

 c++之函数对象与内建函数
c++之函数对象与内建函数
电子说
1.4w人已加入
描述
1.函数对象
-
函数对象(仿函数):
重载函数调用操作的类,其对象常称之为函数对象;
函数对象使用重载()时,其行为类似函数调用,也叫仿函数; - 函数对象本质:
函数对象(仿函数)本质是一个类,不是一个函数。
- 函数对象特点:
函数对象在使用时可以有形参、有返回值。
函数对象可以有自己的状态值。
函数对象可以作为函数形参。
使用示例:
#include < iostream >
using namespace std;
class myfunc
{
public:
myfunc()
{
count = 0;
}
//求和示例,重载()
int operator()(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
//输出示例,count记录函数调用次数
void operator()(string str)
{
count++;
cout < < str < < endl;
}
int count;
};
void print(myfunc& p, string test)
{
p(test);
}
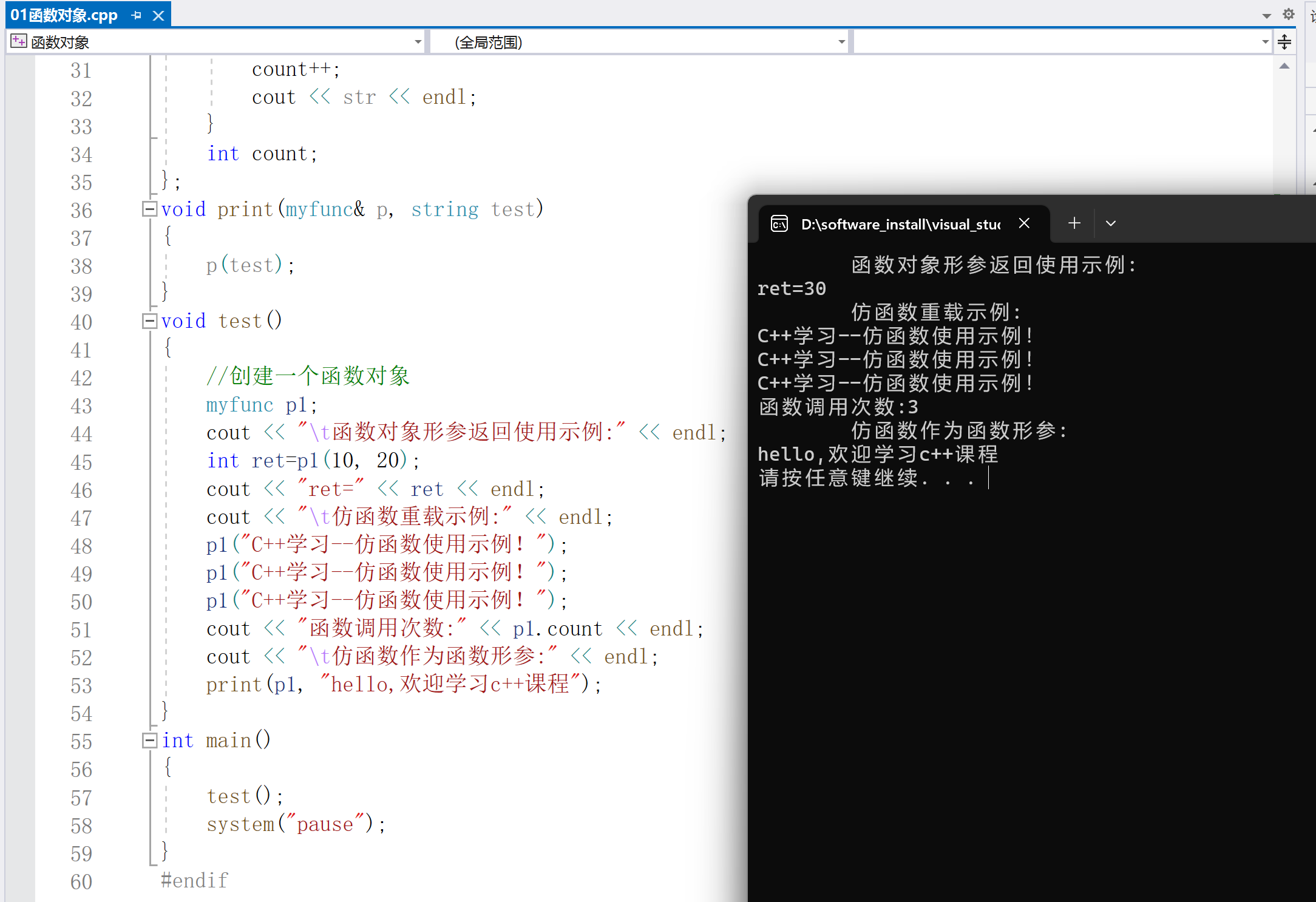
void test()
{
//创建一个函数对象
myfunc p1;
cout < < "t函数对象形参返回使用示例:" < < endl;
int ret=p1(10, 20);
cout < < "ret=" < < ret < < endl;
cout < < "t仿函数重载示例:" < < endl;
p1("C++学习--仿函数使用示例!");
p1("C++学习--仿函数使用示例!");
p1("C++学习--仿函数使用示例!");
cout < < "函数调用次数:" < < p1.count < < endl;
cout < < "t仿函数作为函数形参:" < < endl;
print(p1, "hello,欢迎学习c++课程");
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
}
2.谓词
-
谓词:
函数对象返回值为bool类型,则称之为谓词; -
一元谓词:
仿函数的形参只有一个; -
二元谓词:
仿函数的形参有两个参数;
#include < iostream >
#include < vector >
#include < algorithm >
using namespace std;
class Check
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 5;
}
bool operator()(int a1,int a2)
{
return a1 > a2;
}
};
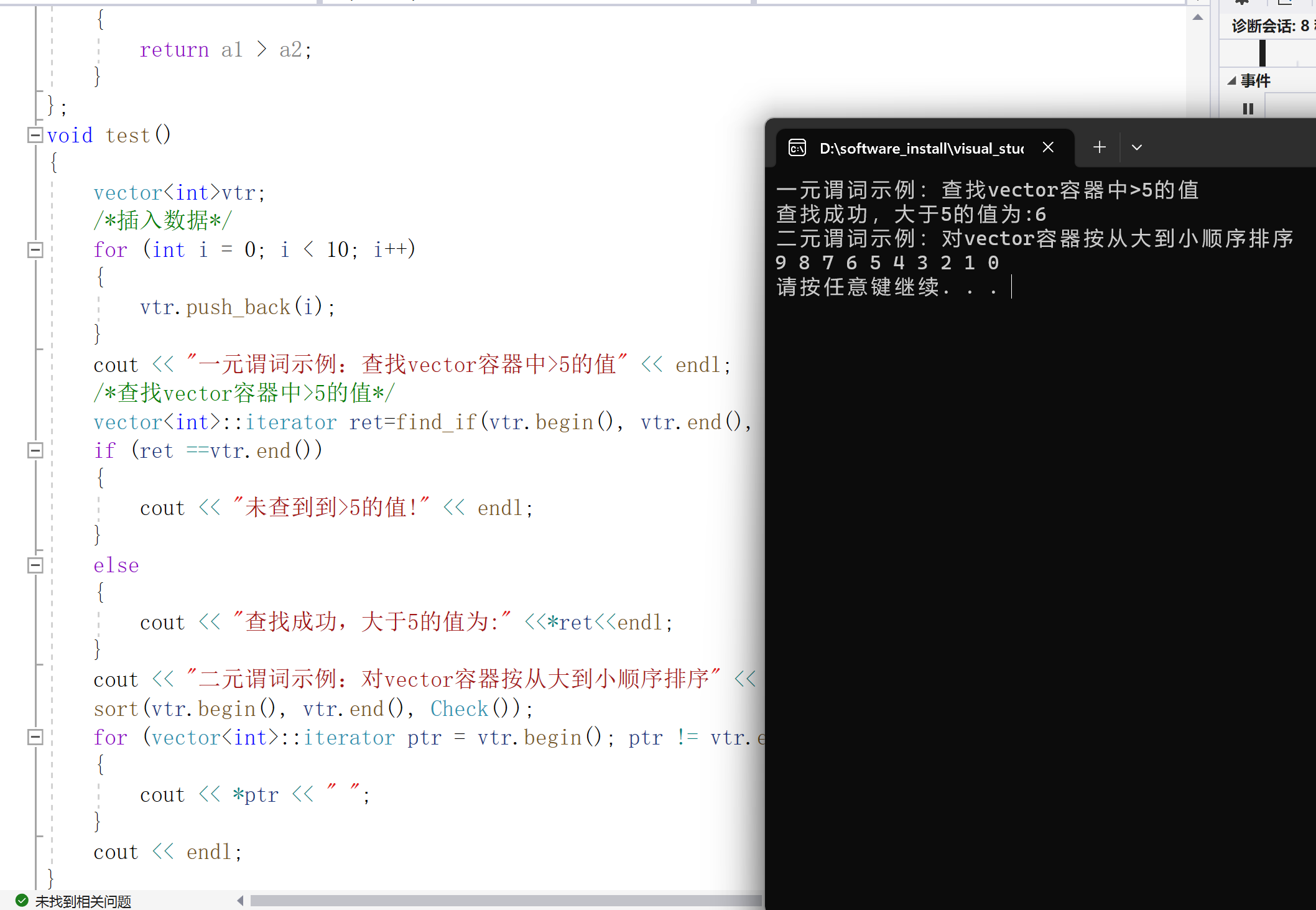
void test()
{
vector< int >vtr;
/*插入数据*/
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
vtr.push_back(i);
}
cout < < "一元谓词示例:查找vector容器中 >5的值" < < endl;
/*查找vector容器中 >5的值*/
vector< int >::iterator ret=find_if(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), Check());//Check() ---匿名函数对象
if (ret ==vtr.end())
{
cout < < "未查到到 >5的值!" < < endl;
}
else
{
cout < < "查找成功,大于5的值为:" < <*ret< ::iterator ptr = vtr.begin(); ptr != vtr.end(); ptr++)
{
cout < < *ptr < < " ";
}
cout < < endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
}
;>
3.内建函数对象
-
内建函数对象:
STL中提供了一些内建函数对象:算术仿函数、关系仿函数、逻辑仿函数 --头文件
3.1算术运算符
- 算术仿函数:实现四则运算。
加法:template T plus
减法:template T minus
乘法:template T mutiplies
除法:template T divides
取模:template T modulus
取反:template T negate --正数变负数,负数变正数
注意:其中negate是一元运算(只有一个参数),其余均为二元运算。
#include < iostream >
using namespace std;
#include < functional >
void test()
{
//negate使用示例:
negate< int > n;
cout < < "negate取反示例:" < < n(188) < < endl;
plus< int > p;
cout < < "plus加法:" < < p(10, 20) < < endl;
minus< float >m;
cout < < "minus减法取绝对值:" < < n(m(10, 20)) < < endl;
multiplies< float >mt;
cout < < "multiplies乘法:" < < mt(5, 3.15) < < endl;
divides< float >d;
cout < < "divides除法:" < < d(10, 3) < < endl;
modulus< int >md;
cout < < "modulus取模:" < < md(10, 3) < < endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
}
3.2关系运算符
- 内建仿函数:关系运算符
大于: templatebool greater
大于等于:templatebool greater_equal
小于: templatebool less
小于等于:templatebool less_equal
等于: templatebool equal_to
不等于: templatebool not_equal_to
#include < iostream >
using namespace std;
#include < functional >
#include < vector >
#include < algorithm >
void print(int val)
{
cout < < val < < " ";
}
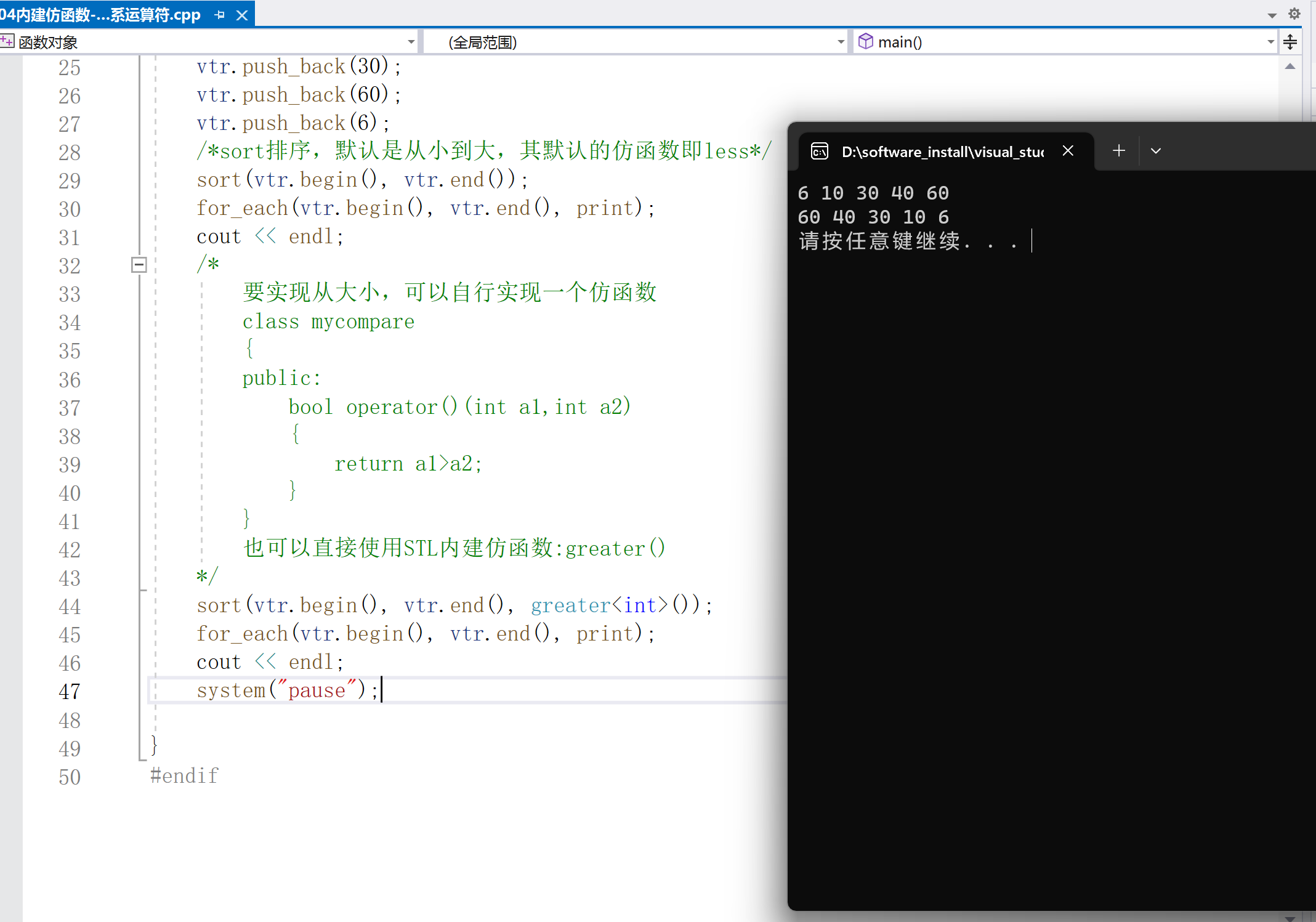
int main()
{
vector< int > vtr;
vtr.push_back(10);
vtr.push_back(40);
vtr.push_back(30);
vtr.push_back(60);
vtr.push_back(6);
/*sort排序,默认是从小到大,其默认的仿函数即less*/
sort(vtr.begin(), vtr.end());
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), print);
cout < < endl;
/*
要实现从大小,可以自行实现一个仿函数
class mycompare
{
public:
bool operator()(int a1,int a2)
{
return a1 >a2;
}
}
也可以直接使用STL内建仿函数:greater()
*/
sort(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), greater< int >());
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), print);
cout < < endl;
system("pause");
}
3.3逻辑运算符
- 内建仿函数--逻辑运算符
逻辑与:templatebool logical_and
逻辑或: templatebool logical_or
逻辑非: templatebool logical_not
#include < iostream >
using namespace std;
#include < vector >
#include < algorithm >
#include < functional >
void print(bool val)
{
cout < < val < < " ";
}
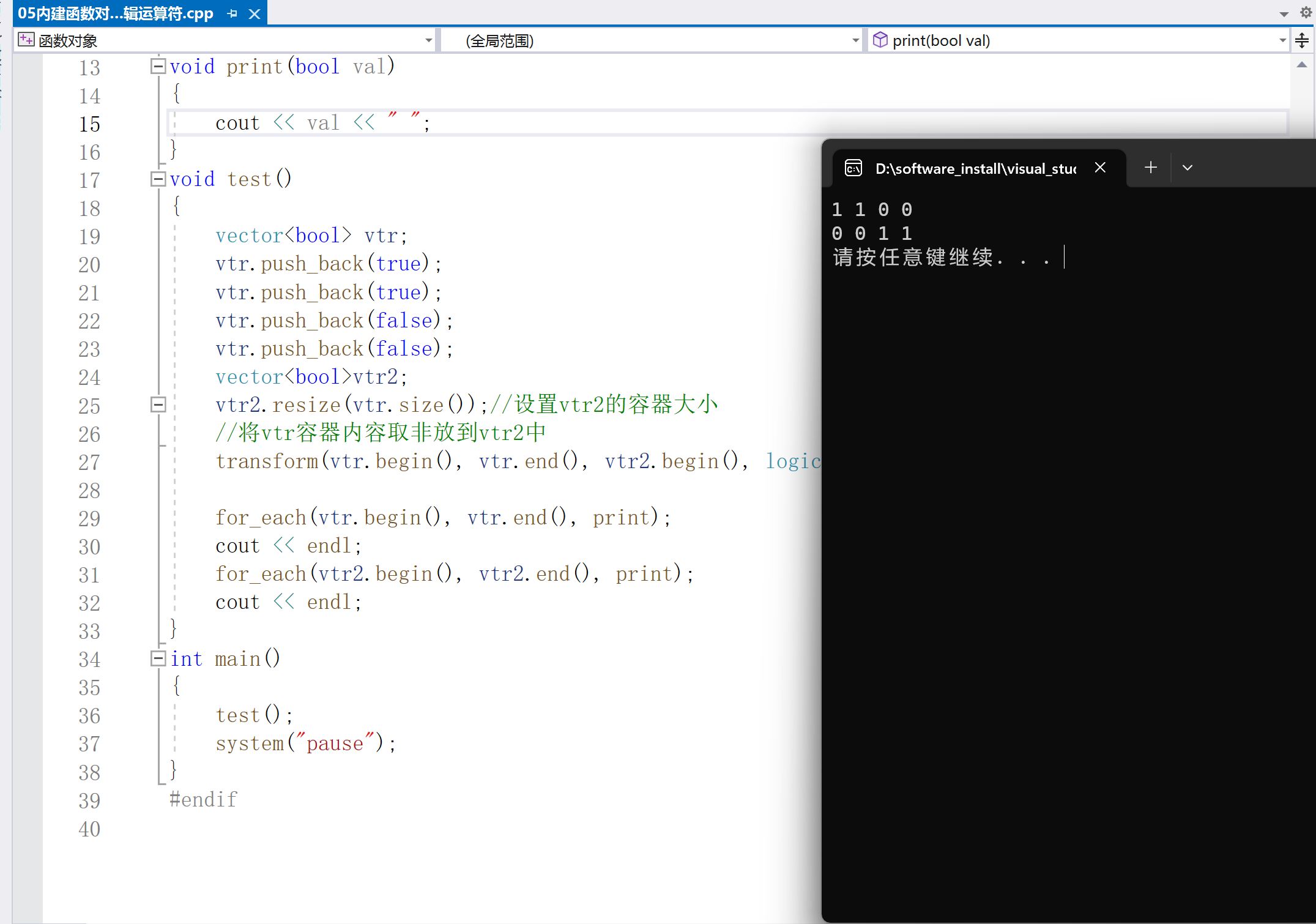
void test()
{
vector vtr;
vtr.push_back(true);
vtr.push_back(true);
vtr.push_back(false);
vtr.push_back(false);
vectorvtr2;
vtr2.resize(vtr.size());//设置vtr2的容器大小
//将vtr容器内容取非放到vtr2中
transform(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), vtr2.begin(), logical_not());
for_each(vtr.begin(), vtr.end(), print);
cout < < endl;
for_each(vtr2.begin(), vtr2.end(), print);
cout < < endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
}
审核编辑:汤梓红
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容侵权或者其他违规问题,请联系本站处理。
举报投诉
-
【乾芯QXS320F开发板试用】TMUFPU内建函数2025-12-11 912
-
C++基础知识之函数12023-04-03 1081
-
浅析C++执行构造函数编程实例2023-03-03 610
-
深度解析C++中的虚函数2023-02-15 1428
-
虚函数,C++开发者如何有效利用2023-02-11 1422
-
如何在MPLAB XC16编译器内建函数2023-01-22 2449
-
在C++中如何用虚函数实现多态2021-09-29 2144
-
C++基础语法之inline 内联函数2021-09-09 2664
-
C++之拷贝构造函数的浅copy及深copy2020-12-24 1224
-
如何在中断C函数中调用C++2019-05-09 992
-
C++课程资料详细资料合集包括了:面向对象程序设计与C++,算法,函数等2018-07-09 1300
-
GCC内建函数问题!!!2018-06-21 1649
-
C++教程之函数的递归调用2010-05-15 544
全部0条评论

快来发表一下你的评论吧 !

