

如何自动化测试你的接口?
电子说
描述
前言
不知道大家的项目是否都有对接口API进行自动化测试,反正像我们这种小公司是没有的。由于最近一直被吐槽项目质量糟糕,只能研发自己看看有什么接口测试方案。那么在本文中,我将探索如何使用 Rest Assured 自动化 API 测试,Rest Assured 是一个基于 Java 的流行的用于测试 RESTful API 的库。
什么是Rest Assured?
Rest Assured 是一个基于 Java 的开源库,主要用于测试RESTful API。它为编写测试用例提供了一种简单直观的 DSL(领域特定语言),这使得开发人员可以轻松编写和维护自动化测试。Rest Assured支持 GET、POST、PUT、DELETE、PATCH 等各种 HTTP 方法,并且可以轻松与流行的测试框架(如 TestNG 和 JUnit)集成。
github地址 :https://github.com/rest-assured/rest-assured
安装Rest Assured
在maven中引入相关依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>io.rest-assured<span class="hljs-name"groupId>
<artifactId>rest-assured<span class="hljs-name"artifactId>
<version>5.3.0<span class="hljs-name"version>
<scope>test<span class="hljs-name"scope>
<span class="hljs-name"dependency>
Rest Assured结构
Rest Assured代码的整体结构分为 3 个主要部分:
- Given
Given是 API 测试的先决条件,可以在其中设置测试所需的一切,例如URL、请求头或参数,或任何需要满足的先决条件。- 可以在“
Given”中设置的内容:URL、请求头、请求参数和请求正文。
- When
When是实际向服务器发送 HTTP 请求并获得响应的时间。可以在When中定义请求方法,如GET、POST、PUT等。
- Then
Then是您检查从服务器获得的响应并确保它符合您的预期的地方。在这您可以检查状态代码、响应正文、标头或任何其他对您的测试很重要的内容。
Show Me Code
我们现在通过一个例子来演示下如何使用Rest Assured,首先我们看下postman的例子:
- 请求参数
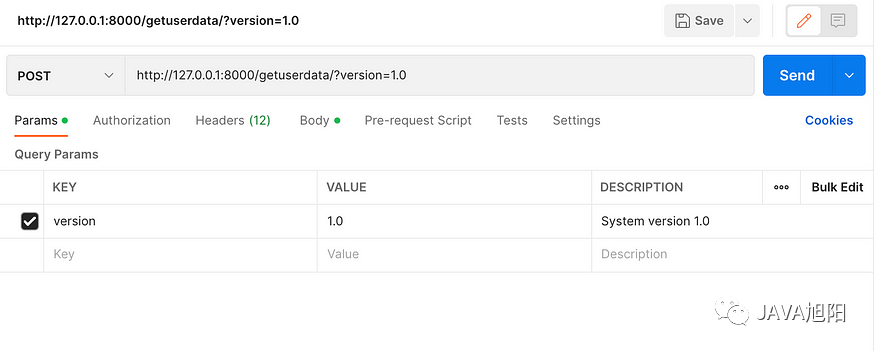
- 请求头
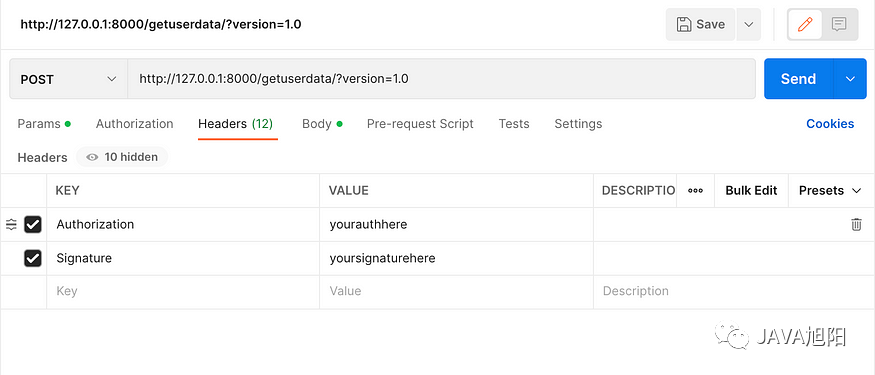
- 请求体
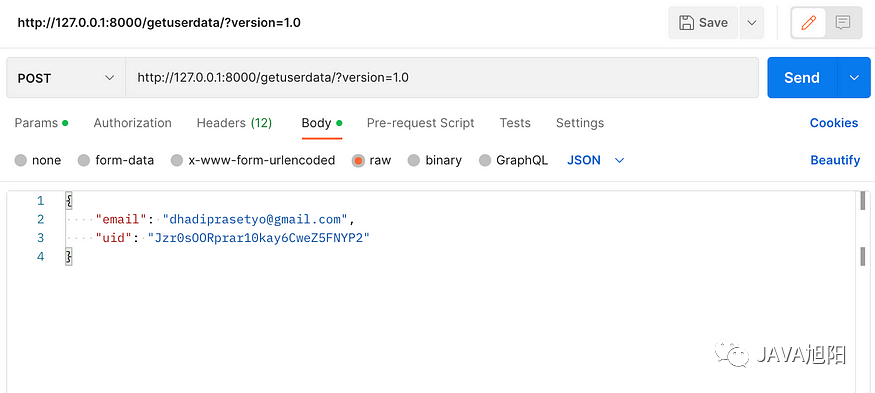
现在我们用Rest Assured这个框架来测试下上面postman的这个接口。
import io.restassured.builder.RequestSpecBuilder;
import io.restassured.response.Response;
import io.restassured.specification.RequestSpecification;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import static io.restassured.RestAssured.given;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.lessThan;
public class TestRestAssured {
@Test
public void testMyApi() {
String jsonBody = "{"email":"dhadiprasetyo@gmail.com","uid":"Jzr0sOORprar10kay6CweZ5FNYP2"}";
Response response = given().baseUri("http://127.0.0.1:8000")
.queryParam("version", "1.0")
.header("Authorization", "yourauthhere")
.header("Signature", "yoursignaturehere")
.body(jsonBody)
.when().post("/getuserdata/")
.then().assertThat().statusCode(200)
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.header("Cache-Control", "max-age=3600")
.body("name", equalTo("Darmawan Hadiprasetyo"))
.time(lessThan(5000L))
.extract().response();
}
}
- 首先我们在
given()中设置前置条件
given().baseUri("http://127.0.0.1:8000")
.queryParam("version", "1.0")
.header("Authorization", "yourauthhere")
.header("Signature", "yoursignaturehere")
.body(jsonBody)
- 然后在
when()中定义请求方法,本例中为POST
.when().post("/getuserdata/")
- 然后我们从我们的请求中断言状态代码、标头、正文和响应时间
.then().assertThat().statusCode(200)
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.header("Cache-Control", "max-age=3600")
.body("name", equalTo("Darmawan Hadiprasetyo"))
.time(lessThan(5000L))
.extract().response();
如何提取响应体?
例如,这将是我们对之前请求的回应:
{
"name": "alvin",
"role": "SDET"
}
以下是我们如何提取这些数据:
JsonPath responseBody = response.jsonPath();
String fullName = responseBody.getString("name");
String role = responseBody.getString("role");
统一抽象封装
在大多数情况下,需要测试许多 API,但前提条件相同,例如 BaseURL、参数和请求头等,为了消除代码中的冗余,我们可以统一抽象封装一个 RequestSpecification 类作为我们的规范构建器,并在我们的其他测试中重用它,如下所示:
import io.restassured.builder.RequestSpecBuilder;
import io.restassured.path.json.JsonPath;
import io.restassured.response.Response;
import io.restassured.specification.RequestSpecification;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import static io.restassured.RestAssured.given;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.equalTo;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.lessThan;
public class TestRestAssured {
public static RequestSpecification requestSpecification() {
return new RequestSpecBuilder().setBaseUri("http://127.0.0.1:8000")
.addQueryParam("version", "1.0")
.addHeader("Authorization", "yourauthhere")
.addHeader("Signature", "yoursignaturehere")
.build();
}
@Test
public void testMyApi() {
String jsonBody = "{"email":"dhadiprasetyo@gmail.com","uid":"Jzr0sOORprar10kay6CweZ5FNYP2"}";
Response response = given().spec(requestSpecification())
.body(jsonBody)
.when().post("/getuserdata/")
.then().assertThat().statusCode(200)
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.header("Cache-Control", "max-age=3600")
.body("name", equalTo("Darmawan Hadiprasetyo"))
.time(lessThan(5000L))
.extract().response();
JsonPath responseBody = response.jsonPath();
String fullName = responseBody.getString("name");
String linkedIn = responseBody.getString("linkedin");
String role = responseBody.getString("role");
}
}
现在,您可以在具有相同前提条件的任何其他需要的测试中重用 requestSpecification() 方法。查看与我们之前代码的区别:
// previous
Response response = given().baseUri("http://127.0.0.1:8000")
.queryParam("version", "1.0")
.header("Authorization", "yourauthhere")
.header("Signature", "yoursignaturehere")
.body(jsonBody)
.when().post("/getuserdata/")
// then
Response response = given().spec(requestSpecification())
.body(jsonBody)
.when().post("/getuserdata/")
通过使用 given().spec(),我们的代码现在变得简单多了。
-
自动化测试的「千里眼」:当RTSM远程控制遇上自动化,测试效率直接拉满!2025-12-11 236
-
电源测试怎么自动化?电源模块自动化测试系统如何实现?2023-12-15 1804
-
基于应用程序编程接口(API)的自动化测试(下)2023-09-20 1540
-
基于应用程序编程接口(API)的自动化测试(上)2023-09-01 1280
-
接口自动化测试流程讲解 企业接口自动化测试步骤2023-07-28 2986
-
什么是自动化测试框架2023-04-18 1443
-
批生产卫星的桌面电接口自动化测试系统综述2021-06-25 949
-
自动化测试系统问答2020-10-12 2508
-
如何对用户界面进行自动化测试2020-03-06 1589
-
七个步骤完成自动化测试2019-07-19 2123
-
自动化测试框架思想和构建2019-07-18 2446
-
ATE自动化测试系统是什么_ATE自动化测试系统介绍2018-05-23 33160
-
基于Web的自动化测试框架的研究2012-11-07 998
-
OPhone自动化测试技术概述2010-05-06 2277
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

