

Linux clock子系统及驱动实例
嵌入式技术
描述
在Linux驱动中,操作时钟只需要简单调用内核提供的通用接口即可,clock驱动通常是由芯片厂商开发的,在Linux启动时clock驱动就已经初始化完成。
本篇介绍Linux clock子系统以及clock驱动的实现。
基本概念
晶振 :晶源振荡器,提供时钟。
PLL :Phase lock loop,锁相环。 用于提升频率。
OSC :oscillator的简写,振荡器。
clock子系统
Linux的时钟子系统由CCF(common clock framework)框架管理, CCF向上给用户提供了通用的时钟接口,向下给驱动开发者提供硬件操作的接口 。 各结构体关系如下:
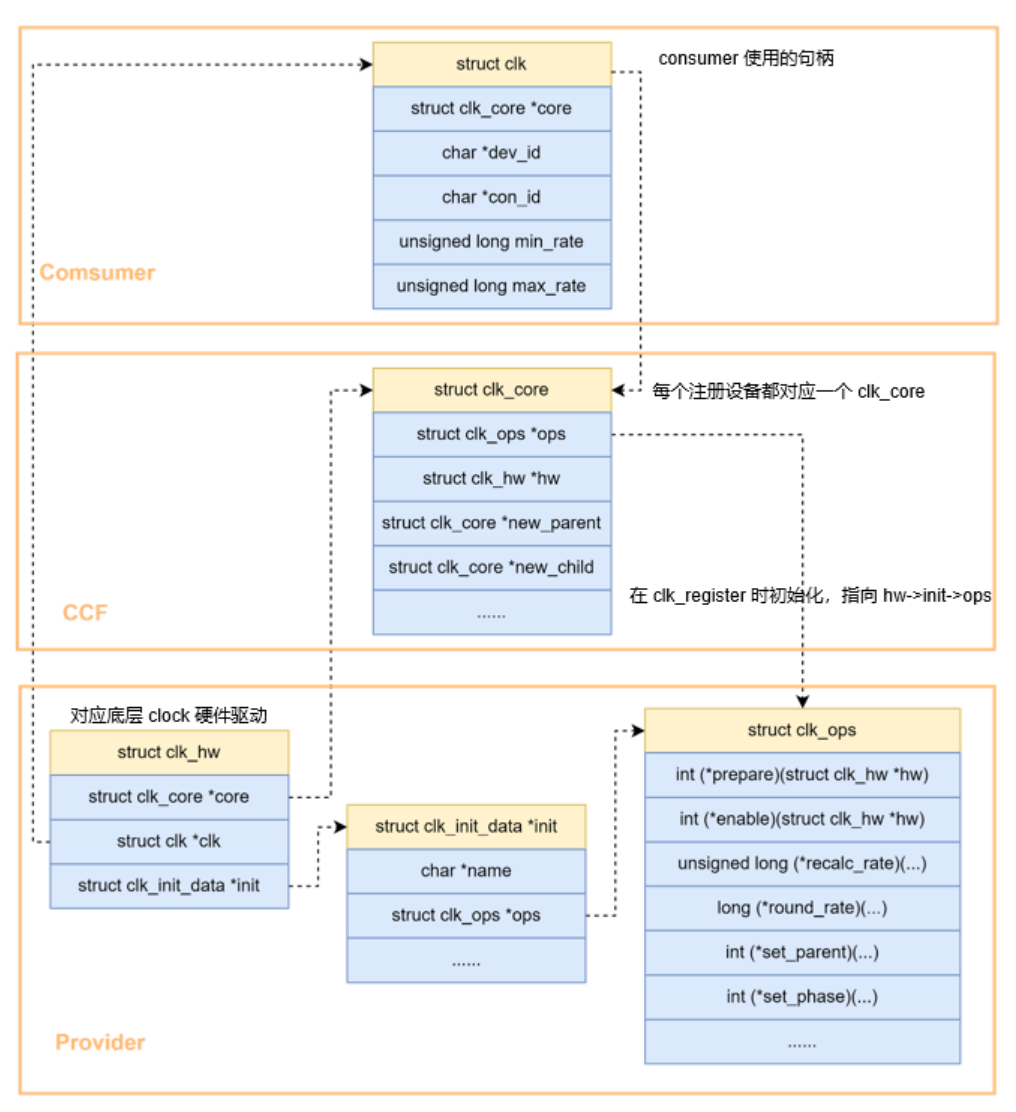
CCF框架比较简单,只有这几个结构体。 CCF框架分为了consumer、ccf和provider三部分。
consumer :
时钟的使用者,clock子系统向consumer的提供通用的时钟API接口,使其可以屏蔽底层硬件差异。 提供给consumer操作的API如下:
struct clk *clk_get(struct device *dev, const char *id);
struct clk *devm_clk_get(struct device *dev, const char *id);
int clk_enable(struct clk *clk);//使能时钟,不会睡眠
void clk_disable(struct clk *clk);//使能时钟,不会睡眠
unsigned long clk_get_rate(struct clk *clk);
void clk_put(struct clk *clk);
long clk_round_rate(struct clk *clk, unsigned long rate);
int clk_set_rate(struct clk *clk, unsigned long rate);
int clk_set_parent(struct clk *clk, struct clk *parent);
struct clk *clk_get_parent(struct clk *clk);
int clk_prepare(struct clk *clk);
void clk_unprepare(struct clk *clk);
int clk_prepare_enable(struct clk *clk) //使能时钟,可能会睡眠
void clk_disable_unprepare(struct clk *clk) //禁止时钟,可能会睡眠
unsigned long clk_get_rate(struct clk *clk) //获取时钟频率
consumer在使用这些API时,必须先调用devm_clk_get()或clk_get()获取一个struct clk *指针句柄,后续都通过传入该句柄来操作,struct clk相当于实例化一个时钟。
ccf :
clock子系统的核心,用一个struct clk_core结构体表示,每个注册设备都对应一个struct clk_core。
provider(时钟的提供者) :
struct clk_hw:表示一个具体的硬件时钟。
struct clk_init_data:struct clk_hw结构体成员,用于表示该时钟下的初始化数据,如时钟名字name、操作函数ops等。
// include/linux/clk-provider.h
struct clk_hw{
struct clk_core *core;
struct clk *clk;
const struct clk_init_data *init;
}
struct clk_init_data{
const char *name; //时钟名字
const struct clk_ops *ops; //时钟硬件操作函数集合
const char *const *parent_names; //父时钟名字
const struct clk_parent_data *parent_data;
const struct clk_hw **parent_hws;
u8 num_parents;
unsigned long flags;
}
struct clk_ops:时钟硬件操作的函数集合,定义了操作硬件的回调函数,consumer在调用clk_set_rate()等API时会调用到struct clk_ops具体指向的函数,这个需要芯片厂商开发clock驱动时去实现。
//include/linux/clk-provider.h
struct clk_ops {
int (*prepare)(struct clk_hw *hw);
void (*unprepare)(struct clk_hw *hw);
int (*is_prepared)(struct clk_hw *hw);
void (*unprepare_unused)(struct clk_hw *hw);
int (*enable)(struct clk_hw *hw);
void (*disable)(struct clk_hw *hw);
int (*is_enabled)(struct clk_hw *hw);
void (*disable_unused)(struct clk_hw *hw);
int (*save_context)(struct clk_hw *hw);
void (*restore_context)(struct clk_hw *hw);
unsigned long (*recalc_rate)(struct clk_hw *hw,
unsigned long parent_rate);
long (*round_rate)(struct clk_hw *hw, unsigned long rate,
unsigned long *parent_rate);
int (*determine_rate)(struct clk_hw *hw,
struct clk_rate_request *req);
int (*set_parent)(struct clk_hw *hw, u8 index);
u8 (*get_parent)(struct clk_hw *hw);
int (*set_rate)(struct clk_hw *hw, unsigned long rate,
unsigned long parent_rate);
int (*set_rate_and_parent)(struct clk_hw *hw,
unsigned long rate,
unsigned long parent_rate, u8 index);
unsigned long (*recalc_accuracy)(struct clk_hw *hw,
unsigned long parent_accuracy);
int (*get_phase)(struct clk_hw *hw);
int (*set_phase)(struct clk_hw *hw, int degrees);
int (*get_duty_cycle)(struct clk_hw *hw,
struct clk_duty *duty);
int (*set_duty_cycle)(struct clk_hw *hw,
struct clk_duty *duty);
int (*init)(struct clk_hw *hw);
void (*terminate)(struct clk_hw *hw);
void (*debug_init)(struct clk_hw *hw, struct dentry *dentry);
};
struct clk_ops中每个函数功能在include/linux/clk-provider.h都有具体的说明,在开发clock驱动时,这些函数并不需要全部实现。下面列举几个最常用,也是经常需要实现的函数。
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| recalc_rate | 通过查询硬件,重新计算此时钟的速率。可选,但建议——如果未设置此操作,则时钟速率初始化为0。 |
| round_rate | 给定目标速率作为输入,返回时钟实际支持的最接近速率。 |
| set_rate | 更改此时钟的速率。请求的速率由第二个参数指定,该参数通常应该是调用.round_rate返回。第三个参数给出了父速率,这对大多数.set_rate实现有帮助。成功返回0,否则返回-EERROR |
| enable | 时钟enable |
| disable | 时钟disable |
时钟API的使用
对于一般的驱动开发(非clock驱动),我们只需要在dts中配置时钟,然后在驱动调用通用的时钟API接口即可。
1、设备树中配置时钟
mmc0:mmc0@0x12345678{
compatible = "xx,xx-mmc0";
......
clocks = < &peri PERI_MCI0 >;//指定mmc0的时钟来自PERI_MCI0,PERI_MCI0的父时钟是peri
clocks-names = "mmc0"; //时钟名,调用devm_clk_get获取时钟时,可以传入该名字
......
};
以mmc的设备节点为例,上述mmc0指定了时钟来自PERI_MCI0,PERI_MCI0的父时钟是peri,并将所指定的时钟给它命名为"mmc0"。
2、驱动中使用API接口
简单的使用:
/* 1、获取时钟 */
host- >clk = devm_clk_get(&pdev- >dev, NULL); //或者devm_clk_get(&pdev- >dev, "mmc0")
if (IS_ERR(host- >clk)) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to find clock source\\n");
ret = PTR_ERR(host- >clk);
goto probe_out_free_dev;
}
/* 2、使能时钟 */
ret = clk_prepare_enable(host- >clk);
if (ret) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to enable clock source.\\n");
goto probe_out_free_dev;
}
probe_out_free_dev:
kfree(host);
在驱动中操作时钟,第一步需要获取struct clk指针句柄,后续都通过该指针进行操作,例如:设置频率:
ret = clk_set_rate(host- >clk, 300000);
获得频率:
ret = clk_get_rate(host- >clk);
注意:devm_clk_get()的两个参数是二选一,可以都传入,也可以只传入一个参数。
像i2c、mmc等这些外设驱动,通常只需要使能门控即可,因为这些外设并不是时钟源,它们只有开关。如果直接调用clk_ser_rate函数设置频率,clk_set_rate会向上传递,即设置它的父时钟频率。例如在该例子中直接调用clk_set_rate函数,最终设置的是时钟源peri的频率。
clock驱动实例
clock驱动在时钟子系统中属于provider,provider是时钟的提供者,即具体的clock驱动。
clock驱动在Linux刚启动的时候就要完成,比initcall都要早期,因此clock驱动是在内核中进行实现。 在内核的drivers/clk目录下,可以看到各个芯片厂商对各自芯片clock驱动的实现:
下面以一个简单的时钟树,举例说明一个芯片的时钟驱动的大致实现过程:
1、时钟树
通常来说,一个芯片的时钟树是比较固定的,例如,以下时钟树:
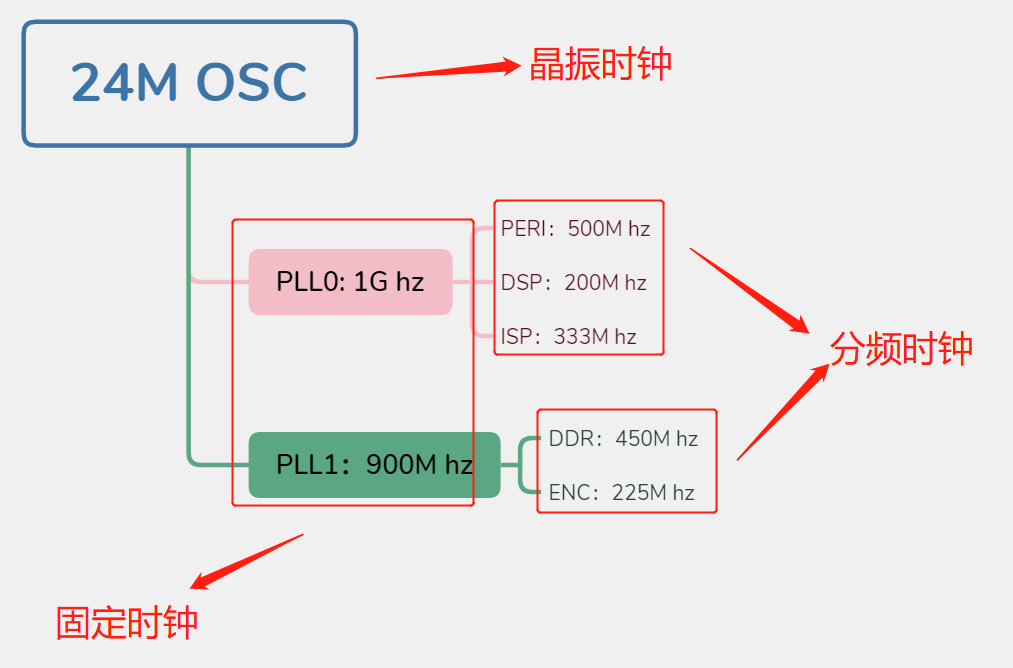
时钟树的 根节点一般是晶振时钟 ,上图根节点为24M晶振时钟。根节点下面是PLL,PLL用于提升频率。PPL0下又分频给PERI、DSP和ISP。PLL1分频给DDR和ENC。
对于PLL来说,PLL的频率可以通过寄存器设置,但通常是固定的,所以PLL属于 固定时钟 。
对PERI、DSP等模块来说,它们的频率来自于PLL的分频,因此这些模块的时钟属于 分频时钟 。
2、设备树
设备树中表示一个时钟源,应有如下属性,例如24M晶振时钟:
clocks{
osc24M:osc24M{
compatible = "fixed-clock";
#clock-cells = < 0 >;
clock-output-name = "osc24M";
clock-frequency = < 24000000 >;
};
};
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| compatible | 驱动匹配名字 |
| #clock-cells | 提供输出时钟的路数。#clock-cells为0时,代表输出一路时钟#clock-cells为1时,代表输出2路时钟。 |
| #clock-output-names | 输出时钟的名字 |
| #clock-frequency | 输出时钟的频率 |
3、驱动实现
clock驱动编写的基本步骤:
- 实现
struct clk_ops相关成员函数 - 定义分配
struct clk_onecell_data结构体,初始化相关数据 - 定义分配
struct clk_init_data结构体,初始化相关数据 - 调用
clk_register将时钟注册进框架 - 调用
clk_register_clkdev注册时钟设备 - 调用
of_clk_add_provider,将clk provider存放到of_clk_provider链表中管理 - 调用
CLK_OF_DECLARE声明驱动
fixed_clk固定时钟实现
fixed_clk针对像PLL这种具有固定频率的时钟,对于PLL,我们只需要实现.recalc_rate函数。
设备树:
#define PLL0_CLK 0
clocks{
osc24M:osc24M{
compatible = "fixed-clock";
#clock-cells = < 0 >;
clock-output-names = "osc24M";
clock-frequency = < 24000000 >;
};
pll0:pll0{
compatible = "xx, choogle-fixed-clk";
#clock-cells = < 0 >;
clock-id = < PLL0_CLK >;
clock-frequency = < 1000000000 >;
clock-output-names = "pll0";
clocks = < &osc24M >;
};
};
驱动:
#include < linux/clk-provier.h >
#include < linux/clkdev.h >
#include < linux/clk.h >
#include < linux/module.h >
#include < linux/of.h >
#include < linux/of_address.h >
#include < linux/platform_device.h >
#include < linux/slab.h >
#include < linux/delay.h >
#define CLOCK_BASE 0X12340000
#define CLOCK_SIZE 0X1000
struct xx_fixed_clk{
void __iomem *reg;//保存映射后寄存器基址
unsigned long fixed_rate;//频率
int id;//clock id
struct clk_hw*;
};
static unsigned long xx_pll0_fixed_clk_recalc_rate(struct clk_hw *hw, unsigned long parent_rate)
{
unsigned long recalc_rate;
//硬件操作:查询寄存器,获得分频系数,计算频率然后返回
return recalc_rate;
}
static struct clk_ops xx_pll0_fixed_clk_ops = {
.recalc_rate = xx_pll0_fixed_clk_recalc_rate,
};
struct clk_ops *xx_fixed_clk_ops[] = {
&xx_pll0_fixed_clk_ops,
};
struct clk * __init xx_register_fixed_clk(const char *name, const char *parent_name,
void __iomem *res_reg, u32 fixed_rate, int id,
const struct clk_ops *ops)
{
struct xx_fixed_clk *fixed_clk;
struct clk *clk;
struct clk_init_data init = {};
fixed_clk = kzalloc(sizeof(*fixed_clk), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!fixed_clk)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
//初始化struct clk_init_data数据
init.name = name;
init.flags = CLK_IS_BASIC;
init.parent_names = parent_name ? &parent_name : NULL;
init.num_parents = parent_name ? 1 : 0;
fixed_clk- >reg = res_reg;//保存映射后的基址
fixed_clk- >fixed_rate = fixed_rate;//保存频率
fixed_clk- >id = id;//保存clock id
fixed_clk- >hw.init = &init;
//时钟注册
clk = clk_register(NULL, &fixed_clk- >hw);
if (IS_ERR(clk))
kfree(fixed_clk);
return clk;
}
static void __init of_xx_fixed_clk_init(struct device_node *np)
{
struct clk_onecell_data *clk_data;
const char *clk_name = np- >name;
const char *parent_name = of_clk_get_parent_name(np, 0);
void __iomem *res_reg = ioremap(CLOCK_BASE, CLOCK_SIZE);//寄存器基址映射
u32 rate = -1;
int clock_id, index, number;
clk_data = kmalloc(sizeof(struct clk_onecell_data), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!clk_data )
return;
number = of_property_count_u32_elems(np, "clock-id");
clk_data- >clks = kcalloc(number, sizeof(struct clk*), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!clk_data- >clks)
goto err_free_data;
of_property_read_u32(np, "clock-frequency", &rate);
/**
* 操作寄存器:初始化PLL时钟频率
* ......
*/
for (index=0; index< number; index++) {
of_property_read_string_index(np, "clock-output-names", index, &clk_name);
of_property_read_u32_index(np, "clock-id", index, &clock_id);
clk_data- >clks[index] = xx_register_fixed_clk(clk_name, parent_name,
res_reg, rate, clock_id, ak_fixed_clk_ops[pll_id]);
if (IS_ERR(clk_data- >clks[index])) {
pr_err("%s register fixed clk failed: clk_name:%s, index = %d\\n",
__func__, clk_name, index);
WARN_ON(true);
continue;
}
clk_register_clkdev(clk_data- >clks[index], clk_name, NULL);//注册时钟设备
}
clk_data- >clk_num = number;
if (number == 1) {
of_clk_add_provider(np, of_clk_src_simple_get, clk_data- >clks[0]);
} else