

自动驾驶路径规划:A*(Astar)算法
描述
1. 最佳优先搜索(Best-First Search)
最佳优先搜索(BFS),又称A算法,是一种启发式搜索算法(Heuristic Algorithm)。[不是广度优先搜索算法( Breadth First Search , BFS )]BFS算法在广度优先搜索的基础上,用启发估价函数对将要被遍历到的点进行估价,然后选择代价小的进行遍历,直到找到目标节点或者遍历完所有点,算法结束。要实现最佳优先搜索我们必须使用一个优先队列(priority queue)来实现,通常采用一个open优先队列和一个closed集,open优先队列用来储存还没有遍历将要遍历的节点,而closed集用来储存已经被遍历过的节点。1.1 最佳优先搜索的过程最佳优先搜索的过程可以被描述为:1、将根节点放入优先队列open中。2、从优先队列中取出优先级最高的节点X。3、根据节点X生成子节点Y:X的子节点Y不在open队列或者closed中,由估价函数计算出估价值,放入open队列中。X的子节点Y在open队列中,且估价值优于open队列中的子节点Y,将open队列中的子节点Y的估价值替换成新的估价值并按优先值排序。X的子节点Y在closed集中,且估价值优于closed集中的子节点Y,将closed集中的子节点Y移除,并将子节点Y加入open优先队列。4、将节点X放入closed集中。5、重复过程2,3,4直到目标节点找到,或者open为空,程序结束。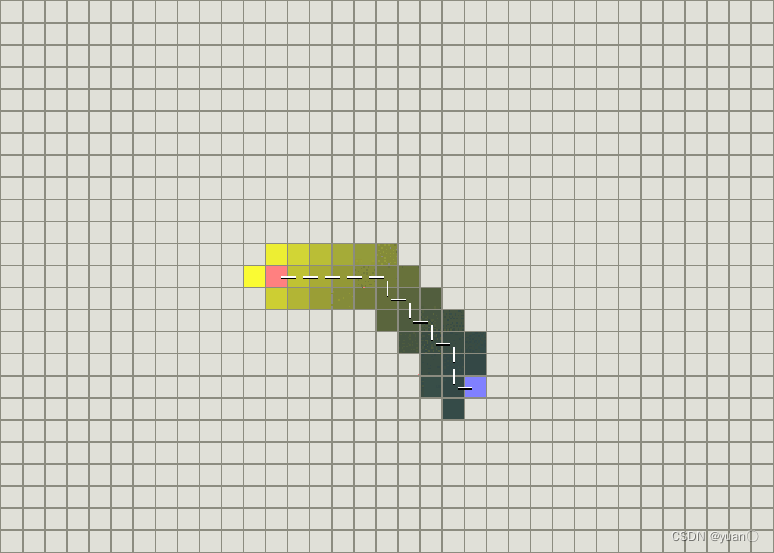 BFS不能保证找到一条最短路径。然而,它比Dijkstra算法快的多,因为它用了一个启发式函数(heuristic function)快速地导向目标结点。这篇博客对BFS进行了详细的介绍用的是罗马尼亚度假问题https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46582817/article/details/115217489
BFS不能保证找到一条最短路径。然而,它比Dijkstra算法快的多,因为它用了一个启发式函数(heuristic function)快速地导向目标结点。这篇博客对BFS进行了详细的介绍用的是罗马尼亚度假问题https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46582817/article/details/115217489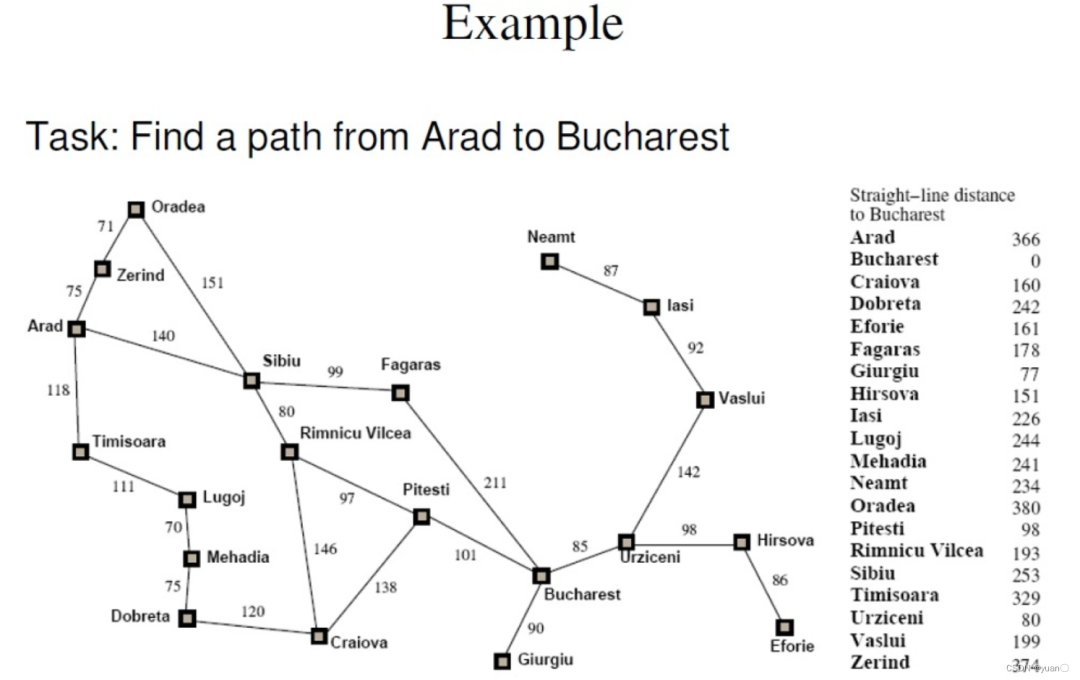
2. A-Star算法
1968年发明的A*算法就是把启发式方法(heuristic approaches)如BFS,和常规方如Dijsktra算法结合在一起的算法。A-Star算法是一种静态路网中求解最短路径最有效的直接搜索方法,也是解决许多搜索问题的有效算法。• 和Dijkstra一样,A*能用于搜索最短路径。• 和BFS一样,A*能用启发式函数引导它自己。左图为Astar算法效果图,右图为Dijkstra算法效果图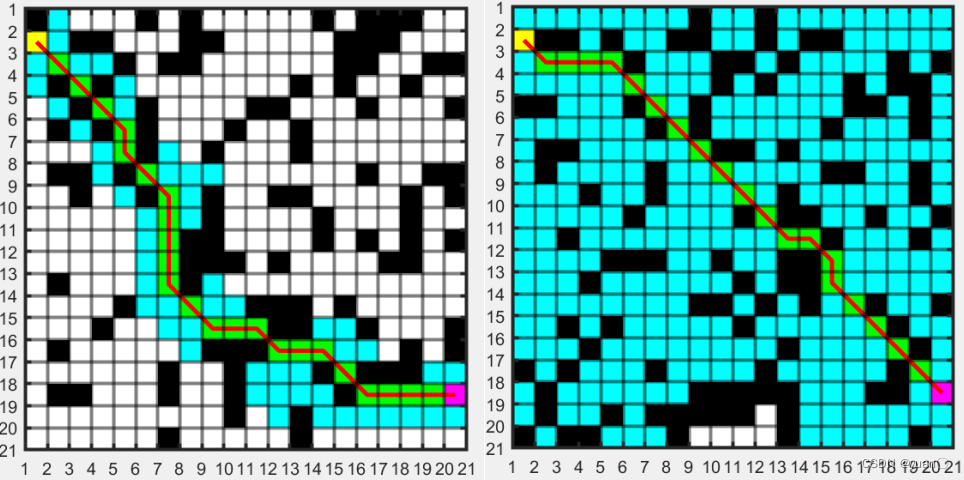 Astar算法与Dijkstra算法的效果差不多,但Astar算法访问的节点数明显比Dijkstra算法少得多,说明其速度更快,运行时间更短。
2.1 Astar算法所属分类
A*算法在最短路径搜索算法中分类为:• 直接搜索算法:直接在实际地图上进行搜索,不经过任何预处理;• 启发式算法:通过启发函数引导算法的搜索方向;• 静态图搜索算法:被搜索的图的权值不随时间变化(后被证明同样可以适用于动态图的搜索 )
2.2 Astar算法基本概念
A*算法启发函数表示为:f(n)=g(n)+h(n)•f(n) 是从初始状态经由状态n到目标状态的代价估计•g(n) 是在状态空间中从初始状态到状态n的实际代价•h(n) 是从状态n到目标状态的最佳路径的估计代价(对于路径搜索问题,状态就是图中的节点,代价就是距离)Astar算法是启发式搜索算法,启发式搜索是在状态空间中对每一个搜索的位置进行评估,得到最好的位置,再从这个位置进行搜索直到目标。这样可以省略大量无谓的搜索路径,提高效率。在启发式搜索中,对位置的估价是十分重要的。采用了不同的估价可以有不同的效果。启发函数(Heuristics Function)(估价函数): H为启发函数,也被认为是一种试探。由于在找到唯一路径前,不确定在前面会出现什么障碍物,计算H的算法(例如,H可采用传统的曼哈顿距离)具体根据实际场景决定父节点(parent): 在路径规划中用于回溯的节点。搜索区域(The Search Area): 前面图中的搜索区域被划分为了简单的二维数组,数组每个元素对应一个小方格,也可以将区域等分成是五角星,矩形等,通常将一个单位的中心点称之为搜索区域节点(Node)。 开放列表(Open List):将路径规划过程中待检测的节点存放于Open List中。关闭列表(Close List): 将路径规划过程中已经检查过的节点放在Close List。
2.3 启发函数单调性的推导
单调性:单调性是Astar算法非常重要的一个性质,它决定了在用Astar算法进行路径搜索时,一定能找到一条最优路径。设父节点的坐标为(x0,y0),它的任意一个子节点的坐标为(xi,yi),所以对两者之间的h(x),就一定满足
Astar算法与Dijkstra算法的效果差不多,但Astar算法访问的节点数明显比Dijkstra算法少得多,说明其速度更快,运行时间更短。
2.1 Astar算法所属分类
A*算法在最短路径搜索算法中分类为:• 直接搜索算法:直接在实际地图上进行搜索,不经过任何预处理;• 启发式算法:通过启发函数引导算法的搜索方向;• 静态图搜索算法:被搜索的图的权值不随时间变化(后被证明同样可以适用于动态图的搜索 )
2.2 Astar算法基本概念
A*算法启发函数表示为:f(n)=g(n)+h(n)•f(n) 是从初始状态经由状态n到目标状态的代价估计•g(n) 是在状态空间中从初始状态到状态n的实际代价•h(n) 是从状态n到目标状态的最佳路径的估计代价(对于路径搜索问题,状态就是图中的节点,代价就是距离)Astar算法是启发式搜索算法,启发式搜索是在状态空间中对每一个搜索的位置进行评估,得到最好的位置,再从这个位置进行搜索直到目标。这样可以省略大量无谓的搜索路径,提高效率。在启发式搜索中,对位置的估价是十分重要的。采用了不同的估价可以有不同的效果。启发函数(Heuristics Function)(估价函数): H为启发函数,也被认为是一种试探。由于在找到唯一路径前,不确定在前面会出现什么障碍物,计算H的算法(例如,H可采用传统的曼哈顿距离)具体根据实际场景决定父节点(parent): 在路径规划中用于回溯的节点。搜索区域(The Search Area): 前面图中的搜索区域被划分为了简单的二维数组,数组每个元素对应一个小方格,也可以将区域等分成是五角星,矩形等,通常将一个单位的中心点称之为搜索区域节点(Node)。 开放列表(Open List):将路径规划过程中待检测的节点存放于Open List中。关闭列表(Close List): 将路径规划过程中已经检查过的节点放在Close List。
2.3 启发函数单调性的推导
单调性:单调性是Astar算法非常重要的一个性质,它决定了在用Astar算法进行路径搜索时,一定能找到一条最优路径。设父节点的坐标为(x0,y0),它的任意一个子节点的坐标为(xi,yi),所以对两者之间的h(x),就一定满足 在Astar算法的运行过程中,后继的f(x)值时大于当前f(x)的值,即f(x)在之后对子节点的搜索扩展是单调递增的,不会像人工势场法一样出现局部极小值,因此使用Astar算法规划出的路径一定是最优路径.2.4 设计代价函数时所需注意的点在使用A*算法的过程中,启发代价的值必须尽量接近于真实值(尽量选取能取到的最大值,这样可以提升搜索效率),以保证规划出的路径尽可能地与实际地图环境相符合。根据所需的模型选择不同的启发代价的计算方法时,同样必须保证启发代价所得的估计值小于真实值。
2.5 代价函数的选择
2.5.1 曼哈顿距离
曼哈顿距离函数在标准坐标系中,表示起始和目标两节点的绝对值总和,其估计值就是从当前点做水平和垂直运动,到达目标点的成本的估计,因此,曼哈顿距离函数中,两点的距离如下
在Astar算法的运行过程中,后继的f(x)值时大于当前f(x)的值,即f(x)在之后对子节点的搜索扩展是单调递增的,不会像人工势场法一样出现局部极小值,因此使用Astar算法规划出的路径一定是最优路径.2.4 设计代价函数时所需注意的点在使用A*算法的过程中,启发代价的值必须尽量接近于真实值(尽量选取能取到的最大值,这样可以提升搜索效率),以保证规划出的路径尽可能地与实际地图环境相符合。根据所需的模型选择不同的启发代价的计算方法时,同样必须保证启发代价所得的估计值小于真实值。
2.5 代价函数的选择
2.5.1 曼哈顿距离
曼哈顿距离函数在标准坐标系中,表示起始和目标两节点的绝对值总和,其估计值就是从当前点做水平和垂直运动,到达目标点的成本的估计,因此,曼哈顿距离函数中,两点的距离如下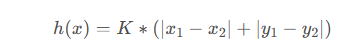 K——相邻两节点之间的距离,即单位距离;
K——相邻两节点之间的距离,即单位距离;(x1,y1)——起始节点的坐标;
(x2,y2)——目标节点的坐标;
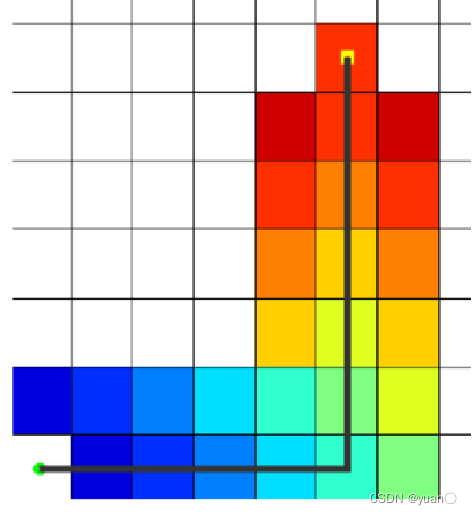 2.5.2 欧几里得距离
欧几里得距离又称为欧式距离,它是衡量两点之间距离远近的最常用的方法之一。欧几里得距离函数的值可以直接看作起始节点和目标节点,在欧式空间中的直线距离,其表达式如下所示
2.5.2 欧几里得距离
欧几里得距离又称为欧式距离,它是衡量两点之间距离远近的最常用的方法之一。欧几里得距离函数的值可以直接看作起始节点和目标节点,在欧式空间中的直线距离,其表达式如下所示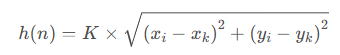 K——相邻两节点之间的距离,即单位距离;
K——相邻两节点之间的距离,即单位距离;(xi,yi)——当前节点的坐标;
(xk,yk)——目标节点的坐标;
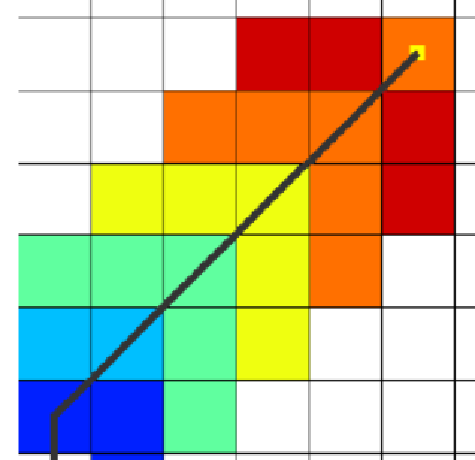 欧几里德距离函数作为启发代价的计算方法时,虽然寻径时搜索空间增加从而导致搜索效率的降低,但其所得的估计值最小;而在使用曼哈顿距离函数时,虽然寻径需要遍历的栅格空间少于欧几里得距离函数,搜索效率较高,但这种方法得到的估计值与欧几里得距离函数相比,距离真实值更远。
2.6 确定最终路径
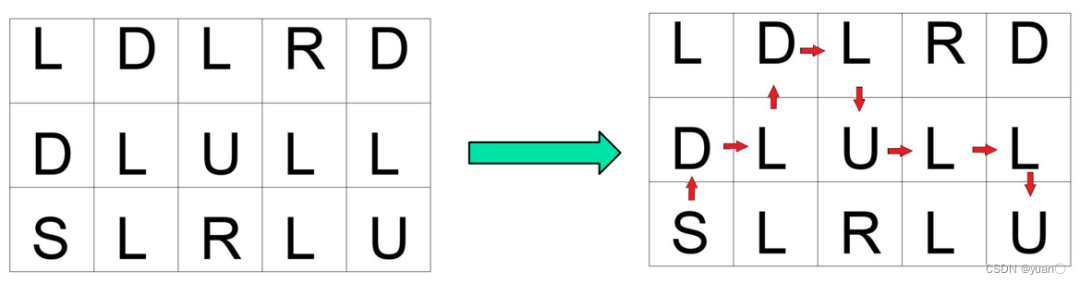
已经确定了目标节点的坐标为,根据此目标节点的位置,和先前设置的方向存储函数之中的方向,从目标节点利用方向反推至起始节点。具体实现的示意图如下
欧几里德距离函数作为启发代价的计算方法时,虽然寻径时搜索空间增加从而导致搜索效率的降低,但其所得的估计值最小;而在使用曼哈顿距离函数时,虽然寻径需要遍历的栅格空间少于欧几里得距离函数,搜索效率较高,但这种方法得到的估计值与欧几里得距离函数相比,距离真实值更远。
2.6 确定最终路径
已经确定了目标节点的坐标为,根据此目标节点的位置,和先前设置的方向存储函数之中的方向,从目标节点利用方向反推至起始节点。具体实现的示意图如下
 2.7 路径平滑
我们需要对规划出的路径进行平滑处理,将路径的转折处转化为平滑的曲线,使之更加符合无人车的实际运动路径。主要有基于B样条曲线的路径优化方法,基于Dubins圆的路径优化方法,和基于Clothoid曲线的路径优化方法,基于贝塞尔曲线的路径平滑算法。
2.7 路径平滑
我们需要对规划出的路径进行平滑处理,将路径的转折处转化为平滑的曲线,使之更加符合无人车的实际运动路径。主要有基于B样条曲线的路径优化方法,基于Dubins圆的路径优化方法,和基于Clothoid曲线的路径优化方法,基于贝塞尔曲线的路径平滑算法。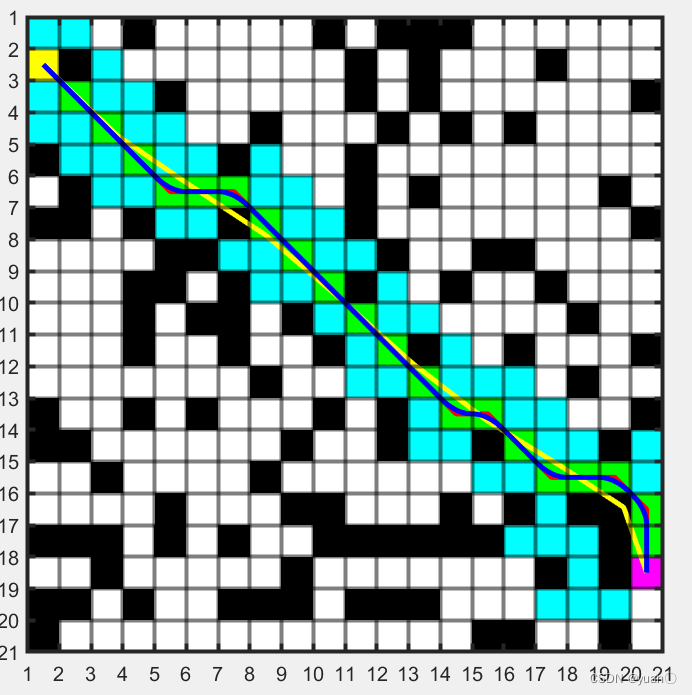 红色为未平滑路径,绿色方块为最终路径,黄色为贝塞尔曲线拟合得到,蓝色为spcrv函数平滑得到。
2.8 Astar算法的优缺点
优点:相对于需要将所有节点展开搜寻的算法,A*算法最大的优点就是引入了启发信息作为向目标点移动的决策辅助,所以不再需要遍历整个地图,降低了计算复杂度,减少了时间损耗少。缺点:基于栅格法来分割地图,精度越高,栅格分的就越小,就会使工作量几何式的增长。估价函数选取的不合理也有可能导致无法规划出最优路径。距离估计与实际值越接近,估价函数取得就越好。估价函数f(n)在g(n)一定的情况下,会或多或少的受距离估计值h(n)的制约,节点距目标点近,h值小,f值相对就小,能保证最短路的搜索向终点的方向进行,明显优于Dijkstra算法的毫无方向的向四周搜索。
2.9 Astar算法流程
红色为未平滑路径,绿色方块为最终路径,黄色为贝塞尔曲线拟合得到,蓝色为spcrv函数平滑得到。
2.8 Astar算法的优缺点
优点:相对于需要将所有节点展开搜寻的算法,A*算法最大的优点就是引入了启发信息作为向目标点移动的决策辅助,所以不再需要遍历整个地图,降低了计算复杂度,减少了时间损耗少。缺点:基于栅格法来分割地图,精度越高,栅格分的就越小,就会使工作量几何式的增长。估价函数选取的不合理也有可能导致无法规划出最优路径。距离估计与实际值越接近,估价函数取得就越好。估价函数f(n)在g(n)一定的情况下,会或多或少的受距离估计值h(n)的制约,节点距目标点近,h值小,f值相对就小,能保证最短路的搜索向终点的方向进行,明显优于Dijkstra算法的毫无方向的向四周搜索。
2.9 Astar算法流程
 如下图所示,绿色是起点A,红色是终点B,一系列蓝色是障碍物,从A移动到B,绕过障碍。
如下图所示,绿色是起点A,红色是终点B,一系列蓝色是障碍物,从A移动到B,绕过障碍。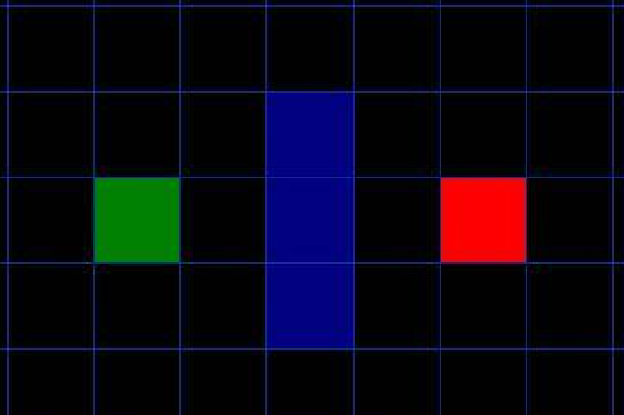 1、用方格(三角形、五角形)划分空间,简化搜索区域。空间被划分为二维数组,数组中每个元素代表空间中的一个方格,可被标记为可行或不可行。未来的路径就是一系列可行方块的集合。Nodes的概念涵盖了一系列可行方块(或其它方块)2、将起点A放到Openlist中,Openlist存放着一系列需要检查的节点(方块)3、给Openlist中每个节点赋值F=G+H (起点为0,横向和纵向的移动代价为 10 ,对角线的移动代价为 14)4、检查Openlist,选取F值最小的节点(此处为A点)。5、将A点从Openlist中删除,放入Closelist中(Closelist中存放不可寻点,即已被访问过的点),把A点临近节点放入Openlist中,并将A点设为临近节点的父节点。
1、用方格(三角形、五角形)划分空间,简化搜索区域。空间被划分为二维数组,数组中每个元素代表空间中的一个方格,可被标记为可行或不可行。未来的路径就是一系列可行方块的集合。Nodes的概念涵盖了一系列可行方块(或其它方块)2、将起点A放到Openlist中,Openlist存放着一系列需要检查的节点(方块)3、给Openlist中每个节点赋值F=G+H (起点为0,横向和纵向的移动代价为 10 ,对角线的移动代价为 14)4、检查Openlist,选取F值最小的节点(此处为A点)。5、将A点从Openlist中删除,放入Closelist中(Closelist中存放不可寻点,即已被访问过的点),把A点临近节点放入Openlist中,并将A点设为临近节点的父节点。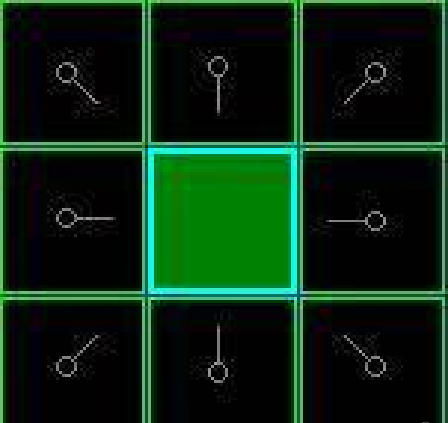 6、给Openlist中每个节点赋值,选取F值最小的节点设为当前节点Node,(若当前节点Node为终点,则寻路结束,若Openlist中没有可寻节点,则寻路失败)
6、给Openlist中每个节点赋值,选取F值最小的节点设为当前节点Node,(若当前节点Node为终点,则寻路结束,若Openlist中没有可寻节点,则寻路失败)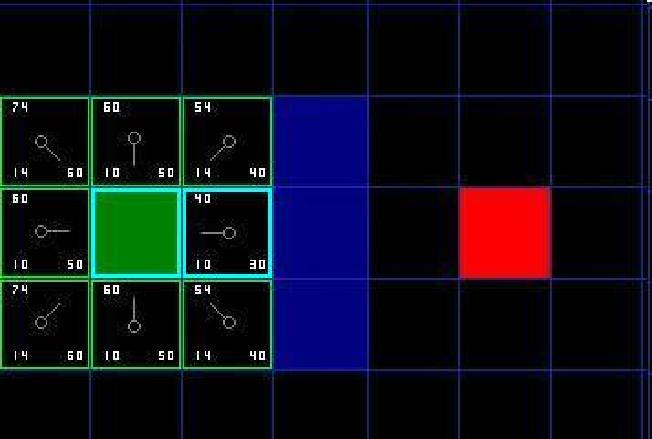 7、检查当前节点Node周围临近节点。忽略Closelist中的节点和不可行节点(障碍),如果临近节点在Openlist中,则对比一下是否从当前节点到临近节点的G值比原G值(直接到临近节点的实际代价值)小,若是,把当前节点作为父节点。否,不做改动。如果临近节点不在Openlist中,将其加入到Openlist中,将当前节点设为它的父节点。8、若上步骤中新节点未造成任何改动,将新节点作为当前节点,重复6,7)中的步骤,直到找到目标节点。
7、检查当前节点Node周围临近节点。忽略Closelist中的节点和不可行节点(障碍),如果临近节点在Openlist中,则对比一下是否从当前节点到临近节点的G值比原G值(直接到临近节点的实际代价值)小,若是,把当前节点作为父节点。否,不做改动。如果临近节点不在Openlist中,将其加入到Openlist中,将当前节点设为它的父节点。8、若上步骤中新节点未造成任何改动,将新节点作为当前节点,重复6,7)中的步骤,直到找到目标节点。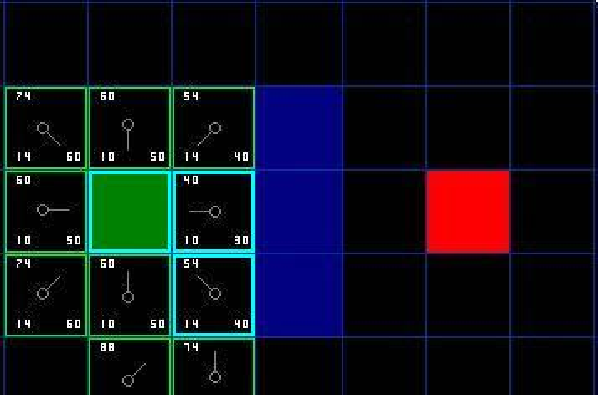 寻找到目标节点
寻找到目标节点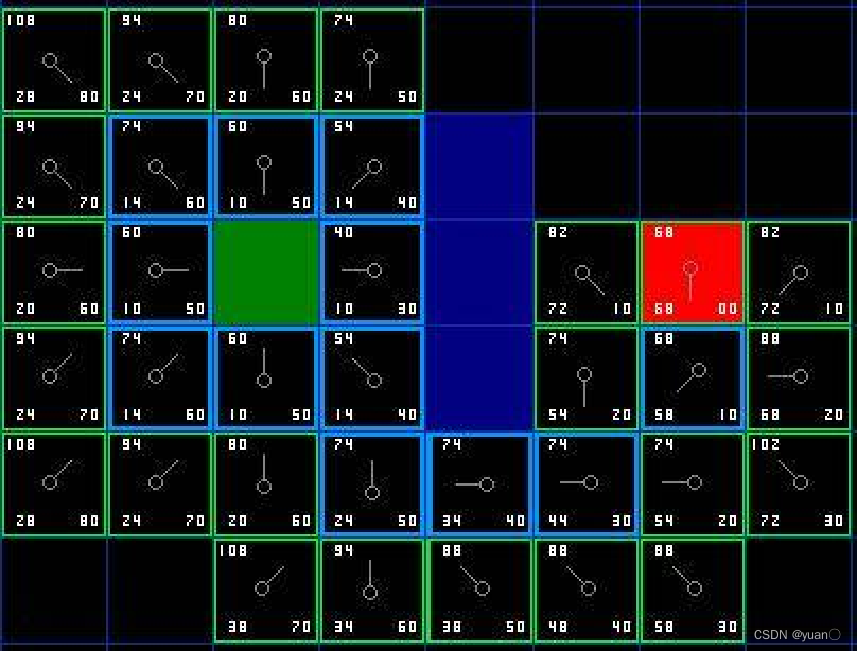 9、从目标节点回溯可以找到初始点,从而确定路径
9、从目标节点回溯可以找到初始点,从而确定路径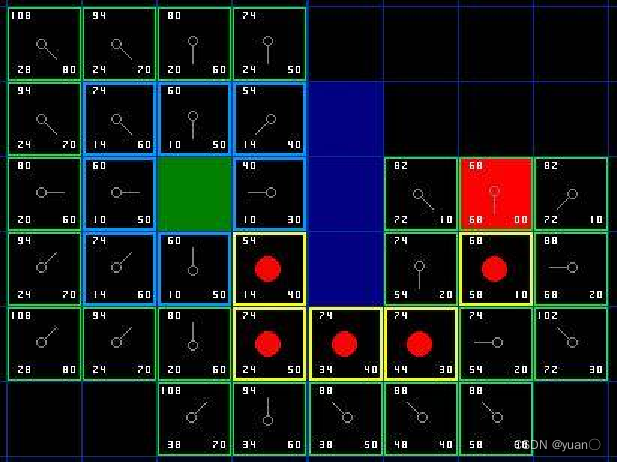 上述描述路径的图片有些错误,具体步骤如下图所示。
上述描述路径的图片有些错误,具体步骤如下图所示。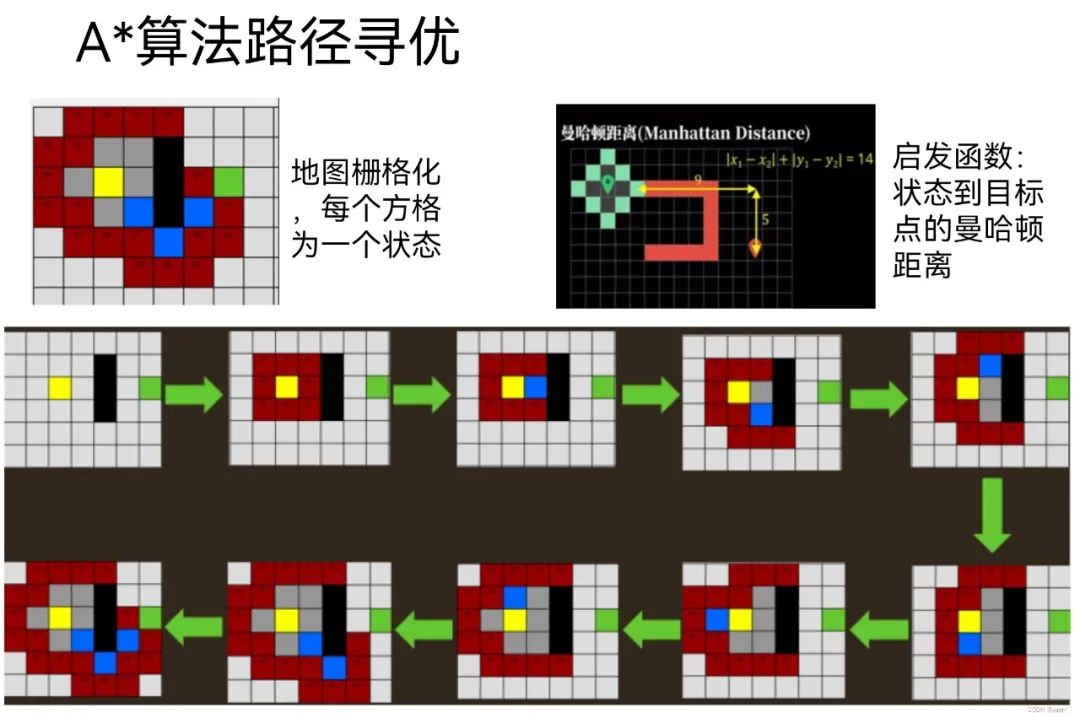
3. 其他Astar算法
3.1 Astar——三维地图规划 3.1.1 3D-Astar原理三维栅格地图,顾名思义不是简单的二维平面,它必须得有三维方向,也就是高度方向上的拓展。栅格地图在XY水平面上的栅格的投影颜色不尽相同,栅格黄色程度越高,表明此处的高度越高。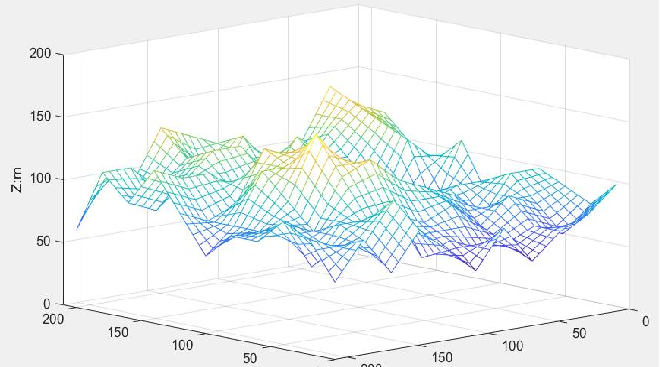 为了使启发代价的值应该尽量接近于真实值,三维栅格地图中仍然选用欧几里得距离作为估价函数计算启发代价的计算方法。但本次实验所处的环境为三维避障空间,因此相较于二维空间的路径规划,我们将公式做三维化推广,具体形式如下:
为了使启发代价的值应该尽量接近于真实值,三维栅格地图中仍然选用欧几里得距离作为估价函数计算启发代价的计算方法。但本次实验所处的环境为三维避障空间,因此相较于二维空间的路径规划,我们将公式做三维化推广,具体形式如下: h(n)——当前节点到目标节点的启发代价值;g(n-1)——当前节点到它的父节点之间的路径代价;D(n-1, n)——当前节点与它的子节点之间的代价值。g(n-1)与二维规划中的距离代价计算方法一致,但D(n-1, n)在计算时用父节点与子节点之间的距离值除以三维避障环境中设定的栅格可通行程度,h(n)也是用当前节点到目标节点的启发代价值除以地图环境中预先设定的栅格可通行程度。
3.1.2 基于MATLAB实现3D-Astar
这里是代码的GitHub地址:https://github.com/ybmasmiling/Astar_3D
h(n)——当前节点到目标节点的启发代价值;g(n-1)——当前节点到它的父节点之间的路径代价;D(n-1, n)——当前节点与它的子节点之间的代价值。g(n-1)与二维规划中的距离代价计算方法一致,但D(n-1, n)在计算时用父节点与子节点之间的距离值除以三维避障环境中设定的栅格可通行程度,h(n)也是用当前节点到目标节点的启发代价值除以地图环境中预先设定的栅格可通行程度。
3.1.2 基于MATLAB实现3D-Astar
这里是代码的GitHub地址:https://github.com/ybmasmiling/Astar_3D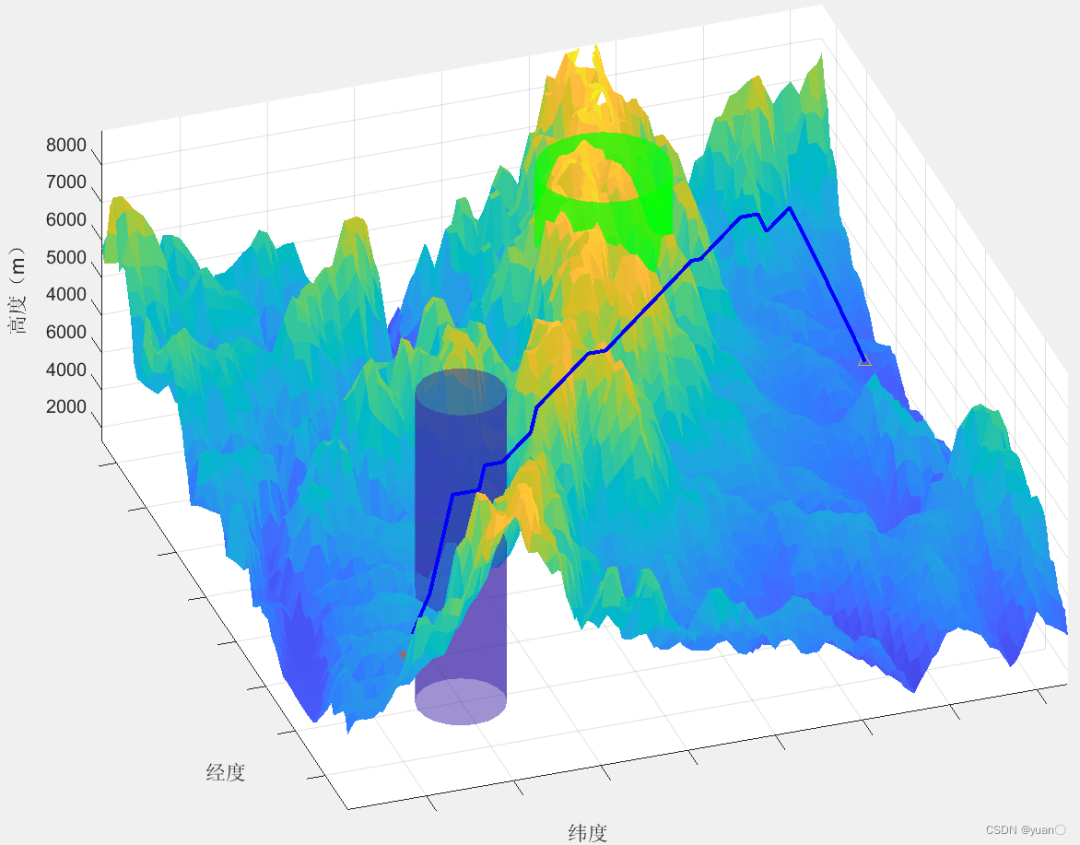
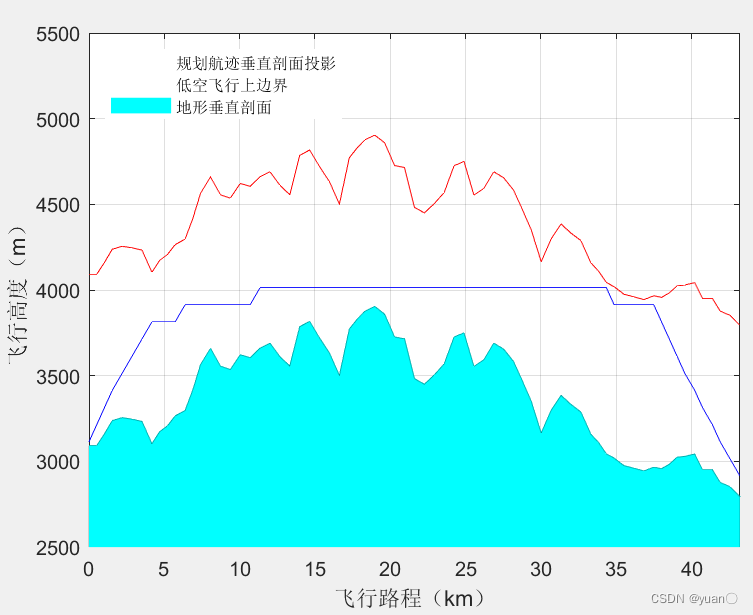 3.2 距离与能量复合Astar算法
经典Astar算法路径规划是取两节点间曼哈顿距离作为距离估计为最优原则搜索路径,从而得到最短路径。搜索路径的过程中并没有考虑实际道路坡度和道路滚动阻力系数对行驶车辆最短路径搜索的影响,也没有考虑在道路上行驶的能量损耗问题,即经典Astar算法搜索的最短路径并非符合实际车辆行驶的最优路径。
3.2.1 最短路径启发函数最短路径启发函数:
3.2 距离与能量复合Astar算法
经典Astar算法路径规划是取两节点间曼哈顿距离作为距离估计为最优原则搜索路径,从而得到最短路径。搜索路径的过程中并没有考虑实际道路坡度和道路滚动阻力系数对行驶车辆最短路径搜索的影响,也没有考虑在道路上行驶的能量损耗问题,即经典Astar算法搜索的最短路径并非符合实际车辆行驶的最优路径。
3.2.1 最短路径启发函数最短路径启发函数:
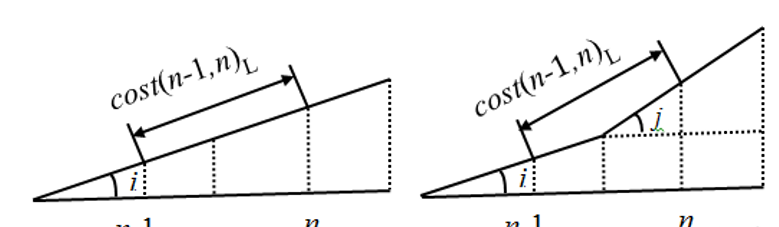 最终得到的最短路径启发函数如下式:
最终得到的最短路径启发函数如下式: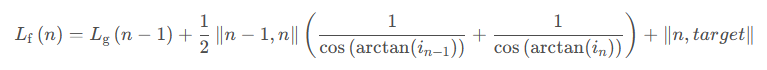 3.2.2 最短道路损耗功启发函数
道路损耗功启发函数:
3.2.2 最短道路损耗功启发函数
道路损耗功启发函数:
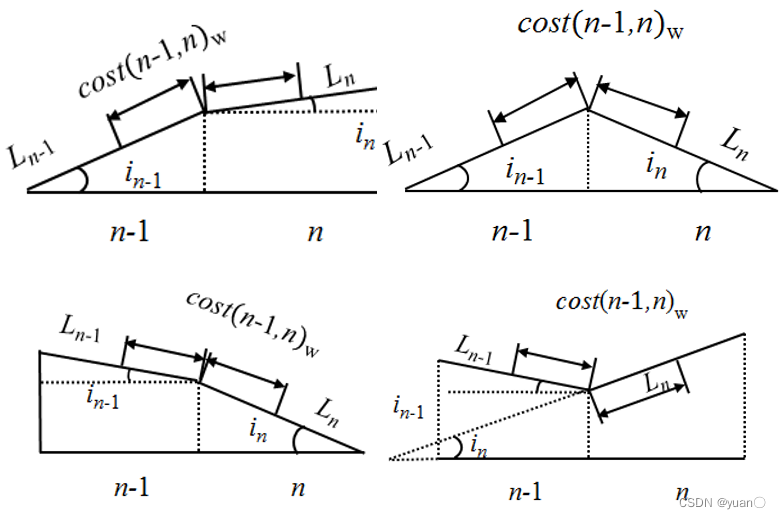 最终得到的最短道路损耗功启发函数如下式:
最终得到的最短道路损耗功启发函数如下式: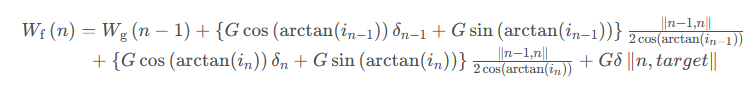 3.2.3 综合启发函数
综合启发函数:
3.2.3 综合启发函数
综合启发函数: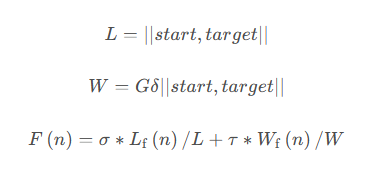
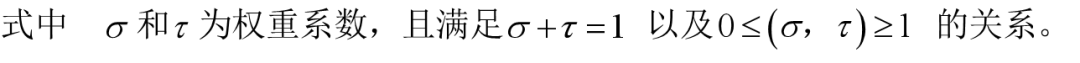 综合式启发函数统一最短路径启发函数和最小道路额外功函数,不同的权重大小决定最短路径启发函数和最小道路额外功函数在综合式启发函数中所占不同的比重。
3.3 双向Astar算法
传统A算法在大环境中搜索,存在着搜索效率低的问题。传统A算法是从起点开始向终点搜索,直到寻到可行路径停止搜索,在搜索路径的前期阶段远g(n)小于h(n),搜索时横向搜索范围窄,纵向搜索范围宽,搜索速度快,在搜索的后期阶段g(n)远大于h(n),搜索时纵向搜索范围窄,横向搜索范围宽,搜索速度慢;**而改进后的双向A搜索算法分别从起点和终点开始搜索,当搜索到相同的当前节点时,搜索结束。**相比于传统A算法,双向A*搜索算法都处于g(n)远小于h(n)阶段,一定程度上提高了算法的搜索效率,缩短搜索时间。
综合式启发函数统一最短路径启发函数和最小道路额外功函数,不同的权重大小决定最短路径启发函数和最小道路额外功函数在综合式启发函数中所占不同的比重。
3.3 双向Astar算法
传统A算法在大环境中搜索,存在着搜索效率低的问题。传统A算法是从起点开始向终点搜索,直到寻到可行路径停止搜索,在搜索路径的前期阶段远g(n)小于h(n),搜索时横向搜索范围窄,纵向搜索范围宽,搜索速度快,在搜索的后期阶段g(n)远大于h(n),搜索时纵向搜索范围窄,横向搜索范围宽,搜索速度慢;**而改进后的双向A搜索算法分别从起点和终点开始搜索,当搜索到相同的当前节点时,搜索结束。**相比于传统A算法,双向A*搜索算法都处于g(n)远小于h(n)阶段,一定程度上提高了算法的搜索效率,缩短搜索时间。
4. MATLAB实现Astar算法
4.1 defColorMap.m 用于初始化地图参数
function [field,cmap] = defColorMap(rows, cols)
cmap = [1 1 1; ... % 1-白色-空地
0 0 0; ... % 2-黑色-静态障碍
1 0 0; ... % 3-红色-动态障碍
1 1 0;... % 4-黄色-起始点
1 0 1;... % 5-品红-目标点
0 1 0; ... % 6-绿色-到目标点的规划路径
0 1 1]; % 7-青色-动态规划的路径
% 构建颜色MAP图
colormap(cmap);
% 定义栅格地图全域,并初始化空白区域
field = ones(rows, cols);
% 障碍物区域
obsRate = 0.3;
obsNum = floor(rows*cols*obsRate);
obsIndex = randi([1,rows*cols],obsNum,1);
field(obsIndex) = 2;
4.2 getChildNode.m
用于获取子节点信息
function childNodes = getChildNode(field,closeList, parentNode)
% 选取父节点周边8个节点作为备选子节点,线性化坐标
% 排除超过边界之外的、位于障碍区的、位于closeList中的
[rows, cols] = size(field);
[row_parentNode, col_parentNode] = ind2sub([rows, cols], parentNode);
childNodes = [];
closeList = closeList(:,1);
% 第1个子节点(右节点)
childNode = [row_parentNode, col_parentNode+1];
if ~(childNode(1) < 1 || childNode(1) > rows ||...
childNode(2) < 1 || childNode(2) > cols)
if field(childNode(1), childNode(2)) ~= 2
childNode_LineIdx = sub2ind([rows, cols], childNode(1), childNode(2));
if ~ismember(childNode_LineIdx, closeList)
childNodes(end+1) = childNode_LineIdx;
end
end
end
% 第2个子节点(右上节点)
childNode = [row_parentNode-1, col_parentNode+1];
child_brother_node_sub1 = [row_parentNode-1, col_parentNode];
child_brother_node_sub2 = [row_parentNode, col_parentNode+1];
if ~(childNode(1) < 1 || childNode(1) > rows ||...
childNode(2) < 1 || childNode(2) > cols)
if field(childNode(1), childNode(2)) ~= 2
if ~(field(child_brother_node_sub1(1), child_brother_node_sub1(2)) == 2 & field(child_brother_node_sub2(1), child_brother_node_sub2(2)) == 2)
childNode_LineIdx = sub2ind([rows, cols], childNode(1), childNode(2));
if ~ismember(childNode_LineIdx, closeList)
childNodes(end+1) = childNode_LineIdx;
end
end
end
end
% 第3个子节点(上节点)
childNode = [row_parentNode-1, col_parentNode];
if ~(childNode(1) < 1 || childNode(1) > rows ||...
childNode(2) < 1 || childNode(2) > cols)
if field(childNode(1), childNode(2)) ~= 2
childNode_LineIdx = sub2ind([rows, cols], childNode(1), childNode(2));
if ~ismember(childNode_LineIdx, closeList)
childNodes(end+1) = childNode_LineIdx;
end
end
end
% 第4个子节点(左上)
childNode = [row_parentNode-1, col_parentNode-1];
child_brother_node_sub1 = [row_parentNode-1, col_parentNode];
child_brother_node_sub2 = [row_parentNode, col_parentNode-1];
if ~(childNode(1) < 1 || childNode(1) > rows ||...
childNode(2) < 1 || childNode(2) > cols)
if field(childNode(1), childNode(2)) ~= 2
if ~(field(child_brother_node_sub1(1), child_brother_node_sub1(2)) == 2 & field(child_brother_node_sub2(1), child_brother_node_sub2(2)) == 2)
childNode_LineIdx = sub2ind([rows, cols], childNode(1), childNode(2));
if ~ismember(childNode_LineIdx, closeList)
childNodes(end+1) = childNode_LineIdx;
end
end
end
end
% 第5个子节点(左节点)
childNode = [row_parentNode, col_parentNode-1];
if ~(childNode(1) < 1 || childNode(1) > rows ||...
childNode(2) < 1 || childNode(2) > cols)
if field(childNode(1), childNode(2)) ~= 2
childNode_LineIdx = sub2ind([rows, cols], childNode(1), childNode(2));
if ~ismember(childNode_LineIdx, closeList)
childNodes(end+1) = childNode_LineIdx;
end
end
end
% 第6个子节点(左下)
childNode = [row_parentNode+1, col_parentNode-1];
child_brother_node_sub1 = [row_parentNode, col_parentNode-1];
child_brother_node_sub2 = [row_parentNode+1, col_parentNode];
if ~(childNode(1) < 1 || childNode(1) > rows ||...
childNode(2) < 1 || childNode(2) > cols)
if field(childNode(1), childNode(2)) ~= 2
if ~(field(child_brother_node_sub1(1), child_brother_node_sub1(2)) == 2 & field(child_brother_node_sub2(1), child_brother_node_sub2(2)) == 2)
childNode_LineIdx = sub2ind([rows, cols], childNode(1), childNode(2));
if ~ismember(childNode_LineIdx, closeList)
childNodes(end+1) = childNode_LineIdx;
end
end
end
end
% 第7个子节点(下)
childNode = [row_parentNode+1, col_parentNode];
if ~(childNode(1) < 1 || childNode(1) > rows ||...
childNode(2) < 1 || childNode(2) > cols)
if field(childNode(1), childNode(2)) ~= 2
childNode_LineIdx = sub2ind([rows, cols], childNode(1), childNode(2));
if ~ismember(childNode_LineIdx, closeList)
childNodes(end+1) = childNode_LineIdx;
end
end
end
% 第8个子节点(右下)
childNode = [row_parentNode+1, col_parentNode+1];
child_brother_node_sub1 = [row_parentNode, col_parentNode+1];
child_brother_node_sub2 = [row_parentNode+1, col_parentNode];
if ~(childNode(1) < 1 || childNode(1) > rows ||...
childNode(2) < 1 || childNode(2) > cols)
if field(childNode(1), childNode(2)) ~= 2
if ~(field(child_brother_node_sub1(1), child_brother_node_sub1(2)) == 2 & field(child_brother_node_sub2(1), child_brother_node_sub2(2)) == 2)
childNode_LineIdx = sub2ind([rows, cols], childNode(1), childNode(2));
if ~ismember(childNode_LineIdx, closeList)
childNodes(end+1) = childNode_LineIdx;
end
end
end
end
4.3 Astar.m
主程序
% 基于栅格地图的机器人路径规划算法
% A*算法
clc
clear
close all
%% 栅格界面、场景定义
% 行数和列数
rows = 20;
cols = 20;
[field,cmap] = defColorMap(rows, cols);
% 起点、终点、障碍物区域
startPos = 2;
goalPos = rows*cols-2;
field(startPos) = 4;
field(goalPos) = 5;
%% 预处理
% 初始化closeList
parentNode = startPos;
closeList = [startPos,0];
% 初始化openList
openList = struct;
childNodes = getChildNode(field,closeList,parentNode);
for i = 1:length(childNodes)
[row_startPos,col_startPos] = ind2sub([rows, cols],startPos);
[row_goalPos,col_goalPos] = ind2sub([rows, cols],goalPos);
[row,col] = ind2sub([rows, cols],childNodes(i));
% 存入openList结构体
openList(i).node = childNodes(i);
openList(i).g = norm([row_startPos,col_startPos] - [row,col]); % 实际代价采用欧式距离
openList(i).h = abs(row_goalPos - row) + abs(col_goalPos - col); % 估计代价采用曼哈顿距离
openList(i).f = openList(i).g + openList(i).h;
end
% 初始化path
for i = 1:rows*cols
path{i,1} = i; % 线性索引值
end
for i = 1:length(openList)
node = openList(i).node;
path{node,2} = [startPos,node];
end
%% 开始搜索
% 从openList开始搜索移动代价最小的节点
[~, idx_min] = min([openList.f]);
parentNode = openList(idx_min).node;
% 进入循环
while true
% 找出父节点的8个子节点,障碍物节点用inf,
childNodes = getChildNode(field, closeList,parentNode);
% 判断这些子节点是否在openList中,若在,则比较更新;没在则追加到openList中
for i = 1:length(childNodes)
% 需要判断的子节点
childNode = childNodes(i);
[in_flag,idx] = ismember(childNode, [openList.node]);
% 计算代价函数
[row_parentNode,col_parentNode] = ind2sub([rows, cols], parentNode);
[row_childNode,col_childNode] = ind2sub([rows, cols], childNode);
[row_goalPos,col_goalPos] = ind2sub([rows, cols],goalPos);
g = openList(idx_min).g + norm( [row_parentNode,col_parentNode] -...
[row_childNode,col_childNode]);
h = abs(row_goalPos - row_childNode) + abs(col_goalPos - col_childNode); % 采用曼哈顿距离进行代价估计
f = g + h;
if in_flag % 若在,比较更新g和f
if f < openList(idx).f
openList(idx).g = g;
openList(idx).h = h;
openList(idx).f = f;
path{childNode,2} = [path{parentNode,2}, childNode];
end
else % 若不在,追加到openList
openList(end+1).node = childNode;
openList(end).g = g;
openList(end).h = h;
openList(end).f = f;
path{childNode,2} = [path{parentNode,2}, childNode];
end
end
% 从openList移出移动代价最小的节点到closeList
closeList(end+1,: ) = [openList(idx_min).node, openList(idx_min).f];
openList(idx_min)= [];
% 重新搜索:从openList搜索移动代价最小的节点
[~, idx_min] = min([openList.f]);
parentNode = openList(idx_min).node;
% 判断是否搜索到终点
if parentNode == goalPos
closeList(end+1,: ) = [openList(idx_min).node, openList(idx_min).f];
break
end
end
%% 画路径
% 找出目标最优路径
path_target = path{goalPos,2};
for i = 1:rows*cols
if ~isempty(path{i,2})
field((path{i,1})) = 7;
end
end
field(startPos) = 4;
field(goalPos) = 5;
field(path_target(2:end-1)) = 6;
% 画栅格图
image(1.5,1.5,field);
grid on;
set(gca,'gridline','-','gridcolor','k','linewidth',2,'GridAlpha',0.5);
set(gca,'xtick',1:cols+1,'ytick',1:rows+1);
axis image;
hold on;
[y0,x0] = ind2sub([rows,cols], path_target);
y = y0 + 0.5;
x = x0 + 0.5;
plot(x,y,'-','Color','r','LineWidth',2.5);
hold on;
points = [x',y'];
M = 10;
[x1,y1] = bezir_n(points, M);
plot(x1,y1,'-','Color','y','LineWidth',2.5);
hold on;
values = spcrv([[x(1) x x(end)];[y(1) y y(end)]],3);
plot(values(1,:),values(2,:), 'b','LineWidth',2.5);
4.4 算法效果
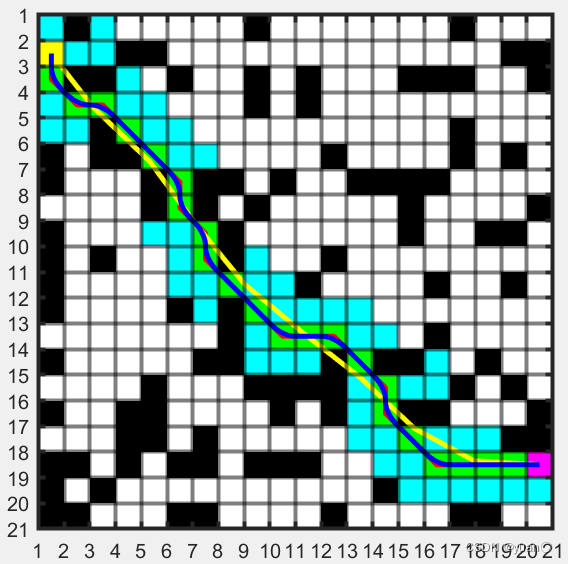 运行总时间
运行总时间 栅格地图大小(20x20)
栅格地图大小(20x20)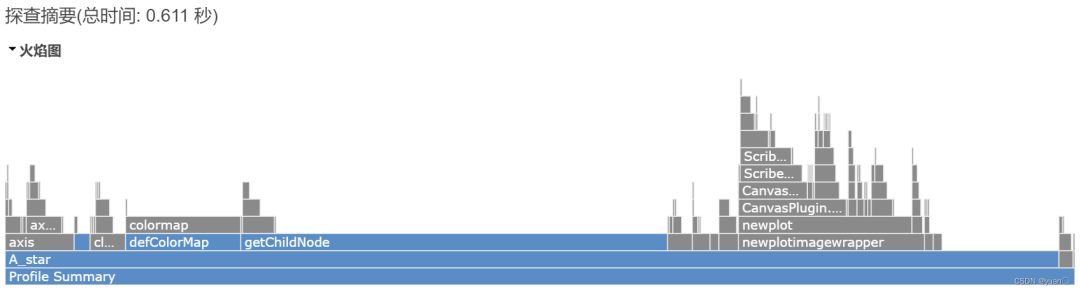 栅格地图大小(30x30)
栅格地图大小(30x30)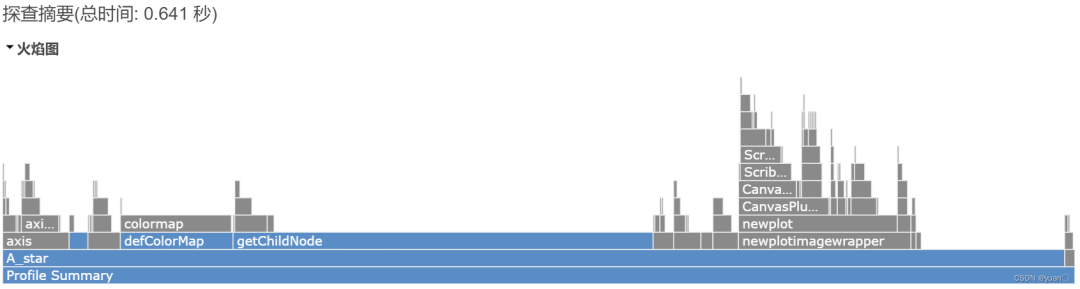 栅格地图大小(40x40)可以看到Astar算法对于栅格地图越大的情况,搜索时间越长,其速度相比Dijkstra有优势(尤其是在地图比较大的时候,优势更明显)。但其总耗时较长,不适用于实时的路径规划,不适用于局部路径规划,适用于全局路径规划。
栅格地图大小(40x40)可以看到Astar算法对于栅格地图越大的情况,搜索时间越长,其速度相比Dijkstra有优势(尤其是在地图比较大的时候,优势更明显)。但其总耗时较长,不适用于实时的路径规划,不适用于局部路径规划,适用于全局路径规划。
5. python实现Astar算法
可以参考这篇文章https://www.jianshu.com/p/5704e67f40aa这篇文章介绍了Astar以及后续的变种算法python 版本的伪代码(来源:https://brilliant.org/wiki/a-star-search/)如下:
make an openlist containing only the starting node
make an empty closed list
while (the destination node has not been reached):
consider the node with the lowest f score in the open list
if (this node is our destination node) :
we are finished
if not:
put the current node in the closed list and look at all of its neighbors
for (each neighbor of the current node):
if (neighbor has lower g value than current and is in the closed list) :
replace the neighbor with the new, lower, g value
current node is now the neighbor's parent
else if (current g value is lower and this neighbor is in the open list ) :
replace the neighbor with the new, lower, g value
change the neighbor's parent to our current node
else if this neighbor is not in both lists:
add it to the open list and set its g
6. Java实现Astar算法
可以参考这篇文章:https://www.jianshu.com/p/950233af52df7. 实践案例—基于ROS实现Astar与DWA算法
本项目以Astar算法作为全局路径规划算法,DWA作为局部路径规划算法,实现效果如下。(具体原理与算法代码解释与说明会在之后的文章附上)
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
-
自动驾驶路径规划技术之A-Star算法2023-03-23 4149
-
FPGA在自动驾驶领域有哪些应用?2024-07-29 8173
-
自动驾驶的到来2017-06-08 7303
-
AI/自动驾驶领域的巅峰会议—国际AI自动驾驶高峰论坛2017-09-13 7352
-
即插即用的自动驾驶LiDAR感知算法盒子 RS-Box2017-12-15 5981
-
UWB主动定位系统在自动驾驶中的应用实践2018-12-14 3186
-
如何让自动驾驶更加安全?2019-05-13 3621
-
你知道有哪几种常见的车辆路径规划算法吗?2021-06-17 2464
-
自动驾驶系统设计及应用的相关资料分享2021-08-30 2300
-
自动驾驶技术的实现2021-09-03 3072
-
自动驾驶汽车四种常用的路径规划算法解析2020-03-08 18302
-
解析自动驾驶汽车路径规划算法2020-07-28 5559
-
自动驾驶中基于图搜索的常用路径规划算法介绍2021-04-25 4188
-
自动驾驶之路径规划2023-06-01 503
-
自动驾驶轨迹规划之路径规划总结2023-06-07 818
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

