

SystemVerilog构建大型电路
描述
Problem 151-review2015_count1k
题目说明
构建一个从 0 到 999(含)计数的计数器,周期为 1000 个周期。复位输入是同步的,应该将计数器复位为 0。
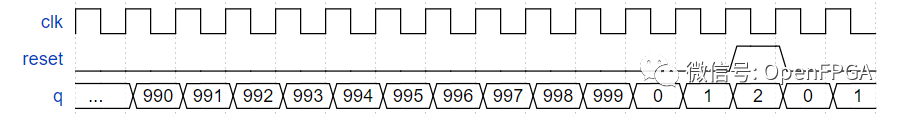
模块端口声明
module top_module ( input clk, input reset, output [9:0] q);
题目解析
module top_module ( input logic clk, input logic reset, output logic[9:0] q); always_ff @( posedge clk ) begin if (reset) begin q <= 10'd0 ; end else if (q == 10'd999) begin q <= 10'd0 ; end else begin q <= q + 10'd1 ; end end endmodule
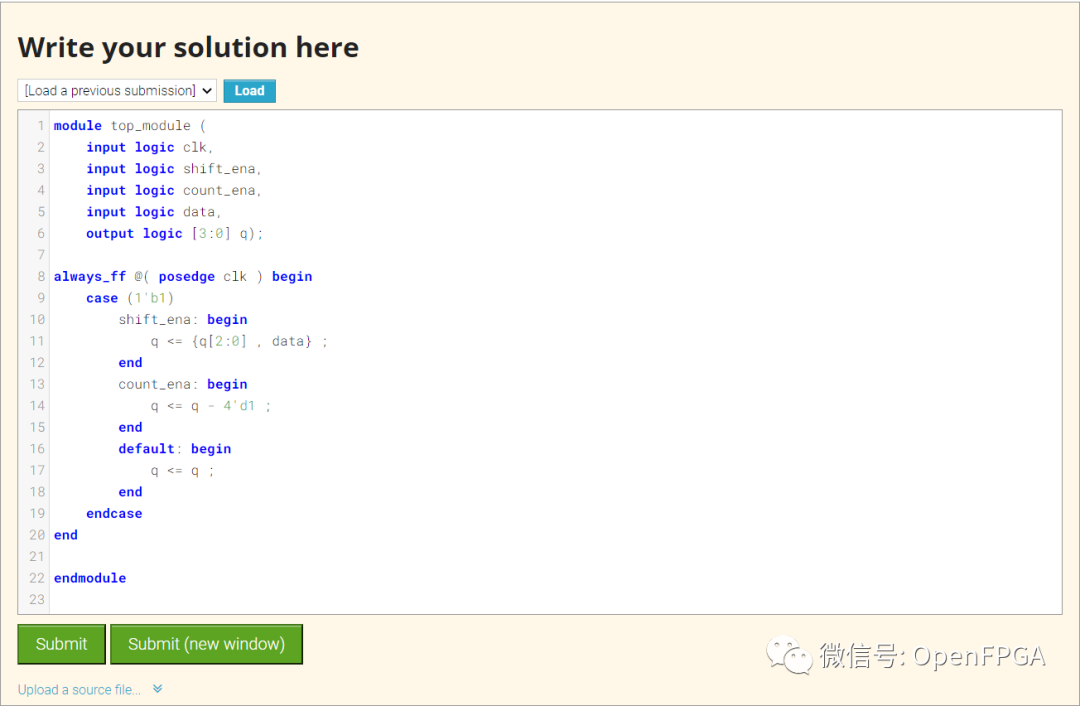
点击Submit,等待一会就能看到下图结果:
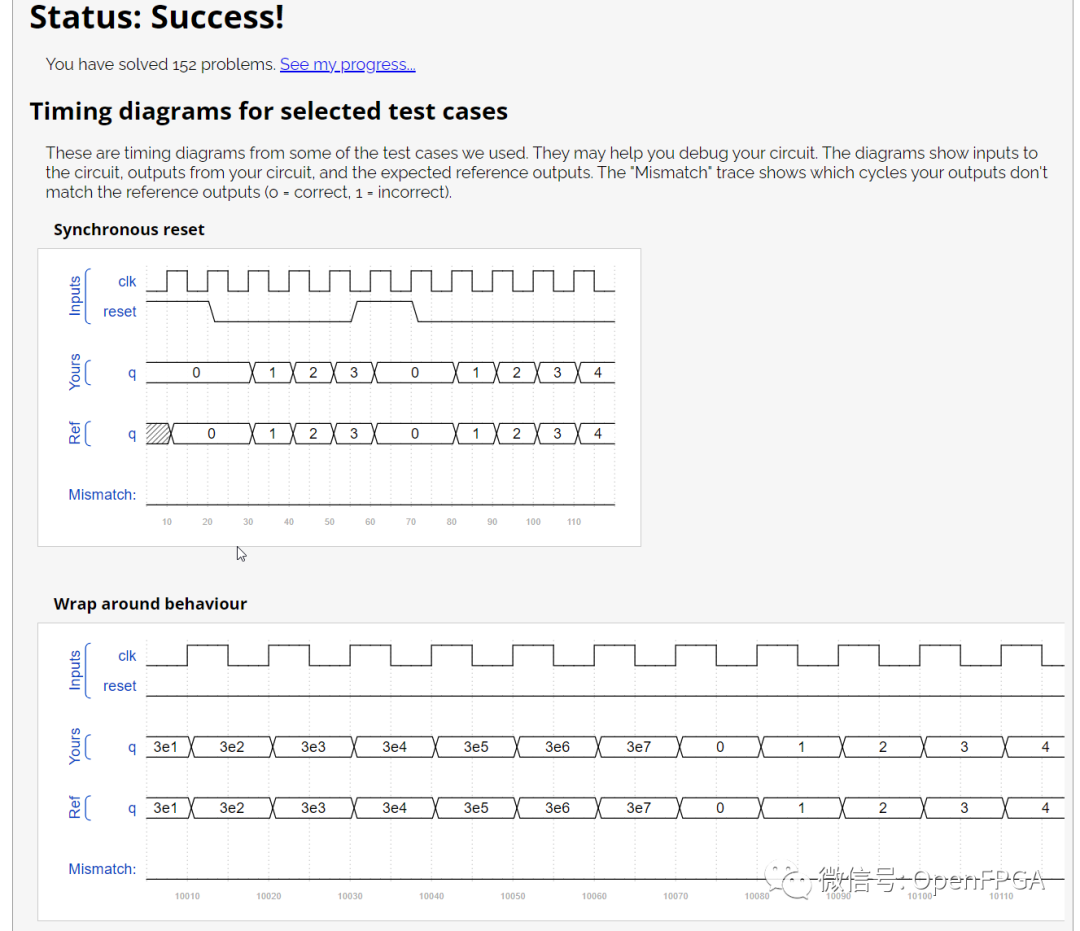
注意图中的Ref是参考波形,Yours是你的代码生成的波形,网站会对比这两个波形,一旦这两者不匹配,仿真结果会变红。
这一题就结束了。
Problem 152-review2015_shiftcount
题目说明
接下来的五道题目,每题构建一个小型的电路,最终组装成为一个复杂的计数器电路。
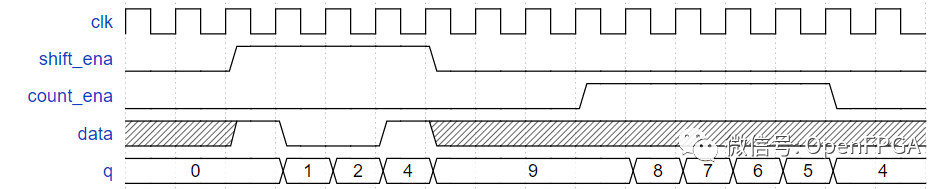
本题设计一个 4bit 位宽的移位寄存器,并具有计数器功能,可向下计数(即计数值递减)。
当移位使能 shift_ena 信号有效时,数据 data 移入移位寄存器,向高位移动(most-significant-bit),即左移。
当计数使能 count_ena 信号有效时,寄存器中现有的数值递减,向下计数。
由于系统不会同时使用移位以及计数功能,因此不需要考虑两者使能信号皆有效的情况。
模块端口声明
module top_module ( input clk, input shift_ena, input count_ena, input data, output [3:0] q);
题目解析
module top_module (
input logic clk,
input logic shift_ena,
input logic count_ena,
input logic data,
output logic [3:0] q);
always_ff @( posedge clk ) begin
case (1'b1)
shift_ena: begin
q <= {q[2:0] , data} ;
end
count_ena: begin
q <= q - 4'd1 ;
end
default: begin
q <= q ;
end
endcase
end
endmodule
点击Submit,等待一会就能看到下图结果:
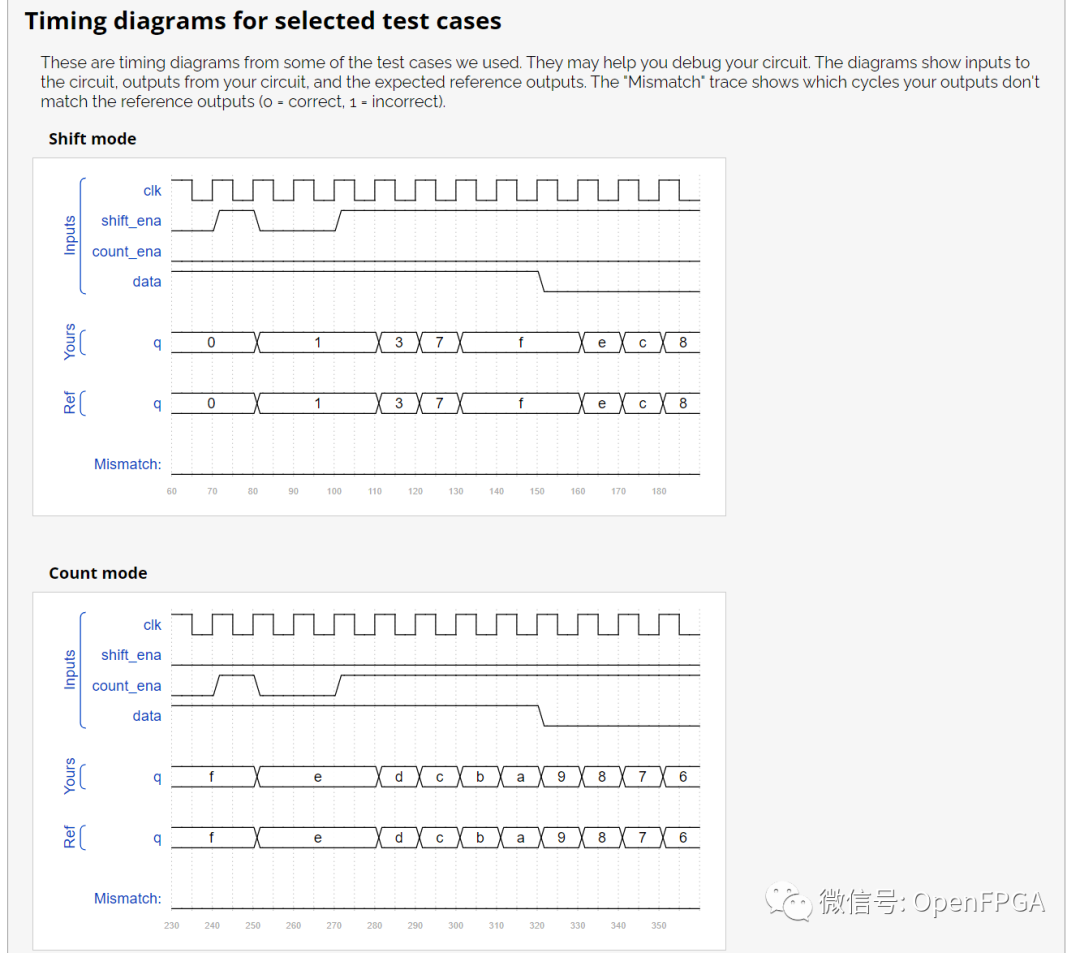
注意图中的Ref是参考波形,Yours是你的代码生成的波形,网站会对比这两个波形,一旦这两者不匹配,仿真结果会变红。
这一题就结束了。
Problem 153-review2015_fsmseq
题目说明
接下来的五道题目,每题构建一个小型的电路,最终组装成为一个复杂的计数器电路。
构建一个在输入比特流中搜索序列 1101 的有限状态机。当找到序列时,应该将start_shifting设置为 1,直到复位。卡在最终状态旨在模拟在尚未实现的更大 FSM 中进入其他状态。我们将在接下来的几个练习中扩展这个 FSM。
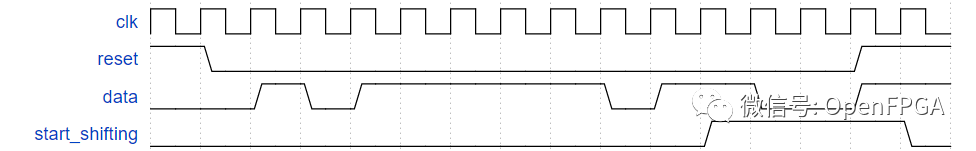
模块端口声明
module top_module ( input clk, input reset, // Synchronous reset input data, output start_shifting);
题目解析
检查一个序列检测状态机是否完备,一个简单的方法是观察所有状态,是否均包括输入分别为 0/1 的情况下的跳转,比如 state[IDLE ] && ~data 和 state[IDLE ] && data 是否均存在于状态跳转条件中。
module top_module (
input logic clk,
input logic reset, // Synchronous reset
input logic data,
output logic start_shifting
);
//define state
typedef enum logic [2:0] { idle = 3'd1 , S0 = 3'd2 ,
S1 = 3'd3 , S2 = 3'd4 , S3 = 3'd5
} state_def ;
state_def cur_state , next_state ;
//describe state transition use combinational logic
always_comb begin
case (cur_state)
idle: begin
next_state = data ? S0 : idle ;
end
S0: begin
next_state = data ? S1 : idle ;
end
S1: begin
next_state = data ? S1 : S2 ;
end
S2: begin
next_state = data ? S3 : idle ;
end
S3: begin
next_state = S3 ;
end
default: begin
next_state = idle ;
end
endcase
end
//describe state sequencer use sequential logic
always_ff @( posedge clk ) begin
if (reset) begin
cur_state <= idle ;
end
else begin
cur_state <= next_state ;
end
end
//describe output decoder use combinational logic
assign start_shifting = (cur_state == S3) ;
endmodule
点击Submit,等待一会就能看到下图结果:
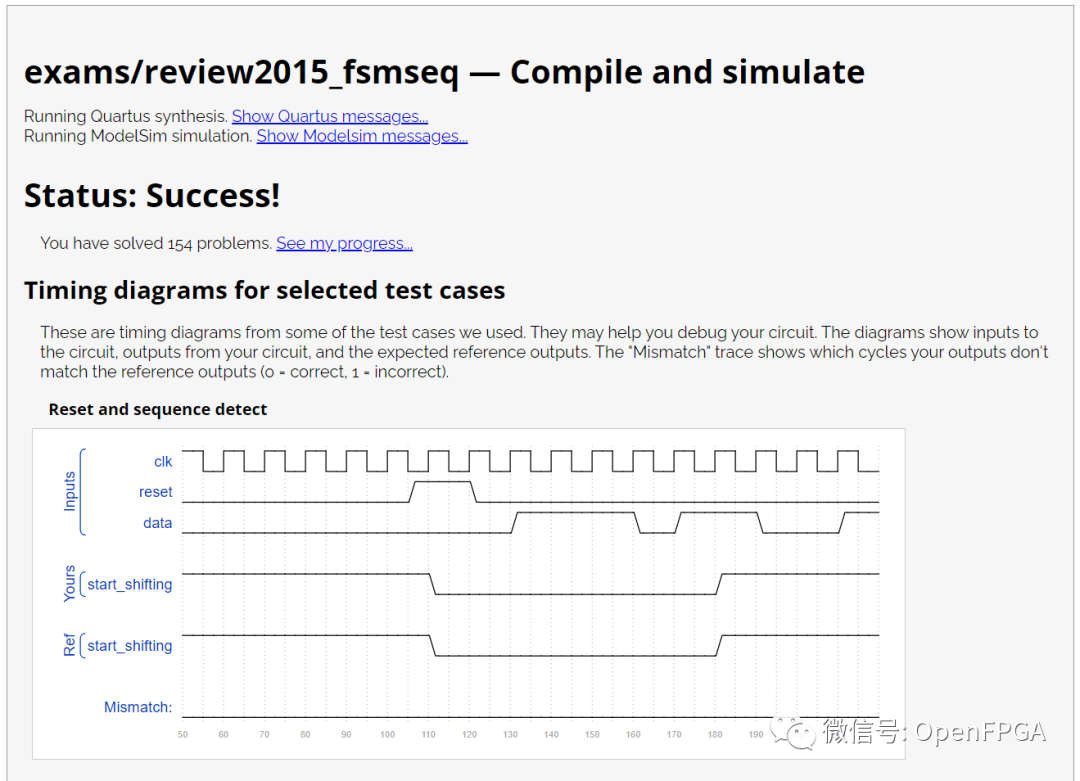
注意图中的Ref是参考波形,Yours是你的代码生成的波形,网站会对比这两个波形,一旦这两者不匹配,仿真结果会变红。
这一题就结束了。
Problem 154-review2015_fsmshift
题目说明
接下来的五道题目,每题构建一个小型的电路,最终组装成为一个复杂的计数器电路。
作为用于控制移位寄存器的 FSM 的一部分,我们希望能够在检测到正确的位模式时启用移位寄存器正好 4 个时钟周期。我们在Exams/review2015_fsmseq中处理序列检测,因此 FSM 的这一部分仅处理启用移位寄存器 4 个周期。
每当 FSM 复位时,将shift_ena断言4 个周期,然后永远为 0(直到复位)。
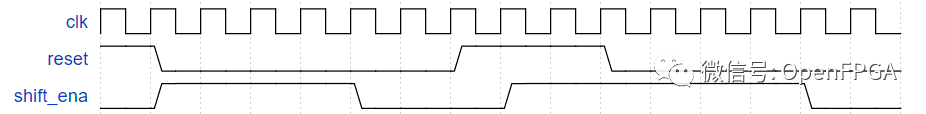 图片来自HDLBits
图片来自HDLBits
模块端口声明
module top_module ( input clk, input reset, // Synchronous reset output shift_ena);
题目解析
题目要求 reset 信号移除后,立即 输出使能信号,因此需要组合逻辑输出。
module top_module (
input logic clk,
input logic reset, // Synchronous reset
output logic shift_ena);
//define state
typedef enum logic { S0 = 1'd0 , S1 = 1'd1 } state_def ;
state_def cur_state , next_state ;
//describe state sequencer use sequential logic
always_ff @( posedge clk ) begin
if (reset) begin
cur_state <= S0 ;
end
else begin
cur_state <= next_state ;
end
end
//describe state transition use combinational logic
always_comb begin
case (cur_state)
S0: begin
next_state = reset ? S0 : S1 ;
end
S1: begin
next_state = reset ? S0 : S1 ;
end
default: begin
next_state = cur_state ;
end
endcase
end
//define counter use sequential logic
var logic [6:0] counter ;
always_ff @( posedge clk ) begin
if (reset) begin
counter <= 7'd0 ;
end
else if (next_state == S1) begin
counter <= counter + 7'd1 ;
end
else begin
counter <= counter ;
end
end
//describe output decoder use sequential logic
assign shift_ena = (cur_state == S0) || (cur_state == S1 && counter < 7'd4) ;
endmodule
点击Submit,等待一会就能看到下图结果:

注意图中无波形。
这一题就结束了。
Problem 155-review2015_fsm
题目说明
本题实现复杂计数器的第四个组件。
在此题之前,我们已经分别实现了 FSM:Enable shift register 以及 FSM:1101 序列检测器。接下来我们继续前进,实现这个复杂计数器的完整 FSM。
复杂计数器需要如下这些功能特性:
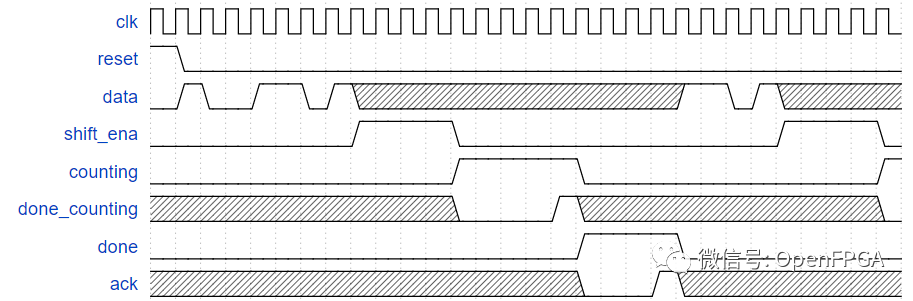
在数据流中检测到特定序列后启动计数器,该序列为: 1101将 4bits 数据输入移位寄存器,作为计数器的初值等待计数器结束计数告知上层应用计数完成,并等待用户通过 ack 信号确认在本题练习中,只需要实现控制状态机,不需要实现数据通路,比如计数器本身以及数据比较器等。
数据流从模块的 data 信号输入,当检测到 1101 序列后,状态机需要置高输出信号 shft_ena 并保持 4 个周期(用于将接下来 4bit 数据输入移位寄存器)。
之后,状态机置高 counting 信号,表示其正在等待计数器完成计数,当计数器完成计数输出 done_counting 信号后,counting 信号置低。
再此后,状态机置高 done 信号通知上层应用计数器计数完成,等待 ack 信号置高后,状态机清除 done 信号,返回空闲状态等待捕获下一个 1101 序列。
本题给出了一个期望输入输出的例子。图中的斜线代表当前信号为 'X', 表示状态机不关心该信号当前的值。比如图例中,一旦 FSM 检测到 1101 序列后,在此次计数器事件完成前,对于当前的数据流不再关心。
模块端口声明
module top_module ( input clk, input reset, // Synchronous reset input data, output shift_ena, output counting, input done_counting, output done, input ack );
题目解析
状态转移图

module top_module (
input logic clk,
input logic reset, // Synchronous reset
input logic data,
output logic shift_ena,
output logic counting,
input logic done_counting,
output logic done,
input logic ack
);
//define state
typedef enum logic [2:0] { idle = 3'd1 , S0 = 3'd2 ,S1 = 3'd3 ,
S2 = 3'd4 , shif = 3'd5 , count = 3'd6 ,
waite = 3'd7
} state_def ;
state_def cur_state , next_state ;
//describe state transition use combinational logic
always_comb begin
case (cur_state)
idle: begin
next_state = data ? S0 : idle ;
end
S0: begin
next_state = data ? S1 : idle ;
end
S1: begin
next_state = data ? S1 : S2 ;
end
S2: begin
next_state = data ? shif : idle ;
end
shif: begin
next_state = counter < 7'd4 ? shif : count ;
end
count: begin
next_state = done_counting ? waite : count ;
end
waite: begin
next_state = ack ? idle : waite ;
end
default: begin
next_state = idle ;
end
endcase
end
//define counter use sequential logic
var logic [6:0] counter ;
always_ff @( posedge clk ) begin
if (reset || next_state != shif) begin
counter <= 7'd0 ;
end
else if (next_state == shif) begin
counter <= counter + 7'd1 ;
end
else begin
counter <= counter ;
end
end
//describe state sequencer use sequential logic
always_ff @( posedge clk ) begin
if (reset) begin
cur_state <= idle ;
end
else begin
cur_state <= next_state ;
end
end
//describe output decoder use combinational logic
assign shift_ena = (cur_state == shif) ;
assign counting = (cur_state == count) ;
assign done = (cur_state == waite) ;
endmodule
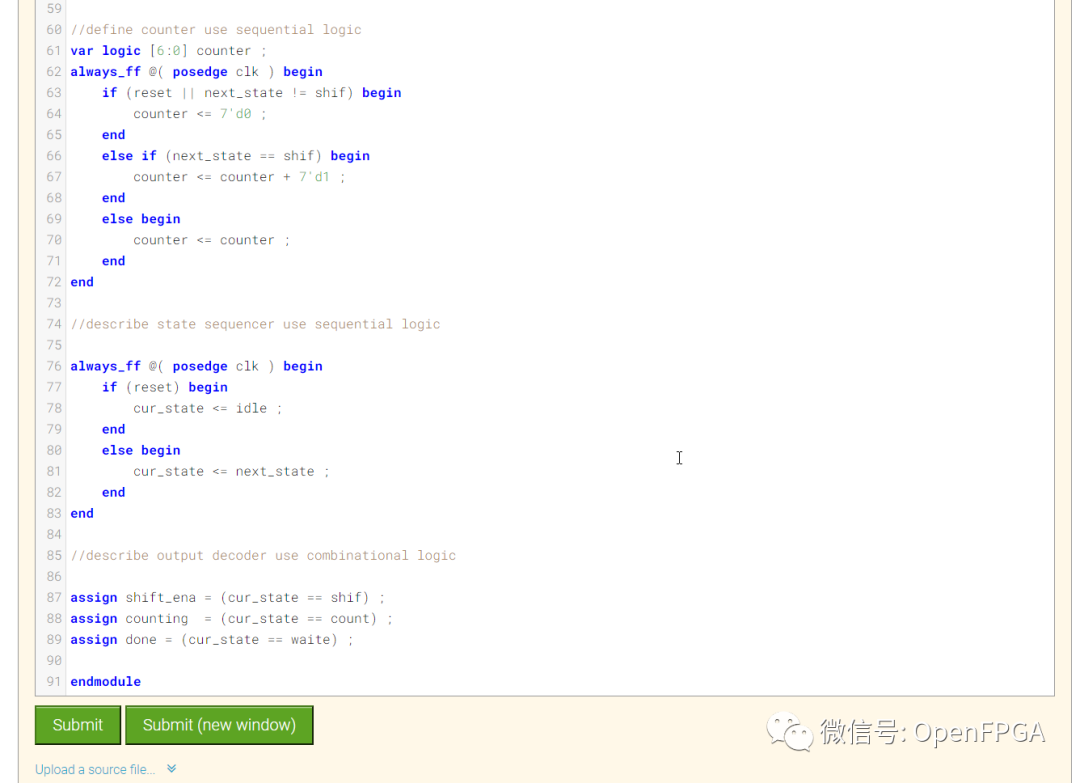
点击Submit,等待一会就能看到下图结果:

注意图中无参考波形。
这一题就结束了。
Problem 156-review2015_fancytimer
题目说明
终于到了完整构建复杂计数器的时候,整体功能已经在上题中讨论,这里不再赘述。
在数据流中检测到序列 1101 后,电路需要将接下来的 4bit 数据移入移位寄存器。4bit 数据决定了计数器的计数周期,称为 delay[3:0]。首先到达的比特作为数据的高位。
之后,状态机置高 counting 信号,表示其正在等待计数器完成计数。在 FSM 中增加计数器状态,计数周期为 (delay[3:0] + 1 )* 1000 个时钟周期。比如 delay = 0 时,计数值为 1000 个周期。delay = 5 代表 6000 个周期。同时输出 count 当前剩余的计数周期,输出当前剩余计数周期的千位(比如,还剩1000个周期输出 1,还剩 999 个周期时输出 0)。当计数停止后,count 的输出可以为任意数。
当计数完成后,电路置高 done 信号通知上层应用计数器计数完成,等待 ack 信号置高后,状态机清除 done 信号,返回空闲状态等待捕获下一个 1101 序列。
本题给出了一个期望输入输出的例子。图中的斜线代表当前信号为 'X', 表示状态机不关心该信号当前的值。比如图例中,一旦 FSM 检测到 1101 序列并读取 delay[3:0] 后,在此次计数器事件完成前,对于当前的数据流不再关心。
在图例中,电路计数周期为 2000 ,因为 delay[3:0] 数值为 4'b0001 。在后续的第二个计数周期中,因为 delay[3:0] = 4‘b1110,所以计数周期为 15000。
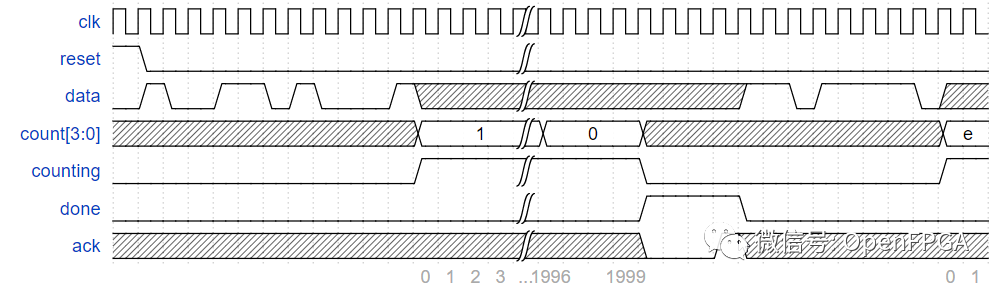 图片来自HDLBits
图片来自HDLBits
模块端口声明
module top_module ( input clk, input reset, // Synchronous reset input data, output [3:0] count, output counting, output done, input ack );
题目解析
module top_module (
input logic clk,
input logic reset, // Synchronous reset
input logic data,
output logic [3:0] count,
output logic counting,
output logic done,
input logic ack
);
//define state
typedef enum logic [2:0] { idle = 3'd1 , S0 = 3'd2 ,S1 = 3'd3 ,
S2 = 3'd4 , shif = 3'd5 , count_t = 3'd6 ,
waite = 3'd7
} state_def ;
state_def cur_state , next_state ;
//describe state transition use combinational logic
always_comb begin
case (cur_state)
idle: begin
next_state = data ? S0 : idle ;
end
S0: begin
next_state = data ? S1 : idle ;
end
S1: begin
next_state = data ? S1 : S2 ;
end
S2: begin
next_state = data ? shif : idle ;
end
shif: begin
next_state = counter_shif < 7'd4 ? shif : count_t ;
end
count_t: begin
next_state = (counter == (delay + 1)*1000 - 1) ? waite : count_t ;
end
waite: begin
next_state = ack ? idle : waite ;
end
default: begin
next_state = idle ;
end
endcase
end
//describe state sequencer use sequential logic
always_ff @( posedge clk ) begin
if (reset) begin
cur_state <= idle ;
end
else begin
cur_state <= next_state ;
end
end
//describe output decoder use combinational logic
assign count = (cur_state == count_t) ? (delay - counter_delay) :4'd0 ;
assign counting = (cur_state == count_t) ;
assign done = (cur_state == waite) ;
//define counter for shift use sequential logic
var logic [6:0] counter_shif ;
always_ff @( posedge clk ) begin
if (reset || next_state != shif) begin
counter_shif <= 7'd0 ;
end
else if (next_state == shif) begin
counter_shif <= counter_shif + 7'd1 ;
end
else begin
counter_shif <= counter_shif ;
end
end
//define counter for count use sequential logic
var logic [15:0] counter ;
always_ff @( posedge clk ) begin
if (reset || next_state != count_t) begin
counter <= 16'd0 ;
end
else if (cur_state == count_t) begin
counter <= counter + 16'd1 ;
end
else begin
counter <= 16'd0 ;
end
end
//shift data into delay use sequential logic
var logic [3:0] delay ;
always_ff @( posedge clk ) begin
if(reset) begin
delay <= 4'd0 ;
end
else begin
if (cur_state == shif) begin
delay <= {delay[2:0] , data} ;
end
end
end
//calculate couter_delay use combinational logic
var logic [3:0] counter_delay ;
always@(*)begin
if(counter <= 999)begin
counter_delay = 4'd0;
end
else if(counter >= 1000 && counter <= 1999)begin
counter_delay = 4'd1;
end
else if(counter >= 2000 && counter <= 2999)begin
counter_delay = 4'd2;
end
else if(counter >= 3000 && counter <= 3999)begin
counter_delay = 4'd3;
end
else if(counter >= 4000 && counter <= 4999)begin
counter_delay = 4'd4;
end
else if(counter >= 5000 && counter <= 5999)begin
counter_delay = 4'd5;
end
else if(counter >= 6000 && counter <= 6999)begin
counter_delay = 4'd6;
end
else if(counter >= 7000 && counter <= 7999)begin
counter_delay = 4'd7;
end
else if(counter >= 8000 && counter <= 8999)begin
counter_delay = 4'd8;
end
else if(counter >= 9000 && counter <= 9999)begin
counter_delay = 4'd9;
end
else if(counter >= 10000 && counter <= 10999)begin
counter_delay = 4'd10;
end
else if(counter >= 11000 && counter <= 11999)begin
counter_delay = 4'd11;
end
else if(counter >= 12000 && counter <= 12999)begin
counter_delay = 4'd12;
end
else if(counter >= 13000 && counter <= 13999)begin
counter_delay = 4'd13;
end
else if(counter >= 14000 && counter <= 14999)begin
counter_delay = 4'd14;
end
else begin
counter_delay = 4'd15;
end
end
endmodule
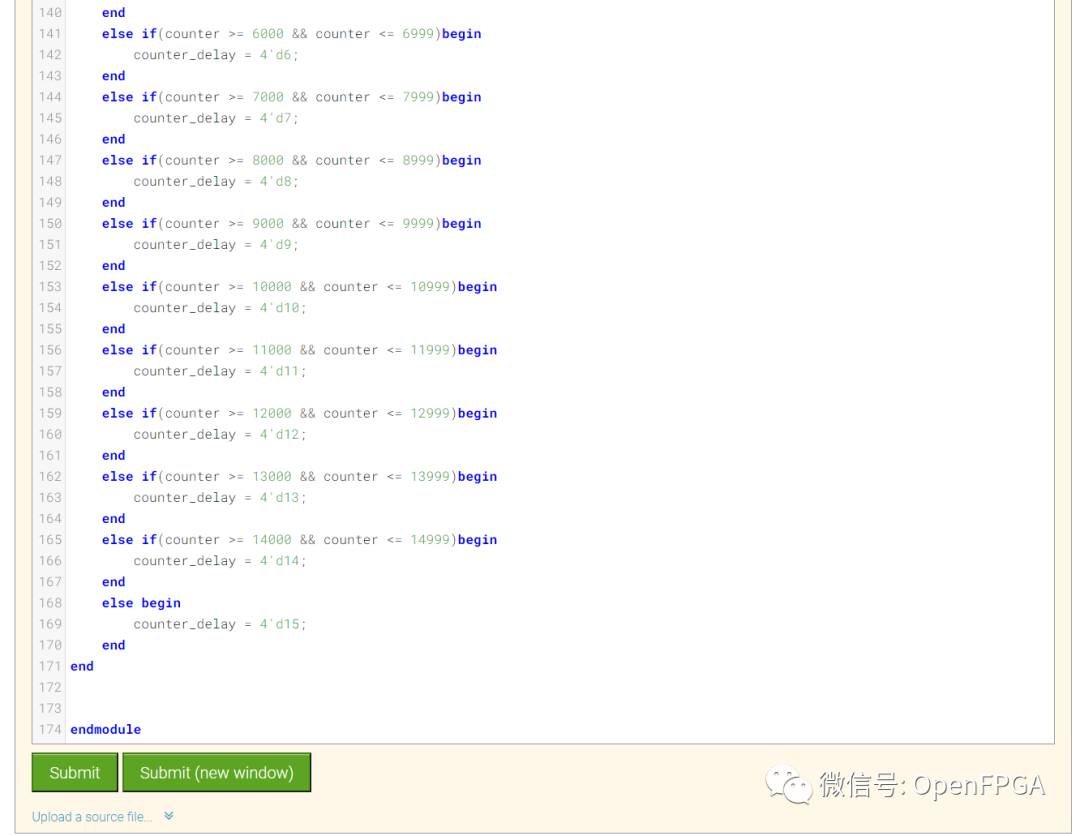
点击Submit,等待一会就能看到下图结果:
注意图中无波形。
这一题就结束了。
Problem 157-review2015_fsmonehot
题目说明
给定以下具有 3 个输入、3 个输出和 10 个状态的状态机:
 图片来自HDLBits
图片来自HDLBits
假定使用以下one-hot编码, 通过检查推导出下一状态逻辑方程和输出逻辑方程: (S, S1, S11, S110, B0, B1, B2, B3, Count, Wait) = (10'b0000000001, 10 'b0000000010, 10'b0000000100, ..., 10'b1000000000)
假设采用one-hot编码,通过检查推导状态转换和输出逻辑方程。仅为该状态机实现状态转换逻辑和输出逻辑(组合逻辑部分)。(测试台将使用非热输入进行测试,以确保不会尝试做更复杂的事情。请参阅fsm3onehot用于描述单热状态机“通过检查”推导逻辑方程的含义。)
编写生成以下等式的代码:
B3_next ,B2 状态的次态(原题写的 B1,应该为笔误)
S_next
S1_next
Count_next
以及下列输出信号
done
counting
shift_ena
模块端口声明
module top_module( input d, input done_counting, input ack, input [9:0] state, // 10-bit one-hot current state output B3_next, output S_next, output S1_next, output Count_next, output Wait_next, output done, output counting, output shift_ena );
题目解析
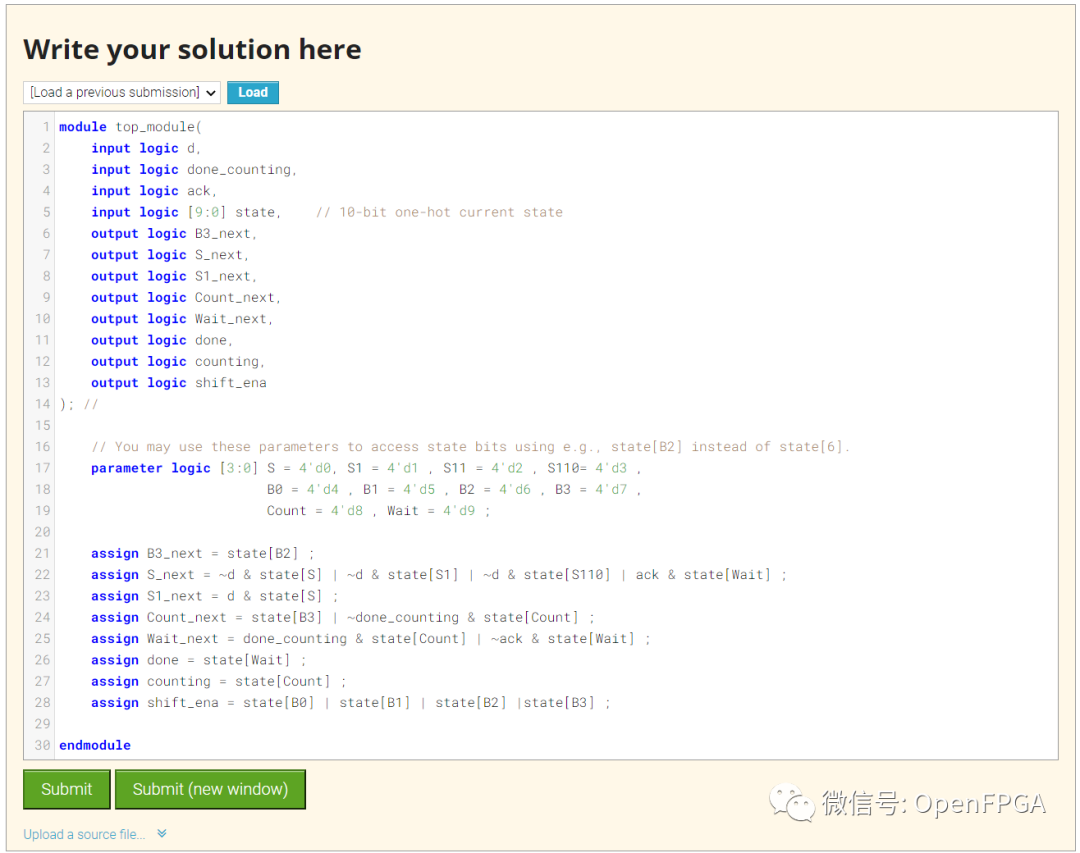
module top_module( input logic d, input logic done_counting, input logic ack, input logic [9:0] state, // 10-bit one-hot current state output logic B3_next, output logic S_next, output logic S1_next, output logic Count_next, output logic Wait_next, output logic done, output logic counting, output logic shift_ena ); // // You may use these parameters to access state bits using e.g., state[B2] instead of state[6]. parameter logic [3:0] S = 4'd0, S1 = 4'd1 , S11 = 4'd2 , S110= 4'd3 , B0 = 4'd4 , B1 = 4'd5 , B2 = 4'd6 , B3 = 4'd7 , Count = 4'd8 , Wait = 4'd9 ; assign B3_next = state[B2] ; assign S_next = ~d & state[S] | ~d & state[S1] | ~d & state[S110] | ack & state[Wait] ; assign S1_next = d & state[S] ; assign Count_next = state[B3] | ~done_counting & state[Count] ; assign Wait_next = done_counting & state[Count] | ~ack & state[Wait] ; assign done = state[Wait] ; assign counting = state[Count] ; assign shift_ena = state[B0] | state[B1] | state[B2] |state[B3] ; endmodule
点击Submit,等待一会就能看到下图结果:
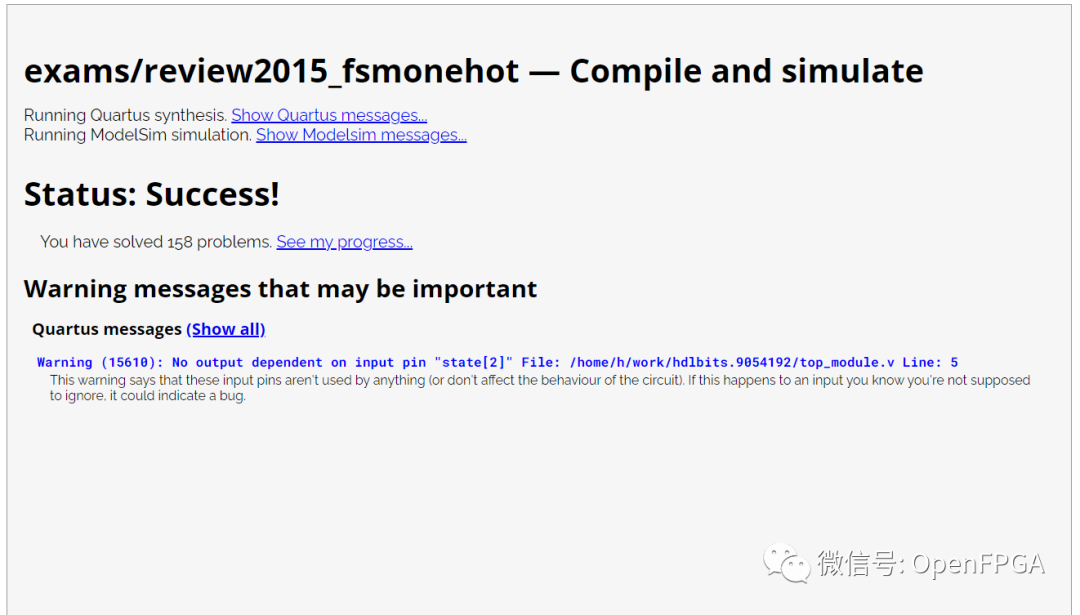
注意图中的Ref是参考波形,Yours是你的代码生成的波形,网站会对比这两个波形,一旦这两者不匹配,仿真结果会变红。
这一题就结束了。
总结
今天的几道题就结束了,今天是大型电路的设计思路,分模块设计。
审核编辑:刘清
-
SystemVerilog在硬件设计部分有哪些优势2023-10-19 2196
-
Systemverilog中的Driving Strength讲解2023-06-14 2465
-
SystemVerilog中的Shallow Copy2022-11-21 1397
-
SystemVerilog中的struct2022-11-07 3197
-
(2)打两拍systemverilog与VHDL编码 精选资料分享2021-07-26 1697
-
SystemVerilog有哪些标准?2021-06-21 1901
-
SystemVerilog的正式验证和混合验证2021-03-29 795
-
做FPGA工程师需要掌握SystemVerilog吗?2017-08-02 6993
-
round robin 的 systemverilog 代码2017-03-14 3695
-
systemverilog学习教程2015-04-01 8484
-
systemverilog--语法详解2014-06-02 4011
-
[启芯公开课] SystemVerilog for Verification2013-06-10 8822
-
基于事件结构的SystemVerilog指称语义2009-12-22 561
-
SystemVerilog Assertion Handbo2009-07-22 1014
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

