

3自由度串联机械臂实现电磁铁搬运功能
电子说
描述
1、功能描述
R308样机是一款拥有3自由度的串联机械臂。本文提供的示例所实现的功能为:在3自由度串联机械臂样机上安装电磁铁,实现电磁铁搬运物品的功能。


2、电子硬件
在这个示例中,我们采用了以下硬件,请大家参考:
| 主控板 | Basra(兼容Arduino Uno) |
| 扩展板 | Bigfish2.1 |
| 舵机 | 270°伺服电机 |
| 电池 | 7.4V锂电池 |
| 其它 | 电磁铁、USB线 |
电路连接说明:
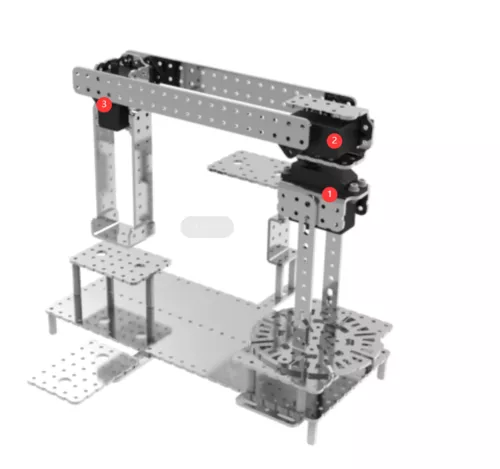
注:
① 270°伺服电机连接在Bigfish扩展板D4 . GND . VCC接口上
② 270°伺服电机连接在Bigfish扩展板D7 . GND . VCC接口上
③ 270°伺服电机连接在Bigfish扩展板D11 . GND . VCC接口上
电磁铁连接在Bigfish扩展板D9,D10接口上
3、运动控制
上位机:Controller 1.0
下位机编程环境:Arduino 1.8.19
3.1初始位置的设定
① 将Controller下位机程序servo_bigfish.ino直接下载到主控板。这段代码供Controller上位机与主控板通信,并允许调试舵机。代码如下:
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
版权说明:Copyright 2023 Robottime(Beijing) Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Distributed under MIT license.See file LICENSE for detail or copy at
https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT
by 机器谱 2023-01-31 https://www.robotway.com/
------------------------------
/*
* Bigfish扩展板舵机口; 4, 7, 11, 3, 8, 12, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19
* 使用软件调节舵机时请拖拽对应序号的控制块
*/
#include
#define ANGLE_VALUE_MIN 0
#define ANGLE_VALUE_MAX 180
#define PWM_VALUE_MIN 500
#define PWM_VALUE_MAX 2500
#define SERVO_NUM 12
Servo myServo[SERVO_NUM];
int data_array[2] = {0,0}; //servo_pin: data_array[0], servo_value: data_array[1];
int servo_port[SERVO_NUM] = {4, 7, 11, 3, 8, 12, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19};
int servo_value[SERVO_NUM] = {};
String data = "";
boolean dataComplete = false;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
while(Serial.available())
{
int B_flag, P_flag, T_flag;
data = Serial.readStringUntil('n');
data.trim();
for(int i=0;i= ANGLE_VALUE_MIN && where <= ANGLE_VALUE_MAX)
{
myServo[which].write(where);
}
else if(where >= PWM_VALUE_MIN && where <= PWM_VALUE_MAX)
{
myServo[which].writeMicroseconds(where);
}
}
int pin2index(int _pin){
int index;
switch(_pin)
{
case 4: index = 0; break;
case 7: index = 1; break;
case 11: index = 2; break;
case 3: index = 3; break;
case 8: index = 4; break;
case 12: index = 5; break;
case 14: index = 6; break;
case 15: index = 7; break;
case 16: index = 8; break;
case 17: index = 9; break;
case 18: index = 10; break;
case 19: index = 11; break;
}
return index;
}
下载完成后,保持主控板和电脑的USB连接,以便利用上位机进行调试。
② 双击打开Controller 1.0b.exe:

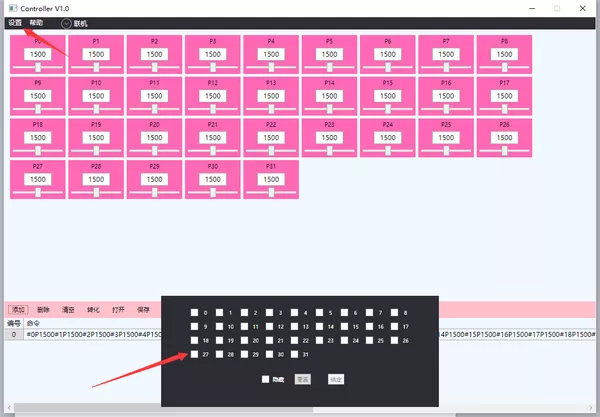
③ 界面左上角选择:设置-面板设置,弹出需要显示的调试块,可通过勾选隐藏不需要调试的舵机块:联机-选择主控板对应端口号以及波特率。
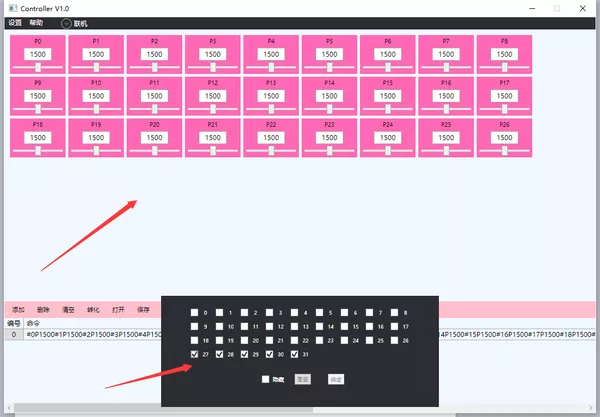
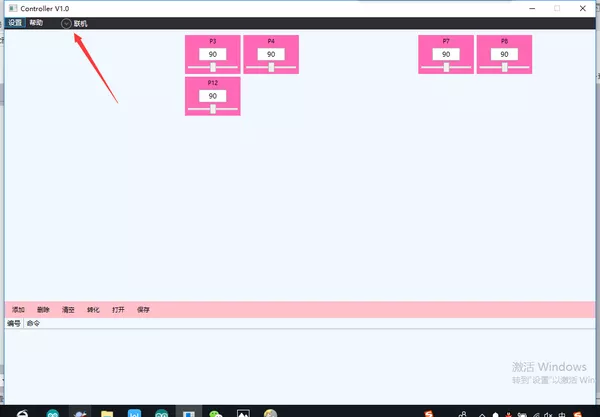
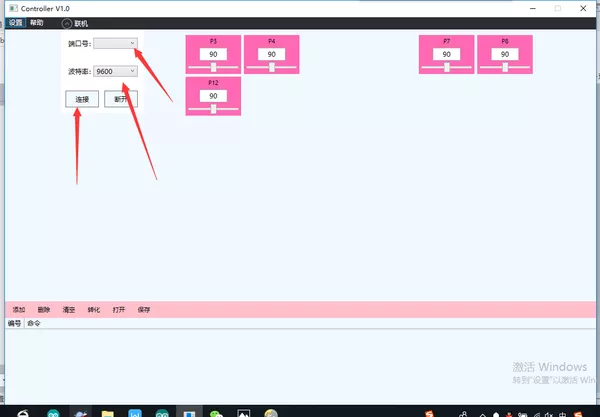
④ 拖动进度条,可以观察相应的舵机角度转动。写好对应的舵机调试角度,勾选左下角添加-转化,获得舵机调试的数组:
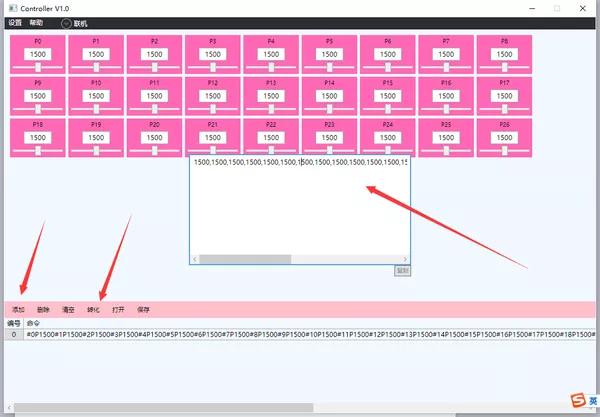
⑤ 将该数组直接复制到相应的Arduino程序中的get_coordinate()部分进行使用。
3.2调试好角度后将电磁铁搬运例程(calculate_angle_test.ino)下载到主控板【程序源码详见 https://www.robotway.com/h-col-191.html】
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
版权说明:Copyright 2023 Robottime(Beijing) Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Distributed under MIT license.See file LICENSE for detail or copy at
https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT
by 机器谱 2023-01-31 https://www.robotway.com/
------------------------------*/
#include
#include
#define SERVO_SPEED 3460 //定义舵机转动快慢的时间
#define ACTION_DELAY 200 //定义所有舵机每个状态时间间隔
#define L1 172
#define L2 160
#define L3 135
Servo myServo[6];
int f = 200; //定义舵机每个状态间转动的次数,以此来确定每个舵机每次转动的角度
int servo_port[6] = {4,7,11,3,8,12}; //定义舵机引脚
int servo_num = sizeof(servo_port) / sizeof(servo_port[0]); //定义舵机数量
float value_init[6] = {1500, 1500, 1500, 0, 0, 0}; //定义舵机初始角度
double theta[3] = {};
float value_pwm[6] = {};
float coordinate[3] = {};
int data_num;
boolean dataComplete = false;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(9, OUTPUT);
pinMode(10, OUTPUT);
for(int i=0;i= 0){
theta[0] = theta0 * 180 / PI;
}
else
{
theta[0] = 180 + theta0 * 180 / PI;
}
theta[1] = 90 - theta1 * 180 / PI;
theta[2] = theta2 * 180 / PI;
// Serial.print("theta0 = ");
// Serial.println(theta[0]);
// Serial.print("theta1 = ");
// Serial.println(theta[1]);
// Serial.print("theta2 = ");
// Serial.println(theta[2]);
// Serial.println("-------------------------------------");
}
void ServoStart(int which)
{
if(!myServo[which].attached())myServo[which].attach(servo_port[which]);
pinMode(servo_port[which], OUTPUT);
}
void ServoStop(int which)
{
myServo[which].detach();
digitalWrite(servo_port[which],LOW);
}
void ServoGo(int which , int where)
{
if(where!=200)
{
if(where==201) ServoStop(which);
else
{
ServoStart(which);
myServo[which].writeMicroseconds(where);
}
}
}
void servo_move(float value0, float value1, float value2, float value3, float value4, float value5)
{
float value_arguments[] = {value0, value1, value2, value3, value4, value5};
float value_delta[servo_num];
for(int i=0;i
审核编辑 黄宇
-
采用LabVIEW实现四自由度机械臂运动控制系统设计2019-05-06 4172
-
推拉电磁铁的结构形式2020-04-22 3133
-
电磁铁的用途概述2023-05-20 24410
-
六自由度机械臂的运动规划2012-02-17 2947
-
基于模糊PD算法的三自由度机械臂遥操作双边控制_邱恒2017-01-21 1052
-
磁铁与电磁铁的设计2017-09-15 1620
-
一种新型7自由度冗余绳驱动机械臂2018-02-27 3333
-
运用BLDC对新型五自由度并联机器人的设计2018-10-07 6850
-
为什么最好的机械臂是7个自由度而不是6个自由度2019-03-17 27687
-
电磁铁工作原理_电磁铁的应用2019-06-03 46903
-
4自由度机械臂的制作图解2019-10-09 11552
-
使用SimMechanics实现六自由度的机械臂仿真研究2019-11-12 1983
-
4自由度串联机械臂的制作2023-03-03 1685
-
Delta并联机械臂实现电磁铁搬运功能2023-03-09 1809
-
4自由度并联机器狗实现行走功能2023-06-18 1584
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

