

一条本该记录到慢日志的SQL是如何被漏掉的?
描述
背景
生产环境中 select count(*) from table 语句执行很慢,已经远超 long_query_time 参数定义的慢查询时间值,但是却没有记录到慢日志中。
在测试环境也很容易复现出该问题,慢查询日志确实没有记录 select count(*) 语句。
慢查询相关参数设置如下:
slow_query_log = 1 #开启慢查询日志 slow_query_log_file = /mydata/3306/log/mysql.slow.log #慢查询日志文件目录 log_queries_not_using_indexes = 1 #开启记录未使用索引的SQL log_slow_admin_statements = 1 #开启记录管理语句 log_slow_slave_statements = 1 #开启主从复制中从库的慢查询 log_throttle_queries_not_using_indexes = 10 #限制每分钟写入慢日志的未用索引的SQL的数量 long_query_time = 2 #定义慢查询的SQL执行时长 min_examined_row_limit = 100 #该SQL检索的行数小于100则不会记录到慢日志
select count(*) 执行原理可以总结如下:InnoDB 存储引擎在执行 select count(*) 时,Server 层遍历读取 InnoDB 层的二级索引或主键,然后按行计数。
因此,慢查询日志不应该没有记录到执行时间超过long_query_time 的 select count(*) 语句。
慢查询日志源码剖析
为了一探到底,在 MySQL 源码中找到了以下记录慢查询日志的相关函数,本文所涉及的 MySQL 数据库版本为 8.0.32。
sql_class.cc 文件中的 update_slow_query_status 函数:
void THD::update_slow_query_status() {
if (my_micro_time() > start_utime + variables.long_query_time)
server_status |= SERVER_QUERY_WAS_SLOW;
}
my_micro_time 函数返回的是当前时间,如果当前时间大于这条 SQL 执行的开始时间加 long_query_time 参数定义的时长,则更新这条 SQL 的 server_status 为 SERVER_QUERY_WAS_SLOW。
log.cc 文件中的 log_slow_applicable 和 log_slow_statement 函数:
bool log_slow_applicable(THD *thd) {
......
bool warn_no_index =
((thd->server_status &
(SERVER_QUERY_NO_INDEX_USED | SERVER_QUERY_NO_GOOD_INDEX_USED)) &&
opt_log_queries_not_using_indexes &&
!(sql_command_flags[thd->lex->sql_command] & CF_STATUS_COMMAND));
bool log_this_query =
((thd->server_status & SERVER_QUERY_WAS_SLOW) || warn_no_index) &&
(thd->get_examined_row_count() >= thd->variables.min_examined_row_limit);
// The docs say slow queries must be counted even when the log is off.
if (log_this_query) thd->status_var.long_query_count++;
/*
Do not log administrative statements unless the appropriate option is
set.
*/
if (thd->enable_slow_log && opt_slow_log) {
bool suppress_logging = log_throttle_qni.log(thd, warn_no_index);
if (!suppress_logging && log_this_query) return true;
}
return false;
}
判断该 SQL 是否满足记录慢查询日志的条件:
server_status 标记为 SERVER_QUERY_WAS_SLOW或 warn_no_index (没有使用索引);
该 SQL 检索的行数 >= min_examined_row_limit 参数定义的行数。
如果该 SQL 同时满足以上记录慢查询日志的条件,那么则调用 log_slow_do 函数写慢查询日志。
void log_slow_statement(THD *thd) {
if (log_slow_applicable(thd)) log_slow_do(thd);
}
MySQL 源码调试
在 MySQL 源码的 debug 环境中,开启 gdb 调试,对相关函数打下断点,这样便可以通过跟踪源码弄清楚一条 SQL 记录慢查询日志过程中函数和变量的情况。
(gdb) b THD::update_slow_query_status (gdb) b log_slow_applicable // 在客户端执行一条 SQL:select count(*) from user_test,跟踪源码执行到 update_slow_query_status函数时,可以发现这时候这条SQL的执行时长已经超过了long_query_time参数值,并且把这条SQL的server_status更新为SERVER_QUERY_WAS_SLOW。 查看堆栈信息如下: (gdb) bt #0 THD::update_slow_query_status (this=0x7f7d6000dcb0) at /root/gdb_mysql/mysql-8.0.32/sql/sql_class.cc:3217 #1 0x000000000329ddaa in dispatch_command (thd=0x7f7d6000dcb0, com_data=0x7f7dc43f1a00, command=COM_QUERY) at /root/gdb_mysql/mysql-8.0.32/sql/sql_parse.cc:2422 #2 0x000000000329a7d3 in do_command (thd=0x7f7d6000dcb0) at /root/gdb_mysql/mysql-8.0.32/sql/sql_parse.cc:1439 #3 0x00000000034b925f in handle_connection (arg=0xc966100) at /root/gdb_mysql/mysql-8.0.32/sql/conn_handler/connection_handler_per_thread.cc:302 #4 0x00000000051e835c in pfs_spawn_thread (arg=0xc9c0940) at /root/gdb_mysql/mysql-8.0.32/storage/perfschema/pfs.cc:2986 #5 0x00007f7ddff35ea5 in start_thread () from /lib64/libpthread.so.0 #6 0x00007f7dde95db0d in clone () from /lib64/libc.so.6 (gdb) n 3218 server_status |= SERVER_QUERY_WAS_SLOW; (gdb) n 3219 }
跟踪源码执行到 log_slow_applicable 函数时,可以发现函数 thd->get_examined_row_count() 的返回值为 0。也就是说这条 SQL 检索的行数为 0 行,小于当前设置的 min_examined_row_limit 参数值 100,所以这条 SQL 没有记录到慢查询日志中。堆栈信息及打印变量输出如下:
(gdb) bt #0 log_slow_applicable (thd=0x7f7d6000dcb0) at /root/gdb_mysql/mysql-8.0.32/sql/log.cc:1592 #1 0x00000000038ce8c5 in log_slow_statement (thd=0x7f7d6000dcb0) at /root/gdb_mysql/mysql-8.0.32/sql/log.cc:1661 #2 0x000000000329dff7 in dispatch_command (thd=0x7f7d6000dcb0, com_data=0x7f7dc43f1a00, command=COM_QUERY) at /root/gdb_mysql/mysql-8.0.32/sql/sql_parse.cc:2456 #3 0x000000000329a7d3 in do_command (thd=0x7f7d6000dcb0) at /root/gdb_mysql/mysql-8.0.32/sql/sql_parse.cc:1439 #4 0x00000000034b925f in handle_connection (arg=0xc966100) at /root/gdb_mysql/mysql-8.0.32/sql/conn_handler/connection_handler_per_thread.cc:302 #5 0x00000000051e835c in pfs_spawn_thread (arg=0xc9c0940) at /root/gdb_mysql/mysql-8.0.32/storage/perfschema/pfs.cc:2986 #6 0x00007f7ddff35ea5 in start_thread () from /lib64/libpthread.so.0 #7 0x00007f7dde95db0d in clone () from /lib64/libc.so.6 (gdb) p thd->get_examined_row_count() //打印 thd->get_examined_row_count() 当前返回值 $4 = 0 (gdb) p thd->variables.min_examined_row_limit //打印 min_examined_row_limit 变量值 $5 = 100
原因
通过跟踪源码,可以查明 select count(*) from table 语句没有写入到慢日志中是因为 MySQL 把此类 SQL 的检索行数计算为 0 行,小于 min_examined_row_limit 参数值。
因此,把 min_examined_row_limit 参数设置为 0 后,再次执行 select count(*),可以看到在慢查询日志中,这条 SQL 执行完成后就被记录了。且慢查询日志中的信息显示这条 SQL 检索的行数为 0 行,返回的行数为 1 行。
所以要想把慢的 select count(*) 记录到慢查询日志中,min_examined_row_limit 这个参数必须保持为默认值 0。
但是生产环境中一般会开启 log_queries_not_using_indexes 参数,为了避免慢查询日志记录检索行数较少的全表扫描的 SQL,需要设置 min_examined_row_limit 为某个大于 0 的值。
# User@Host: root[root] @ localhost [] Id: 8 # Query_time: 2.833550 Lock_time: 0.000013 Rows_sent: 1 Rows_examined: 0 use testdb; SET timestamp=1681844004; select count(*) from user_test;
提交 BUG
在 InnoDB 存储引擎中,每次执行 select count(*) from table 都会遍历全表或二级索引然后统计行数,不应该把 Rows_examined 计算成 0。
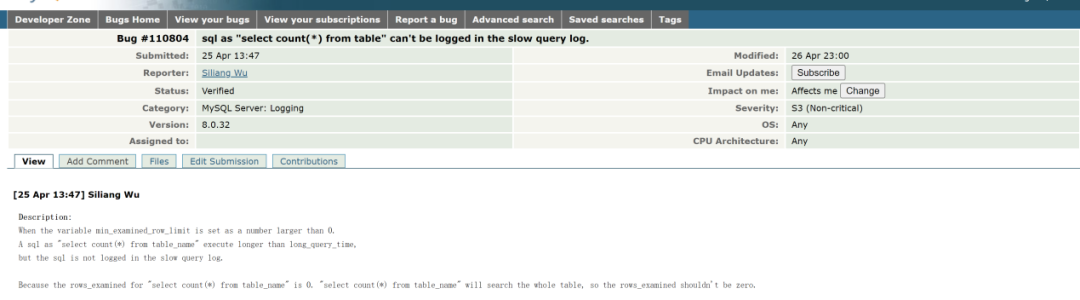
MySQL 官方确认 #110804
结语
虽然现在的 MySQL 数据库大多数部署在云上或者使用了数据库管理平台收集慢查询,慢查询日志可能不是首选的排查问题 SQL 的方法。
但是对于没有额外配置慢查询监控的 MySQL,慢查询日志仍然是一个非常好的定位慢 SQL 的方法,配合 pt-query-digest 工具使用分析某段时间的 TOP SQL 也十分方便。
并且数据库管理平台收集的慢查询数据需要额外的数据库存放,一般都会设置保留一段时间,如果要回溯更早的慢 SQL 就只能通过慢查询日志了。
审核编辑:刘清
-
Database数据库SQL语句2013-03-01 2830
-
Labview 删除Access数据库一条记录,已知删除记录的Record index2013-10-19 5196
-
labview如何更新一条记录呢?、求大神帮助2014-11-29 4088
-
API信息全掌控,方便你的日志管理——阿里云推出API网关打通日志服务2018-02-06 2592
-
Oracle删除重复记录只保留一条数据解决步骤2019-07-05 3169
-
NAS网络存储中如何查看日志记录?2019-11-06 3788
-
如何打开和关闭日志记录语句编译2020-04-22 1412
-
记录sql也很慢的原因2020-06-15 1860
-
使用InTouch的SQL Access把数据记录到Micr2010-07-08 1108
-
一条SQL语句是怎么被执行的2021-09-12 1945
-
如何将HTTP里面的Header信息记录到访问日志里2022-07-01 3648
-
SQL优化思路与经典案例分析2022-10-27 1516
-
sql优化常用的几种方法2022-11-14 6296
-
数据库编程大赛:一条SQL计算扑克牌24点2023-12-21 1223
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

