

DWT跟踪组件调试
描述
DWT跟踪组件
跟踪组件:数据观察点与跟踪(DWT)

DWT 中有剩余的计数器,它们典型地用于程序代码的“性能速写”(profiling)。通过编程它们,就可以让它们在计数器溢出时发出事件(以跟踪数据包的形式)。
最典型地,就是使用 CYCCNT寄存器来测量执行某个 任务所花的周期数 ,这也可以用作时间基准相关的目的(操作系统中统计 CPU使用率可以用到它)。
Cortex-M中的DWT
在 Cortex-M 里面有一个外设叫 DWT(Data Watchpoint and Trace),是用于系统调试及跟踪。

它有一个32位的寄存器叫CYCCNT,它是一个向上的计数器,记录的是内核时钟运行的个数,内核时钟跳动一次,该计数器就加1,精度非常高,如果内核时钟是72M,那精度就是1/72M = 14ns,而程序的运行时间都是微秒级别的,所以14ns的精度是远远够的。
最长能记录的时间为:59.65s。计算方法为2的32次方/72000000。
当CYCCNT溢出之后,会清0重新开始向上计数。
使用方法
要实现延时的功能,总共涉及到三个寄存器:DEMCR 、DWT_CTRL、DWT_CYCCNT,分别用于开启DWT功能、开启CYCCNT及获得系统时钟计数值。
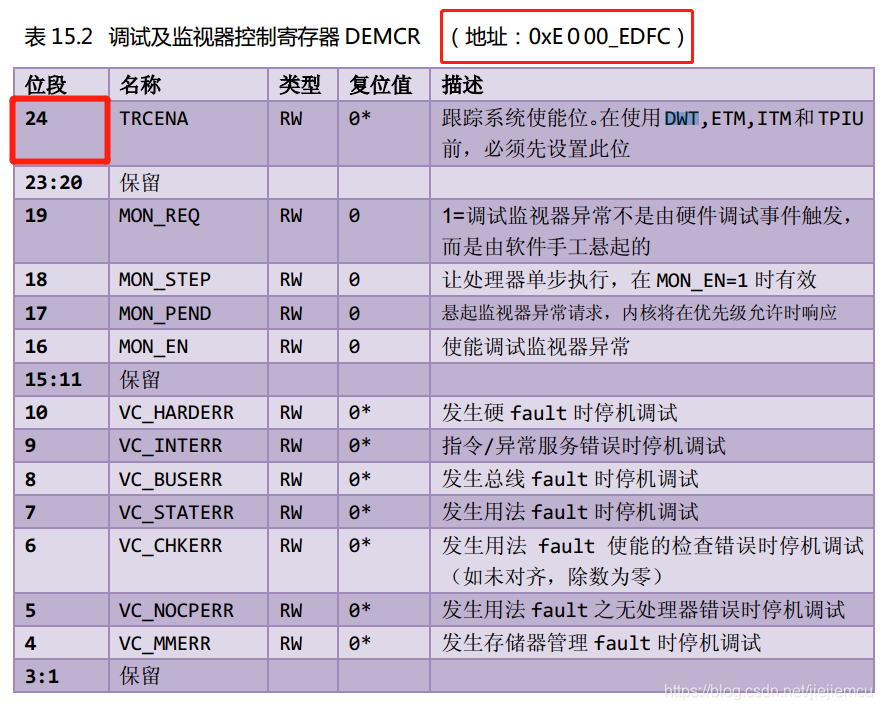
DEMCR
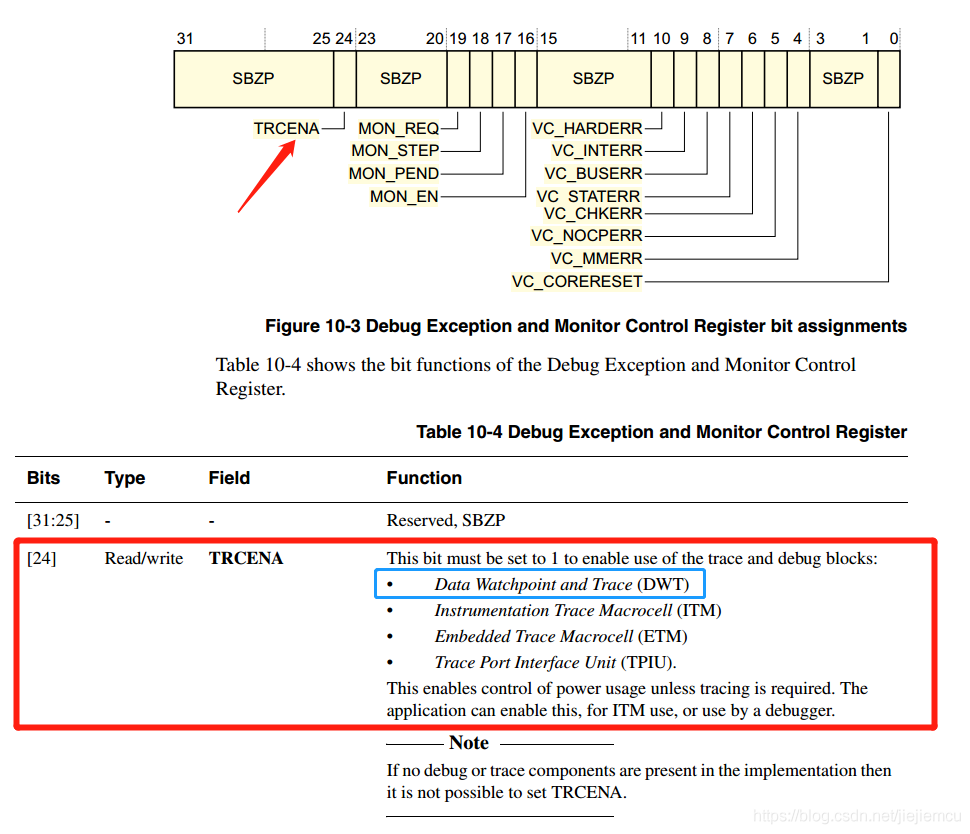
想要使能DWT外设,需要由另外的内核调试寄存器DEMCR的位24控制,写1使能(划重点啦,要考试!!)。DEMCR的地址是0xE000 EDFC
关于DWT_CYCCNT
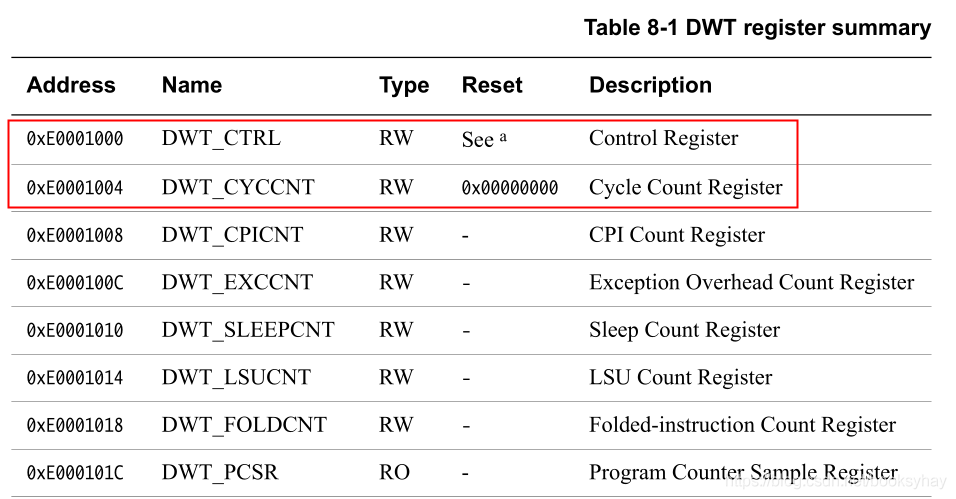
使能DWT_CYCCNT寄存器之前,先清0。让我们看看DWT_CYCCNT的基地址,从ARM-Cortex-M手册中可以看到其基地址是0xE000 1004,复位默认值是0,而且它的类型是可读可写的,我们往0xE000 1004这个地址写0就将DWT_CYCCNT清0了。
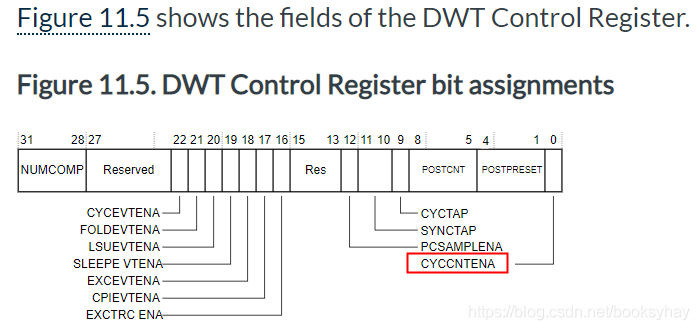
关于CYCCNTENA
CYCCNTENA Enable the CYCCNT counter. If not enabled, the counter does not count and no event is generated for PS sampling or CYCCNTENA. In normal use, the debugger must initialize the CYCCNT counter to 0.
它是DWT控制寄存器的第一位,写1使能,则启用CYCCNT计数器,否则CYCCNT计数器将不会工作。
【 https://developer.arm.com/documentation/ddi0337/e/system-debug/dwt/summary-and-description-of-the-dwt-registers?lang=en 】
综上所述
想要使用DWT的CYCCNT步骤:
- 先使能DWT外设,这个由另外内核调试寄存器 DEMCR 的位24控制,写1使能
- 使能CYCCNT寄存器之前,先清 0。
- 使能CYCCNT寄存器,这个由DWT的CYCCNTENA 控制,也就是DWT控制寄存器的位0控制,写1使能
寄存器定义:
//0xE000EDFC DEMCR RW Debug Exception and Monitor Control Register.
//使能DWT模块的功能位
#define DEMCR ( *(unsigned int *)0xE000EDFC )
#define TRCENA ( 0x01 < < 24) // DEMCR的DWT使能位
//0xE0001000 DWT_CTRL RW The Debug Watchpoint and Trace (DWT) unit
//使能CYCCNT计数器开始计数
#define DWT_CTRL ( *(unsigned int *)0xE0001000 )
#define CYCCNTENA ( 0x01 < < 0 ) // DWT的SYCCNT使能位
//0xE0001004 DWT_CYCCNT RW Cycle Count register,
//CYCCNT计数器的内部值(32位无符号)
#define DWT_CYCCNT ( *(unsigned int *)0xE0001004) //显示或设置处理器的周期计数值
用法示例:
vvolatile unsigned int *DWT_CYCCNT ;
volatile unsigned int *DWT_CONTROL ;
volatile unsigned int *SCB_DEMCR ;
void reset_timer(){
DWT_CYCCNT = (int *)0xE0001004; //address of the register
DWT_CONTROL = (int *)0xE0001000; //address of the register
SCB_DEMCR = (int *)0xE000EDFC; //address of the register
*SCB_DEMCR = *SCB_DEMCR | 0x01000000;
*DWT_CYCCNT = 0; // reset the counter
*DWT_CONTROL = 0;
}
void start_timer(){
*DWT_CONTROL = *DWT_CONTROL | 1 ; // enable the counter
}
void stop_timer(){
*DWT_CONTROL = *DWT_CONTROL | 0 ; // disable the counter
}
unsigned int getCycles(){
return *DWT_CYCCNT;
}
main(){
....
reset_timer(); //reset timer
start_timer(); //start timer
//Code to profile
...
myFunction();
...
stop_timer(); //stop timer
numCycles = getCycles(); //read number of cycles
...
}
示例2:
#define start_timer() *((volatile uint32_t*)0xE0001000) = 0x40000001 // Enable CYCCNT register
#define stop_timer() *((volatile uint32_t*)0xE0001000) = 0x40000000 // Disable CYCCNT register
#define get_timer() *((volatile uint32_t*)0xE0001004) // Get value from CYCCNT register
/***********
* How to use:
* uint32_t it1, it2; // start and stop flag
start_timer(); // start the timer.
it1 = get_timer(); // store current cycle-count in a local
// do something
it2 = get_timer() - it1; // Derive the cycle-count difference
stop_timer(); // If timer is not needed any more, stop
print_int(it2); // Display the difference
****/
示例3:
#define DWT_CR *(uint32_t *)0xE0001000
#define DWT_CYCCNT *(uint32_t *)0xE0001004
#define DEM_CR *(uint32_t *)0xE000EDFC
#define DEM_CR_TRCENA (1 < < 24)
#define DWT_CR_CYCCNTENA (1 < < 0)
/* 初始化时间戳 */
void CPU_TS_TmrInit(void)
{
/* 使能DWT外设 */
DEM_CR |= (uint32_t)DEM_CR_TRCENA;
/* DWT CYCCNT寄存器计数清0 */
DWT_CYCCNT = (uint32_t)0u;
/* 使能Cortex-M3 DWT CYCCNT寄存器 */
DWT_CR |= (uint32_t)DWT_CR_CYCCNTENA;
}
uint32_t OS_TS_GET(void)
{
return ((uint32_t)DWT_CYCCNT);
}
-
详解DWT跟踪组件的单片机调试技巧2022-10-03 1005
-
DWT跟踪组件使用方法2022-10-09 2720
-
一个超级实用的单片机调试组件2023-04-10 3476
-
数据观察点及跟踪DWT2025-12-11 31
-
DWT的相关资料下载2022-02-07 925
-
在STM32F10x中支持哪几种调试接口呢2022-03-02 1997
-
如何使用或启用STM32CubeIDE DWT?2023-01-30 566
-
如何使用高级配置和电源接口(ACPI)支持CoreSight跟踪组件2023-08-08 600
-
使用RealView MDK进行SW调试和实时跟踪2008-08-02 4827
-
关于CoreSight中调试和跟踪的相关内容2020-11-03 2760
-
STM32“隐藏的定时器”-DWT2021-12-04 799
-
详解CoreSight技术中的调试和跟踪功能2022-04-12 6226
-
一个超级实用的单片机调试组件!2023-05-23 695
-
RISC-V调试和完善的跟踪解决方案2023-07-14 406
-
揭秘单片机调试利器值之DWT跟踪组件2024-02-28 1888
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

