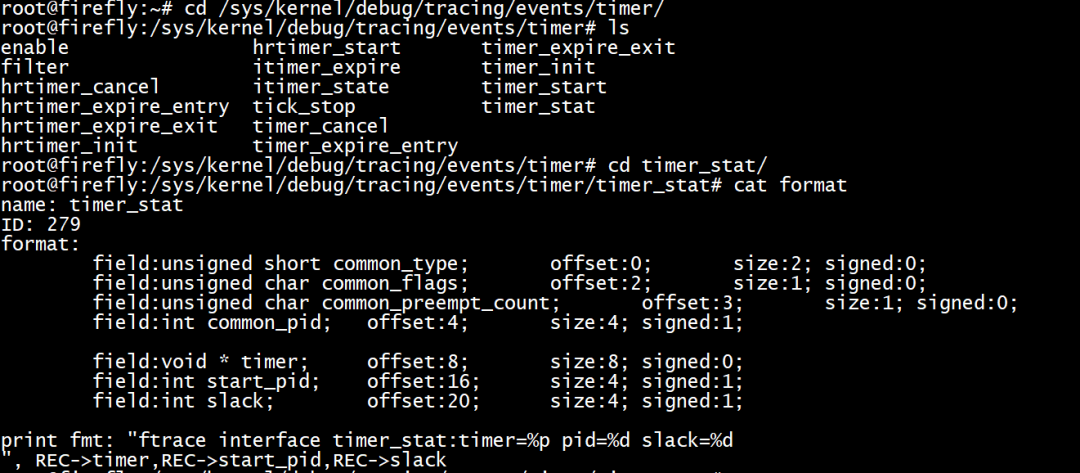
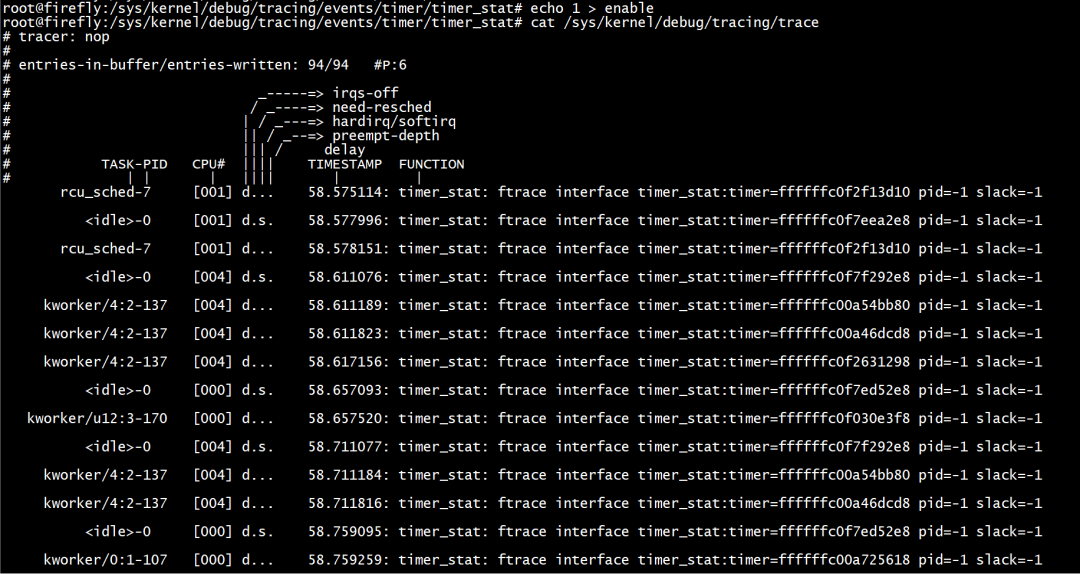
使能跟踪点后,查看trace点的输出。
编译为独立的ko文件
内核还提供了一个跟踪点的例子,在samples/trace_events 目录下。
trace_event_init()创建内核线程一个名为event-sample内核线程。
static int __init trace_event_init(void)
{
simple_tsk = kthread_run(simple_thread, NULL, "event-sample");
if (IS_ERR(simple_tsk))
return -1;
return 0;
}
kthread_should_stop()用于创建的线程检查结束标志,并决定是否退出。
static int simple_thread(void *arg)
{
int cnt = 0;
while (!kthread_should_stop())
simple_thread_func(cnt++);
return 0;
}
set_current_state() 来设置进程的状态,设置为TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE表示是可以被信号和wake_up()唤醒的,当信号到来时,进程会被设置为可运行。
schedule_timeout()将当前task调度出cpu,重新调度间隔为HZ。接着trace_开头的函数就会依次打印跟踪点的信息。
static void simple_thread_func(int cnt)
{
int array[6];
int len = cnt % 5;
int i;
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
schedule_timeout(HZ);
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
array[i] = i + 1;
array[i] = 0;
/* Silly tracepoints */
trace_foo_bar("hello", cnt, array, random_strings[len],
tsk_cpus_allowed(current));
trace_foo_with_template_simple("HELLO", cnt);
trace_foo_bar_with_cond("Some times print", cnt);
trace_foo_with_template_cond("prints other times", cnt);
trace_foo_with_template_print("I have to be different", cnt);
}
trace_foo_with_template_simple跟踪点的实现方式也是使用的TRACE_EVENT ()宏,这里不再赘述。
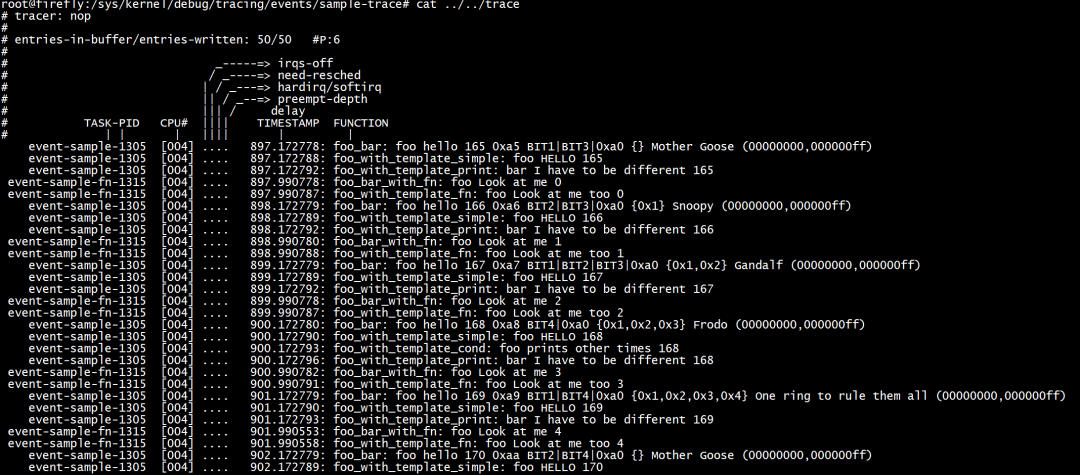
最后将文件编译为ko拷贝到设备上insmod后,即可看到sys目录下已经有新增的节点。
cd /home/zhongyi/code/rk3399_linux_release_v2.5.1_20210301/kernel/samples/trace_events make -C /home/zhongyi/code/rk3399_linux_release_v2.5.1_20210301/kernel/ M=$(pwd) modules
root@firefly:/sys/kernel/debug/tracing# cat available_events | grep sample sample-trace:foo_bar sample-trace:foo_bar_with_cond race:foo_bar_with_fn sample-trace:foo_with_template_simple sample-trace:foo_with_template_cond sample-trace:foo_with_template_fn sample-trace:foo_with_template_print power:pstate_sample
root@firefly:/sys/kernel/debug/tracing# cd events/sample-trace/ root@firefly:/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/sample-trace# ls enable foo_bar_with_cond foo_with_template_fn filter foo_bar_with_fn foo_with_template_print foo_bar foo_with_template_cond foo_with_templ_simple root@firefly:/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/sample-trace# echo 1 > enable root@firefly:/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/sample-trace# cat /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace
TRACE_EVENT_CONDITION()
在某些情况下,跟踪点只有在某个条件发生时才会被调用,类似于
if (cond) trace_foo();
TRACE_EVENT_CONDITION()宏就是这个作用,它和TRACE_EVENT()相比只是在参数中多加了一个cond条件。TP_CONDITION()会对条件做个判断。
TRACE_EVENT(name, proto, args, struct, assign, printk) TRACE_EVENT_CONDITION(name, proto, args, cond, struct, assign, printk)
详细使用方法可以参考trace-events-sample.h。
TRACE_EVENT_FN()
TRACE_EVENT_FN()是在跟踪点使能前和使能后分别打印一些信息。相比于TRACE_EVENT(),TRACE_EVENT_FN()多了两个参数reg和unreg,
TRACE_EVENT(name, proto, args, struct, assign, printk) TRACE_EVENT_FN( name, proto, args, struct, assign, printk, reg, unreg)
reg 和unreg原型为
void reg(void)
reg函数在跟踪点使能前打印,unreg函数在跟踪点使能后打印。reg 和unreg可以根据实际情况置其中一个为NULL,也可以全部置为NULL。
详细使用方法可以参考trace-events-sample.h。
审核编辑:刘清
-
如何对基于μTrace和Trace32的LPC86x进行边界扫描2023-08-17 510
-
Linux ftrace工具宏定义2023-07-20 1472
-
Trace功能的添加、组态及测试2023-03-08 2026
-
heap_trace_init_tohost 的 sysviewtrace_proc解析错误如何解决?2023-03-02 352
-
Systemverilog event的示例2022-10-17 2216
-
劳特巴赫trace32使用介绍(一)2021-12-28 4012
-
怎样通过trace生成系统cpu的loading图2021-06-28 1609
-
Trace - Deembed Files2021-02-01 553
-
利用tracepoint梳理调度器框架及主要流程2020-10-30 2747
-
Best Trace路由跟踪工具2018-04-13 786
-
TRACE32多核策略2017-09-12 863
-
Trace thickness2009-12-29 1775
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

