

 C语言实现单链表-增删改查
C语言实现单链表-增删改查
描述
链表是由一连串节点组成的数据结构,每个节点包含一个数据值和一个指向下一个节点的指针。链表可以在头部和尾部插入和删除节点,因此可以在任何地方插入和删除节点,从而使其变得灵活和易于实现。
链表通常用于实现有序集合,例如队列和双向链表。链表的优点是可以快速随机访问节点,而缺点是插入和删除操作相对慢一些,因为需要移动节点。此外,链表的长度通常受限于内存空间,因此当链表变得很长时,可能需要通过分页或链表分段等方式来管理其内存。
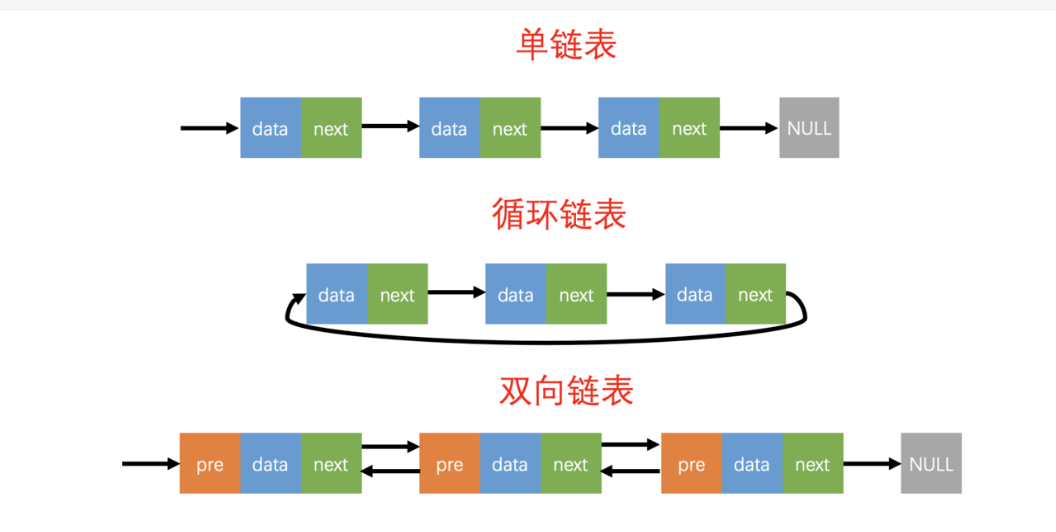
下面是一套封装好的单链表框架,包括创建链表、插入节点、删除节点、修改节点、遍历节点和清空链表等常见操作,其中每个节点存储一个结构体变量,该结构体中包含一个名为data的int类型成员。
#include
#include
// 链表节点结构体
typedef struct ListNode {
int data; // 节点数据
struct ListNode *next; // 下一个节点的指针
} ListNode;
// 创建一个新节点
ListNode *createNode(int data) {
ListNode *node = (ListNode*) malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
node->data = data;
node->next = NULL;
return node;
}
// 在链表头部插入一个新节点
ListNode *insertNodeAtHead(ListNode *head, int data) {
ListNode *node = createNode(data);
node->next = head;
return node;
}
// 在链表尾部插入一个新节点
ListNode *insertNodeAtTail(ListNode *head, int data) {
ListNode *node = createNode(data);
if(head == NULL) {
return node;
} else {
ListNode *current = head;
while(current->next != NULL) {
current = current->next;
}
current->next = node;
return head;
}
}
// 删除链表中第一个值为data的节点
ListNode *deleteNode(ListNode *head, int data) {
if(head == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
if(head->data == data) {
ListNode *current = head;
head = head->next;
free(current);
return head;
}
ListNode *current = head;
while(current->next != NULL && current->next->data != data) {
current = current->next;
}
if(current->next != NULL) {
ListNode *deleteNode = current->next;
current->next = deleteNode->next;
free(deleteNode);
}
return head;
}
// 修改链表中第一个值为oldData的节点的数据为newData
void updateNode(ListNode *head, int oldData, int newData) {
ListNode *current = head;
while(current != NULL) {
if(current->data == oldData) {
current->data = newData;
break;
} else {
current = current->next;
}
}
}
// 遍历链表
void traverseList(ListNode *head) {
ListNode *current = head;
while(current != NULL) {
printf("%d ", current->data);
current = current->next;
}
printf("
");
}
// 清空链表,释放所有节点的内存空间
void clearList(ListNode *head) {
while(head != NULL) {
ListNode *current = head;
head = head->next;
free(current);
}
}
// 示例程序
int main() {
ListNode *head = NULL;
head = insertNodeAtHead(head, 1);
head = insertNodeAtHead(head, 2);
head = insertNodeAtTail(head, 3);
traverseList(head);
head = deleteNode(head, 2);
traverseList(head);
updateNode(head, 1, 4);
traverseList(head);
clearList(head);
return 0;
}
在上述代码中,定义了一个节点结构体ListNode,其中包含一个int类型的data成员和一个指向下一个节点的指针。接着定义了用于创建新节点、插入节点、删除节点、修改节点、遍历节点和清空链表等操作的子函数,并在main函数中演示了这些操作的使用例子。在使用完链表后一定要调用clearList函数释放内存空间。
审核编辑:汤梓红
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
-
mysql数据库的增删改查sql语句2023-11-16 2002
-
SQLite数据库增删改查2023-08-28 1794
-
Qt(C++)使用SQLite数据库完成数据增删改查2023-06-21 2819
-
Mybatis自动生成增删改查代码2023-01-13 1634
-
python是如何实现hbase增删改查的2021-10-19 1636
-
laravel框架如何进行简单的增删改查和文件上传2020-04-26 1285
-
如何用php调用mysql数据库实现增删改查2020-04-09 2191
-
使用jpa和thymeleaf做增删改查示例2020-04-01 880
-
PHP数据库教程之增删改查的数据高级操作资料免费下载2019-07-02 1248
-
基于SpringBoot mybatis方式的增删改查实现2019-06-18 2001
-
使用DOM对XML读取进行增删改查2019-06-12 707
-
C语言实现单链表举例2011-07-11 1093
-
LINQ的增删改查源码 v0.12010-02-08 427
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

