

介绍一下CAN Bootloader的整个实现过程
接口/总线/驱动
描述
Bootloader 介绍
大多数Bootloader 包含两种操作模式。
- 启动加载模式
- 下载模式
对于大多数汽车软件开发者来说,从客户需求的角度,他们更多关心Bootloader的下载模式。下面我们将从CAN Bootloader的一般需求入手,来介绍一下CAN Bootloader 的整个实现过程。
CAN Bootloader 简述
通过CAN网络升级一般需要考虑下面几个方向。
01 针对单一节点
CAN网络是串行结构,在对节点升级的时候,不能被别的节点影响,也不能影响到别的节点。这里就需要进行点对点升级。在OEM 的规范中会对每一个ECU 都有自己的诊断ID。一般情况下针对CAN网络的ECU有。
两个接收ID
- 功能寻址ID
- 物理寻址ID
一个发送ID
- 诊断发送ID
这样可以确保点对点的操作,和其他节点互相不干扰。
02 节点的智能设计
在CAN网络中实现数据更新,最进本的就是master ECU 把数据有效的传输给Slave ECU, 这样Slave ECU 对自身的flash 进行操作。在这个过程中需要对数据进行一定要求。
- 保证数据传递的有效性-->传输过程没有错误
- 保证数据本身的真实性--> 未被篡改
- 保证数据发送方的可靠性-->被授权的ECU
- 保证数据本身的正确性--> 是否与Bootloader 兼容
- 等等需求
这里对传输过程的保证,汽车OEM 一般通过UDS 让Master ECU 和 Slave 进行交互。通过握手协议,以及一些routine 来对上面需求进行一一实现。
针对UDS 这里不一一介绍,可以翻阅14229 自行查询。
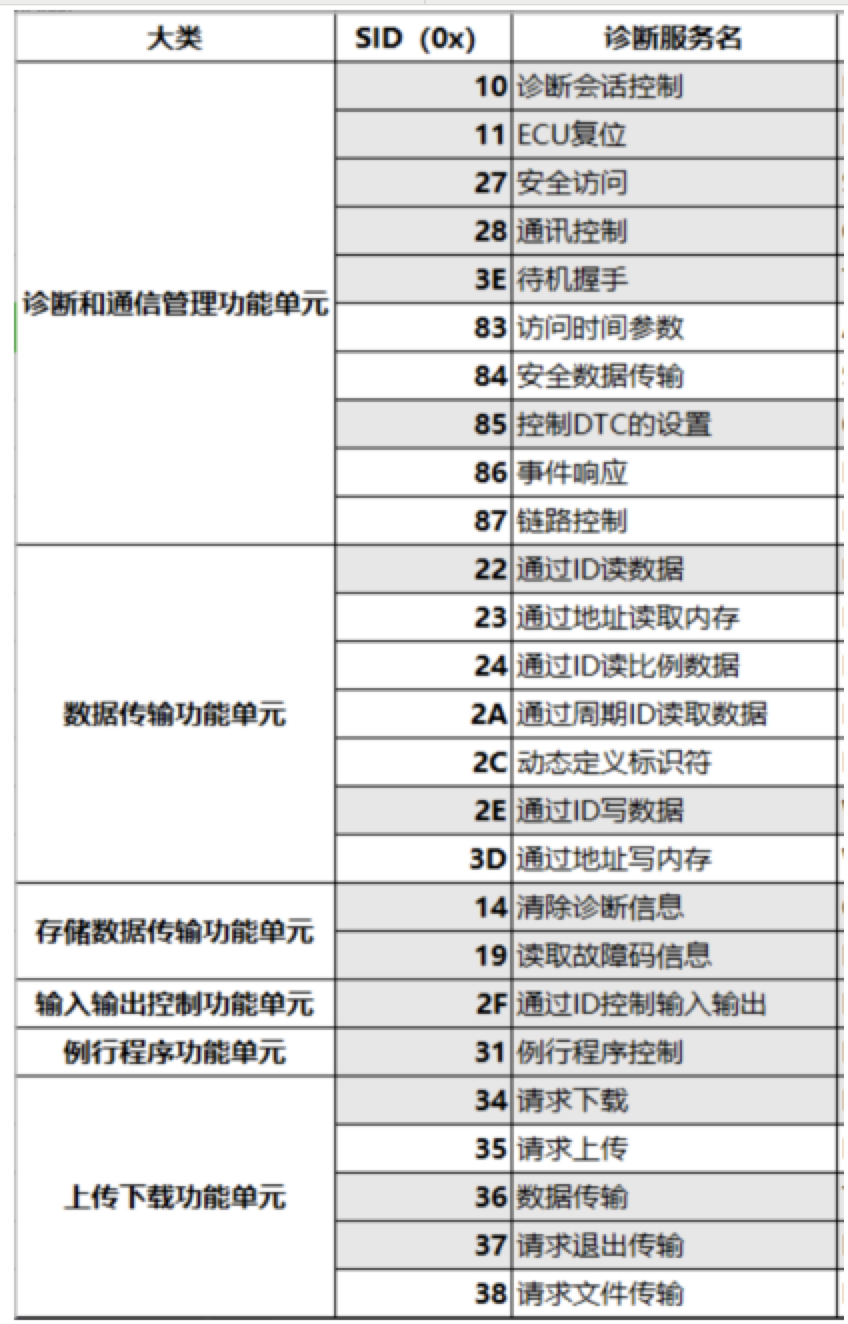
注意这里缺少新版的 0x29 服务。
UDS诊断29认证服务-Authentication Service
03 进入Bootloader 模式
一般来说这里有一下几种方式
- APP 主动跳转至 Bootloader 模式
- 上电启动由于Bootloader 检测APP 失效,主动停留在Bootloader
- APP 软件异常,自动复位到Bootloader 模式下。
这里针对OEM 的升级需求,一般是 第一种, APP 主动跳转至Bootloader 模式。因为Bootloader 不一定都是需要依赖UDS的,这里统一叫Bootloader 模式,OEM 的 UDS 的规范里面的名称叫做programming session。
一般来说OEM 会在APP 里面先进行session 跳转,身份验证。
最后通过 10 02 命令让APP 跳转到Bootloader 模式下。
在我们进行bootloader设计的时候,可以通过任何特定方式,注意这里的特定方式不能是随随便便就可以触发 的,防止误触进入bootloader 模式。
因为跳转的逻辑是 APP 检测到一定的条件,然后 对某些寄存器,或者某些Bootloader 可读的内存空间进行写flag. 随后进行reset. 这样在reset完成之后, bootloader 会检测到,这次不需要跳转至APP 了。
04 对bootloader的要求
从实际的研发需求出发,这里列出了一些常用的需求。实际OEM 的bootloader 可能会细化需求,但是最终都是为了下面的目的提出来的需求。
- 多次数据更新
- 刷写速度,传输速度
- 差分更新
- 身份验证
- 数据格式的标准化
- 对数据的完整性,有效性等进行校验
- 对APP 的有效性进行校验
- 上位机方便友好
OEM 对Bootloader 的基本要求
在OEM 的需求里,在刷写过程一般分为三个步骤。
- 前处理
- 刷写
- 后处理
分别是做什么的呢?
前处理

需求各不相同,但是目的基本都一致。
- 避免其他节点对升级过程的影响
- 避免自身节点对升级过程的影响
- 避免自身节点对其他节点的影响
刷写

通过一系列的UDS 命令进行 点对点 交互。其目的和前面提到的一致。
- 发送数据的ECU 可靠
- 数据传输过程可靠
- 数据有效性(识别有没有被篡改)
- 数据加密解密数据安全
- 等等
后处理

解除自身的特殊状态。更新配置参数等等。
这里面 ECU 需要做好和APP 的相互校验。需要达到
- APP 是否有效,Bootloader 需要能判断出
- APP 运行时无效,需要能有效进入Bootloader模式。
- APP 无效, Bootloader 不应该跳入
- 等等
Bootloader的设计与实现
总结一句话
最基本的Bootloader通过传输协议把数据可靠的写入指定的内存空间
通过上面的分析,总结一下我们需要实现哪些功能。
01 控制器最小系统
单纯运行Bootloader的软件,这里是不需要os的。只需要一个while(1) + 中断系统顺序执行即可。
本文以Aurix Tricore芯片示例代码介绍。
启动代码
static void __StartUpSoftware(void);
static void __StartUpSoftware_Phase2(void);
static void __StartUpSoftware_Phase3ApplicationResetPath(void);
static void __StartUpSoftware_Phase3PowerOnResetPath(void);
static void __StartUpSoftware_Phase4(void);
static void __StartUpSoftware_Phase5(void);
static void __StartUpSoftware_Phase6(void);
static void __Core0_start(void);
main 函数
这里面实现很简单,只需要判断是否进入app. 如果不进入app. 就只需要监听通讯接口的数据,进行相对应的操作即可。
int main(void)
{
if(*((uint32_t *)APP_EXE_FLAG_START_ADDR)==0x80001000){
CAN_BOOT_JumpToApplication(APP_START_ADDR);
}
__set_PRIMASK(0);//开启总中断
CAN_Configuration(1000000);
while (1)
{
if(CAN1_CanRxMsgFlag){
CAN_BOOT_ExecutiveCommand(&CAN1_RxMessage);
CAN1_CanRxMsgFlag = 0;
}
}
}
02 通讯驱动
这里面采用的是比较简单的CAN 通讯。
一般来说因为上位机在传输数据的时候,速度是很快的。我们bootloader里面的CAN 接收需要采用中断的模式进行收发。
对于CAN 的参数配置。
波特率
typedef struct {
unsigned char SJW;
unsigned char BS1;
unsigned char BS2;
unsigned short PreScale;
} tCAN_BaudRate;
可以根据芯片手册的原理进行配置。

这里面对于Bootloader来说,比较重要的就是波特率和收发报文ID 以及中断模式。
因为这些是需要和上位机进行配合的。
这里给出以下Mcal 代码初始化CAN时候的形参。可以大概看出需要初始化的内容
/*******************************************************************************
** Traceability : [cover parentID={196A1432-EAB1-461a-BD6C-259784BF6397}] **
** **
** Syntax : void Can_17_McmCan_Init **
** ( **
** const Can_17_McmCan_ConfigType* const Config **
** ) **
** **
** Description : Driver Module Initialization function **
** * This function initializes: **
** * Static variables, including flags **
** * CAN HW Unit global hardware settings **
** * Controller specific settings for each CAN Controller **
** All CAN Controllers will be in state CANIF_CS_STOPPED after initialization**
** [/cover] **
** **
** Service ID : 0x00 **
** **
** Sync/Async : Synchronous **
** **
** Reentrancy : Non-Reentrant **
** **
** Parameters(in) : Config - Pointer to all cores CAN driver configuration **
** **
** Parameters (out) : none **
** **
** Return value : none **
** **
*******************************************************************************/
对于bootloader来说,这里只需要三个接口
初始 化,收,发
void CAN_Configuration_init(uint32_t BaudRate);
uint8_t CAN_WriteData(CanTxMsg *TxMessage);
uint16_t Read_CAN_Address(void);
03 内存驱动
首先看一下内存分配
PFLASH

DFLASH

一般来说 被刷的软件格式是Hex 或S19. 针对这两种格式就不说了。
code 和 data 可以根据主机厂需求分为两个或多个Hex.
所以这里需要对Pflash 和 DFlash 都进行操作。
需要注意的是两个不同的flash 操作的 扇区大小是不一样的。Mcal提供的接口已经做了相对应的处理。
对于bootloader来说,需要的接口 擦除 和 写入。
/*******************************************************************************
** Syntax : FlsLoader_ReturnType FlsLoader_Write( **
** const FlsLoader_AddressType TargetAddress, **
** const FlsLoader_LengthType Length, **
** const uint8* const SourceAddressPtr) **
** **
** Service ID : 0x31 **
** **
** Sync/Async : Synchronous **
** **
** Reentrancy : Non Reentrant **
** **
** Parameters(in) : Length: Number of bytes to be written. It should be **
** multiple of the following page sizes of the **
** selected Flash for write. **
** PFlash: 32 Bytes **
** DFlash: 8 Bytes **
** SourceAddressPtr: Pointer to source data buffer **
** TargetAddress: Target address in Flash memory. **
** It should be aligned to the following page sizes **
** of the selected Flash for write. **
** PFlash: 32 Bytes **
** DFlash: 8 Bytes **
** **
** Parameters (out) : None **
** **
** Return value : FLSLOADER_E_OK: Successful execution. **
** FLSLOADER_E_BUSY: Flash is busy with erase/write **
** operation. **
** FLSLOADER_E_NOT_OK: Returned when DET, Sequence error, **
** Program/Erase verify errors occur, SourceAddressPtr is**
** null pointer. **
** FLSLOADER_E_LOCKED: Programming a locked sector. **
** **
** Description : This function is used to program a page of internal **
** Flash. Sectors of PFlash and DFlash can be programmed. **
*******************************************************************************/
/*******************************************************************************
** Syntax : FlsLoader_ReturnType FlsLoader_Erase( **
** const FlsLoader_AddressType TargetAddress, **
** const FlsLoader_LengthType Length **
** ) **
** **
** Service ID : 0x32 **
** **
** Sync/Async : Synchronous **
** **
** Reentrancy : Non Reentrant **
** **
** Parameters(in) : Length: Number of Flash (PFlash or DFlash) sectors to **
** be erased. Note: Number of sectors should lie within **
** single Flash bank. Erase operation across the Flash **
** banks is not supported. **
** TargetAddress: Target address in Flash memory. It **
** should be aligned to the following sector sizes of the **
** selected Flash for erase. **
** PFlash: 16 Kbyte **
** DFlash: 4 Kbyte **
** **
** Parameters (out) : None **
** **
** Return value : FLSLOADER_E_OK: Successful completion. **
** FLSLOADER_E_BUSY: Flash is busy with erase/write **
** operation. **
** FLSLOADER_E_NOT_OK: Returned when DET, Sequence error, **
** Erase verify errors occur. **
** FLSLOADER_E_LOCKED: Sector is protected. **
** **
** Description : This function erases the logical sectors of the **
internal Flash. The completion of this operation is **
denoted by clearing of busy status flag or error. **
04 额外需求库
这里比如需要对数据进行CRC 校验
需要对数据包进行数据解密用到的加密算法
等等
05 交互逻辑 上层应用
根据具体的OEM 需求实现的功能。比如说。配置参数的交换,与APP软件的有效位相互校验,等等需求。这里无法给出对应代码。
总结 一张图

- 相关推荐
- 热点推荐
- CAN总线
- 上位机
- bootloader
- ECU软件
- DFlash
-
CAN的实现原理是什么?说一下CAN总线的特点有哪些?2023-08-14 3486
-
科普一下CAN总线的基础知识2023-05-16 4450
-
STM32单片机Bootloader的实现2023-01-11 7995
-
记录一下bootloader升级Bug分析及复现最后解决的整个过程2022-11-22 6906
-
BootLoader启动过程的显示策略研究与实现2022-04-02 710
-
介绍一下avr芯片的启动过程2022-02-28 1222
-
通过程序来实现stm32的bootloader2022-01-17 674
-
华大HC32F460 Bootloader及应用程序的实现2021-11-23 2939
-
STM8单片机为例,如何实现Bootloader?2021-04-12 4111
-
单片机的Bootloader可以实现用户轻松升级程序2020-10-23 5437
-
Bootloader是什么Bootloader的介绍和过程详细解2018-12-11 2620
-
认识一下这款名叫“CAN总线存储器”的神器2018-05-20 8817
-
AVR914 CAN UART based Bootloader for AT90CAN32_AT90CAN64_AT90CAN1282017-09-21 994
-
STM32 Bootloader实现2017-08-26 9190
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

