

SpringBoot的核心注解2
电子说
描述
他会调用 ((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh();方法,我们点进来看
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
这点代码似曾相识啊 没错,就是一个spring的bean的加载过程我在,解析springIOC加载过程的时候介绍过这里面的方法,如果你看过Spring源码的话 ,应该知道这些方法都是做什么的。现在我们不关心其他的,我们来看一个方法叫做 onRefresh();方法
protected void onRefresh() throws BeansException {
// For subclasses: do nothing by default.
}
他在这里并没有实现,但是我们找他的其他实现,我们来找
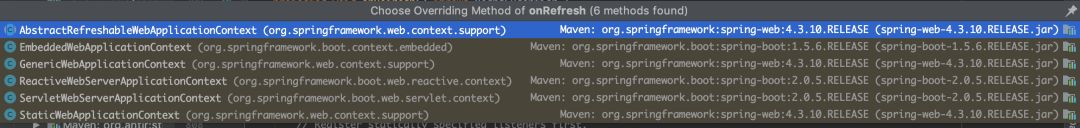
我们既然要找Tomcat那就肯定跟web有关,我们可以看到有个ServletWebServerApplicationContext
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
我们可以看到有一个createWebServer();方法他是创建web容器的,而Tomcat不就是web容器,那他是怎么创建的呢,我们继续看
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context",
ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}
factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());他是通过工厂的方式创建的
public interface ServletWebServerFactory {
WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers);
}
可以看到 它是一个接口,为什么会是接口。因为我们不止是Tomcat一种web容器。

我们看到还有Jetty,那我们来看TomcatServletWebServerFactory
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory
: createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
那这块代码,就是我们要寻找的内置Tomcat,在这个过程当中,我们可以看到创建Tomcat的一个流程。因为run方法里面加载的东西很多,所以今天就浅谈到这里。如果不明白的话, 我们在用另一种方式来理解下,
大家要应该都知道stater举点例子
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot<span class="hljs-name"groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis<span class="hljs-name"artifactId>
<span class="hljs-name"dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot<span class="hljs-name"groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-freemarker<span class="hljs-name"artifactId>
<span class="hljs-name"dependency>
所以我们不防不定义一个stater来理解下,我们做一个需求,就是定制化不同的人跟大家说你们好,我们来看
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot<span class="hljs-name"groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent<span class="hljs-name"artifactId>
<version>2.1.4.RELEASE<span class="hljs-name"version>
<relativePath/>
<span class="hljs-name"parent>
<groupId>com.zgw<span class="hljs-name"groupId>
<artifactId>gw-spring-boot-srater<span class="hljs-name"artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT<span class="hljs-name"version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot<span class="hljs-name"groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure<span class="hljs-name"artifactId>
<span class="hljs-name"dependency>
<span class="hljs-name"dependencies>
我们先来看maven配置写入版本号,如果自定义一个stater的话必须依赖spring-boot-autoconfigure这个包,我们先看下项目目录
public class GwServiceImpl implements GwService{
@Autowired
GwProperties properties;
@Override
public void Hello()
{
String name=properties.getName();
System.out.println(name+"说:你们好啊");
}
}
我们做的就是通过配置文件来定制name这个是具体实现
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.gwname")
public class GwProperties {
String name="zgw";
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
这个类可以通过@ConfigurationProperties读取配置文件
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(GwService.class) //扫描类
@EnableConfigurationProperties(GwProperties.class) //让配置类生效
public class GwAutoConfiguration {
/**
* 功能描述 托管给spring
* @author zgw
* @return
*/
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public GwService gwService()
{
return new GwServiceImpl();
}
}
这个为配置类,为什么这么写因为,spring-boot的stater都是这么写的,我们可以参照他仿写stater,以达到自动配置的目的,然后我们在通过spring.factories也来进行配置
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.gw.GwAutoConfiguration
然后这样一个简单的stater就完成了,然后可以进行maven的打包,在其他项目引入就可以使用,在这里列出代码地址
- 相关推荐
- 热点推荐
- XML
- spring
- Boot
- 注解
- SpringBoot
-
SpringBoot核心注解由几个注解组成2023-12-03 1315
-
一个注解搞定SpringBoot接口防刷2023-11-28 774
-
springboot核心注解2023-11-23 1103
-
什么是 SpringBoot?2023-04-07 2122
-
Java注解及其底层原理解析22023-02-09 959
-
求一种SpringBoot定时任务动态管理通用解决方案2023-02-03 1427
-
Spring Boot常用注解与使用方式2022-07-08 2024
-
Spring Boot中常见的各类型注解的使用方式2022-06-20 2386
-
Spring Boot的注解原理是什么2021-08-27 2590
-
SpringBoot配置Mybatis的2个错误和修正2019-04-19 1114
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

