

11个C++代码片段助您解决日常编程问题
嵌入式技术
1412人已加入
描述
C++ 是使用最广泛的编程语言之一。它每天被数百万程序员使用,是竞争性编程的首选语言。在这里,我们列出 11 个 C++ 代码片段,它们可以帮助您解决日常编程问题。现在,让我们开始吧。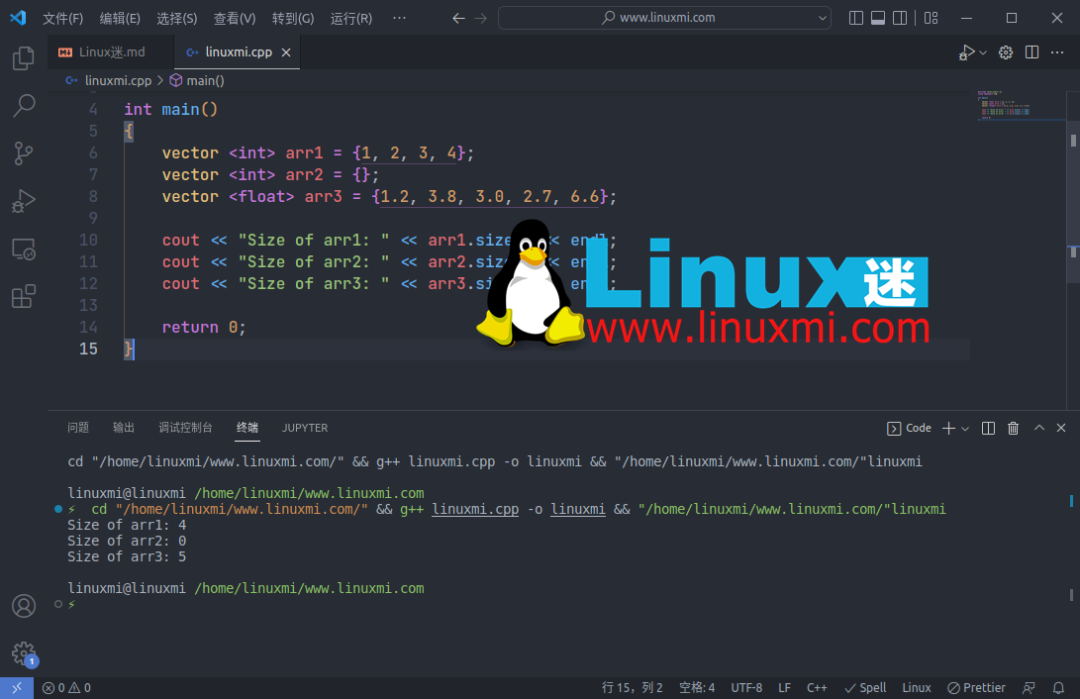
 有时直接理解复杂的代码并不容易。您应该遵循一些基本的编程原则,例如记录代码、重构等,以使您的代码更加健壮。
有时直接理解复杂的代码并不容易。您应该遵循一些基本的编程原则,例如记录代码、重构等,以使您的代码更加健壮。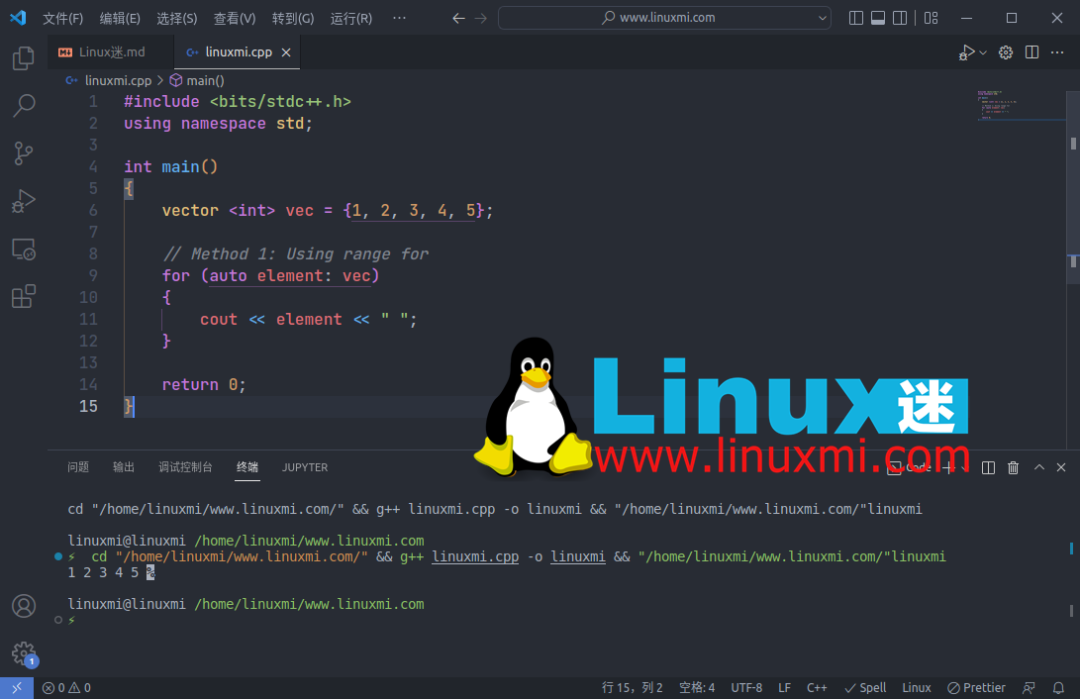
1. 找出向量的大小
您可以使用size()函数找到向量的大小。
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector <int> arr1 = {1, 2, 3, 4};
vector <int> arr2 = {};
vector <float> arr3 = {1.2, 3.8, 3.0, 2.7, 6.6};
cout << "Size of arr1: " << arr1.size() << endl;
cout << "Size of arr2: " << arr2.size() << endl;
cout << "Size of arr3: " << arr3.size() << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
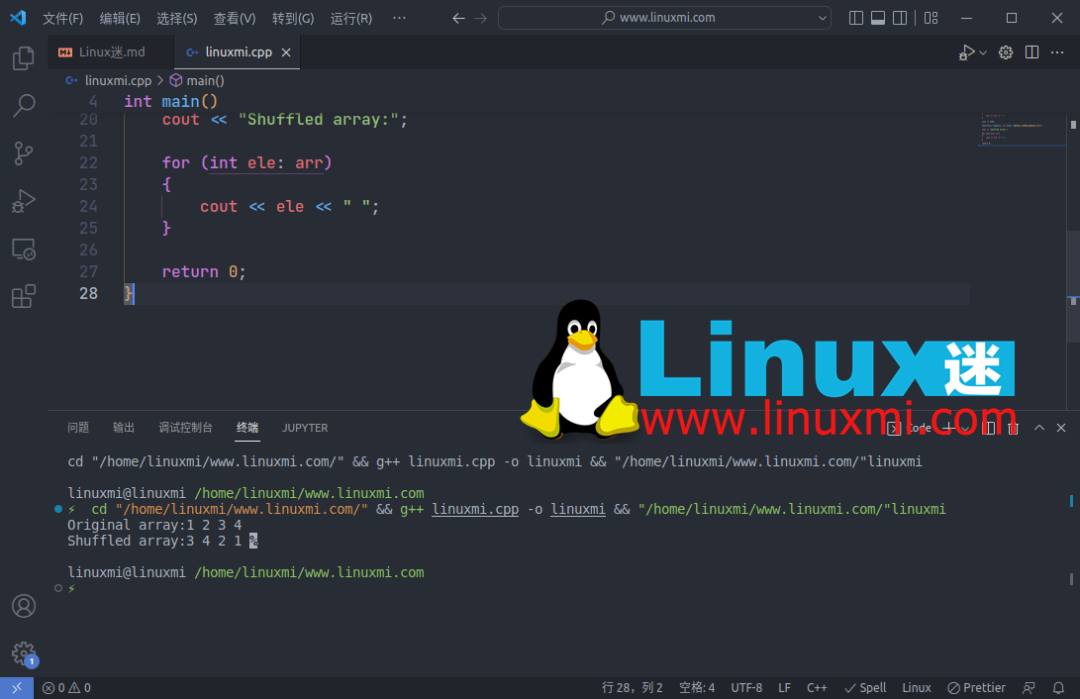
2. 随机排列数组
您可以使用shuffle()函数在 C++ 中对数组进行随机排列。
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector <int> arr = {1, 2, 3, 4};
unsigned seed = 0;
cout << "Original array:";
for (int ele: arr)
{
cout << ele << " ";
}
cout << endl;
shuffle(arr.begin(), arr.end(), default_random_engine(seed));
cout << "Shuffled array:";
for (int ele: arr)
{
cout << ele << " ";
}
return 0;
}
输出:
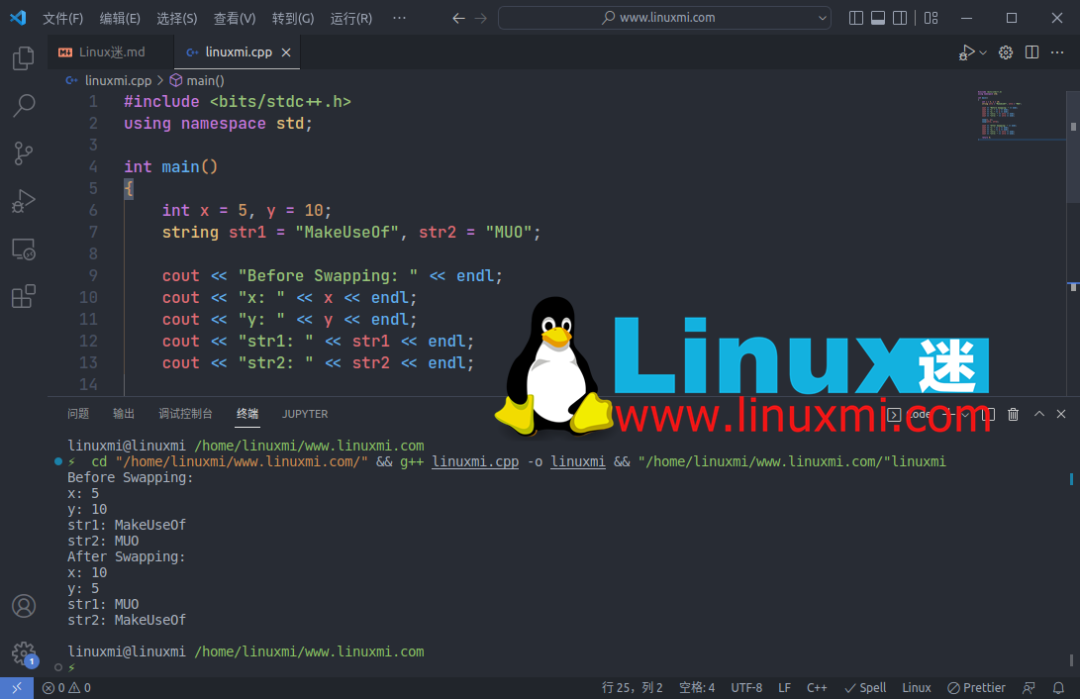
3. 在 C++ 中交换两个变量
您可以使用 C++ STL 库的内置 swap() 函数在 C++ 中交换两个变量。
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = 5, y = 10;
string str1 = "MakeUseOf", str2 = "MUO";
cout << "Before Swapping: " << endl;
cout << "x: " << x << endl;
cout << "y: " << y << endl;
cout << "str1: " << str1 << endl;
cout << "str2: " << str2 << endl;
swap(x, y);
swap(str1, str2);
cout << "After Swapping: " << endl;
cout << "x: " << x << endl;
cout << "y: " << y << endl;
cout << "str1: " << str1 << endl;
cout << "str2: " << str2 << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
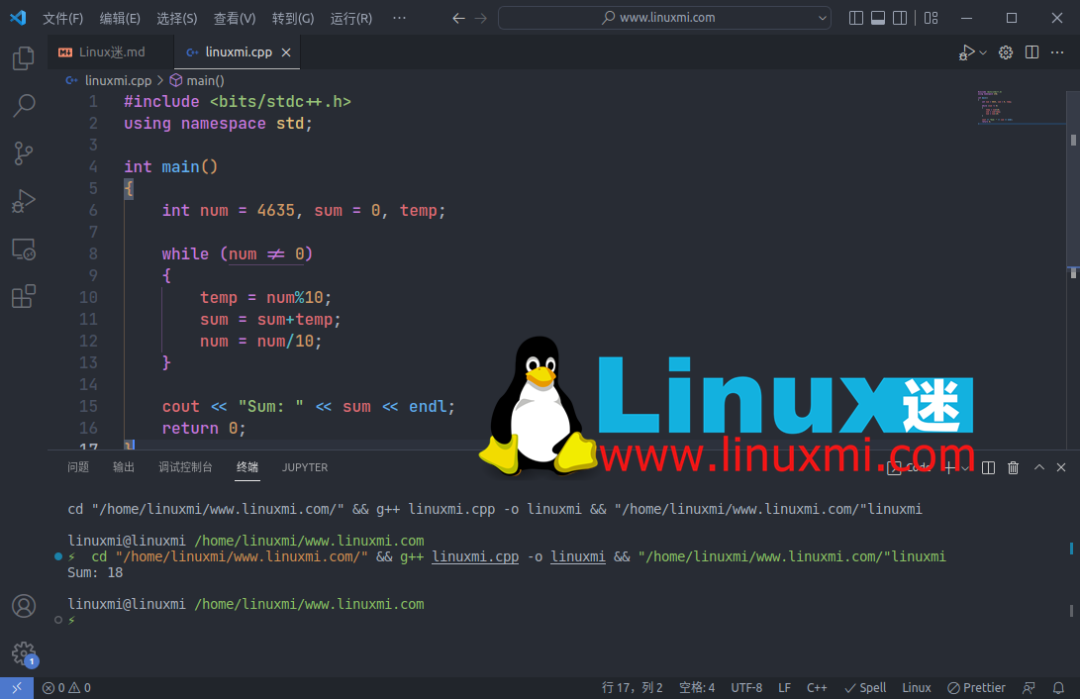
4. 求一个数的位数之和
您可以使用以下过程找到数字的数字总和:- 初始化一个 sum 变量来存储结果。
- 通过对 10 执行取模运算来找到数字的余数。
- 将余数与总和相加。
- 将数字除以 10。
- 当数字大于 10 时,从步骤 2 开始重复该过程。
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num = 4635, sum = 0, temp;
while (num != 0)
{
temp = num%10;
sum = sum+temp;
num = num/10;
}
cout << "Sum: " << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
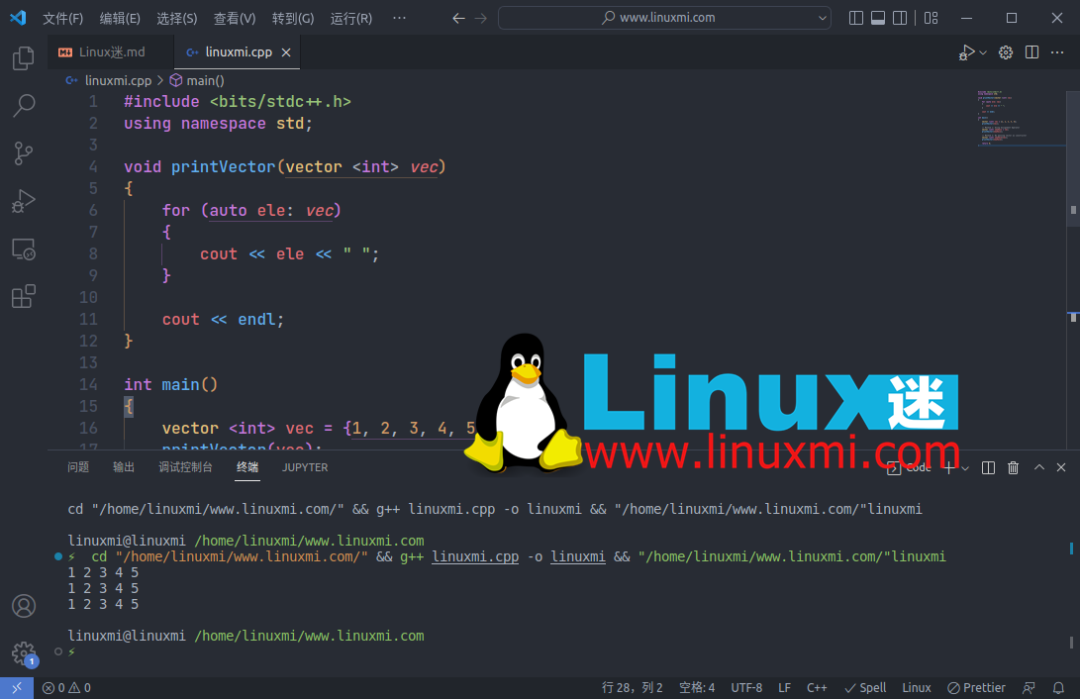
5. 将一个向量复制到另一个向量
在 C++ 中有多种方法可以将一个向量复制到另一个向量。您可以使用赋值运算符或将向量作为构造函数传递来执行相同操作。
using namespace std;
void printVector(vector <int> vec)
{
for (auto ele: vec)
{
cout << ele << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
vector <int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
printVector(vec);
// Method 1: Using Assignment Operator
vector <int> newVec1 = vec;
printVector(newVec1);
// Method 2: By passing vector as constructor
vector <int> newVec2(vec);
printVector(newVec2);
return 0;
}
输出:
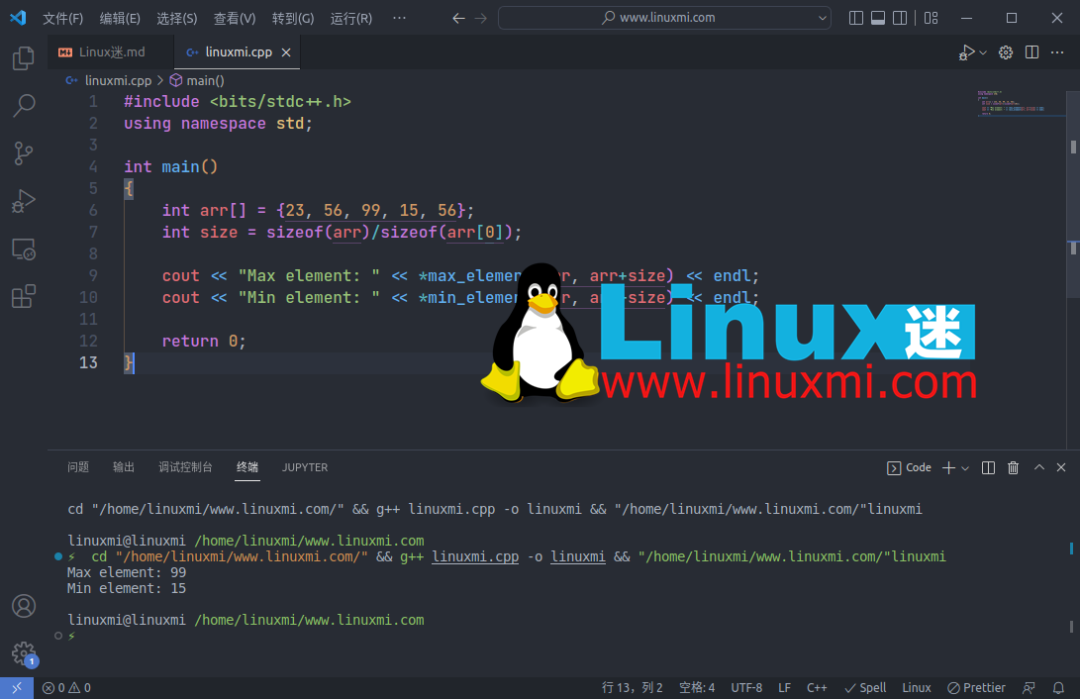
6. 找出数组的最大和最小元素
您可以分别使用max_element()和min_element()函数从数组中找到最大和最小元素。
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[] = {23, 56, 99, 15, 56};
int size = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << "Max element: " << *max_element(arr, arr+size) << endl;
cout << "Min element: " << *min_element(arr, arr+size) << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
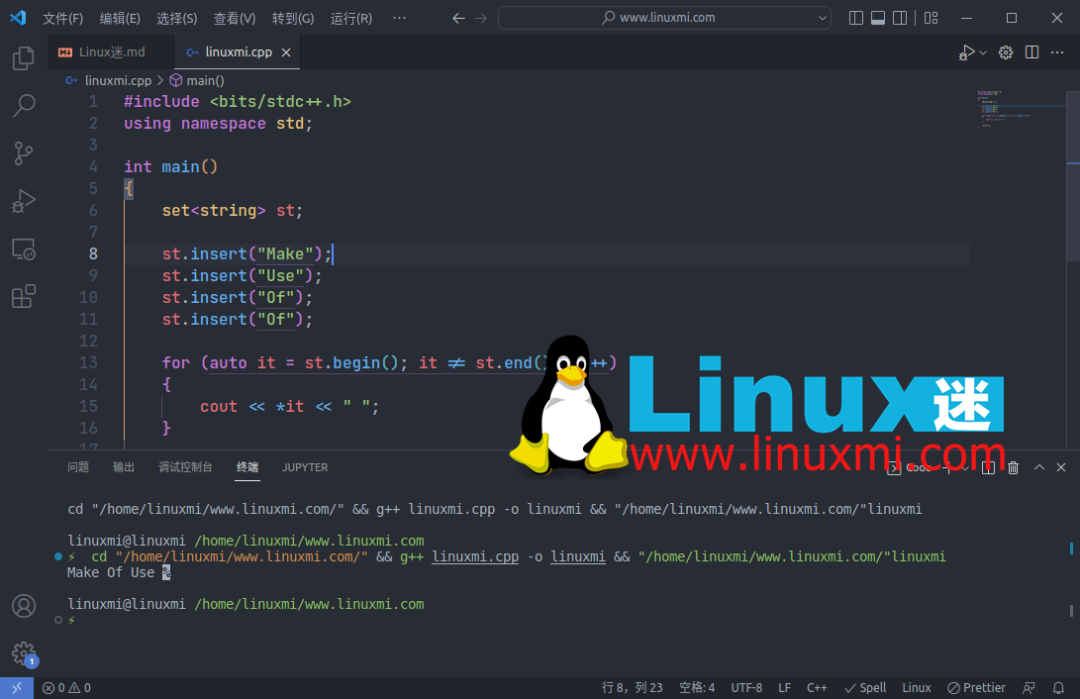
7. 在集合中插入元素
您可以使用insert()函数在集合中插入元素。此函数接受元素作为将插入集合中的参数。
using namespace std;
int main()
{
set<string> st;
st.insert("Make");
st.insert("Use");
st.insert("Of");
st.insert("Of");
for (auto it = st.begin(); it != st.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
return 0;
}
输出:
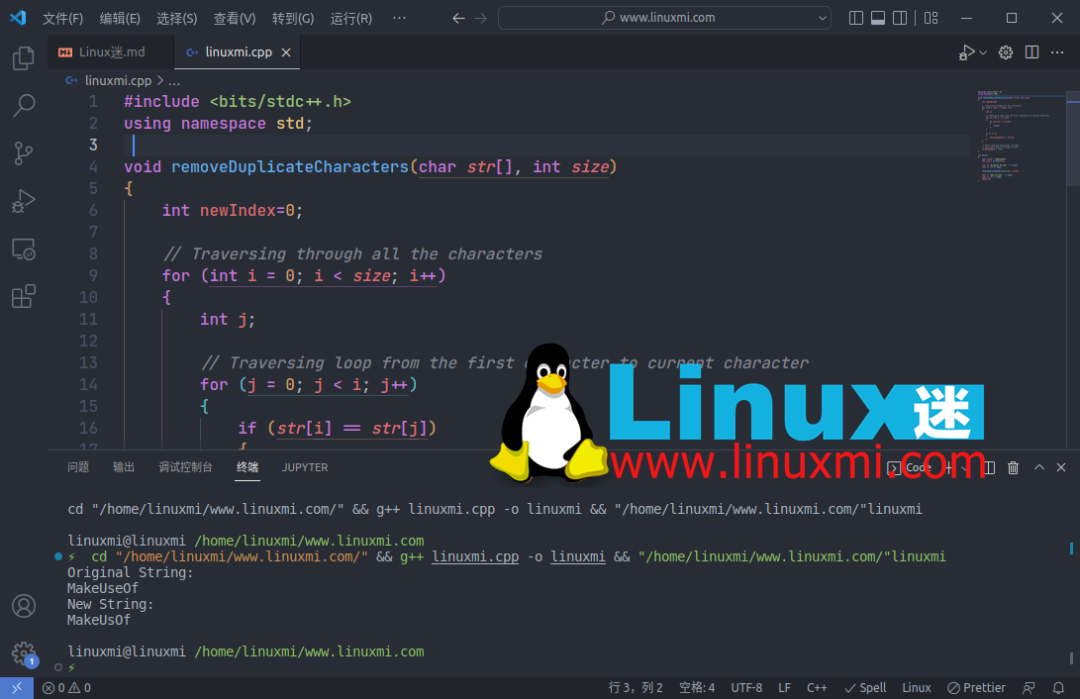
8.从字符串中删除重复项
您可以使用以下方法从字符串中删除重复字符:
using namespace std;
void removeDuplicateCharacters(char str[], int size)
{
int newIndex=0;
// Traversing through all the characters
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
int j;
// Traversing loop from the first character to current character
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
if (str[i] == str[j])
{
break;
}
}
if (j == i)
{
str[newIndex++] = str[i];
}
}
// After removing duplicates, we make
// the vacant part of string to null
str[newIndex] = '�';
}
int main()
{
char str[] = "MakeUseOf";
int size = strlen(str);
cout << "Original String: " << endl;
cout << str << endl;
removeDuplicateCharacters(str, size);
cout << "New String: " << endl;
cout << str << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
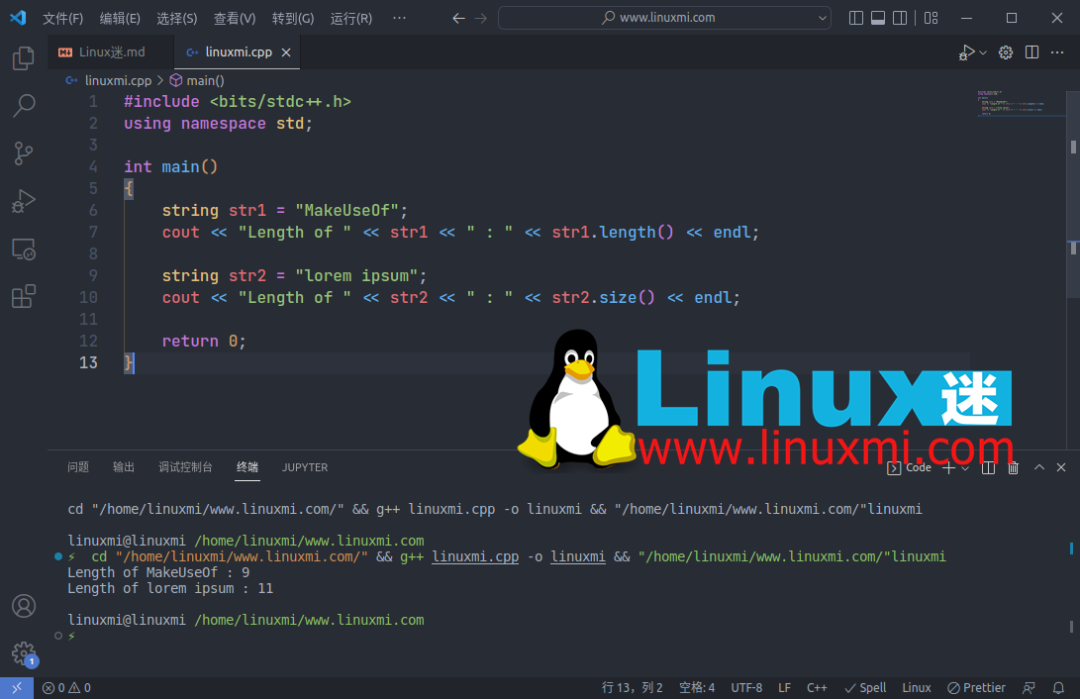
9. 求 C++ 字符串的长度
您可以使用 length() 函数找到 C++ 字符串的长度。或者,您也可以使用 size()函数(它是length()函数的别名)。
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str1 = "MakeUseOf";
cout << "Length of " << str1 << " : " << str1.length() << endl;
string str2 = "lorem ipsum";
cout << "Length of " << str2 << " : " << str2.size() << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
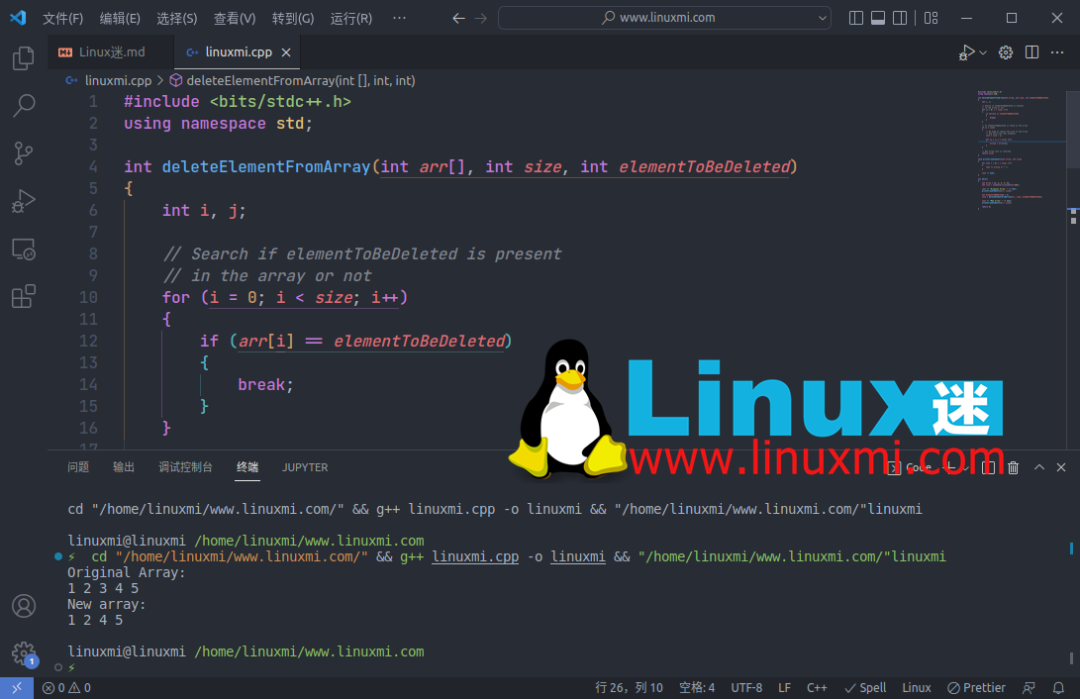
10. 从数组中删除一个元素
您可以使用以下方法从数组中删除元素:
using namespace std;
int deleteElementFromArray(int arr[], int size, int elementToBeDeleted)
{
int i, j;
// Search if elementToBeDeleted is present
// in the array or not
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
if (arr[i] == elementToBeDeleted)
{
break;
}
}
// If elementToBeDeleted is found in the array
if (i < size)
{
// We need to reduce the size of the array
// and shift the rest elements
size = size - 1;
for (j = i; j < size; j++)
{
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
}
}
// New array size is returned
return size;
}
void printArrayElements(int arr[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int size = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << "Original Array: " << endl;
printArrayElements(arr, size);
int elementToBeDeleted = 3;
size = deleteElementFromArray(arr, size, elementToBeDeleted);
cout << "New array: " << endl;
printArrayElements(arr, size);
return 0;
}
输出: 有时直接理解复杂的代码并不容易。您应该遵循一些基本的编程原则,例如记录代码、重构等,以使您的代码更加健壮。
有时直接理解复杂的代码并不容易。您应该遵循一些基本的编程原则,例如记录代码、重构等,以使您的代码更加健壮。11. 遍历向量
您可以通过多种方式遍历向量。以下是三种最常用的遍历向量的方法:使用范围for(range for)
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector <int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// Method 1: Using range for
for (auto element: vec)
{
cout << element << " ";
}
return 0;
}
使用索引
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector <int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// Method 2: Using indexing
for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++)
{
cout << vec[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
使用迭代器的引用
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector <int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// Method 3: Using reference of the iterator
for (auto it = begin(vec); it != end(vec); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
return 0;
}
上述三个代码将显示相同的输出:
使用 C++ 代码片段
使用这些 C++ 代码片段来解决您的日常编程问题。无论您使用 C++ 编写简单程序还是竞争性编程,这些代码片段都可以派上用场。 审核编辑:汤梓红
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
-
写好C++代码需要遵循的10个最佳实践2022-09-19 1072
-
编程语言中一个奇怪的代码结构2023-11-01 984
-
Google C++编程指南2017-11-29 4782
-
Visual C++ 6.0 MFC时尚编程百例源代码2008-10-15 1928
-
C++编程调试秘笈2021-06-01 803
-
C++ Socket网络编程大全源代码下载2021-06-21 1410
-
C++ GUI Qt4编程(第二版)配套源代码汇总2021-08-03 1687
-
STM32 C++编程系列二:STM32 C++代码封装初探2021-12-08 979
-
C和C++实物精选《C专家编程》2022-01-17 997
-
C++代码需要遵循的10个最佳实践2022-10-18 1406
-
C与C++混合编程是什么2023-02-14 2817
-
20个解决日常问题的Python代码片段!2023-03-13 1432
-
c++怎么开始编程2023-11-27 1717
-
C++简史:C++是如何开始的2024-01-11 1460
-
C2000 DCSM ROM代码片段/ROP漏洞2024-08-28 366
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

