

AGIEval:准确考察基础模型类人能力的基准评估工具
电子说
描述
对基础模型在处理人类任务时的一般能力做出准确评估,已经成为通用人工智能(AGI)开发和应用领域的一大重要问题。基于人工数据集的传统基准往往无法准确反映模型能力是否达到人类水平。
近日,微软的一个华人研究团队发布了一项新型基准测试 AGIEval,这项基准测试专门用于对基础模型的类人能力做准确考察(涵盖高考、法学入学考试、数学竞赛和律师资格考试等)。
该研究团队使用此项基准评估了当前最先进的多个基础模型,包括 GPT-4、ChatGPT 和 Text-Davinci-003 等。
令人印象深刻的是,GPT-4 在 SAT、LSAT 和数学竞赛中的表现均超过人类平均水平,在 SAT 数学测试中达成 95% 的准确率,在中国高考英语测试中准确率亦达到 92.5%,证明了当代基础模型的非凡性能。
与之对应,研究人员发现 GPT-4,在需要复杂推理或涉及特定领域知识的任务中表现尚不理想。
通过对模型能力(理解、知识、推理和计算等)的全面分析,有助于揭示这些模型的优势和局限性,为增强其通用能力的未来发展方向提供支持。通过测试涉及人类认知和决策能力的任务,AGIEval 能够对基础模型在现实场景中的性能做出更可靠、更有意义的评估。
测试中的全部数据、代码和模型输出均通过此 https URL(https://github.com/microsoft/AGIEval)发布。
AGIEval 项目介绍
AGIEval 是一项考察基础模型类人能力的基准测试,专门用于评估基础模型在人类认知和问题解决相关任务中表现出的一般能力。
该基准选取 20 种面向普通人类考生的官方、公开、高标准往常和资格考试,包括普通大学入学考试(中国高考和美国 SAT 考试)、法学入学考试、数学竞赛、律师资格考试、国家公务员考试等等。
关于此基准的完整描述,请参阅论文《AGIEval:准确考察基础模型类人能力的基准评估工具》(https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.06364.pdf)。
任务与数据
AGIEval v1.0 包含 20 项任务,具体为 2 项完形填空任务(高考数学)和 18 项多选题回答任务。在选择题部分,高物理和 JEC-QA 部分对应一个或多个正确答案,其余任务则仅有一个正确答案。
下表所示,为测试题目的完整列表。
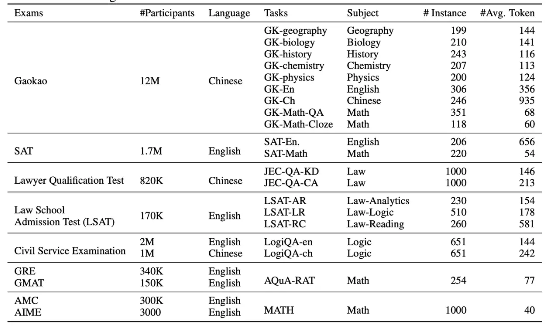
可以在 data/v1 文件夹内下载到除 JEC-QA 以外的所有后处理数据。关于 JEC-QA 部分,请前往 JEC-QA 网站获取数据。
使用 JEC-QA 训练数据的前 1000 个实例作为测试集。所有数据集的数据格式如下:
{
"passage": null,
"question": "设集合 $A=\{x \mid x \geq 1\}, B=\{x \mid-1-1\}$",
"(B)$\{x \mid x \geq 1\}$",
"(C)$\{x \mid-1
其中高考语言、高考英语、两科 logiqa、全部 LSAT 和 SAT 均可使用 passage 字段。多选任务的答案保存在 label 字段内。完形填空任务的答案保存在 answer 字段内。
我们还在 data/v1/few_shot_prompts 文件中提供了小样本学习的提示词。
基线系统
我们在 AGIEval v1.0 上评估了基准系统的性能。基线系统基于以下模型:text-davinci-003、ChatGPT (gpt-3.5-turbo) 和 GPT-4。您可以按照以下步骤重现测试结果:
1.在 openai_api.py 文件中填写您的 OpenAI API 密钥。
2.运行 run_prediction.py 文件以获取结果。
模型输出
您可以在 Onedrive 链接(https://1drv.ms/u/s!Amt8n9AJEyxcg8YQKFm1rSEyV9GU_A?e=VEfJVS)中下载到基线系统的零样本、零样本思维链、少样本和少样本思维链输出。请注意,我们修复了 SAT-en 实例中的 52 处拼写错误,并将很快发布更新后的数据集输出。
评估
您可以运行 post_process_and_evaluation.py 文件来获取评估结果。
引用
如果您需要在研究中使用 AGIEval 数据集或代码,请引用论文:
@misc{zhong2023agieval,
title={AGIEval: A Human-Centric Benchmark for Evaluating Foundation Models},
author={Wanjun Zhong and Ruixiang Cui and Yiduo Guo and Yaobo Liang and Shuai Lu and Yanlin Wang and Amin Saied and Weizhu Chen and Nan Duan},
year={2023},
eprint={2304.06364},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL}
}
在使用时,请务必在您的论文中引用所有独立数据集。我们提供以下引用信息:
@inproceedings{ling-etal-2017-program,
title = "Program Induction by Rationale Generation: Learning to Solve and Explain Algebraic Word Problems",
author = "Ling, Wang and
Yogatama, Dani and
Dyer, Chris and
Blunsom, Phil",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers)",
month = jul,
year = "2017",
address = "Vancouver, Canada",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/P17-1015",
doi = "10.18653/v1/P17-1015",
pages = "158--167",
abstract = "Solving algebraic word problems requires executing a series of arithmetic operations{---}a program{---}to obtain a final answer. However, since programs can be arbitrarily complicated, inducing them directly from question-answer pairs is a formidable challenge. To make this task more feasible, we solve these problems by generating answer rationales, sequences of natural language and human-readable mathematical expressions that derive the final answer through a series of small steps. Although rationales do not explicitly specify programs, they provide a scaffolding for their structure via intermediate milestones. To evaluate our approach, we have created a new 100,000-sample dataset of questions, answers and rationales. Experimental results show that indirect supervision of program learning via answer rationales is a promising strategy for inducing arithmetic programs.",
}
@inproceedings{hendrycksmath2021,
title={Measuring Mathematical Problem Solving With the MATH Dataset},
author={Dan Hendrycks and Collin Burns and Saurav Kadavath and Akul Arora and Steven Basart and Eric Tang and Dawn Song and Jacob Steinhardt},
journal={NeurIPS},
year={2021}
}
@inproceedings{Liu2020LogiQAAC,
title={LogiQA: A Challenge Dataset for Machine Reading Comprehension with Logical Reasoning},
author={Jian Liu and Leyang Cui and Hanmeng Liu and Dandan Huang and Yile Wang and Yue Zhang},
booktitle={International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence},
year={2020}
}
@inproceedings{zhong2019jec,
title={JEC-QA: A Legal-Domain Question Answering Dataset},
author={Zhong, Haoxi and Xiao, Chaojun and Tu, Cunchao and Zhang, Tianyang and Liu, Zhiyuan and Sun, Maosong},
booktitle={Proceedings of AAAI},
year={2020},
}
@article{Wang2021FromLT,
title={From LSAT: The Progress and Challenges of Complex Reasoning},
author={Siyuan Wang and Zhongkun Liu and Wanjun Zhong and Ming Zhou and Zhongyu Wei and Zhumin Chen and Nan Duan},
journal={IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing},
year={2021},
volume={30},
pages={2201-2216}
}
审核编辑 :李倩
-
【大语言模型:原理与工程实践】大语言模型的评测2024-05-07 1728
-
Al大模型机器人2024-07-05 2345
-
用于准确的CPU功率检测的快速功率模型化2023-02-03 1972
-
HarmonyOS/OpenHarmony应用开发-Stage模型ArkTS语言扩展能力基类2023-04-26 3171
-
飞行品质评估模型设计2017-11-29 832
-
基于IWD和RBNN的高校科研能力评估模型2017-12-04 821
-
机器学习之模型评估的方法总结2018-09-13 3232
-
DEKRA德凯功能安全评估工具帮助审核员更科学、准确的完成评估工作2022-08-16 1664
-
上交清华提出中文大模型的知识评估基准C-Eval,辅助模型开发而非打榜2023-05-24 1535
-
王小川大模型首亮相!70亿参数霸榜,清北抢先用2023-06-15 1124
-
NVIDIA文本嵌入模型NV-Embed的精度基准2024-08-23 2980
-
如何评估AI大模型的效果2024-10-23 4613
-
如何评估 ChatGPT 输出内容的准确性2024-10-25 1651
-
大模型工具的 “京东答案”2025-08-25 441
-
量化评估企业软件测试能力的评估工具包2025-08-27 593
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

